Effect of ground fissure activity on groundwater level migration
-
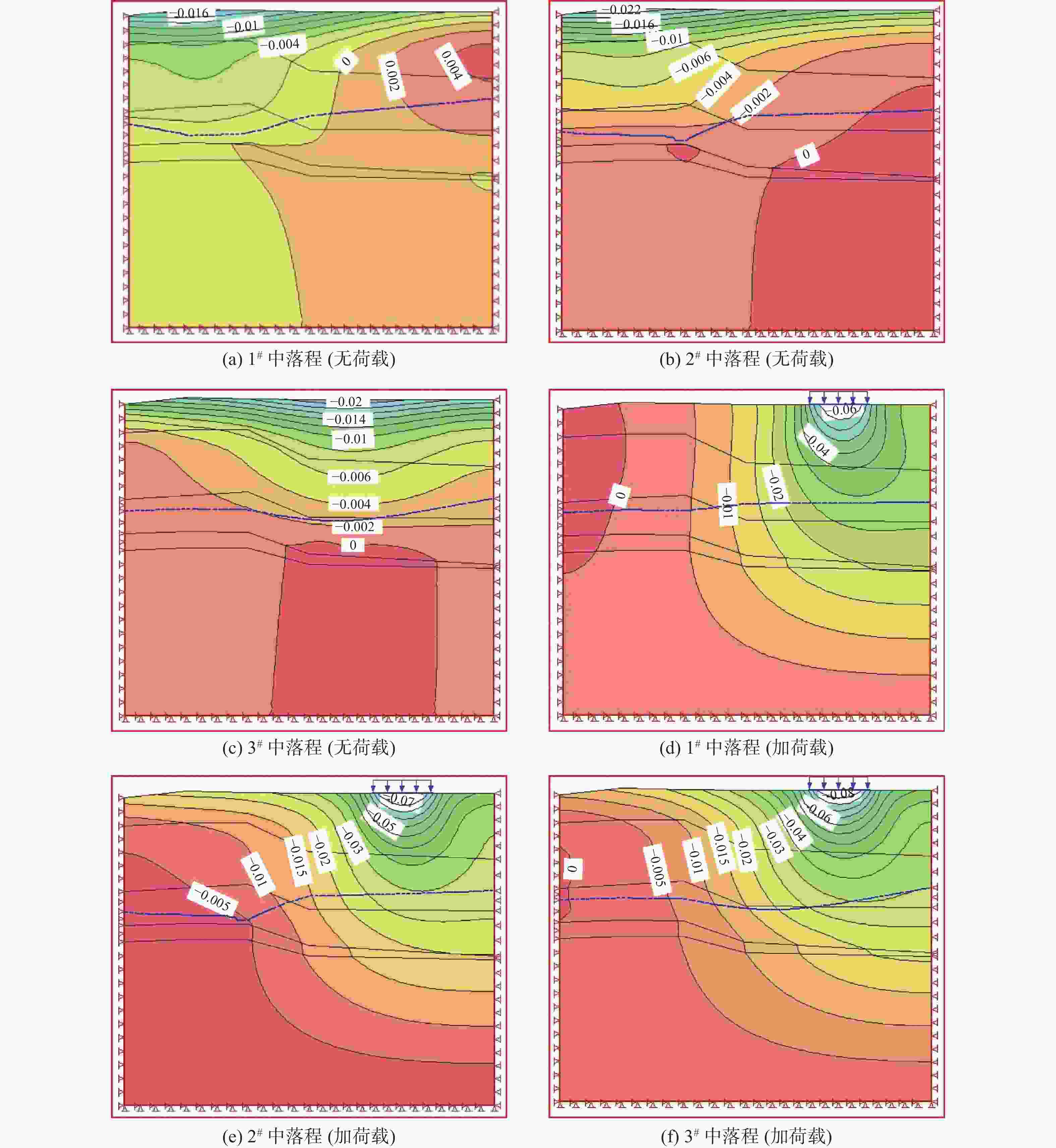
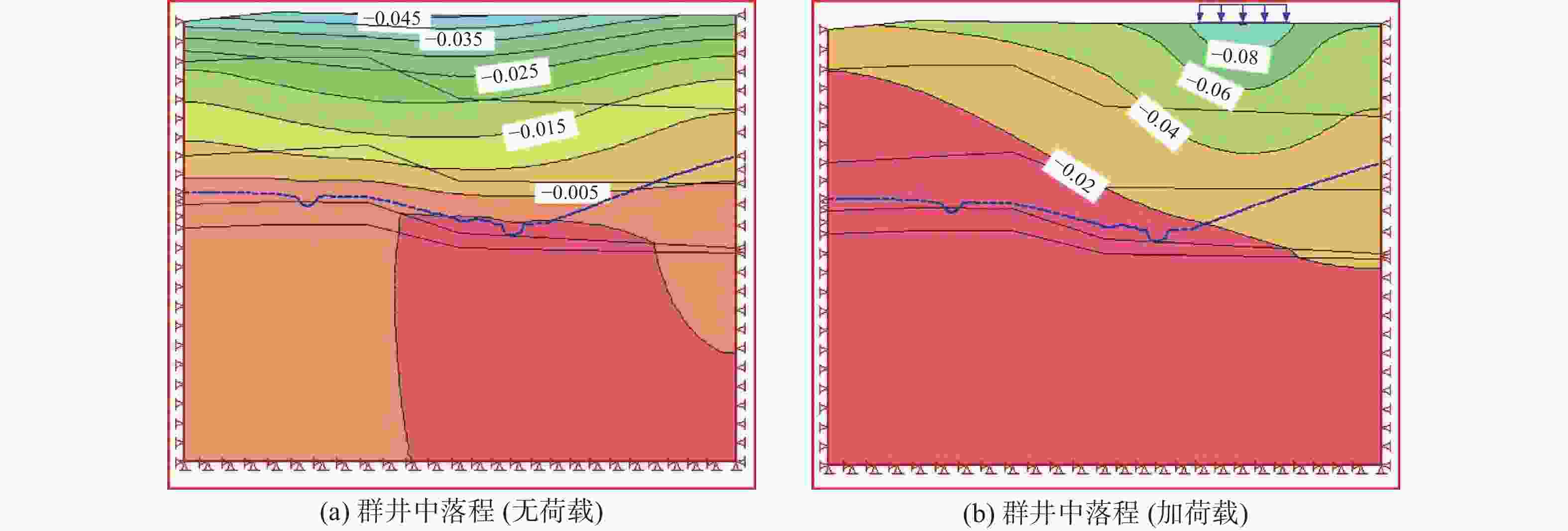
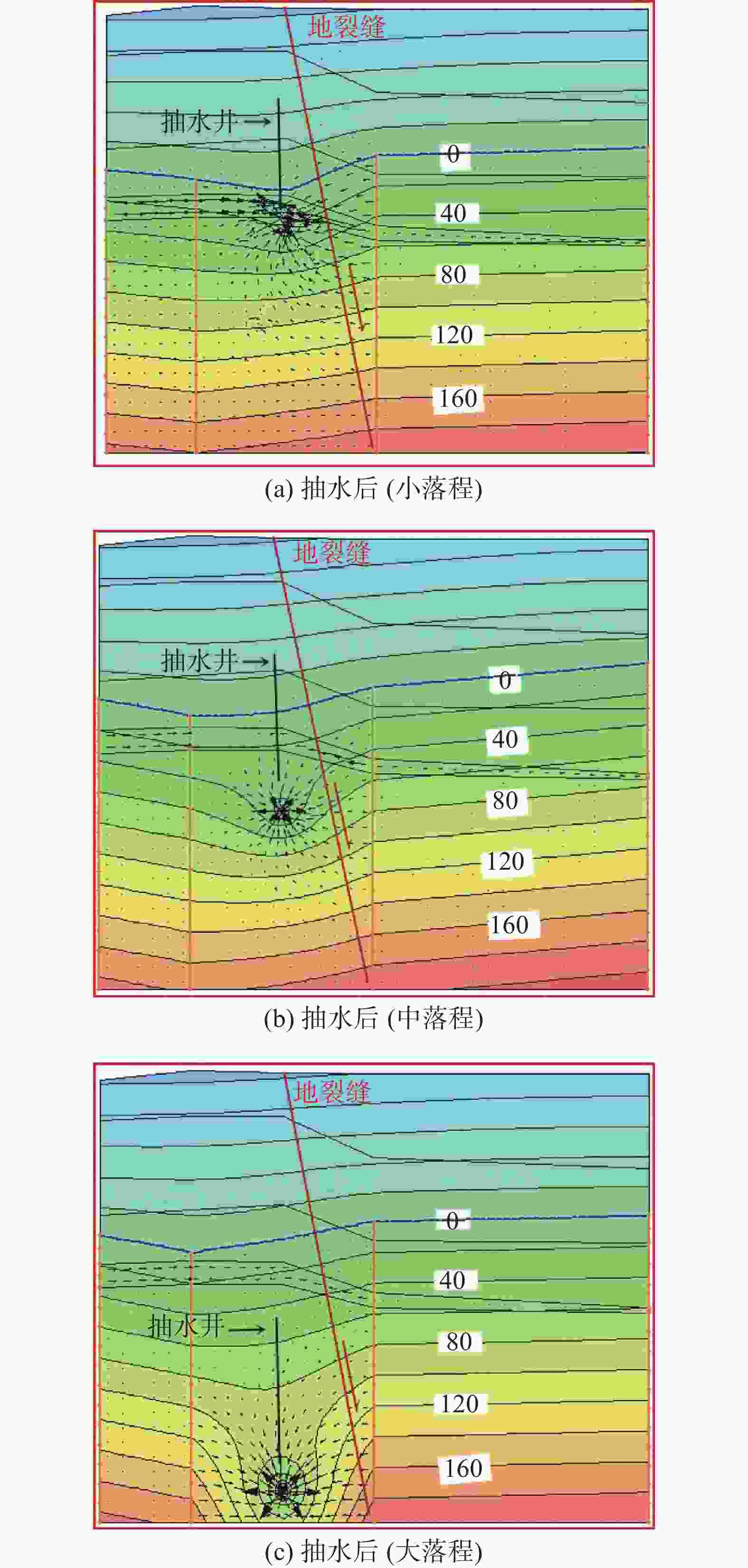
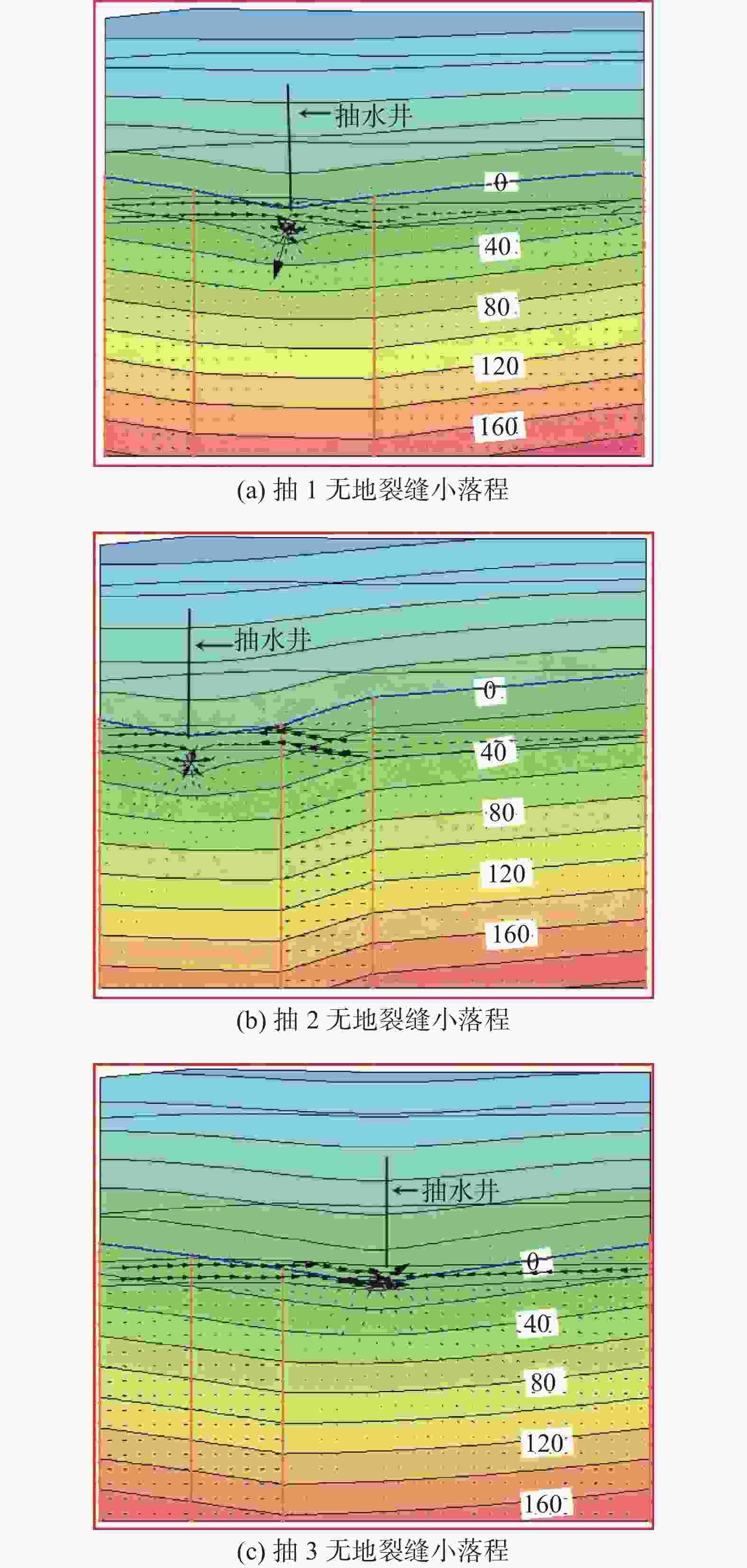
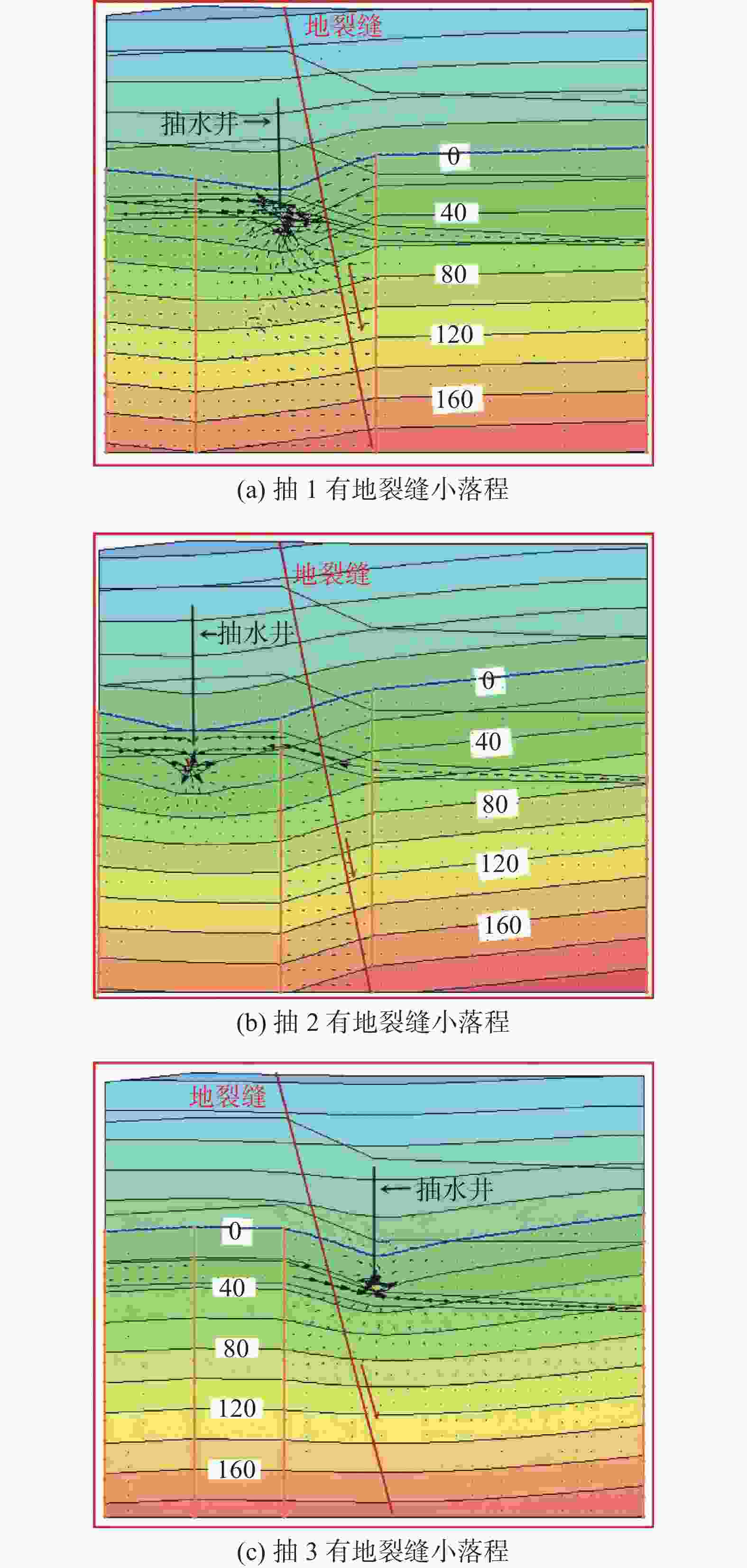
摘要: 为了研究地裂缝活动对地下水运移的影响,在西安市劳动路跨地裂缝试验场地开展水文地质抽水试验,采用Geo-Studio软件建立跨地裂缝水文地质试验模型,进行渗流分析。结果表明:地裂缝带上抽水井涌水量最大,地裂缝下盘稳定后的涌水量是上盘涌水量的3倍左右;地裂缝带含水层厚度最大、渗透性最好,下盘居中,上盘含水层厚度最小、渗透性最差;对于同一抽水井,抽水与加荷共同作用下产生的垂直位移是只有抽水作用情况下的4倍左右,对于群井,两者共同作用下产生的垂直位移是单独抽水作用下的2倍左右;在抽水作用下,由于地裂缝上下盘地层差异,孔隙水压力下降引起的有效应力增加会导致两侧土体的不均匀压缩,加剧了地裂缝的发展;无地裂缝时,各抽水井补给效果相差不大;有地裂缝时,根据不同的地层情况,地裂缝会表现出隔水和透水的两面性。Abstract: To study the influence of ground fissure activity on groundwater migration, hydrogeological pumping tests were conducted at the cross-ground fissure test site on Laodong Road in Xi’an, and a cross-ground fissure hydrogeological test model was established using Geo-Studio software for seepage analysis. The results show that the water inflow of the pumping well on the ground fissure zone is the largest, and the water inflow after the stability of the lower side of the ground fissure is roughly three times that after the stability of the hanging wall. The thickness of the aquifer in the ground fissure zone is the largest and the permeability of the ground fissure zone is the strongest, the footwall is in the middle, and the hanging wall has the smallest thickness and the worst permeability. For the same pumping well, the vertical displacement generated by the combined pumping action and load action is about 4 times that of the single pumping action. For a group of wells, the vertical displacement generated by the combined action of the two is about twice that of the single pumping action. Under the action of water pumping, due to the difference between the hanging wall and footwall of the ground fissure, the increase of effective stress caused by the decrease of pore water pressure will lead to the uneven compression of the soil on both sides and aggravate the development of the ground fissure. When there is no ground fissure, the recharge effect of each pumping well is similar; when there are ground fissures, according to different soil conditions, the ground fissures will show water resistance and permeability.
-
Key words:
- ground fissure /
- pumping test /
- groundwater migration /
- pore water pressure /
- permeability coefficient
-
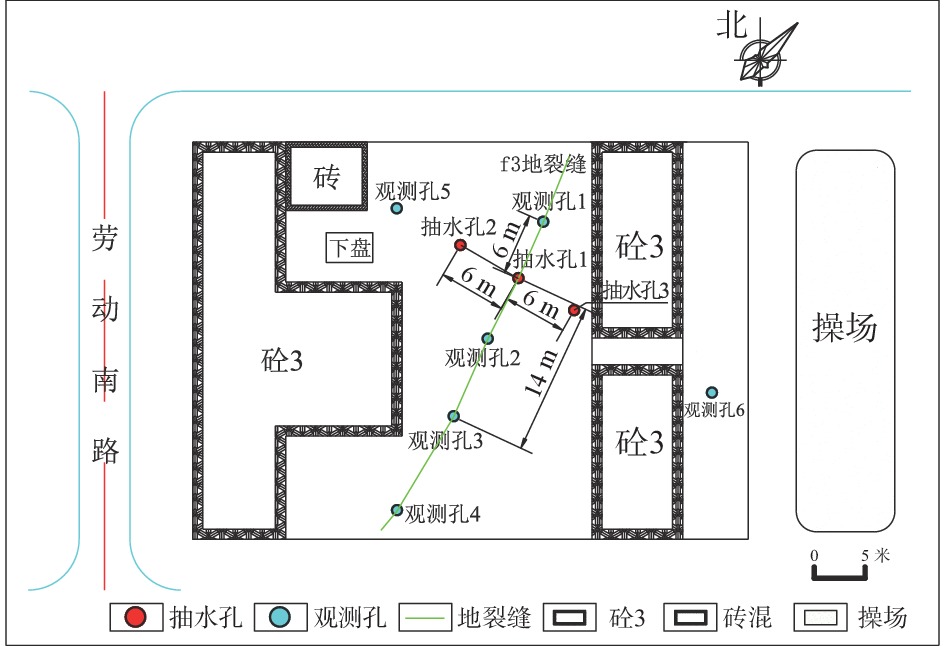
表 1 4组抽水试验涌水量统计表
m3/d 落程 1号
抽水井2号
抽水井3号
抽水井群井 1号
抽水井2号
抽水井3号
抽水井小落程 125.34 118.13 45.04 67.6 67.6 38.7 中落程 156.82 156.82 51.96 106.7 106.7 45 大落程 202.25 186.34 51.96 130.29 143.19 38.7 表 2 1号抽水井计算出的渗透系数
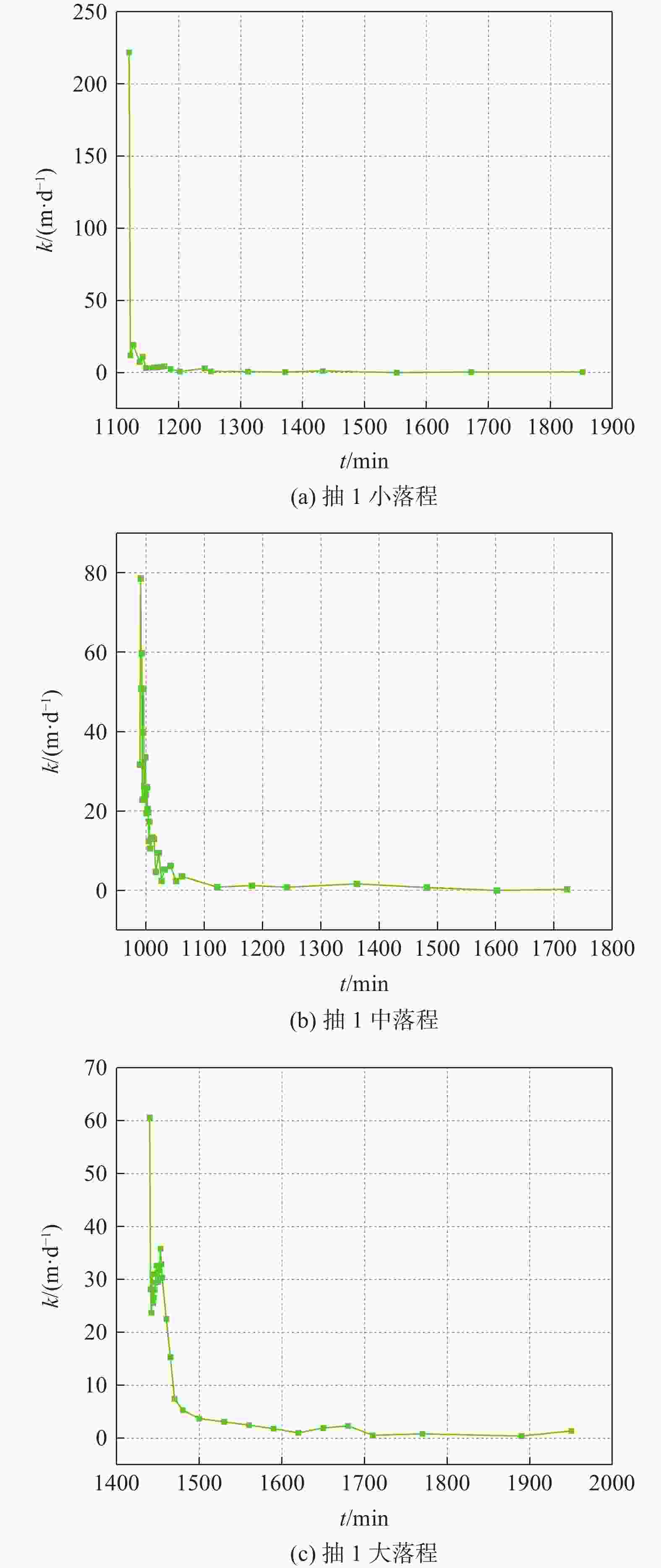
落程 流量Q/(m3·d−1) 降深S/m 恢复时间t/min 渗透系数k/(m·d−1) k取值/(m·d−1) 小落程 125.34 4.59 1342 2.000 2.420 中落程 156.82 7.96 1572 2.790 大落程 202.25 17.71 1120 2.469 表 3 1,2,3号抽水井及群井的渗透系数
m/d 井号 1号
抽水井2号
抽水井3号
抽水井群井 1号
抽水井2号
抽水井3号
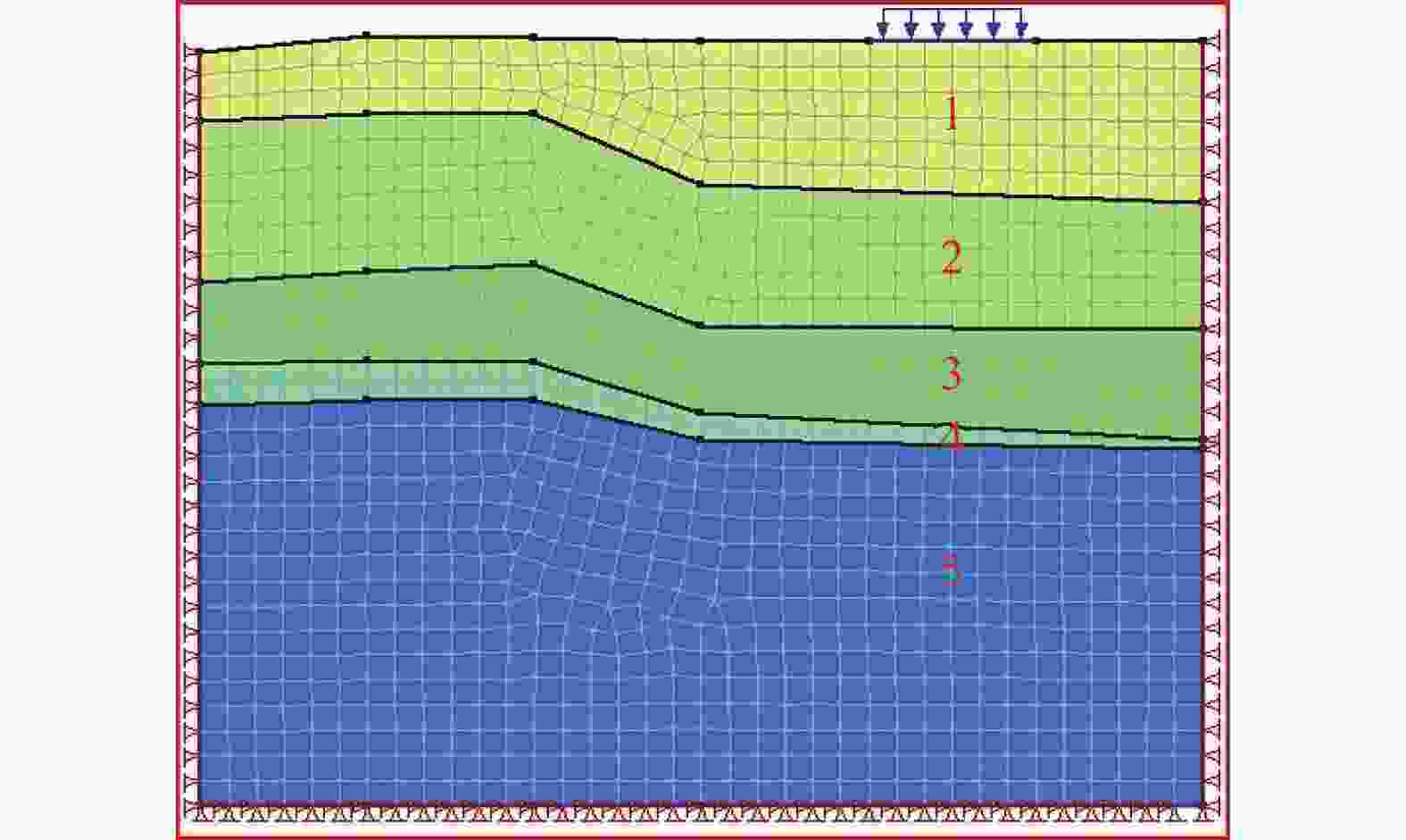
抽水井渗透系数 2.420 2.049 1.618 2.232 2.087 1.676 表 4 水文地质试验模型材料参数
层号 地层名称 重度
/(kN·m−3)弹性
模量
/MPa泊松比 体积压缩系数
/kPa−1饱和体积含水量
/m3渗透
系数
/(cm·s−1)1 填土 17.1 7 0.35 1.43×10-4 0.43 4.63×10−3 2 黄土 18.5 8 0.35 1.00×10-4 0.45 2.38×10−4 3 古土壤 19.8 10 0.35 1.25×10-4 0.42 1.62×10−4 4 中砂 19.1 4 0.25 2.50×10−5 0.55 3.19×10−2 5 粉质黏土 19.6 7 0.35 1.43×10-4 0.42 1.50×10−5 -
[1] 李志明, 杨旭东, 兰剑梅, 等. 河北邢台柏乡地裂缝成因分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2010,37(2):135-138. (LI Z M, YANG X D, LAN J M, et al. An analysis of earth fissure at Baixiang County, Xingtai City[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2010,37(2):135-138. (in Chinese)LI Z M, YANG X D, LAN J M, et al. An analysis of earth fissure at Baixiang County, Xingtai City[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2010, 37(2): 135-138. (in Chinese) [2] AYALEW L, YAMAGISHI H, REIK G. Ground cracks in Ethiopian Rift Valley: facts and uncertainties[J]. Engineering Geology,2004,75(3/4):309-324. [3] 邵长庆, 杨 强, 李 浩, 等. 活动断层作用下地裂缝开裂机理研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(4):34-41. (SHAO C Q, YANG Q, LI H, et al. A study of the cracking mechanism of ground fissures under the action of active faults[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(4):34-41. (in Chinese)SHAO C Q, YANG Q, LI H, et al. A study of the cracking mechanism of ground fissures under the action of active faults[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(4): 34-41. (in Chinese) [4] 孟振江, 彭建兵, 李 超, 等. 耦合型地裂缝活动特征与成因机制模拟研究——以北京宋庄地裂缝为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(3):138-148. (MENG Z J, PENG J B, LI C, et al. A simulation study of the activity characteristics and genetic mechanism of coupled ground fissures: exemplified by the Songzhuang ground fissure in Beijing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(3):138-148. (in Chinese)MENG Z J, PENG J B, LI C, et al. A simulation study of the activity characteristics and genetic mechanism of coupled ground fissures: exemplified by the Songzhuang ground fissure in Beijing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(3): 138-148. (in Chinese) [5] 贾润幸, 方维萱, 张建国, 等. 山西清徐—太谷地区地裂缝形成机理[J]. 地质通报,2022,41(7):1282-1290. (JIA R X, FANG W X, ZHANG J G, et al. The formation mechanism of ground fissures in Qingxu-Taigu area, Shanxi Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2022,41(7):1282-1290. (in Chinese)JIA R X, FANG W X, ZHANG J G, et al. The formation mechanism of ground fissures in Qingxu-Taigu area, Shanxi Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2022, 41(7): 1282-1290. (in Chinese) [6] 彭建兵, 范 文, 李喜安, 等. 汾渭盆地地裂缝成因研究中的若干关键问题[J]. 工程地质学报,2007,15(4):433-440. (PENG J B, FAN W, LI X A, et al. Some key questions in the formation of ground fissures in the Fen-Wei basin[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2007,15(4):433-440. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2007.04.001PENG J B, FAN W, LI X A, et al. Some key questions in the formation of ground fissures in the Fen-Wei basin[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2007, 15(4): 433-440. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2007.04.001 [7] 武 强, 陈佩佩, 张 宇, 等. 我国城市地裂缝灾害问题与对策[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2002,13(2):70-72,79. (WU Q, CHEN P P, ZHANG Y, et al. The problem and countermeasure of ground fracture in city[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2002,13(2):70-72,79. (in Chinese)WU Q, CHEN P P, ZHANG Y, et al. The problem and countermeasure of ground fracture in city[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2002, 13(2): 70-72,79. (in Chinese) [8] 曾健峰. 地裂缝场地地下水位对高速铁路路基动力响应的影响研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2022. (ZENG J F. Study on influence of groundwater in ground fissure site on dynamic response of high-speed railway subgrade[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2022. (in Chinese)ZENG J F. Study on influence of groundwater in ground fissure site on dynamic response of high-speed railway subgrade[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2022. (in Chinese) [9] 徐明祥, 黄强兵, 王庆兵, 等. 西安地裂缝地段浅埋暗挖地铁隧道施工沉降规律[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(1):161-170. (XU M X, HUANG Q B, WANG Q B, et al. Settlement rules of shallow-buried metro tunnel construction in the Xi’an ground fissure section[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(1):161-170. (in Chinese)XU M X, HUANG Q B, WANG Q B, et al. Settlement rules of shallow-buried metro tunnel construction in the Xi’an ground fissure section[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(1): 161-170. (in Chinese) [10] 郭夏涛. 基于FLAC3D的西安f5地裂缝数值模拟与防治对策研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2021. (GUO X T. Study on numerical simulation and prevention and control of ground fissure in Xi’an f5 based on FLAC3D[D]. Xi’an: Chang'an University, 2021. (in Chinese)GUO X T. Study on numerical simulation and prevention and control of ground fissure in Xi’an f5 based on FLAC3D[D]. Xi’an: Chang'an University, 2021. (in Chinese) [11] 孟宏特. 西安地裂缝抽水活动机理及安全避让距离研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2021. (MENG H T. Study on the mechanism of ground fissure movement during pumping and the safety avoidance distance of Xi’an ground fissure[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2021. (in Chinese)MENG H T. Study on the mechanism of ground fissure movement during pumping and the safety avoidance distance of Xi’an ground fissure[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2021. (in Chinese) [12] 王富辉, 徐张建, 燕建龙, 等. 西安地裂缝勘察特殊情况探讨[J]. 岩土工程技术,2022,36(6):431-436. (WANG F H, XU Z J, YAN J L, et al. Discussion on special cases in investigations of Xi’an ground fissures[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique,2022,36(6):431-436. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2022.06.001WANG F H, XU Z J, YAN J L, et al. Discussion on special cases in investigations of Xi’an ground fissures[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique, 2022, 36(6): 431-436. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2022.06.001 [13] 张 鹏, 刘 帅, 文成龙. 西安地裂缝二类场地勘察标志层识别及勘探孔深度确定[J]. 岩土工程技术,2018,32(4):163-166. (ZHANG P, LIU S, WEN C L. Identification of marker layer and determination depth of bore hole in Xi’an ground fissure second class site[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique,2018,32(4):163-166. (in Chinese)ZHANG P, LIU S, WEN C L. Identification of marker layer and determination depth of bore hole in Xi’an ground fissure second class site[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique, 2018, 32(4): 163-166. (in Chinese) [14] 任雅哲, 丰成君, 戚帮申, 等. 北京顺义断裂活动对首都机场地裂缝影响定量研究[J]. 地质力学学报,2023,29(5):685-703. (REN Y Z, FENG C J, QI B S, et al. Quantitative research of the impact of Shunyi fault activity on the ground fissures in the Beijing Capital International Airport, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2023,29(5):685-703. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2023063REN Y Z, FENG C J, QI B S, et al. Quantitative research of the impact of Shunyi fault activity on the ground fissures in the Beijing Capital International Airport, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2023, 29(5): 685-703. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2023063 [15] 国家质量技术监督局, 中华人民共和国建设部. 地下铁道、轻轨交通岩土工程勘察规范: GB 50307–1999[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 1999. (The State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision, Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Code on geotechnical investigations for metro and light rail transit: GB 50307–1999[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 1999. (in Chinese)The State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision, Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Code on geotechnical investigations for metro and light rail transit: GB 50307–1999[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 1999. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: