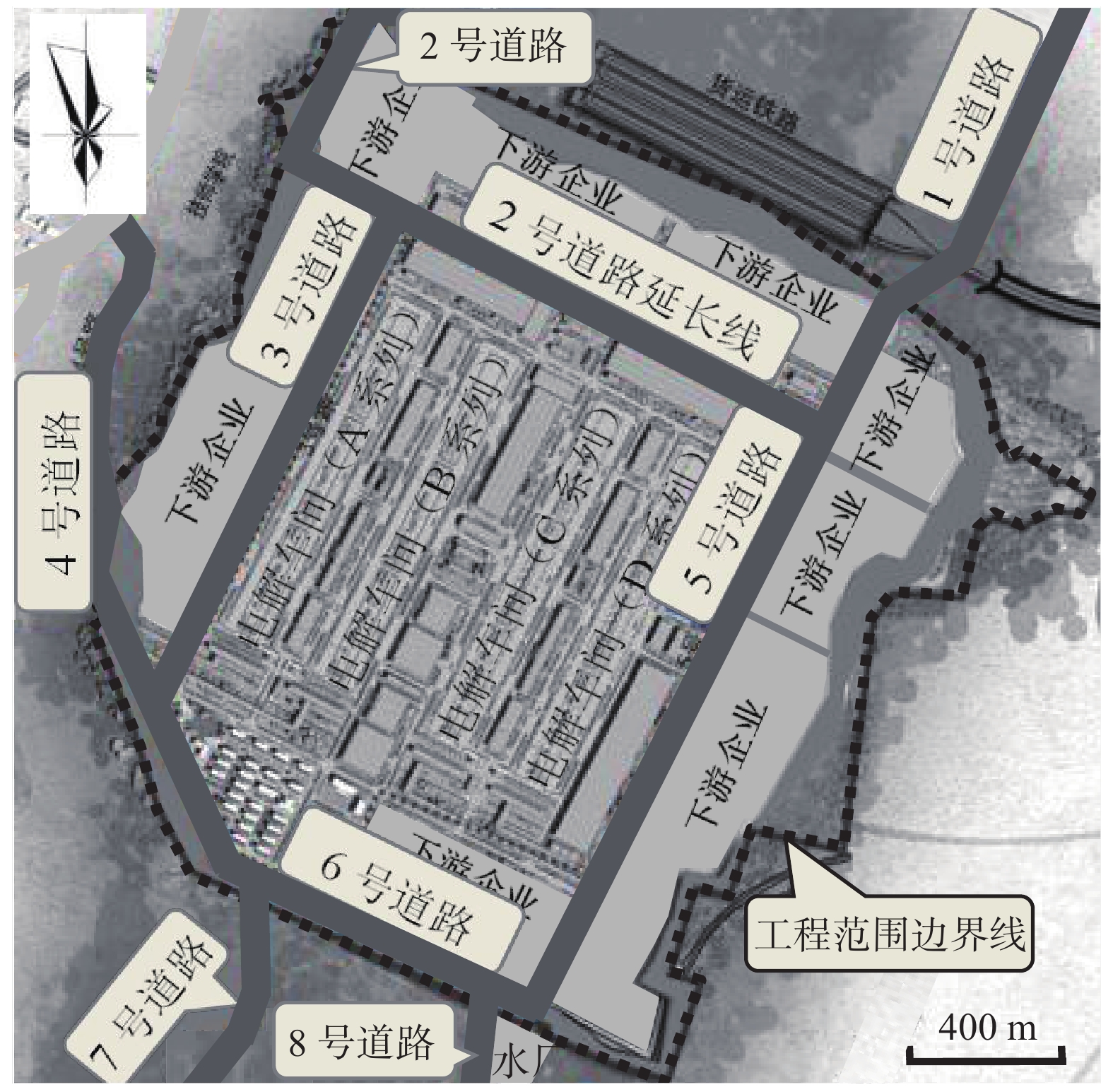
Field test on dynamic compaction treatment of large area high-fill red clay foundation
-
摘要: 以云南碳中和示范产业园基础设施建设项目大面积高填方工程为研究背景,针对红黏土回填地基填筑工艺及强夯处理效果开展试验研究。试验结果表明,在5000 kN·m能级工况下,强夯法处理红黏土采用土石分层堆填地基效果显著,4种填筑工况中,工况2(采用石料粒径≤300 mm、土石体积比5∶5的土石分层堆填)的地基强夯加固效果最优,地基承载力特征值可达240 kPa以上,变形模量大于14 MPa。根据本次强夯试验测试结果,结合云南地区强夯地基处理工程经验,对本地区红黏土回填地基强夯处理施工提出了具体建议。试验研究成果可为类似大面积高填方红黏土回填地基的设计与施工提供借鉴。Abstract: Taking the large-scale high-fill engineering of the infrastructure construction project of Yunnan Carbon Neutral Demonstration Industrial Park as the research background, experimental research was conducted on the filling process and dynamic compaction treatment effect of the red clay backfill foundation. The experimental results show that under the energy level of 5000 kN·m, the dynamic compaction method has significant effects on treating the red clay soil-rock layered fill foundation. Among the four filling conditions, condition 2 (using soil-rock layered fill with stone particle size ≤300 mm and soil-rock volume ratio of 5∶5) has the best dynamic compaction reinforcement effect on the foundation, with a characteristic value of foundation bearing capacity of over 240 kPa and a deformation modulus of more than 14 MPa. Based on the test results of this experiment and combined with the experience in Yunnan, specific suggestions for the construction of red clay backfill foundation dynamic compaction treatment in this region are proposed. The experimental research results can provide a reference for the design and construction of similar large-scale high-fill red clay backfill foundations.
-
Key words:
- high-fill foundation /
- red clay /
- filling process /
- dynamic compaction treatment
-
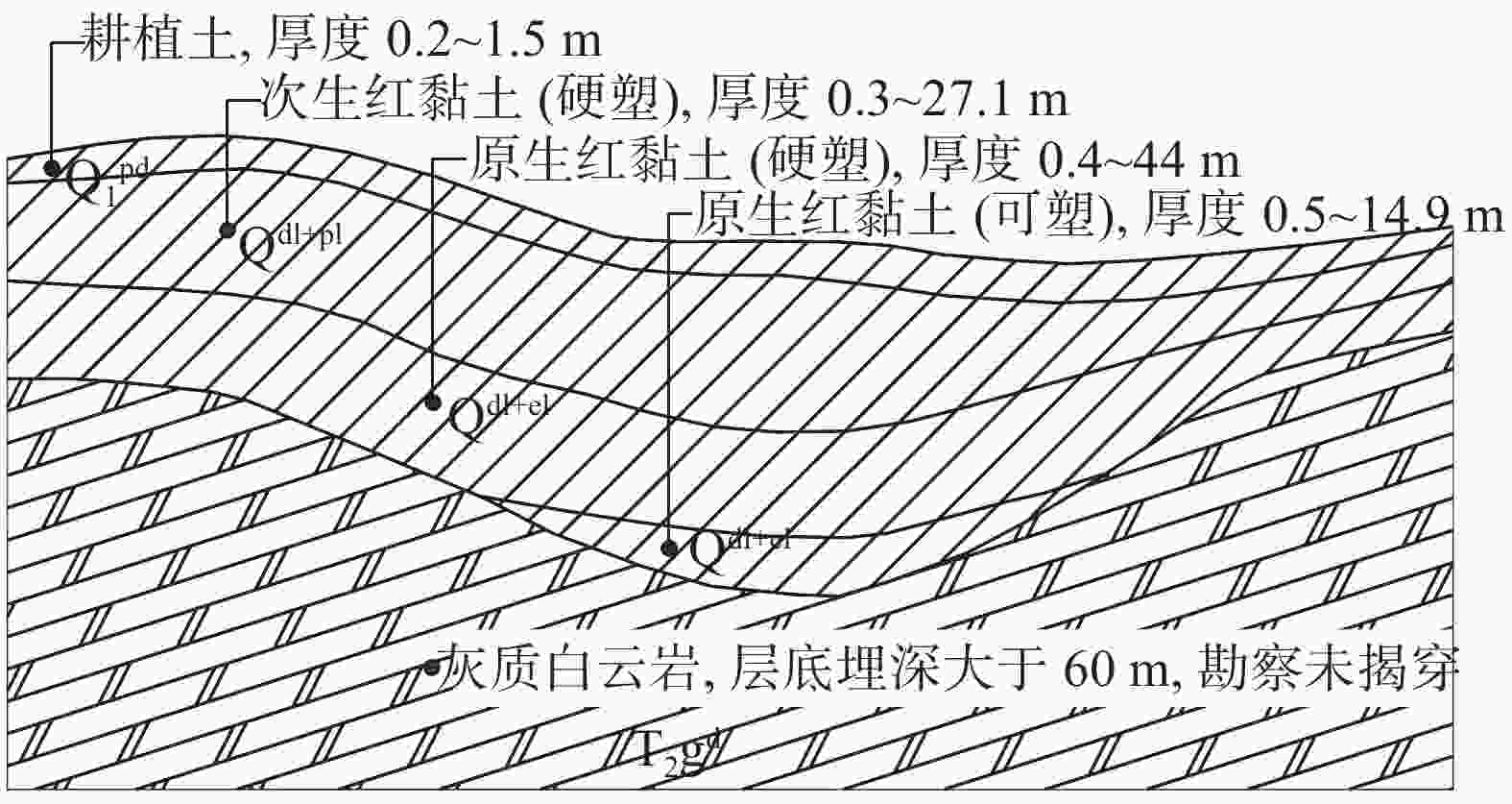
表 1 红黏土主要物理力学性质指标
土层代号及名称 天然重度
γ/(kN·m−3)天然含水量
w/%天然
孔隙比e液性指数
IL含水比
αw液塑比
Ir自由膨胀率
δef/%固结快剪 直接快剪 黏聚力
ck/kPa内摩擦角
φk/(°)黏聚力
cq/kPa内摩擦角
φq/(°)Qdl+pl 次生红黏土(硬塑) 17.3 44.0 1.292 0.18 0.67 1.67 25.4 56.7 11.2 39.5 9.9 Qdl+el 原生红黏土(硬塑) 17.4 43.8 1.259 0.13 0.64 1.67 32.1 60.7 11.6 43.3 10.3 Qdl+el 原生红黏土(可塑) 17.1 49.4 1.433 0.36 0.74 1.67 33.0 39.8 9.7 25.4 6.8 表 2 各试验工况施工参数设计表
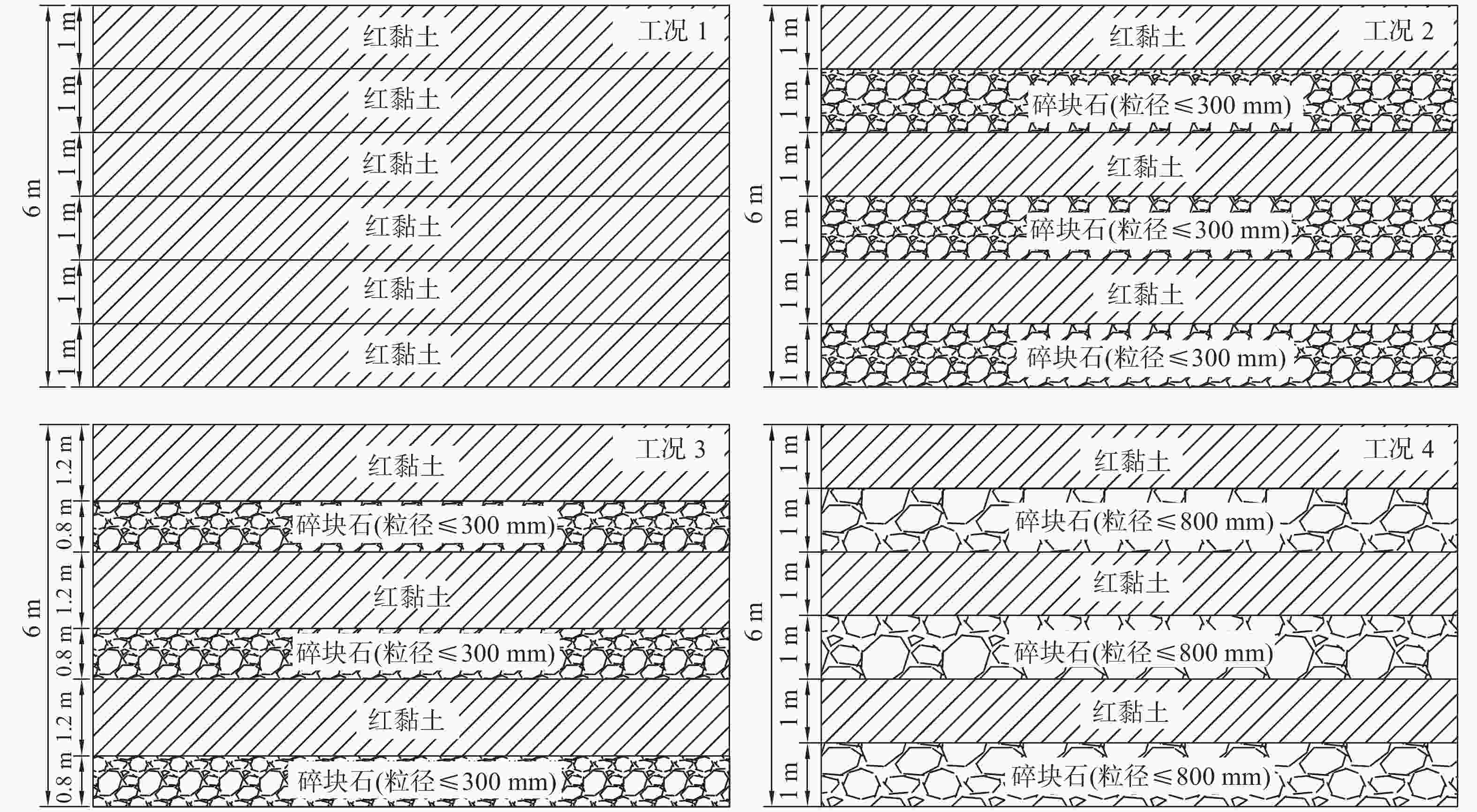
试验区 试验工况 土石比 石料粒径
/mm夯锤直径
d/m点夯 满夯 能级
/(kN·m)夯点布置 单点击数 夯击遍数 能级
/(kN·m)夯点布置 单点击数 夯击遍数 A1 工况1 6:0 2.52 5000 5 m×5 m
正方形布置12 2 2000 d/3搭接 3 1 工况2 5:5 ≤300 A2 工况3 6:4 ≤300 工况4 5:5 ≤800 表 3 各试验工况夯沉量统计表
测试
工况夯击
序数夯击
数/击单点累计
夯沉量
/mm最后两击
平均夯沉量
/mm场地强夯
前后沉降量
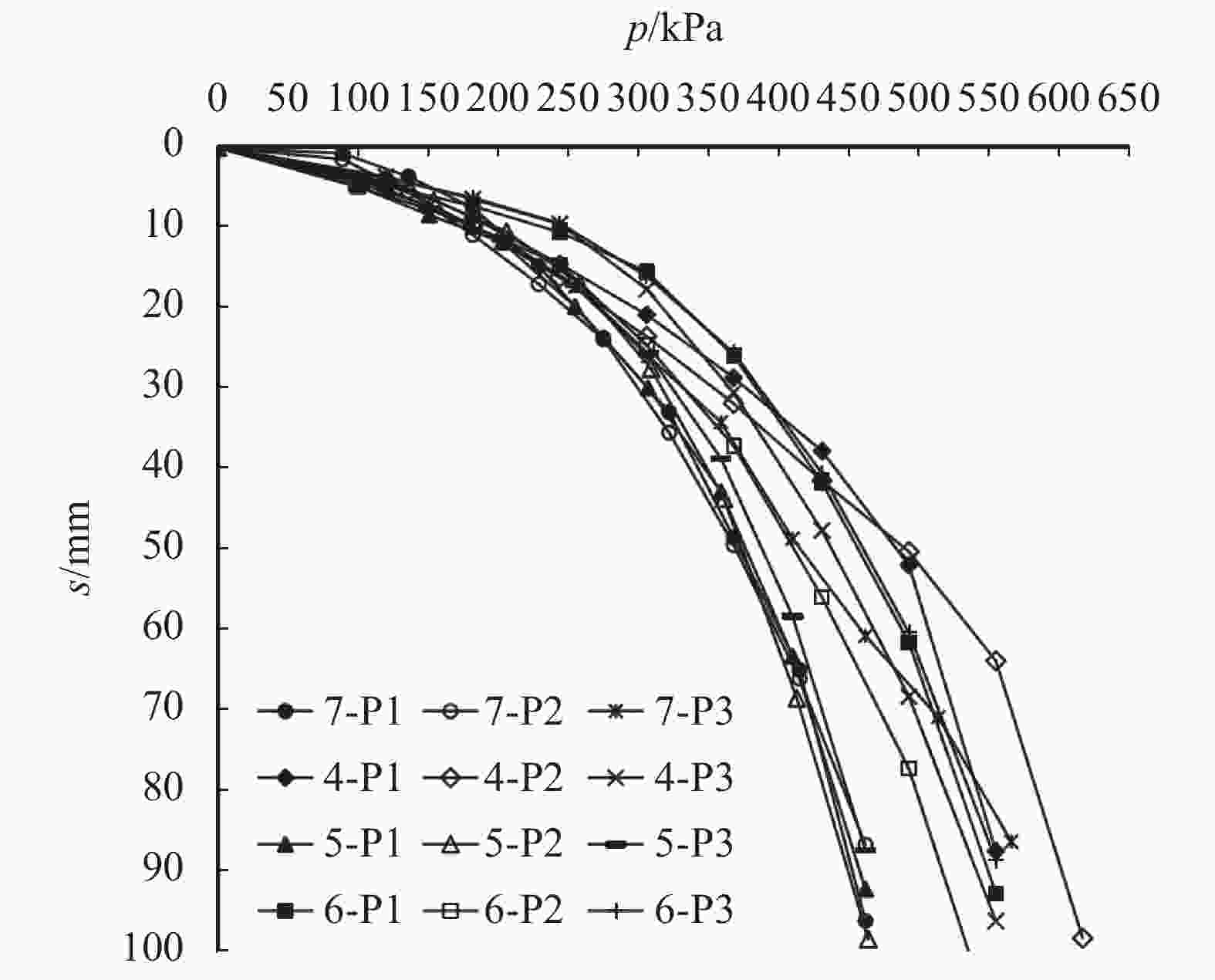
/mm工况1 第一序 5~7 1440~3000 125~625 640~1150 第一序(补) 5~7 1090~2460 160~490 第二序 7~8 1400~2490 80~475 第二序(补) 5 960~1880 155~460 工况2 第一序 9~11 1580~3284 44.0~97.5 50~320 第二序 9~11 1637~2946 21.5~98.5 工况3 第一序 8~13 247~497 7.5~38.0 360~750 第二序 10~13 265~344 7.5~13.0 工况4 第一序 6~11 68~262 11.0~66.5 350~680 第二序 8~11 250~330 10.5~20.0 表 4 载荷试验成果统计表
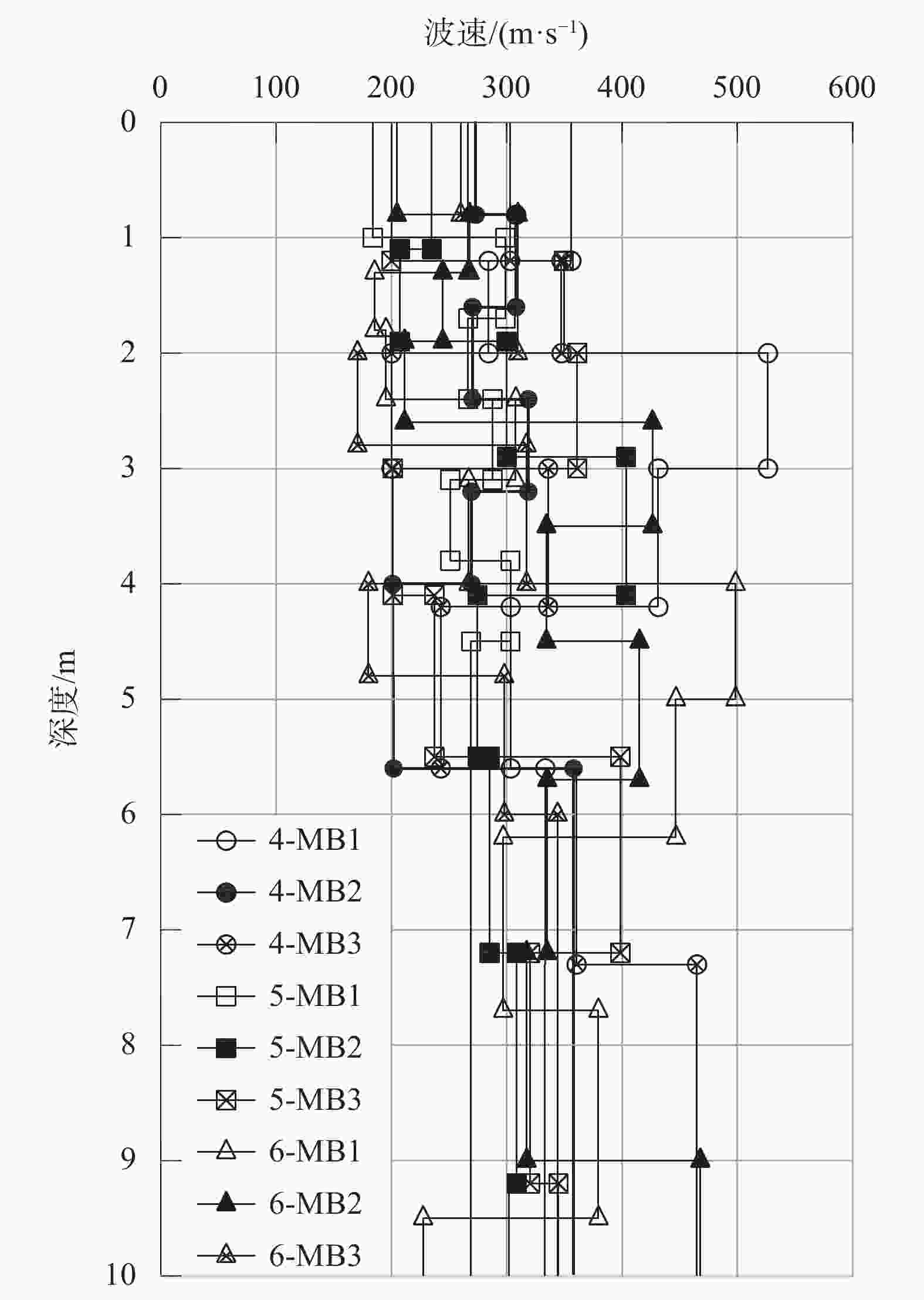
试验位置 承载力特征值/kPa 对应沉降量/mm 变形模量/MPa 工况1 7-P1 225 14.14 16 7-P2 207 14.14 15 7-P3 226 14.14 16 工况2 4-P1 246 14.72 17 4-P2 278 20.20 14 4-P3 244 9.53 26 工况3 5-P1 203 11.82 18 5-P2 206 10.49 20 5-P3 203 11.43 18 工况4 6-P1 244 10.57 24 6-P2 244 14.57 17 6-P3 244 9.46 27 表 5 现场剪切试验成果统计表
试验工况 试验状态 试验深度
/m黏聚力
c/kPa内摩擦角
φ/(°)含水率
w/%工况1 自然 1.2 45.3 15.7 36 浸水 1.3 36.6 13.2 44 工况2 自然 0.8 72.9 15.9 34 浸水 0.7 59.7 14.0 38 工况3 自然 0.8 64.9 15.7 33 浸水 0.8 55.1 12.6 37 工况4 自然 0.7 71.7 16.0 36 浸水 0.6 58.8 12.9 43 表 6 标准贯入试验成果统计表
孔号 试验段深度/m 标贯击数平均值/击 标贯击数修正值/击 HHK1 1.2~5.8 8 7.6 HHK2 4.9~6.1 9 7.8 HHK3 1.4~5.4 10.5 9.9 HHK4 1.0~5.6 8 7.6 HHK5 1.3~5.7 8.3 7.8 HHK6 1.2~6.1 8 7.6 表 7 重型圆锥动力触探试验成果统计表
试验位置 界限值/击 修正值/击 工况2 夯墩 3~25 11.2 墩间土 3~27 10.4 工况3 夯墩 2~30 8.8 墩间土 2~30 9.3 工况4 夯墩 2~27 9.6 墩间土 2~23 7.3 表 8 土石分层强夯施工主要参数建议表
土石
体积比石料粒径
/mm填土
厚度/m施工
方式能级
/(kN·m)夯点布置 单点
击数/击夯击
遍数/遍5:5 ≤300 6 点夯 5000 5 m×5 m
正方形布置12 2 满夯 2000 d/3搭接 3 1 -
[1] 刘 宏, 李攀峰, 张倬元, 等. 山区机场高填方地基变形与稳定性系统研究[J]. 地球科学进展,2004,19(S1):324-328. (LIU H, LI P F, ZHANG Z Y, et al. A systematic research on the deformation and stability of high embankment of airport in mountainous area[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences,2004,19(S1):324-328. (in Chinese)LIU H, LI P F, ZHANG Z Y, et al. A systematic research on the deformation and stability of high embankment of airport in mountainous area[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 2004, 19(S1): 324-328. (in Chinese) [2] 杜玉明, 刘利民. 强夯法在高填方地基处理中的应用[J]. 煤炭工程,2015,47(11):58-59. (DU Y M, LIU L M. Application of dynamic compaction in high embankment foundation treatment[J]. Coal Engineering,2015,47(11):58-59. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11799/ce201511019DU Y M, LIU L M. Application of dynamic compaction in high embankment foundation treatment[J]. Coal Engineering, 2015, 47(11): 58-59. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11799/ce201511019 [3] 何兆益, 周虎鑫, 吴国雄. 攀枝花机场高填方地基强夯处理试验研究[J]. 重庆交通学院学报,2002,21(1):51-55. (HE Z Y, ZHOU H X, WU G X. The field test study of high embankment foundation compaction in Panzhi-Hua airport[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University,2002,21(1):51-55. (in Chinese)HE Z Y, ZHOU H X, WU G X. The field test study of high embankment foundation compaction in Panzhi-Hua airport[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2002, 21(1): 51-55. (in Chinese) [4] 王程亮. 山区机场已填筑高填方地基再处理方法研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2015. (WANG C L. Study on retreatment method for high-fill foundation of airports in mountainous regions[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2015. (in Chinese)WANG C L. Study on retreatment method for high-fill foundation of airports in mountainous regions[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2015. (in Chinese) [5] 臧亚君, 刘东燕, 蒋克锋, 等. 西南某机场高填方地基稳定性分析[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2007,3(4):711-715. (ZANG Y J, LIU D Y, JIANG K F, et al. Stability analysis on high embankment foundation of an airport in southwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering,2007,3(4):711-715. (in Chinese)ZANG Y J, LIU D Y, JIANG K F, et al. Stability analysis on high embankment foundation of an airport in southwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2007, 3(4): 711-715. (in Chinese) [6] 杜伟飞, 郑建国, 刘争宏, 等. 黄土高填方地基沉降规律及排气条件影响[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(1):325-331. (DU W F, ZHENG J G, LIU Z H, et al. Settlement behavior of high loess-filled foundation and impact from exhaust conditions[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2019,40(1):325-331. (in Chinese)DU W F, ZHENG J G, LIU Z H, et al. Settlement behavior of high loess-filled foundation and impact from exhaust conditions[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(1): 325-331. (in Chinese) [7] 侯 森, 任 庚, 韩黎明, 等. 承德机场高填方地基工后沉降预测[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2017,13(S1):279-284. (HOU S, REN G, HAN L M, et al. Post-construction settlement prediction of the high embankment of Chengde airport[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering,2017,13(S1):279-284. (in Chinese)HOU S, REN G, HAN L M, et al. Post-construction settlement prediction of the high embankment of Chengde airport[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2017, 13(S1): 279-284. (in Chinese) [8] 葛苗苗, 李 宁, 张 炜, 等. 黄土高填方沉降规律分析及工后沉降反演预测[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2017,36(3):745-753. (GE M M, LI N, ZHANG W, et al. Settlement behavior and inverse prediction of post-construction settlement of high filled loess embankment[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2017,36(3):745-753. (in Chinese)GE M M, LI N, ZHANG W, et al. Settlement behavior and inverse prediction of post-construction settlement of high filled loess embankment[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(3): 745-753. (in Chinese) [9] 朱才辉, 李 宁, 刘明振, 等. 吕梁机场黄土高填方地基工后沉降时空规律分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2013,35(2):293-301. (ZHU C H, LI N, LIU M Z, et al. Spatiotemporal laws of post-construction settlement of loess-filled foundation of Lüliang Airport[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2013,35(2):293-301. (in Chinese)ZHU C H, LI N, LIU M Z, et al. Spatiotemporal laws of post-construction settlement of loess-filled foundation of Lüliang Airport[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(2): 293-301. (in Chinese) [10] 李 杰. 高能级强夯在红黏土地基的应用研究[J]. 福建建设科技,2019(4):55-58. (LI J. Application research of high-level dynamic compaction on red clay foundation[J]. Fujian Construction Science & Technology,2019(4):55-58. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3943.2019.04.017LI J. Application research of high-level dynamic compaction on red clay foundation[J]. Fujian Construction Science & Technology, 2019(4): 55-58. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3943.2019.04.017 [11] 袁剑波, 时林军, 刘建华. 红粘土填方路基强夯加固效果检测与分析[J]. 中外公路, 2010, 30(5): 34-38. (YUAN J B, SHI L J, LIU J H. Detection and analysis of dynamic compaction reinforcement effect of red clay filled roadbed[J]. Journal of China & Foreign Highway, 2010, 30(5): 34-38. (in Chinese)YUAN J B, SHI L J, LIU J H. Detection and analysis of dynamic compaction reinforcement effect of red clay filled roadbed[J]. Journal of China & Foreign Highway, 2010, 30(5): 34-38. (in Chinese) [12] 郜安安. 强夯法加固红黏土高填方路基效果分析[J]. 山西交通科技,2020(1):40-42,49. (GAO A A. Analysis on the effect of dynamic compaction to reinforce red clay high fill subgrade[J]. Shanxi Science & Technology of Communications,2020(1):40-42,49. (in Chinese)GAO A A. Analysis on the effect of dynamic compaction to reinforce red clay high fill subgrade[J]. Shanxi Science & Technology of Communications, 2020(1): 40-42,49. (in Chinese) [13] 曾建南. 浅谈土石分层堆填强夯处理地基施工技术[J]. 建筑知识,2017,37(8):42-43. (ZENG J N. Talking about the construction technology of soil and water slope treated by dynamic compaction[J]. Architectural Practice,2017,37(8):42-43. (in Chinese)ZENG J N. Talking about the construction technology of soil and water slope treated by dynamic compaction[J]. Architectural Practice, 2017, 37(8): 42-43. (in Chinese) [14] 工业和信息化部. 强夯地基技术规程: YS/T 5209–2018[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2019. (Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Technical specification for dynamic compaction foundation: YS/T 5209–2018[S]. Beijing: China Planning Publishing House, 2019. (in Chinese)Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Technical specification for dynamic compaction foundation: YS/T 5209–2018[S]. Beijing: China Planning Publishing House, 2019. (in Chinese) [15] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑地基检测技术规范: JGJ 340–2015[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2015. (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Technical code for testing of building foundation soils: JGJ 340–2015[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2015. (in Chinese)Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Technical code for testing of building foundation soils: JGJ 340–2015[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2015. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: