Design practice of deep and complex foundation pit based on local conditions and displacement control
-
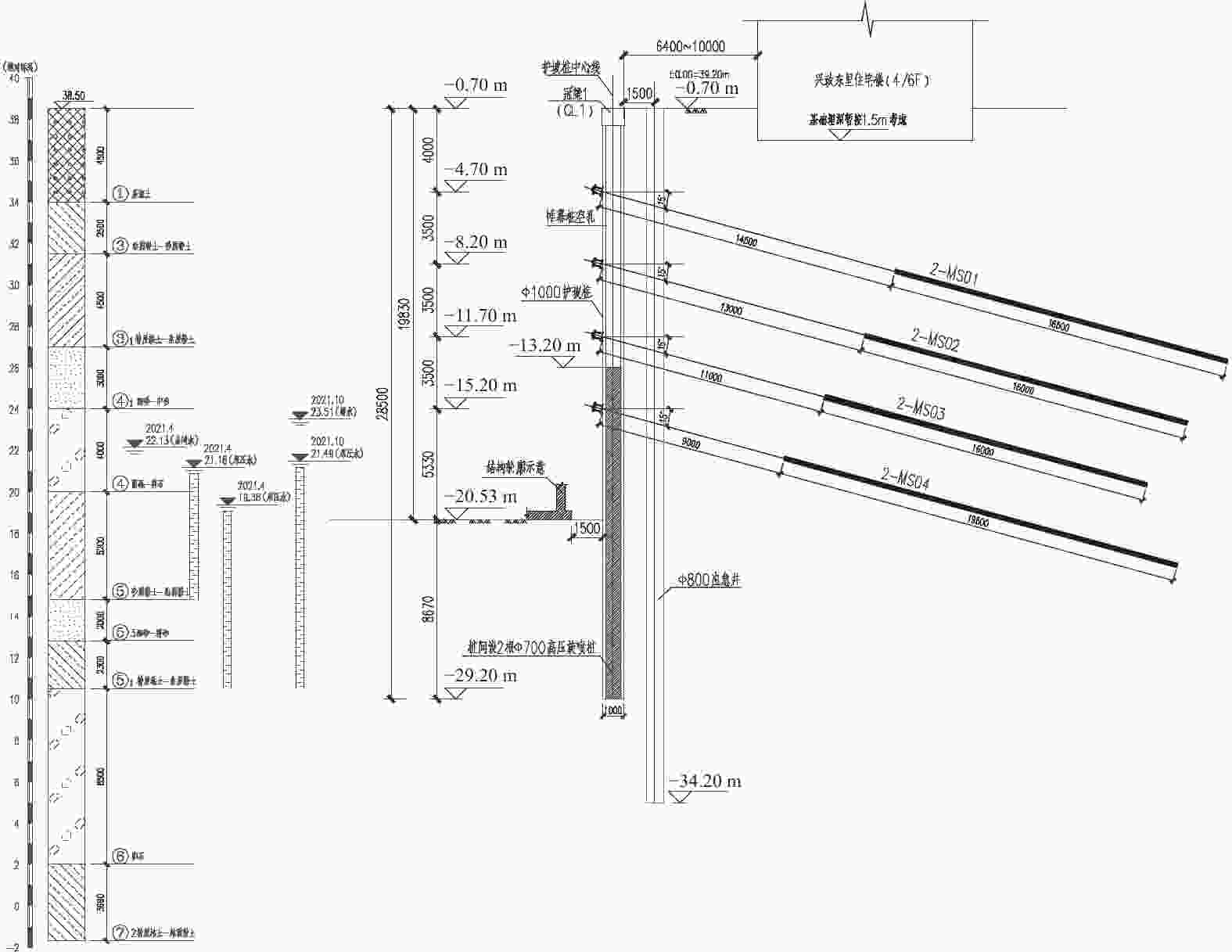
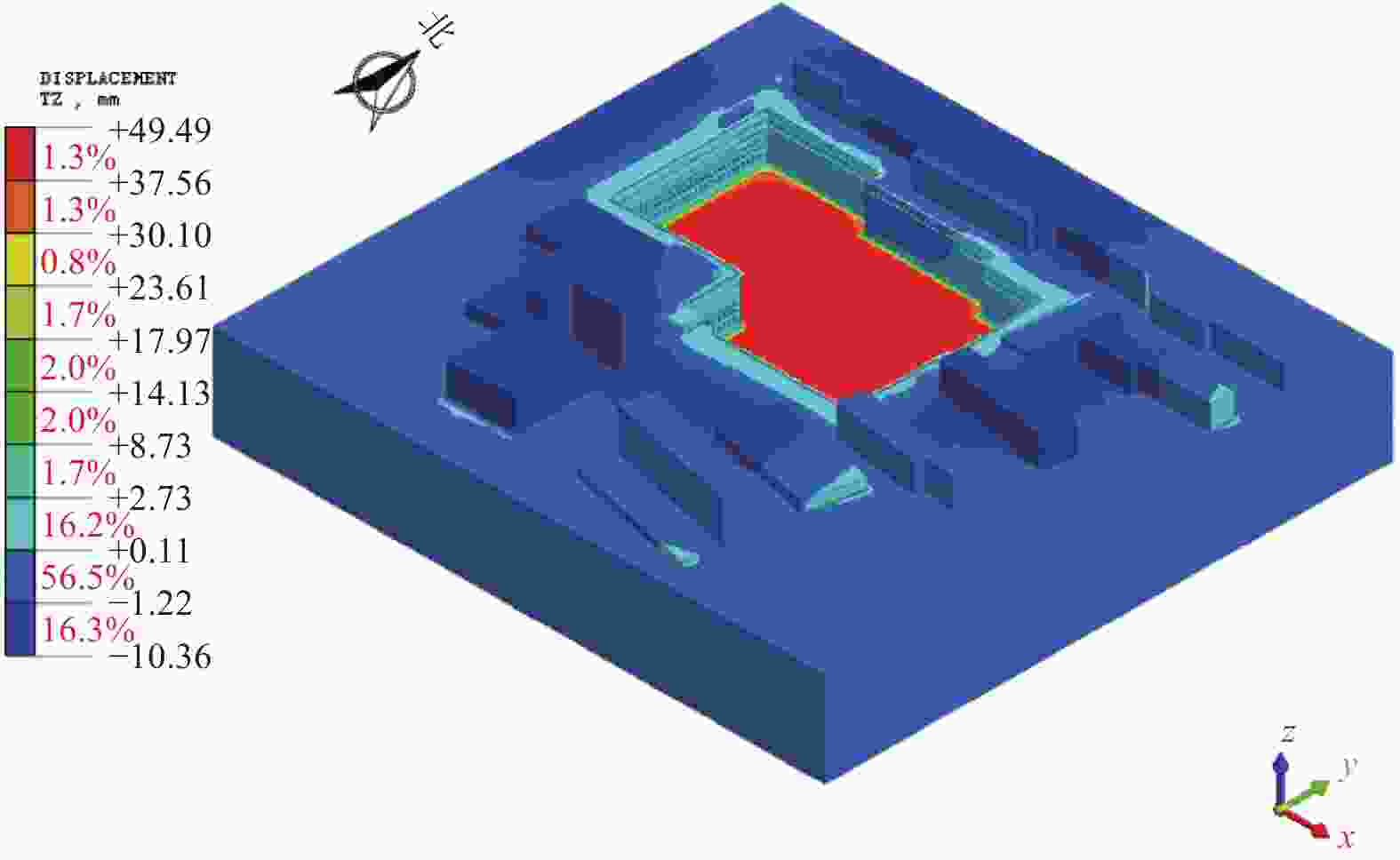
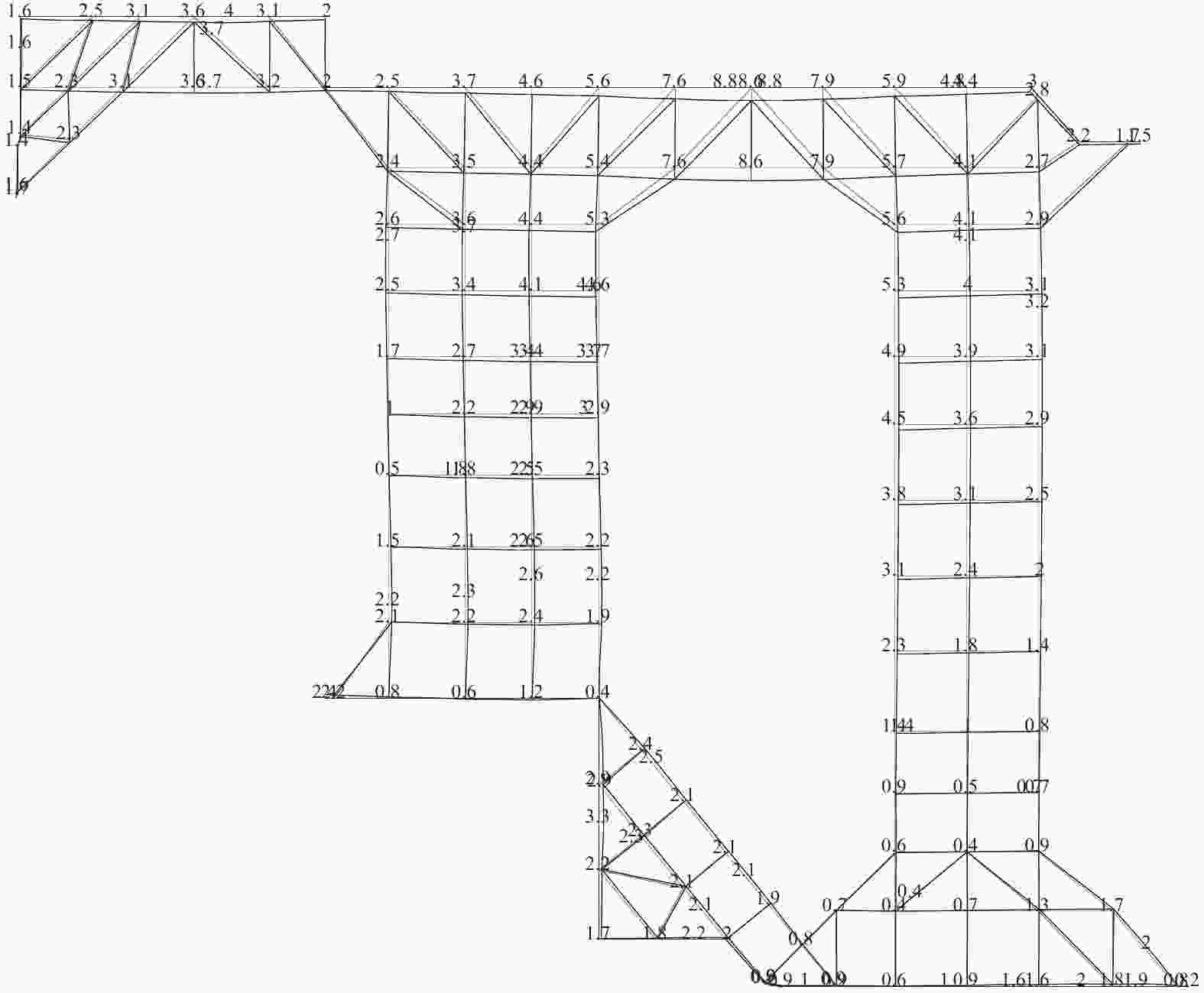
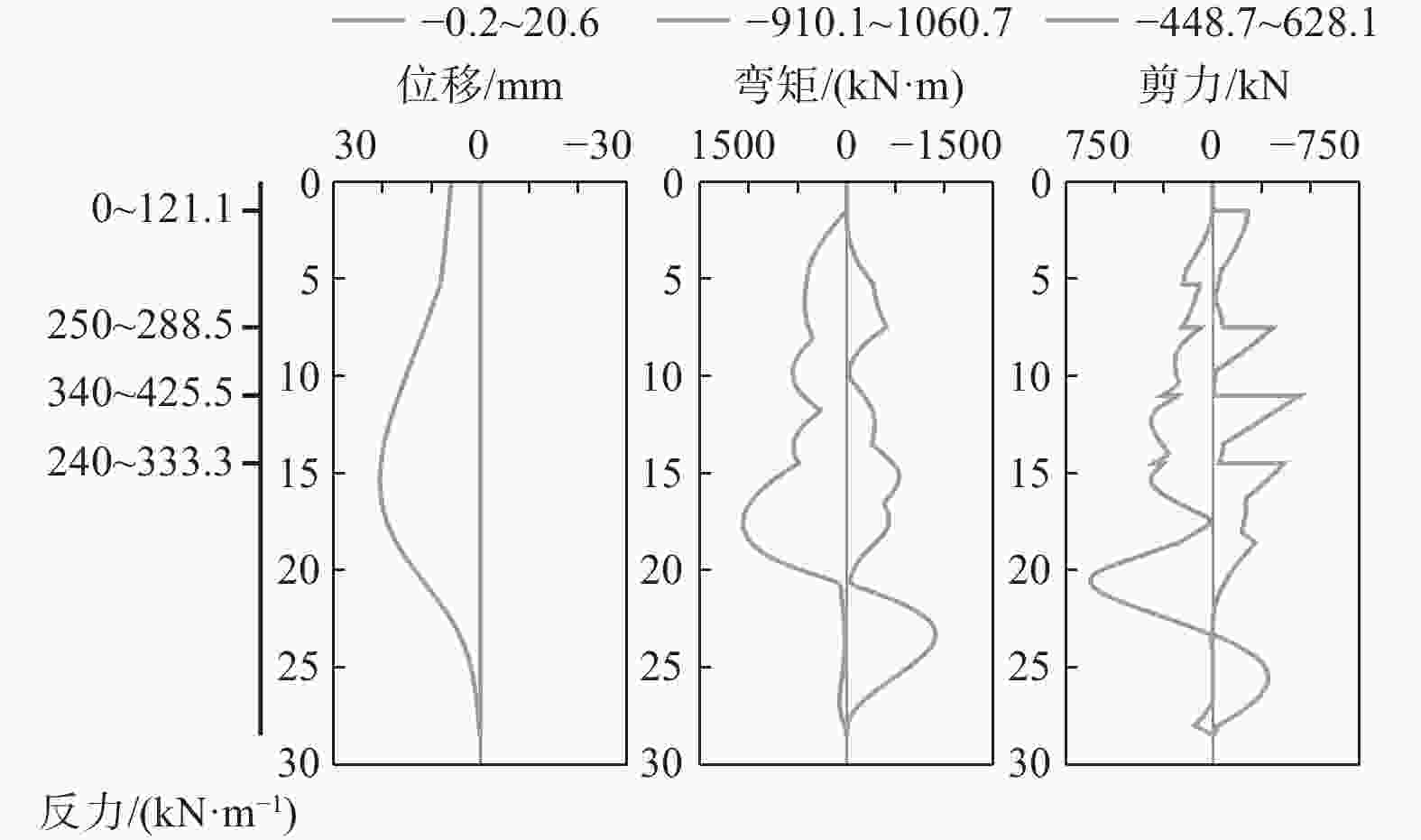
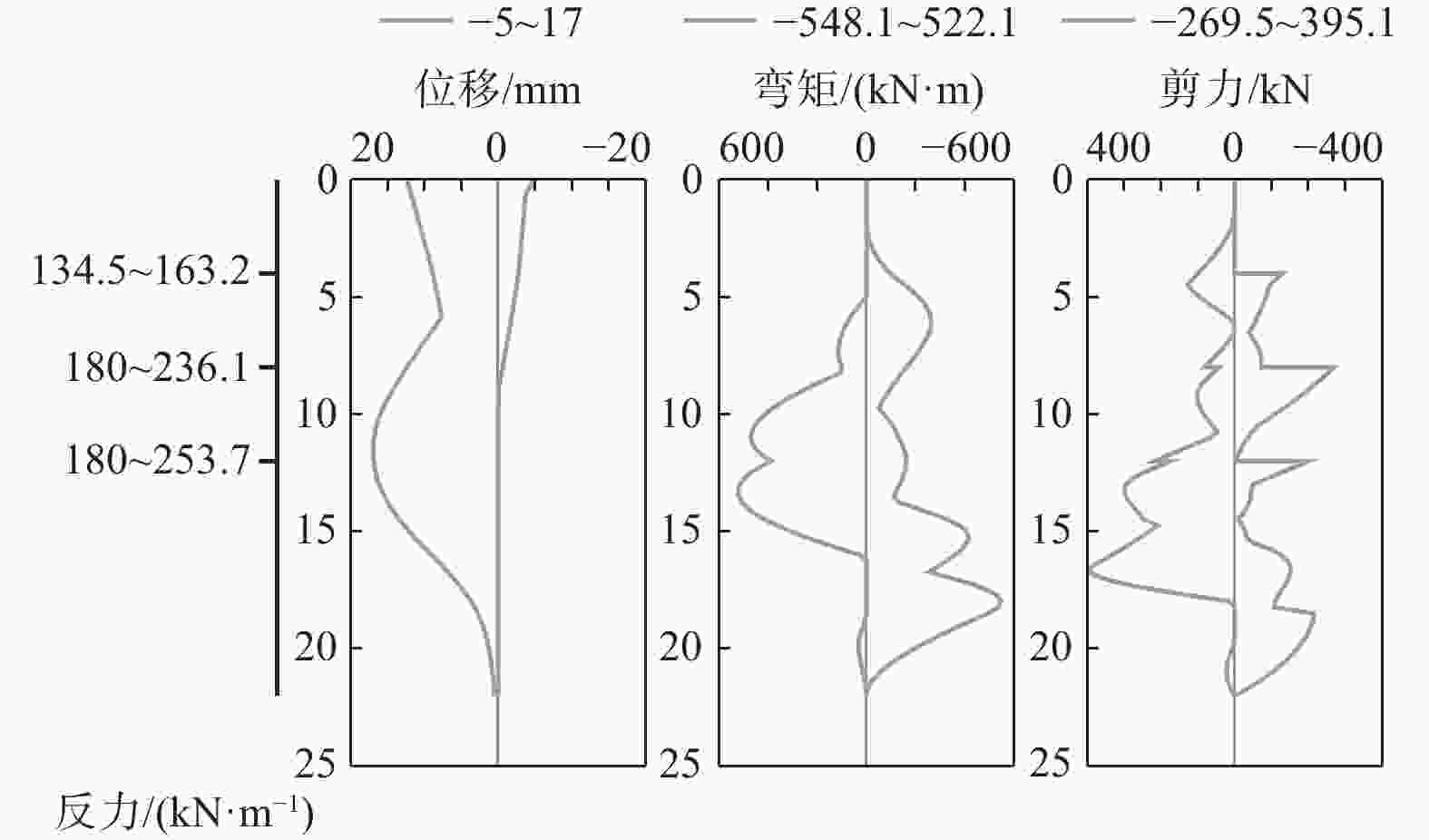
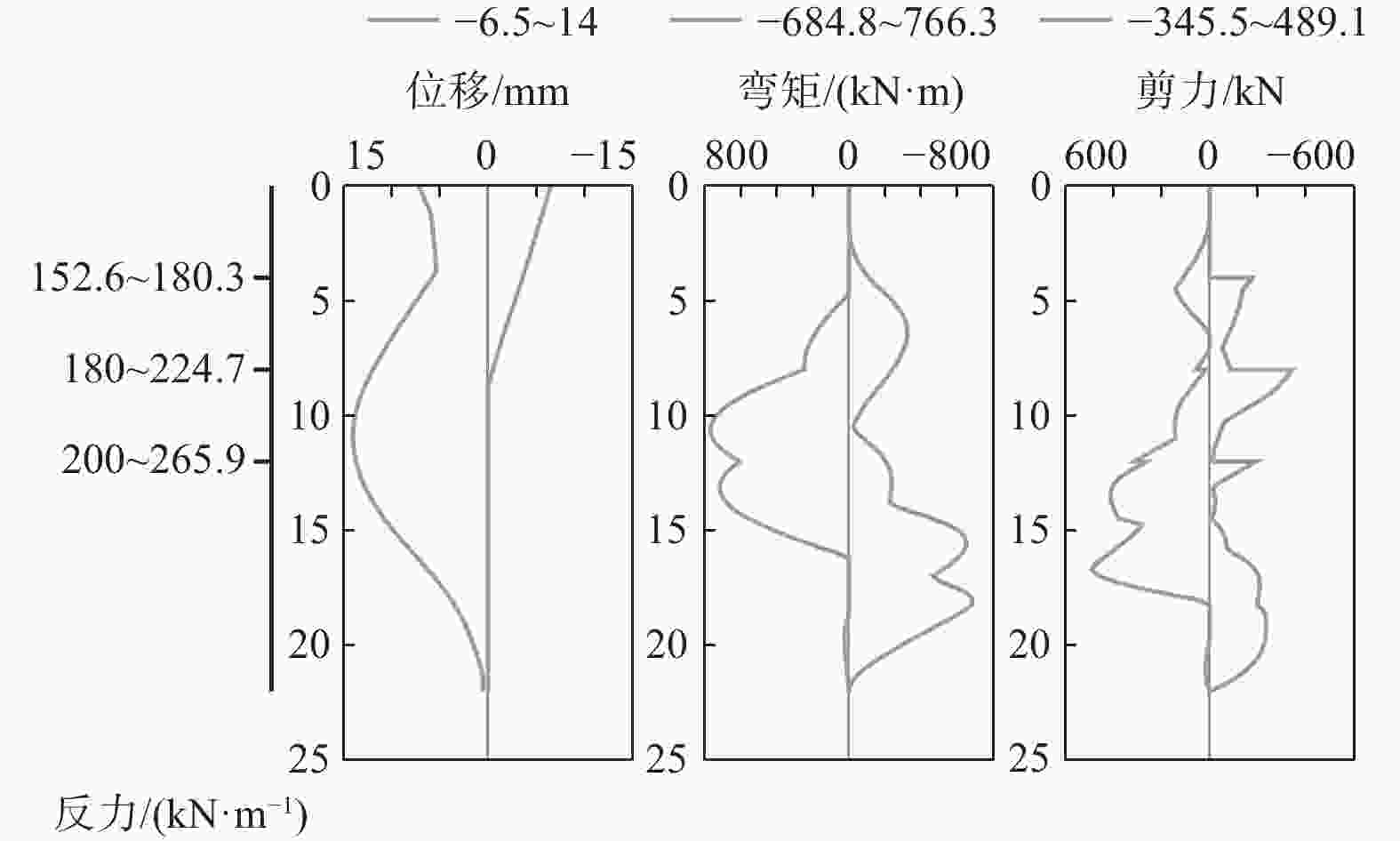
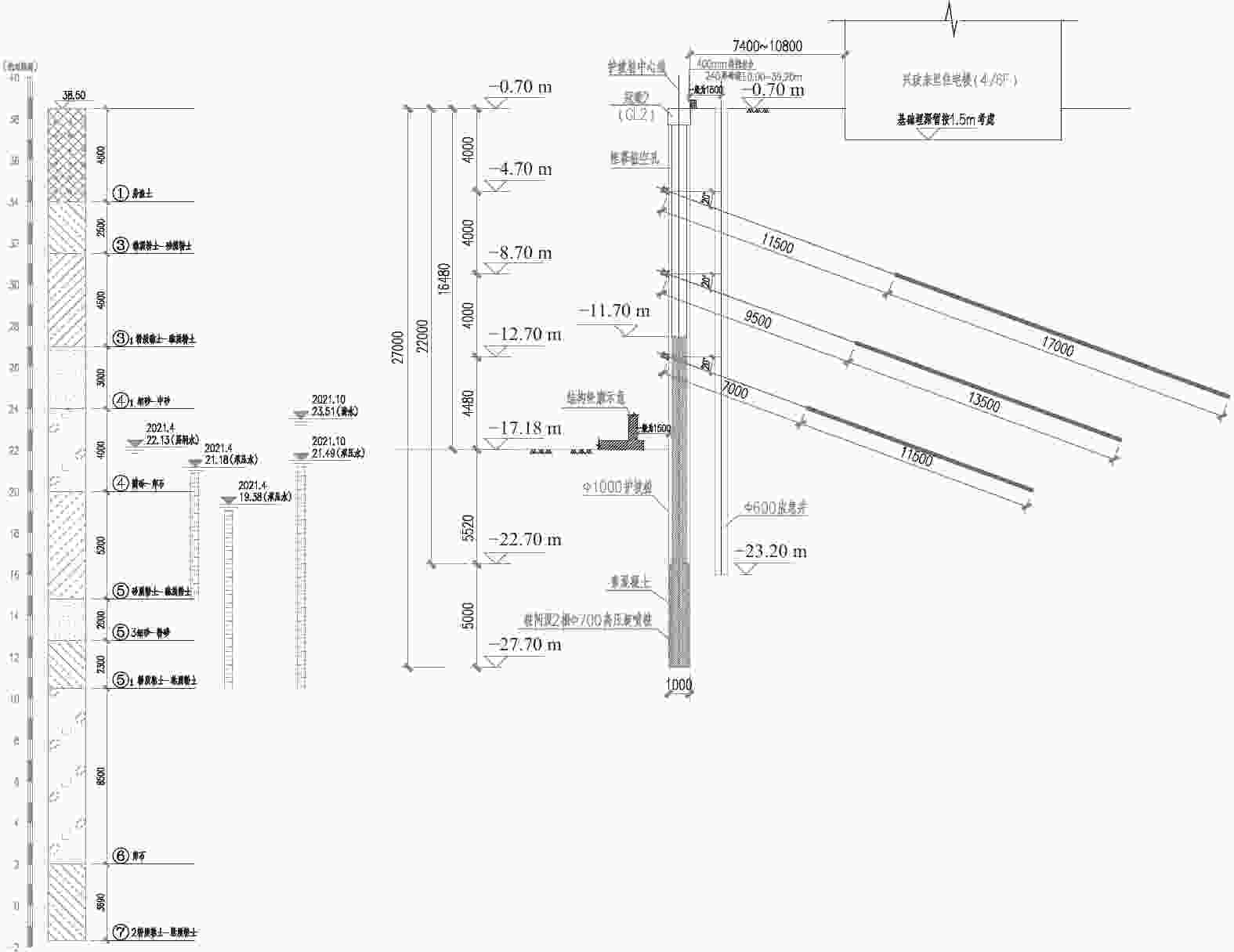
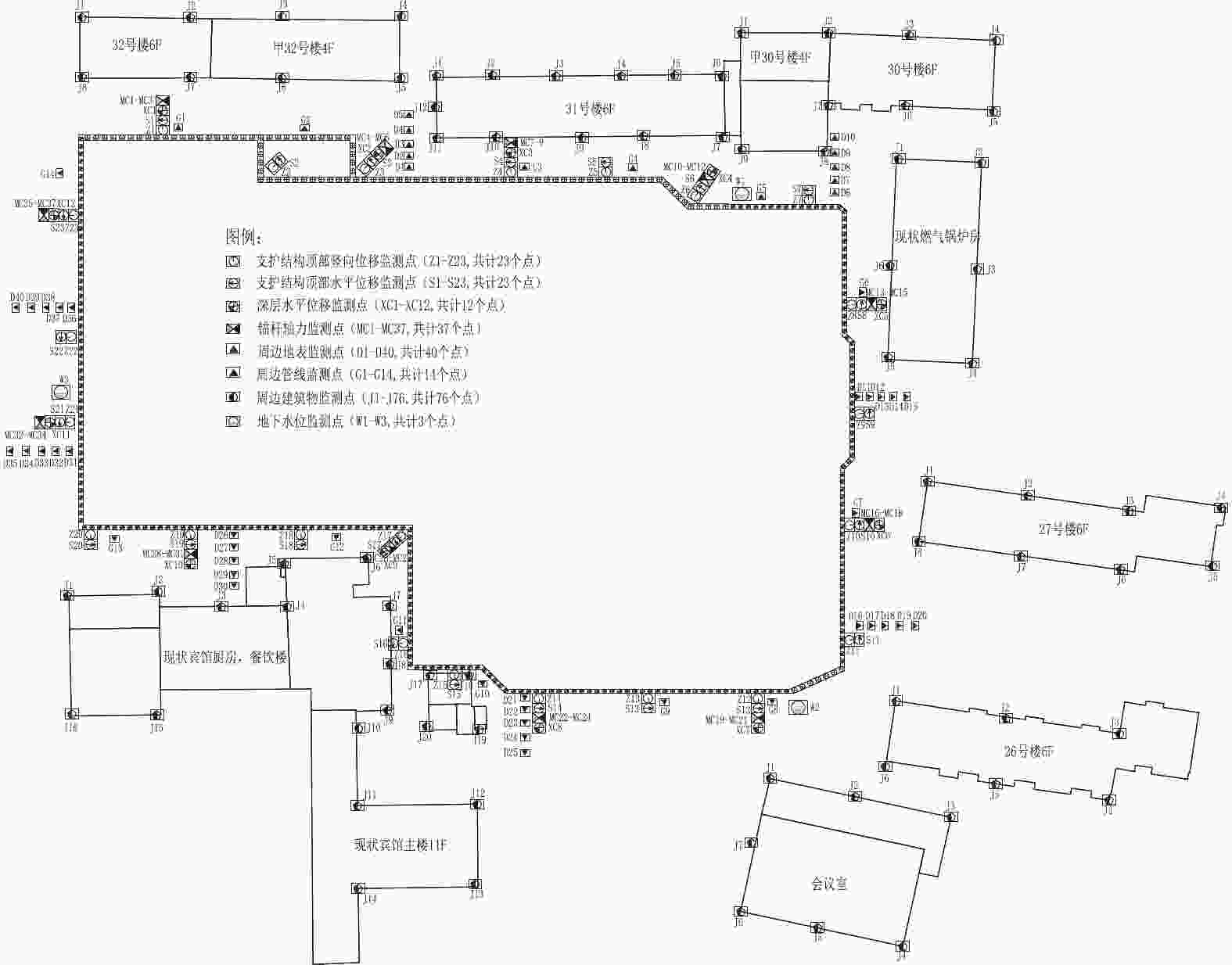
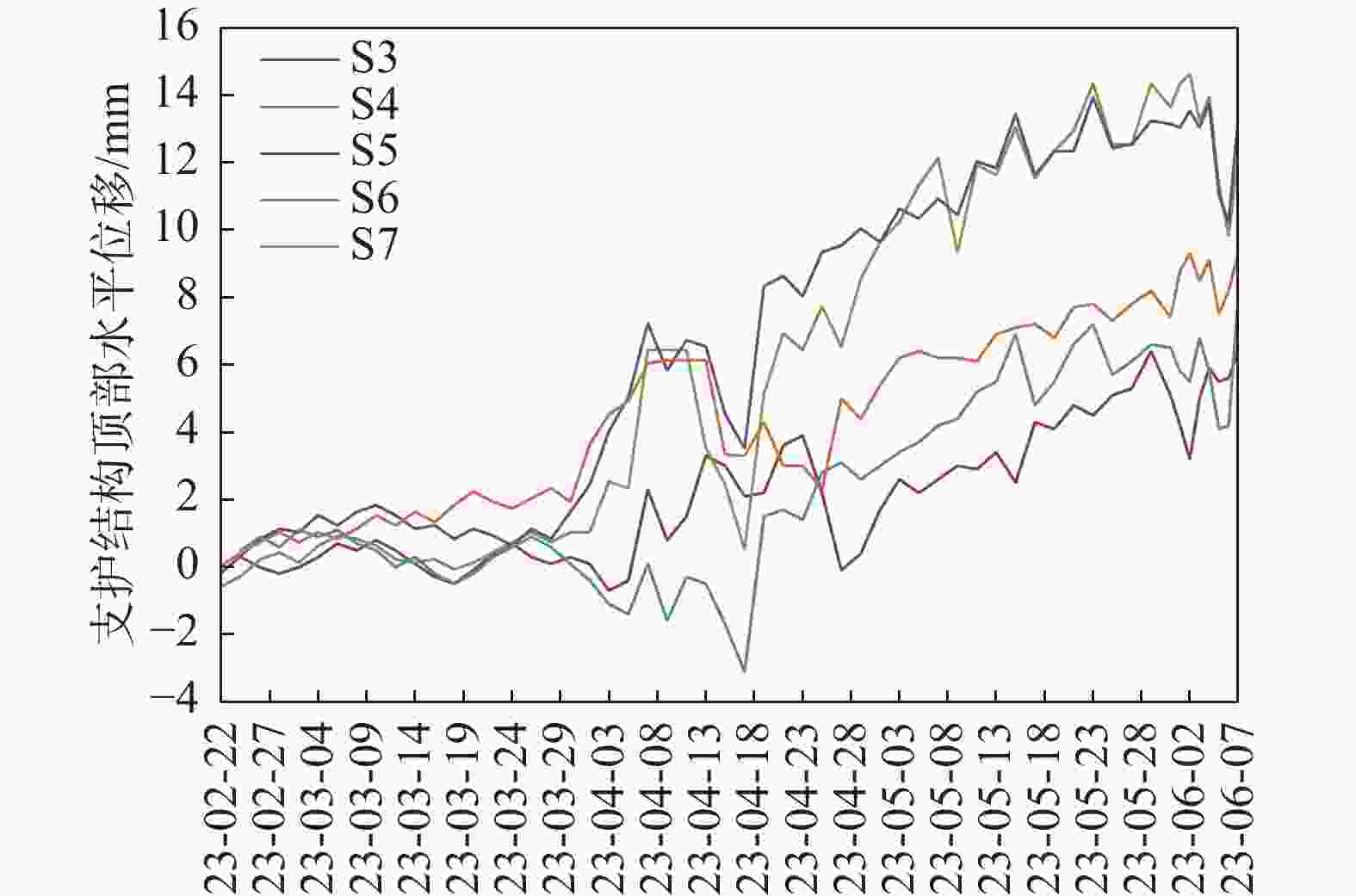
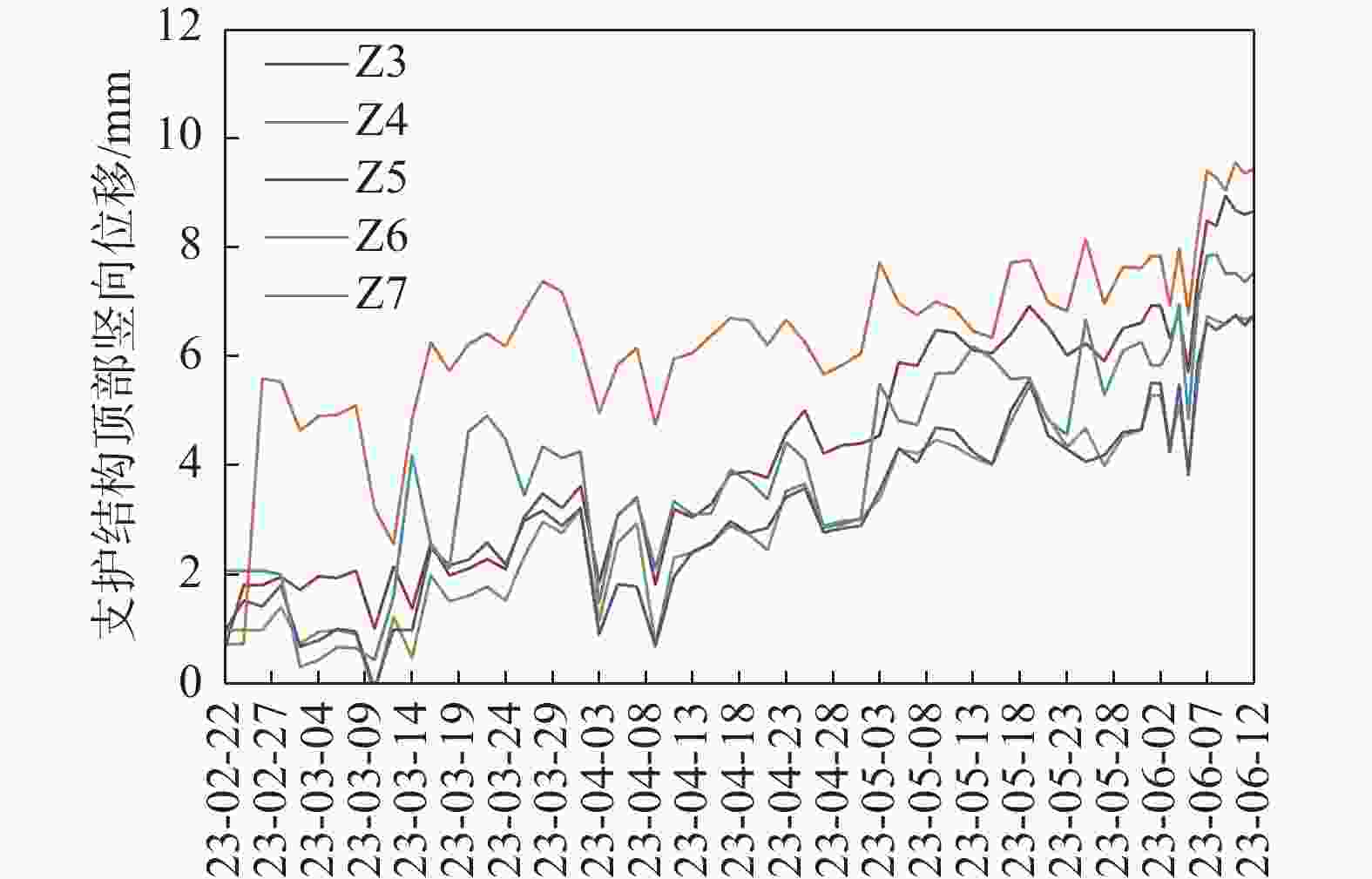
摘要: 北京城区某基坑深度约16.5 m,局部加深部位约20.4 m,基坑周边分布大量管线与住宅楼,开挖深度范围内涉及多层地下水。基坑地下水控制设计采用厚搭接落底式帷幕隔水,有效地解决了地下水渗漏问题,抑制了周边地层附加沉降,对控制周边建筑变形起到了积极作用;于基坑周边及局部深坑外围因地制宜布设应急减压井,有效地保障了水下锚杆施工,同时对承压水突涌起到了积极的防控作用。基坑支护设计遵循位移控制设计理念,通过数值分析与理论计算相结合对深基坑变形进行预测,提出支护结构位移控制标准,根据周边环境的敏感程度选取不同刚度的支护体系,并有针对性地提出锚杆施工工艺要求及地下水控制配合措施,在节约工期和造价的同时有效地保障了基坑及周边环境的安全和正常使用。Abstract: A foundation pit excavation was located in Beijing urban area with a depth of approximately 16.5 meters, with a local deepened area of up to 20.4 meters. Surrounding the excavation were numerous utility lines and residential buildings, as well as multiple layers of groundwater within the excavation depth range. The groundwater control design utilized a thick overlapping bottom-fall curtain wall to effectively solve the problem of groundwater seepage, suppressed the additional settlement of surrounding soil layers, and played a positive role in controlling the deformation of surrounding buildings. According to the local condition, emergency depressurization wells were set up around the excavation and in the local deepened area, effectively ensuring the construction of water-submerged anchor rods and playing a positive role in preventing the sudden surge of confined water. The foundation pit support design adhered to the principle of displacement control, combining numerical and theoretical calculations to predict the deformation of deep foundation pit. A standard for the displacement control of support structures was proposed, and different stiffness support systems were selected based on the degree of sensitivity of the surrounding environment. Specific requirements were also made for the construction process of anchor rods and water control measures to effectively ensure the safety and normal use of the foundation pit and surrounding environment while saving time and costs.
-
表 1 主要地层物理力学参数表
地层 重度
/(kN·m−3)c/kPa φ/(°) m
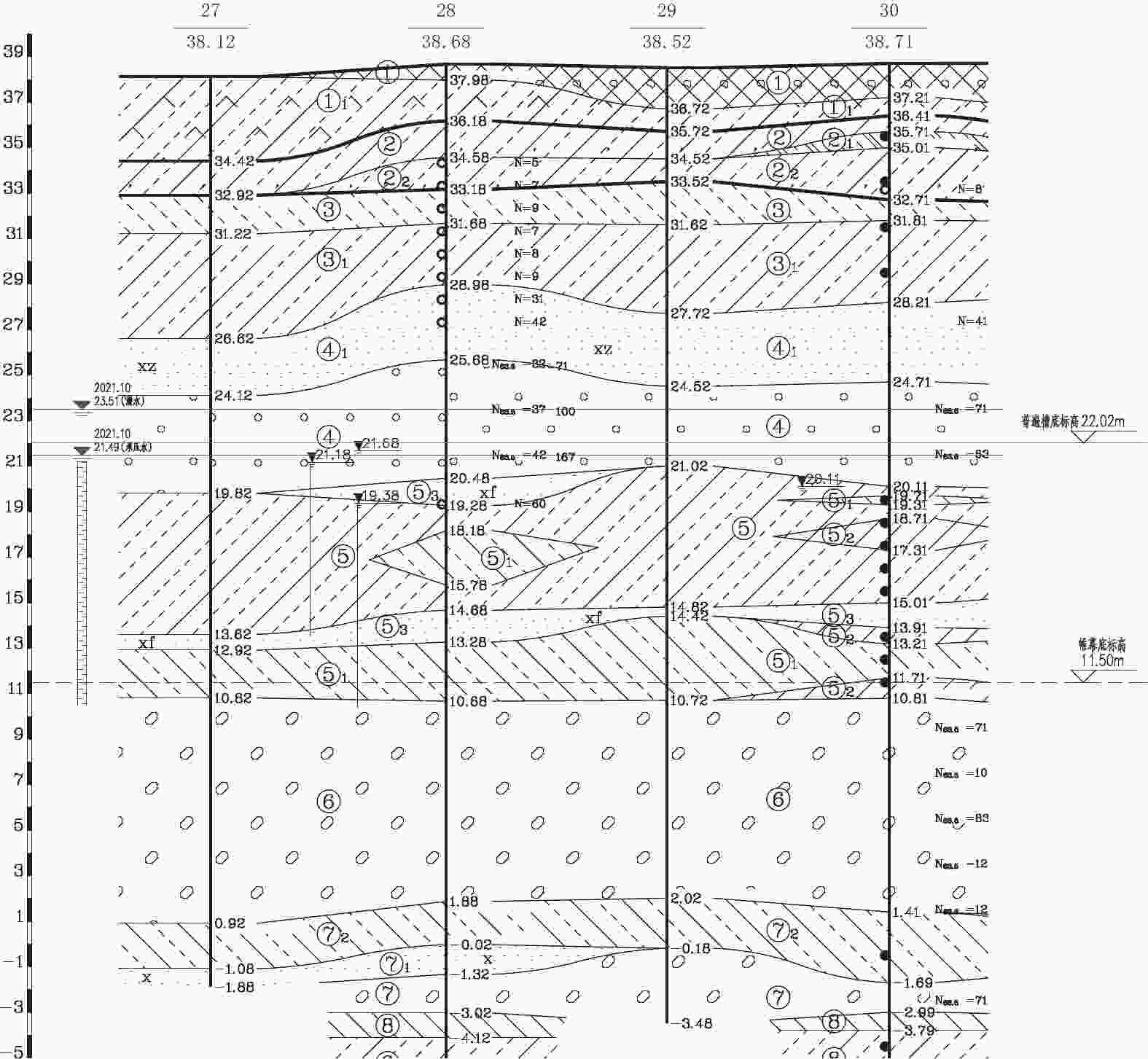
/(MPa·m−2)qs/kPa ①房渣土 19 8 12 4.96 25 ③砂质粉土–黏质粉土 20 22 25 24.4 65 ③1粉质黏土–黏质粉土 19.9 25 20 17 55 ④1细砂–中砂 20.4 0 30 30 100 ④圆砾–卵石 21 0 45 72 160 ⑤黏质粉土–砂质粉土 20 20 25 24 75 ⑤1粉质黏土–黏质粉土 20 25 22 19.96 65 ⑥卵石 21.5 0 45 72 200 表 2 地下水水位量测情况
地下水
类型稳定水位(水头) 含水层 埋深/m 标高/m 第1层
(潜水)14.79~15.96 22.83~23.51 ④层、⑤层 第2层
(承压水)16.77~17.52 21.24~21.49 ⑥层 表 3 周边建筑物变形监测值统计表
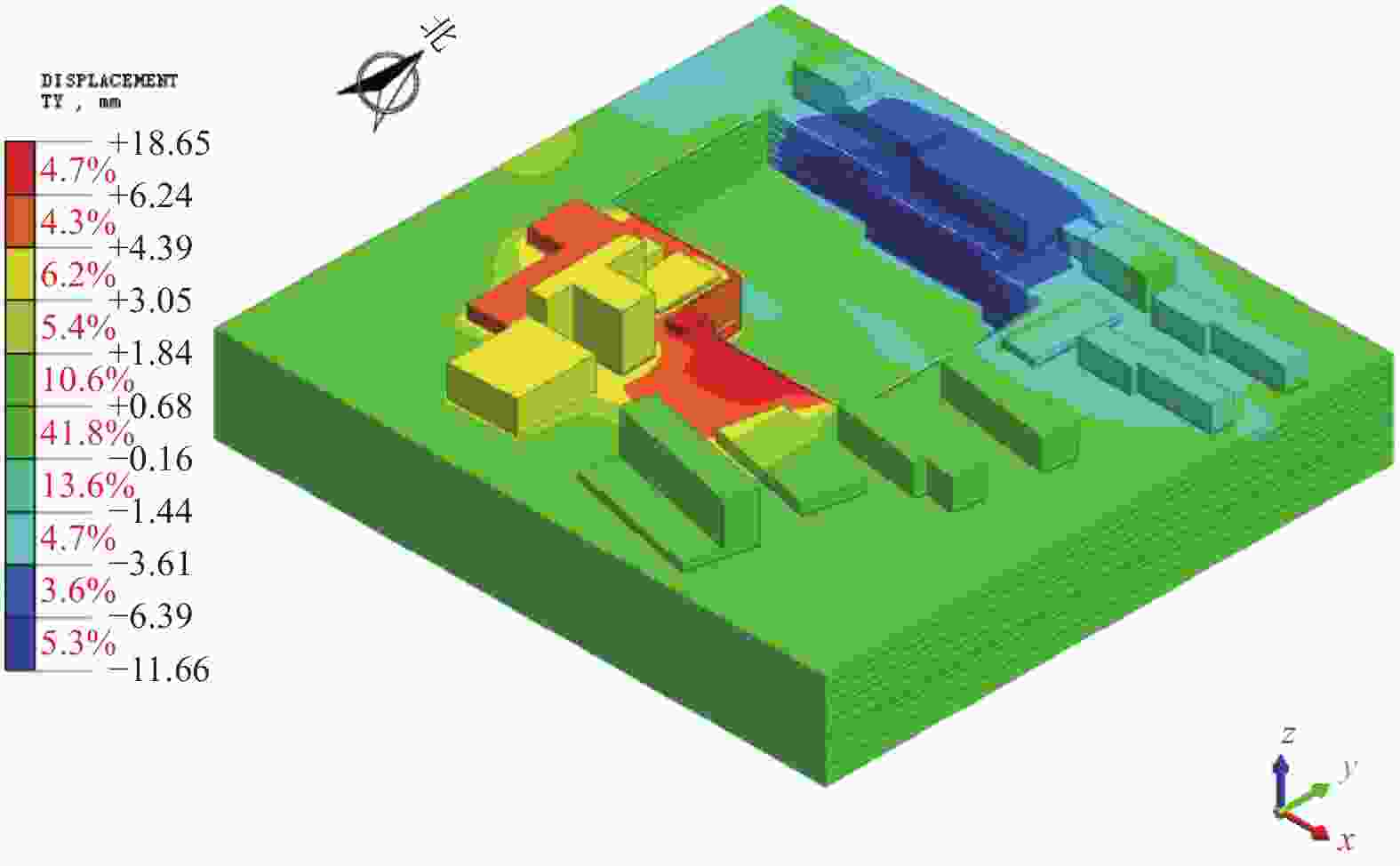
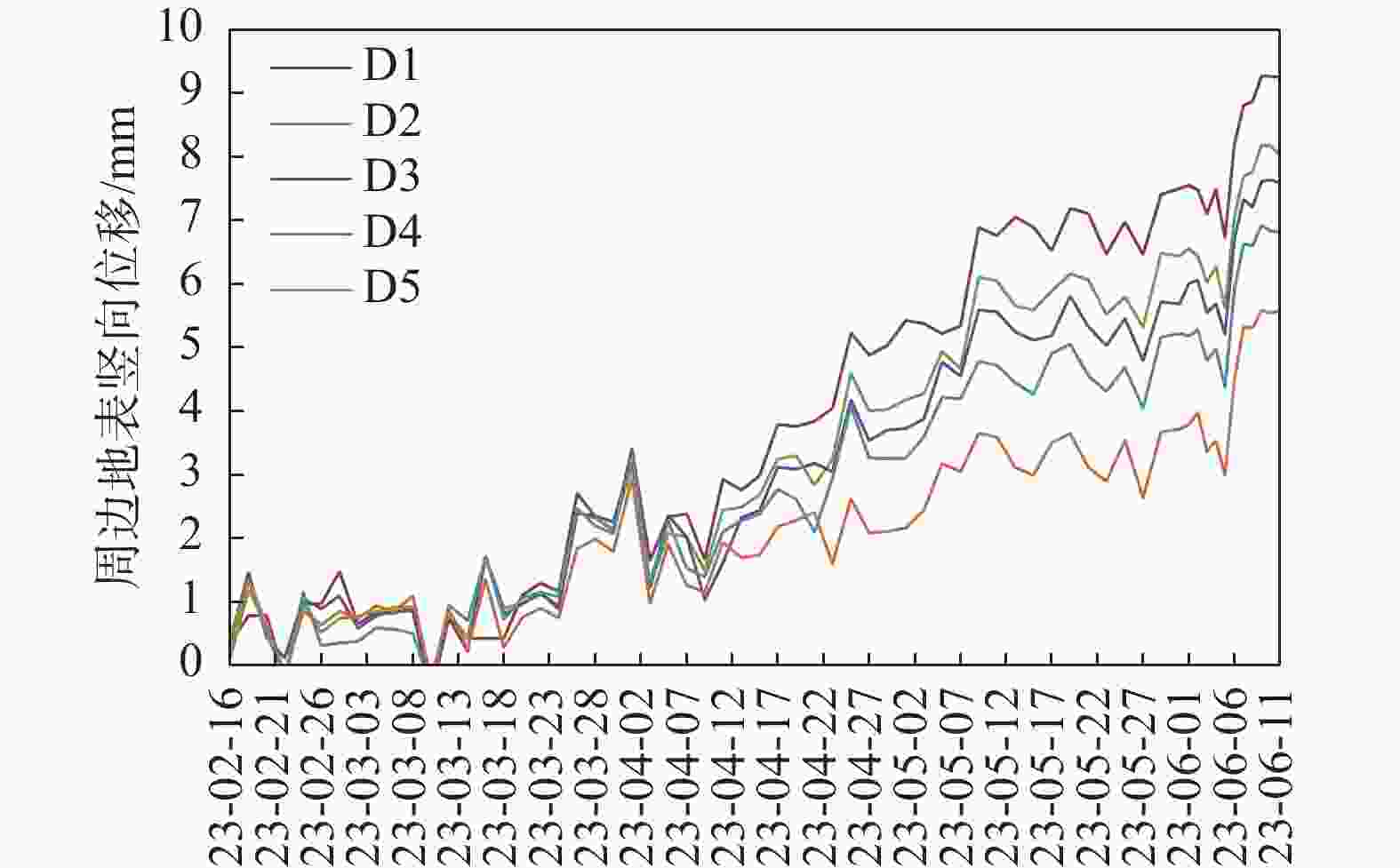
mm 楼座 隆起 沉降 楼座 隆起 沉降 26号楼 0.5 −2.9 32号楼 0.7 −3.6 27号楼 3.5 −2.8 锅炉房 2.7 −2.3 30号楼 0.6 −4.0 水泵房 9.4 −1.5 31号楼 5.5 −8.6 区政府 1.9 −2.5 -
[1] 郑 刚, 焦 莹, 李 竹. 软土地区深基坑工程存在的变形与稳定问题及其控制——基坑变形的控制指标及控制值的若干问题[J]. 施工技术,2011,40(8):8-14. (ZHENG G, JIAO Y, LI Z. Stability and deformation problems during deep foundation excavation in soft soil area and their control measures-allowable deformation control and unconventional deformation[J]. Construction Technology,2011,40(8):8-14. (in Chinese)ZHENG G, JIAO Y, LI Z. Stability and deformation problems during deep foundation excavation in soft soil area and their control measures-allowable deformation control and unconventional deformation[J]. Construction Technology, 2011, 40(8): 8-14. (in Chinese) [2] 徐杨青. 深基坑工程优化设计理论与动态变形控制研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2001. (XU Y Q. Study of optimum-design theory and dynamic displacement-controlling of deep excavation[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2001. (in Chinese)XU Y Q. Study of optimum-design theory and dynamic displacement-controlling of deep excavation[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2001. (in Chinese) [3] 侯学渊, 杨 敏. 软土地基变形控制设计理论和工程实践[M]. 上海: 同济大学出版社, 1996. (HOU X Y, YANG M. Design theory and engineering practice of the deformation control for soft soil[M]. Shanghai: Tongji University Press, 1996. (in Chinese)HOU X Y, YANG M. Design theory and engineering practice of the deformation control for soft soil[M]. Shanghai: Tongji University Press, 1996. (in Chinese) [4] 郑 刚, 李志伟. 不同围护结构变形形式的基坑开挖对邻近建筑物的影响对比分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2012,34(6):969-977. (ZHENG G, LI Z W. Comparative analysis of responses of buildings adjacent to excavations with different deformation modes of retaining walls[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2012,34(6):969-977. (in Chinese)ZHENG G, LI Z W. Comparative analysis of responses of buildings adjacent to excavations with different deformation modes of retaining walls[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2012, 34(6): 969-977. (in Chinese) [5] 郑 刚, 李志伟. 基坑开挖对邻近不同楼层建筑物影响的有限元分析[J]. 天津大学学报,2012,45(9):829-837. (ZHENG G, LI Z W. Finite element analysis of response of building with different storeys adjacent to pit excavation[J]. Journal of Tianjin University,2012,45(9):829-837. (in Chinese)ZHENG G, LI Z W. Finite element analysis of response of building with different storeys adjacent to pit excavation[J]. Journal of Tianjin University, 2012, 45(9): 829-837. (in Chinese) [6] 郑 刚, 王 琦, 邓 旭, 等. 不同围护结构变形模式对坑外既有隧道变形影响的对比分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2015,37(7):1181-1194. (ZHENG G, WANG Q, DENG X, et al. Comparative analysis of influences of different deformation modes of retaining structures on deformation of existing tunnels outside excavations[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2015,37(7):1181-1194. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201507003ZHENG G, WANG Q, DENG X, et al. Comparative analysis of influences of different deformation modes of retaining structures on deformation of existing tunnels outside excavations[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(7): 1181-1194. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201507003 [7] CLOUGH G W, DUNCAN J M. Finite element analyses of retaining wall behavior[J]. Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division,1971,97(12):1657-1673. doi: 10.1061/JSFEAQ.0001713 [8] 沈 健, 王建华, 高绍武. 基于“m”法的深基坑支护结构三维分析方法[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2005,1(4):530-533. (SHEN J, WANG J H, GAO S W. 3-D analysis method of retaining structure of deep excavation based on “M” method[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering,2005,1(4):530-533. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0836.2005.04.012SHEN J, WANG J H, GAO S W. 3-D analysis method of retaining structure of deep excavation based on “M” method[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2005, 1(4): 530-533. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0836.2005.04.012 [9] CHAMBOSSE G, OTTERBEIN R. State of the art of compensation grouting in Germany[C]//Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. Istanbul, Turkey: SIMSG, 2001: 1511-1514. [10] AU S K A, SOGA K, BOLTON M D. Effect of multiple injection on long-term compensation grouting-laboratory and numerical studies[C]//Proceedings of the International Symposium on Geotechnical Aspects of Underground Construction in Soft Ground. Toulouse, 2002: 657-661. [11] 侯学渊, 刘国彬, 黄院雄. 城市基坑工程发展的几点看法[J]. 施工技术,2000,29(1):5-7. (HOU X Y, LIU G B, HUANG Y X. Several views on the development of urban foundation work[J]. Construction Technology,2000,29(1):5-7. (in Chinese)HOU X Y, LIU G B, HUANG Y X. Several views on the development of urban foundation work[J]. Construction Technology, 2000, 29(1): 5-7. (in Chinese) [12] 易小明, 张顶立, 李鹏飞. 隧道下穿时地表房屋变形开裂的定量评估[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2008,27(11):2288-2294. (YI X M, ZHANG D L, LI P F. Quantitative evaluation of house deformation and cracks caused by tunnel-crossing[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2008,27(11):2288-2294. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.11.016YI X M, ZHANG D L, LI P F. Quantitative evaluation of house deformation and cracks caused by tunnel-crossing[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(11): 2288-2294. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.11.016 [13] 李云安, 钟玉芳, 张鸿昌. 影响基坑变形的实质性状态变量分析[J]. 地质与勘探,2000,36(2):49-52. (LI Y A, ZHONG Y F, ZHANG H C. Analysis of substantial state varaiables influencing deformation of foundation pit[J]. Geology and Prospecting,2000,36(2):49-52. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2000.02.017LI Y A, ZHONG Y F, ZHANG H C. Analysis of substantial state varaiables influencing deformation of foundation pit[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2000, 36(2): 49-52. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2000.02.017 [14] 李云安, 葛修润, 张鸿昌. 深基坑工程变形控制与有限元数值模拟分析[J]. 地质与勘探,2001,37(5):73-76. (LI Y A, GE X R, ZHANG H C. Deformation control of deep excavation engineering and analysis of numerical simulation with finite element method[J]. Geology and Prospecting,2001,37(5):73-76. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2001.05.019LI Y A, GE X R, ZHANG H C. Deformation control of deep excavation engineering and analysis of numerical simulation with finite element method[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2001, 37(5): 73-76. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2001.05.019 [15] LONG M. Database for retaining wall and ground movements due to deep excavations[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2001,127(3):203-224. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2001)127:3(203) [16] 王曙光. 复杂周边环境基坑工程变形控制技术[J]. 岩土工程学报,2013,35(S1):474-477. (WANG S G. Deformation control of excavation engineering with complicated surroundings[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2013,35(S1):474-477. (in Chinese)WANG S G. Deformation control of excavation engineering with complicated surroundings[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(S1): 474-477. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: