Mechanism analysis of bedrock landslides in coal measures of Guangdong Province: a case study of the Lishui Wentouling landslide, Foshan City
-
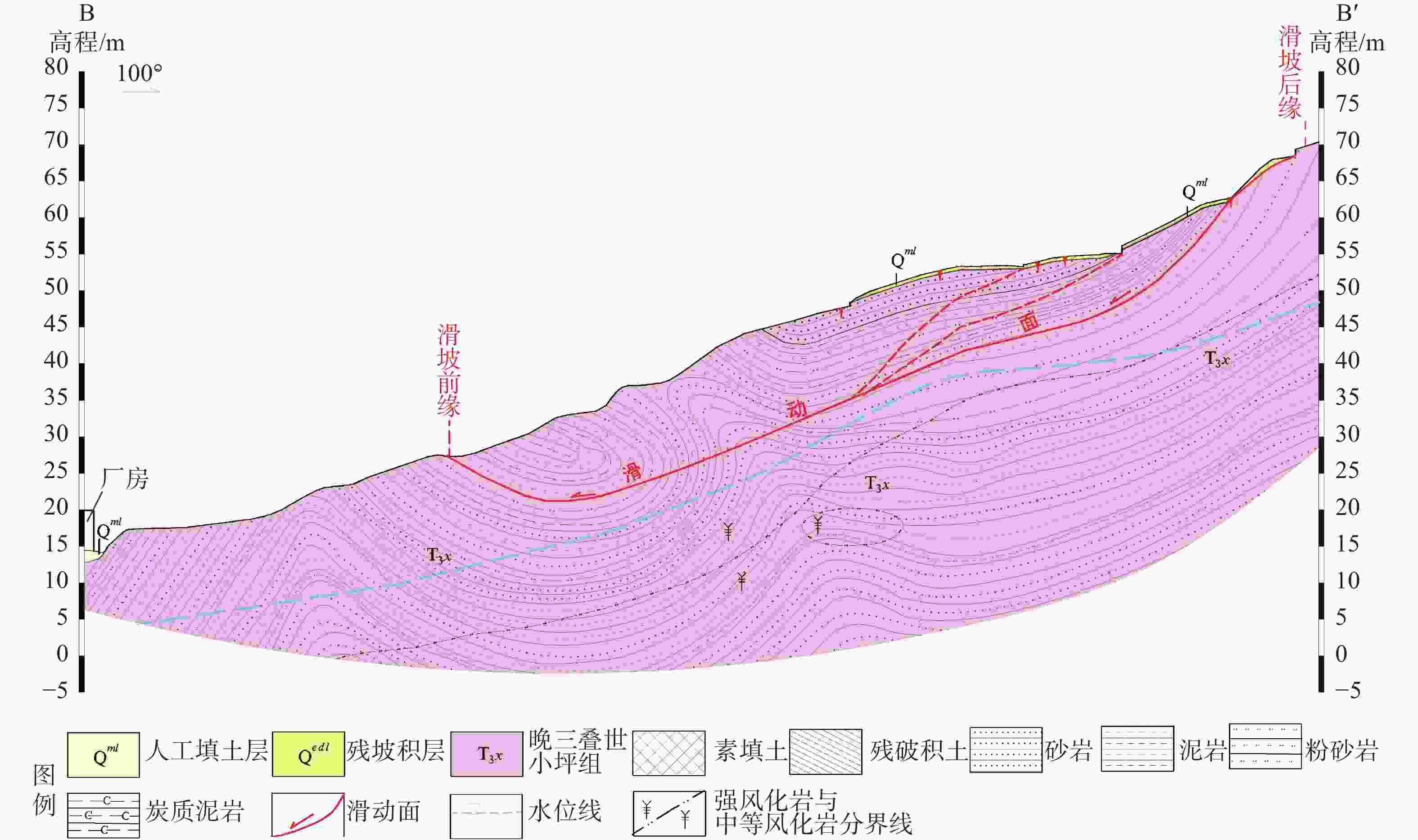
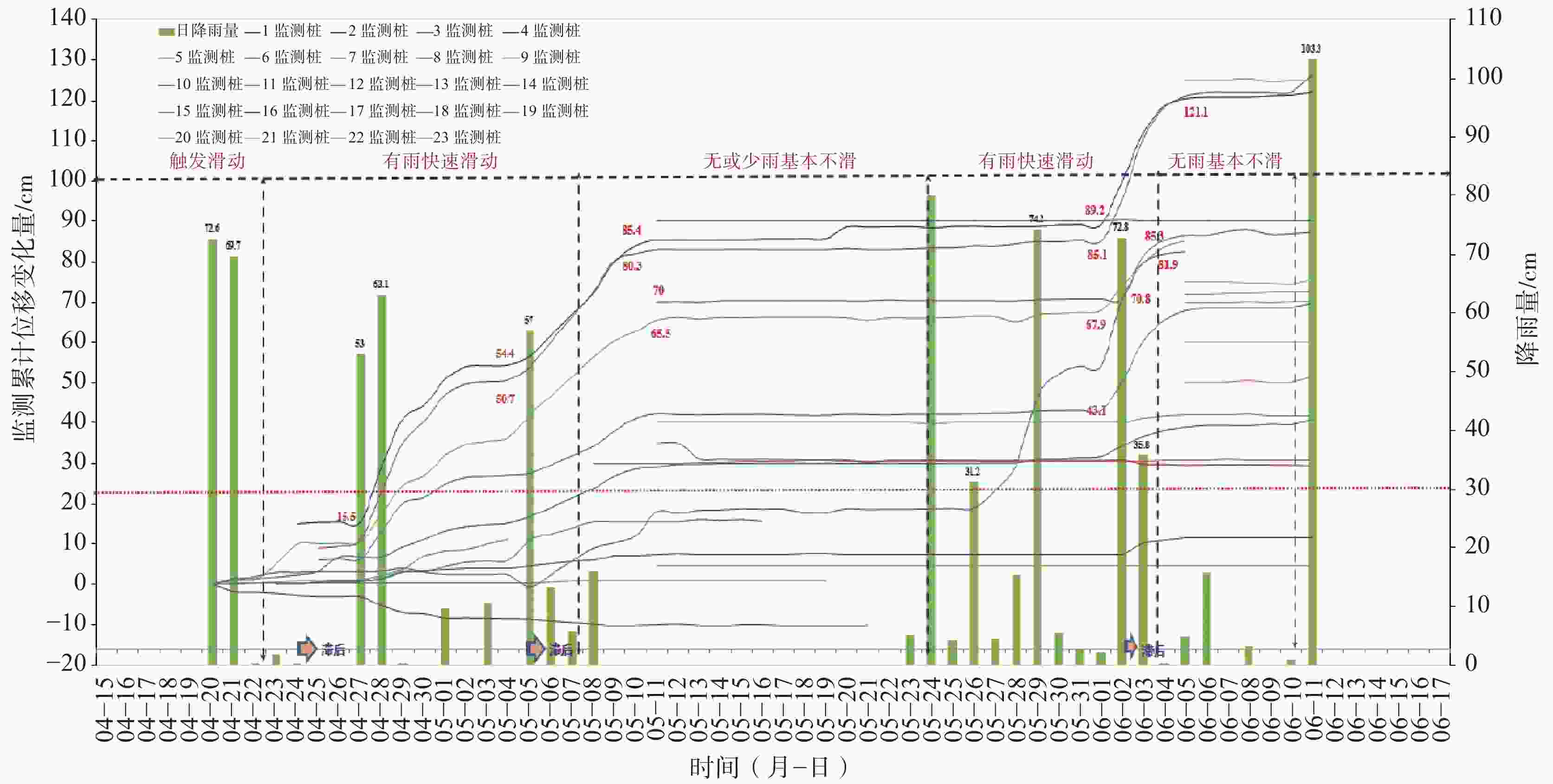
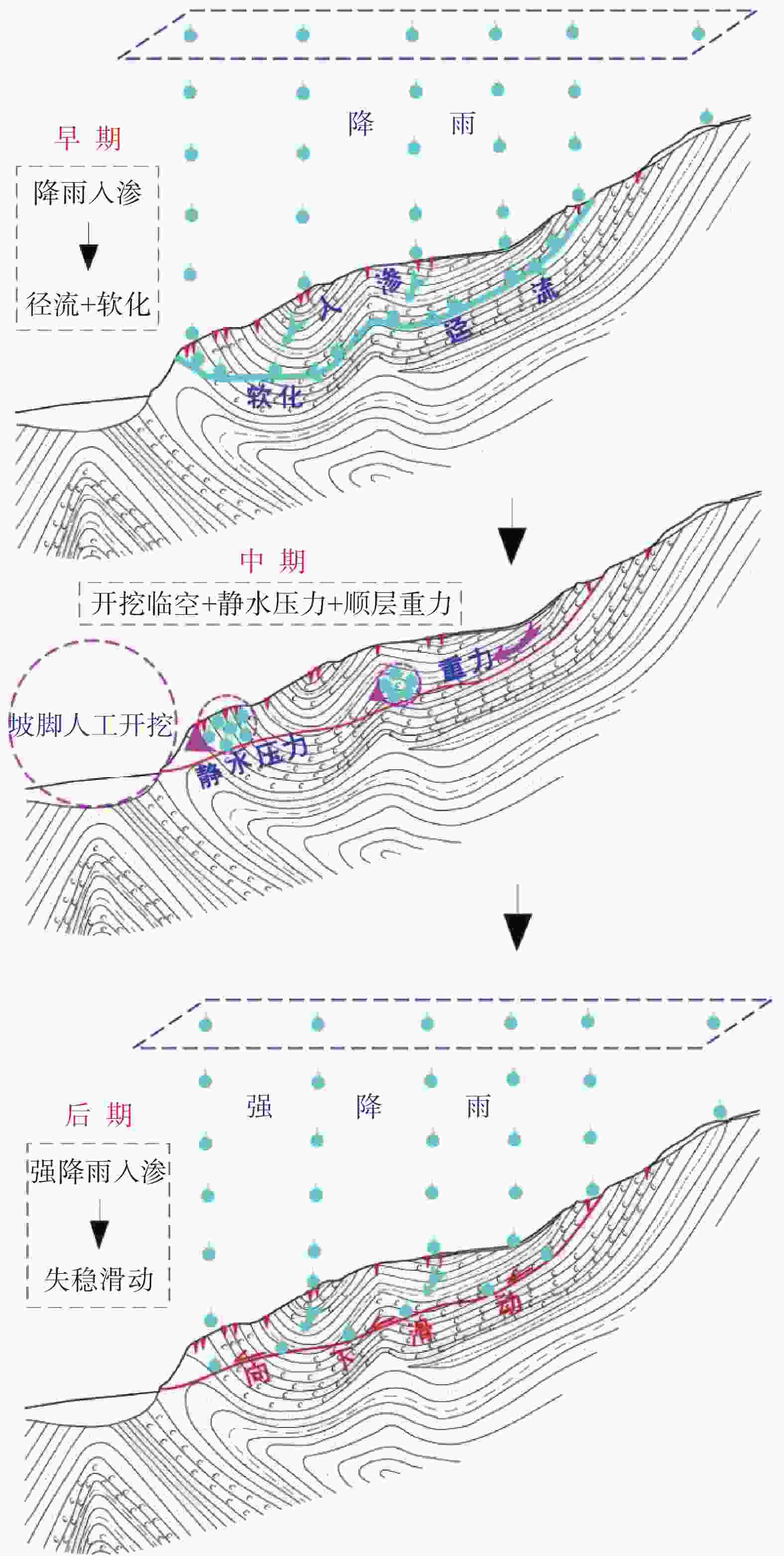
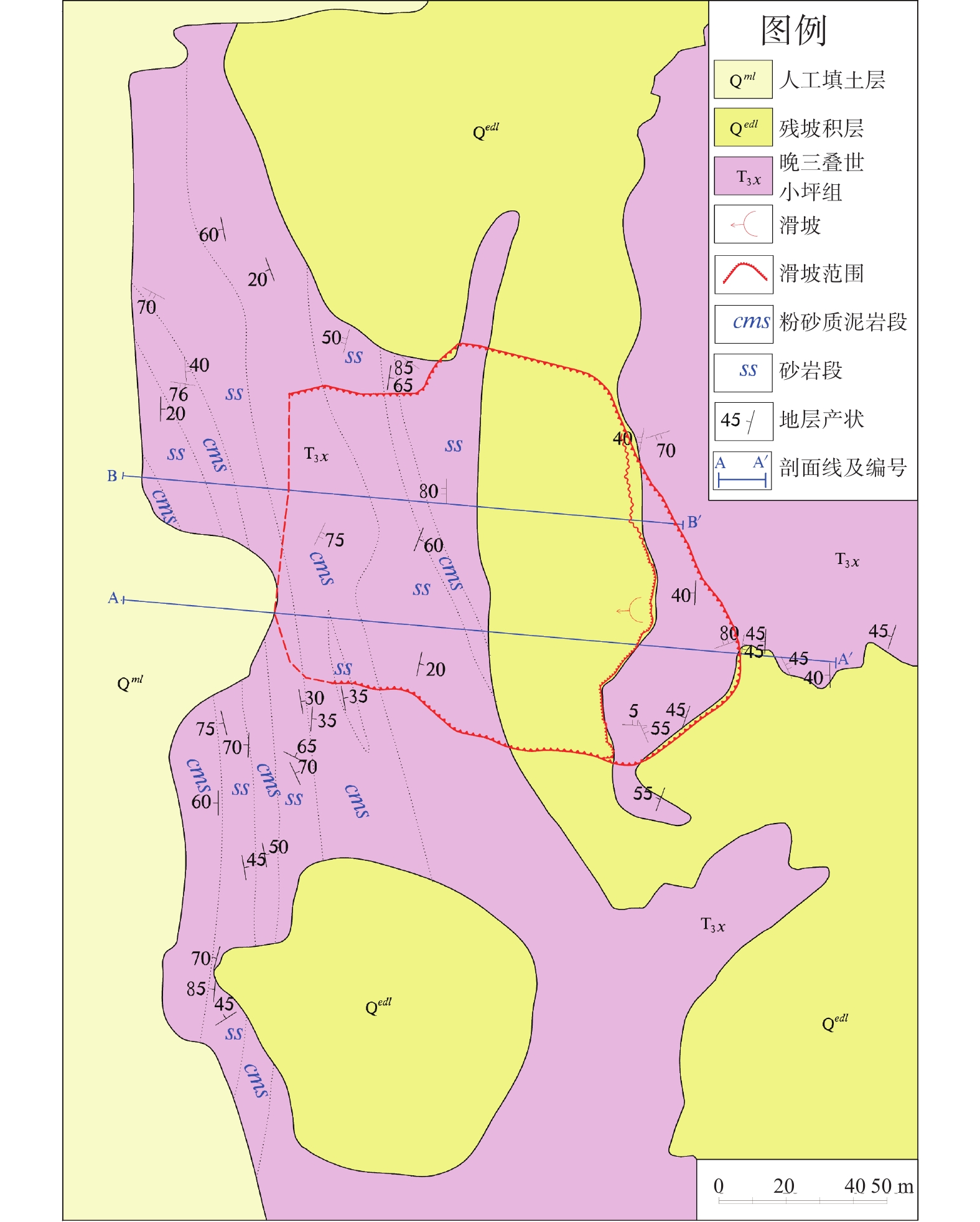
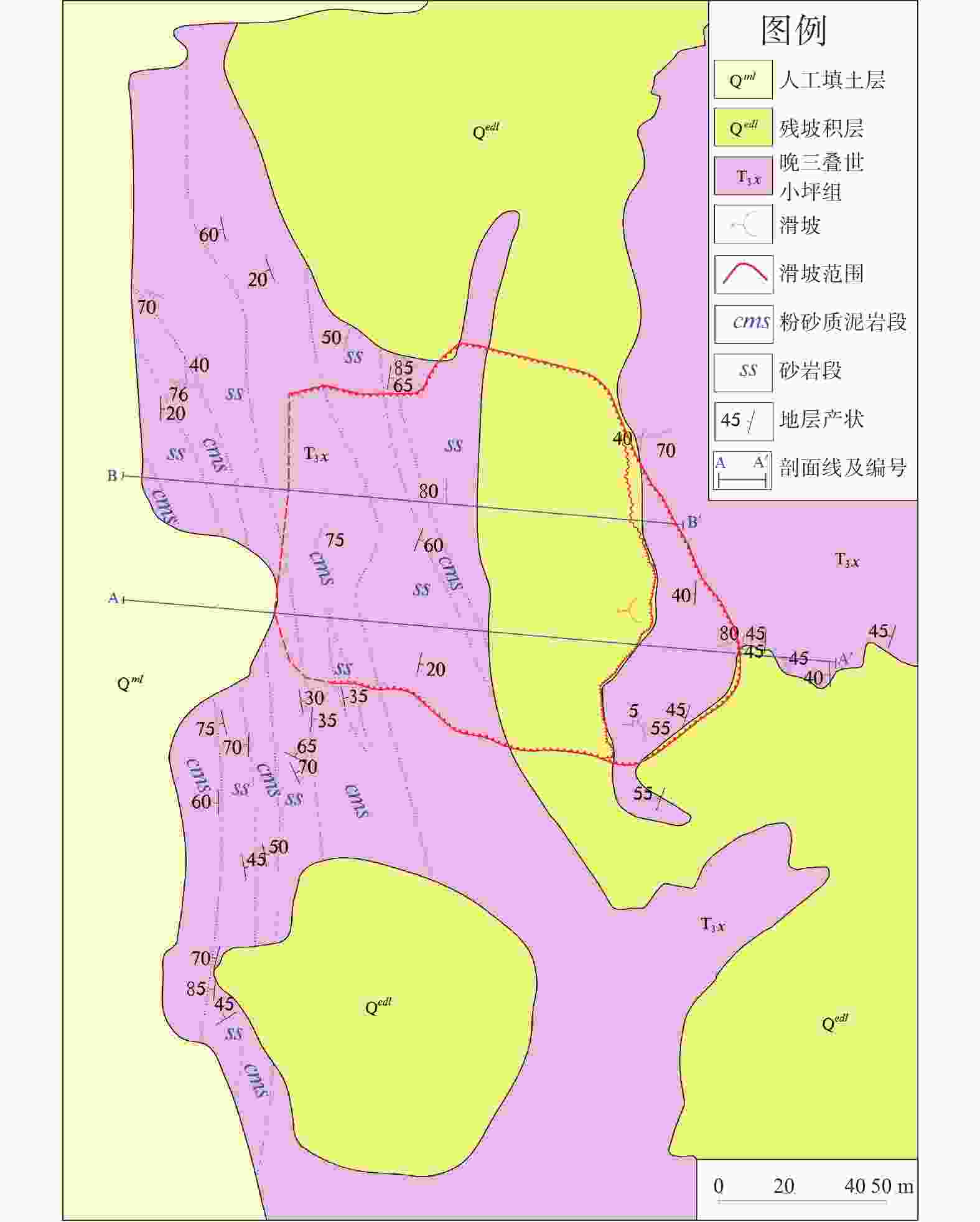
摘要: 以佛山市里水文头岭山体滑坡为例,通过调查、钻探和监测等手段,查明滑坡区地质环境条件和灾害特征,分析了影响因素和滑动机理。结果表明:(1)总体呈雨量越大滑动越快特点,滑动雨量阖值约30 mm;(2)煤系地层发育、顺向坡和褶皱构造作用是滑坡形成的内在因素,反倾粗砂岩条带被开挖和长期雨水入渗在粗砂岩条带位置积蓄形成静水压力作用是滑坡形成的间接诱发因素,强降雨作用是滑坡形成的直接诱发因素;(3)滑动机理模式为:早期雨水入渗并沿炭质泥岩界面径流,软化并加速滑动面形成;中期坡脚开挖临空,叠加坡上岩土体重力和坡脚静水压力,共同向下作用贯通滑面;后期强降雨诱发滑坡。研究成果可供同类煤系地层滑坡的调查评价、监测预警和后续防范治理参考。Abstract: The Lishui Wentouling landslide, Foshan City was investigated through investigation, drilling, and monitoring methods. The geological environmental conditions and disaster characteristics of the landslide area were identified, and the influencing factors and sliding mechanism were analyzed. The results show that: (1) the overall trend is that the larger the rainfall, the faster the sliding, with a sliding rainfall value of about 30 mm; (2) The development of coal bearing strata, along slope and fold structures are inherent factors in the formation of landslides. The excavation and long-term infiltration of rainwater into the coarse sandstone belt, resulting in static water pressure, are indirect triggering factors for landslide formation. Heavy rainfall is the direct triggering factor for landslide formation; (3) The sliding mechanism mode is characterized by early infiltration of rainwater and accelerated formation of sliding surfaces along the interface of carbonaceous mudstone due to softening of runoff. In the middle stage, excavation at the foot of the slope, combined with the gravity of the rock and soil mass on the slope and the static water pressure at the foot of the slope, acts downwards to penetrate the sliding surface. In the later stage, heavy rainfall induces landslides. This research can provide reference for the investigation, evaluation, monitoring, early warning, and subsequent prevention and control of landslides in similar coal bearing strata.
-
Key words:
- coal-bearing strata /
- bedrock landslide /
- formation mechanism
-
表 1 各监测桩基本情况表
所在滑坡位置 监测桩编号 监测时间(月-日) 坡脚前缘 1号 04-20—06-11 2号 04-20—05-20,之后损坏 3号 04-20—05-19,之后损坏 4号 04-23—06-11 5号 04-23—05-17,之后损坏 9号 04-20—06-06,之后损坏 10号 04-20—06-06,之后损坏 11号 04-20—05-05,之后损坏 坡体中部 12号 05-08—06-11 13号 05-11—06-11 14号 05-11—06-11 15号 05-11—06-11 17号 05-11—06-11 两侧周界 19号 06-05—06-11 20号 06-05—06-11 21号 06-05—06-11 22号 06-05—06-11 23号 06-05—06-11 坡顶后缘 6号 04-23—06-11 7号 04-25—06-11 8号 04-25—06-11 16号 05-11—06-11 18号 06-06—06-11 -
[1] 广东省自然资源厅. 广东省地质灾害防治“十四五”规划[S]. 2022年. (Guangdong Provincial Department of Natural Resources. The 14th Five Year Plan for Geological Disasters in Guangdong Province (2022). (in Chinese)Guangdong Provincial Department of Natural Resources. The 14th Five Year Plan for Geological Disasters in Guangdong Province (2022). (in Chinese) [2] 黄润秋. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2007,26(3):433-454. (HUANG R Q. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in China since the 20th century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2007,26(3):433-454. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.03.001HUANG R Q. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in China since the 20th century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(3): 433-454. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.03.001 [3] 邹正盛, 方 斌, 张 征. 西宁市林家崖滑坡稳定性研究[J]. 工程地质学报,1998,6(3):199-204. (ZOU Z S, FANG B, ZHANG Z. Research on stability of Linjiaya landslide, Xining city[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,1998,6(3):199-204. (in Chinese)ZOU Z S, FANG B, ZHANG Z. Research on stability of Linjiaya landslide, Xining city[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 1998, 6(3): 199-204. (in Chinese) [4] 张加桂. 三峡库区巫山县新城址工业区滑坡的成因机制研究[J]. 工程地质学报,1999,7(3):237-242. (ZHANG J G. Occurrence mechanism of landslide industrial zone of in the new town of Wushan county, the Three-Gorges reservoir region[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,1999,7(3):237-242. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.1999.03.008ZHANG J G. Occurrence mechanism of landslide industrial zone of in the new town of Wushan county, the Three-Gorges reservoir region[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 1999, 7(3): 237-242. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.1999.03.008 [5] 成国文, 李 晓, 许家美, 等. 重庆涪陵五中滑坡特征及成因分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2009,17(2):220-227. (CHENG G W, LI X, XU J M, et al. Characteristics and causes of landslide at fuling fifth middle school in Chongqing[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2009,17(2):220-227. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.02.011CHENG G W, LI X, XU J M, et al. Characteristics and causes of landslide at fuling fifth middle school in Chongqing[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2009, 17(2): 220-227. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.02.011 [6] 张伟锋, 黄润秋, 裴向军. 大光包滑坡运动特征及其过程分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2015,23(5):866-885. (ZHANG W F, HUANG R Q, PEI X J. Analysis on kinematics characteristics and movement process of Daguangbao landslide[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2015,23(5):866-885. (in Chinese)ZHANG W F, HUANG R Q, PEI X J. Analysis on kinematics characteristics and movement process of Daguangbao landslide[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2015, 23(5): 866-885. (in Chinese) [7] 许 强, 李为乐, 董秀军, 等. 四川茂县叠溪镇新磨村滑坡特征与成因机制初步研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2017,36(11):2612-2628. (XU Q, LI W L, DONG X J, et al. The Xinmocun landslide on June 24, 2017 in Maoxian, Sichuan: characteristics and failure mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2017,36(11):2612-2628. (in Chinese)XU Q, LI W L, DONG X J, et al. The Xinmocun landslide on June 24, 2017 in Maoxian, Sichuan: characteristics and failure mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(11): 2612-2628. (in Chinese) [8] 朱赛楠, 殷跃平, 李 滨. 大型层状基岩滑坡软弱夹层演化特征研究——以重庆武隆鸡尾山滑坡为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(6):1638-1647. (ZHU S N, YIN Y P, LI B. Evolution characteristics of weak intercalation in massive layered rockslides–a case study of Jiweishan rockslide in Wulong, Chongqing[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(6):1638-1647. (in Chinese)ZHU S N, YIN Y P, LI B. Evolution characteristics of weak intercalation in massive layered rockslides–a case study of Jiweishan rockslide in Wulong, Chongqing[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(6): 1638-1647. (in Chinese) [9] 郝念学, 李星宇. 永善县城东部滑坡演化及复活滑动机理分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2021,29(S1):152-159. (HE N X, LI X Y. Analysis of the evolution and resurgence sliding mechanism of landslides in the eastern part of Yongshan county[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021,29(S1):152-159. (in Chinese)HE N X, LI X Y. Analysis of the evolution and resurgence sliding mechanism of landslides in the eastern part of Yongshan county[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2021, 29(S1): 152-159. (in Chinese) [10] 胡 莹, 宋盛渊, 于崇嘉, 等. 延吉市小河龙滑坡成因机制与稳定性分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2021,29(S1):144-151. (HU Y, SONG S Y, YU C J, et al. Genesis mechanism and stability analysis of the Xiaohelong landslide in Yanji city[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021,29(S1):144-151. (in Chinese)HU Y, SONG S Y, YU C J, et al. Genesis mechanism and stability analysis of the Xiaohelong landslide in Yanji city[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2021, 29(S1): 144-151. (in Chinese) [11] 易 巍. 广东省煤系地层不同坡体结构的病害模式及防治对策[J]. 铁道建筑, 2015(9): 94-97. (YI W. Disease modes and control measures of different slope structures in coal measure strata in Guangdong Province[J]. Railway Engineering, 2015(9): 94-97. (in Chinese)YI W. Disease modes and control measures of different slope structures in coal measure strata in Guangdong Province[J]. Railway Engineering, 2015(9): 94-97. (in Chinese) [12] 赵华鹏. 顺倾向煤系地层边坡稳定性研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2016. (ZHAO H P. Study on the stability of the bedding coal strata slope[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Technology, 2016. (in Chinese)ZHAO H P. Study on the stability of the bedding coal strata slope[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Technology, 2016. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: