Formulation mechanism of bottom layer material for road improvement by top pipe sludge
-
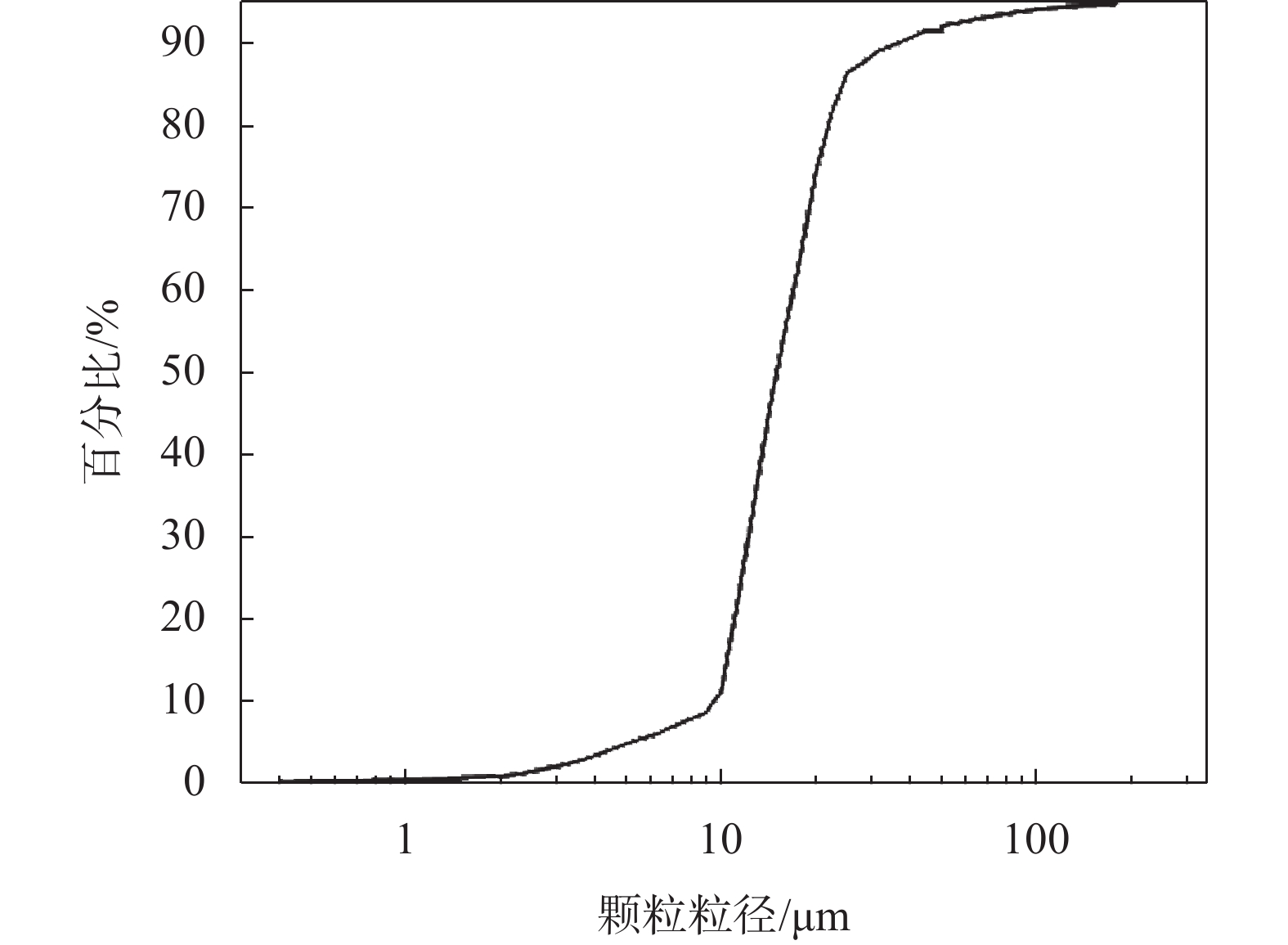
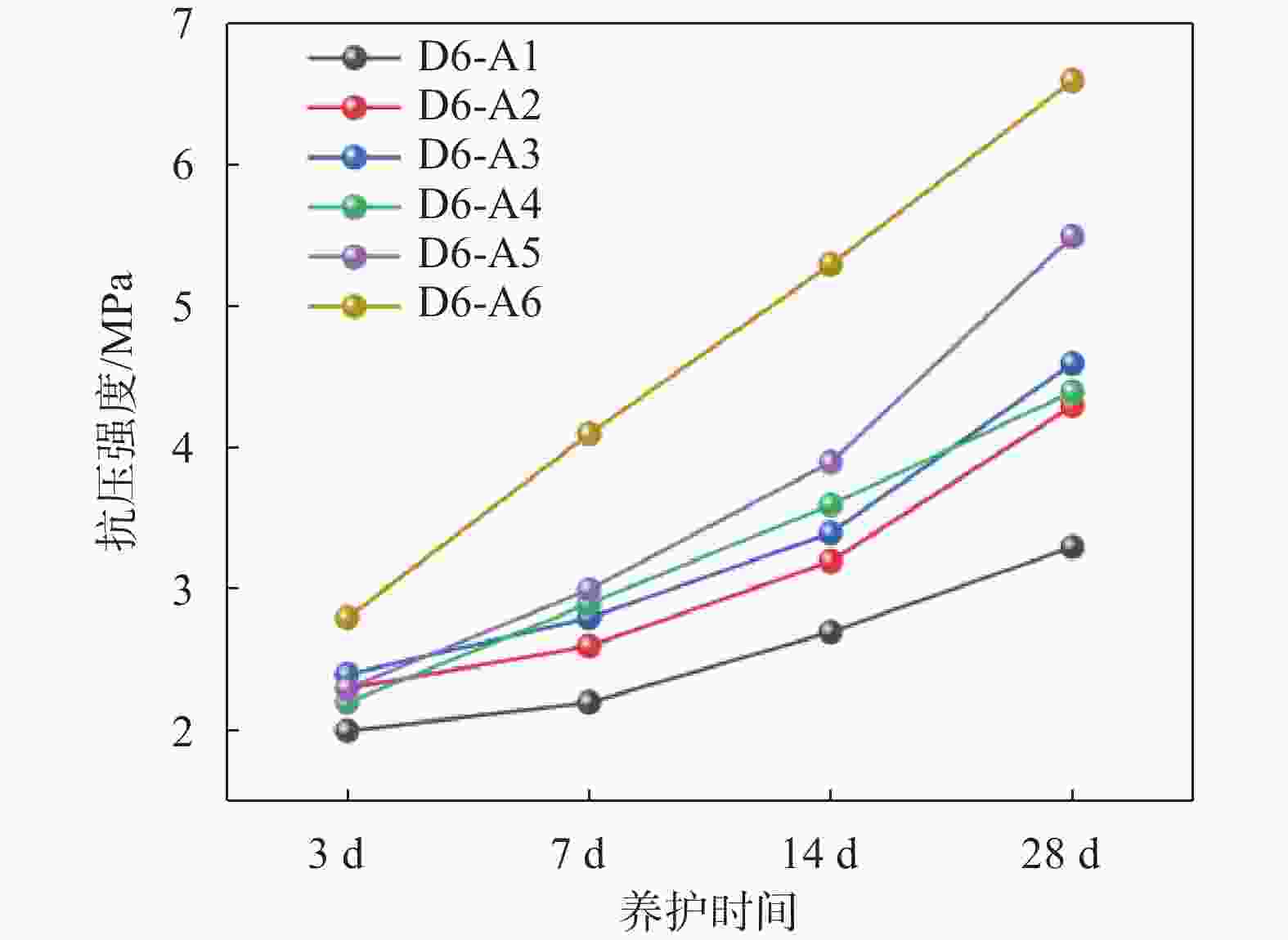
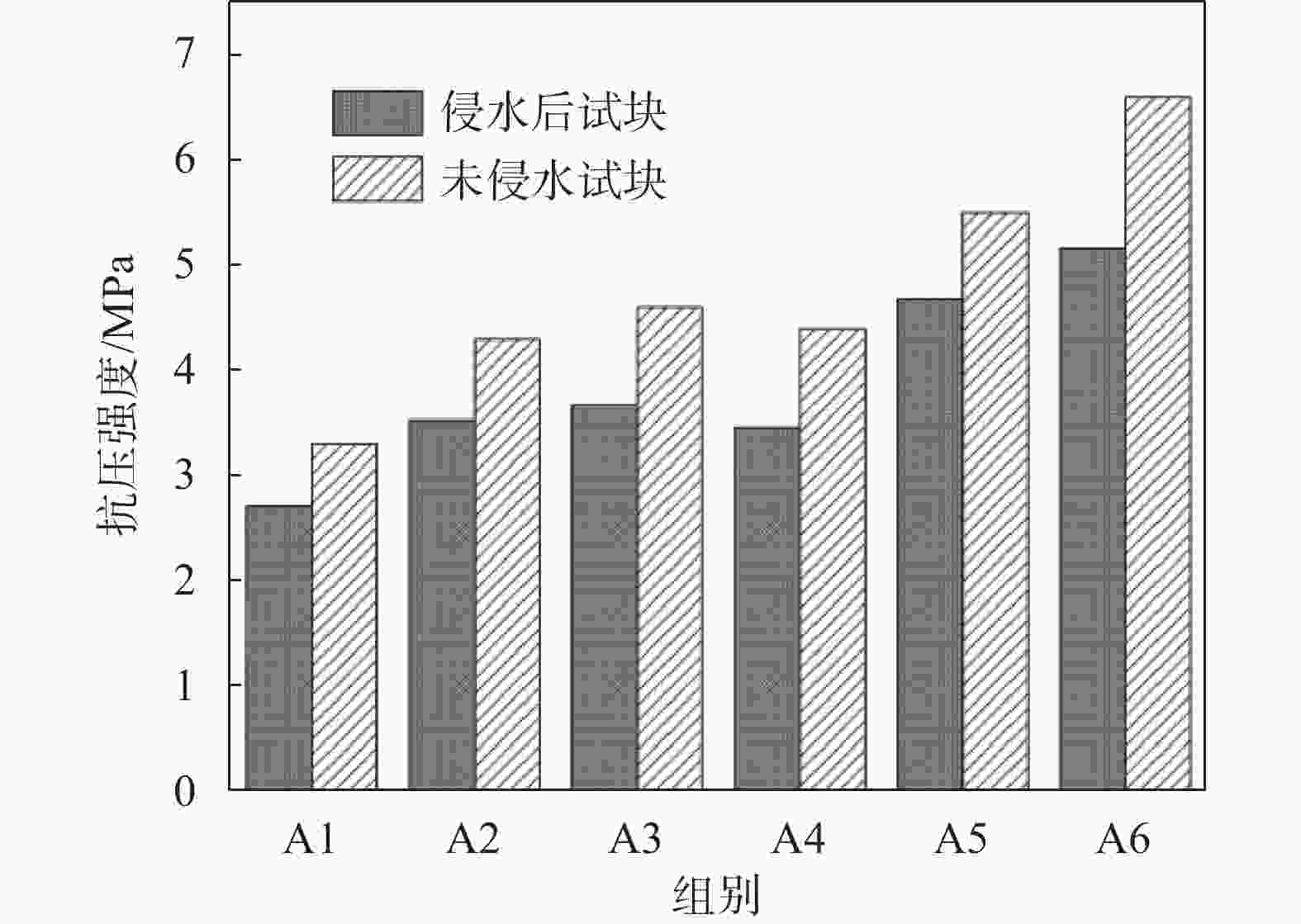
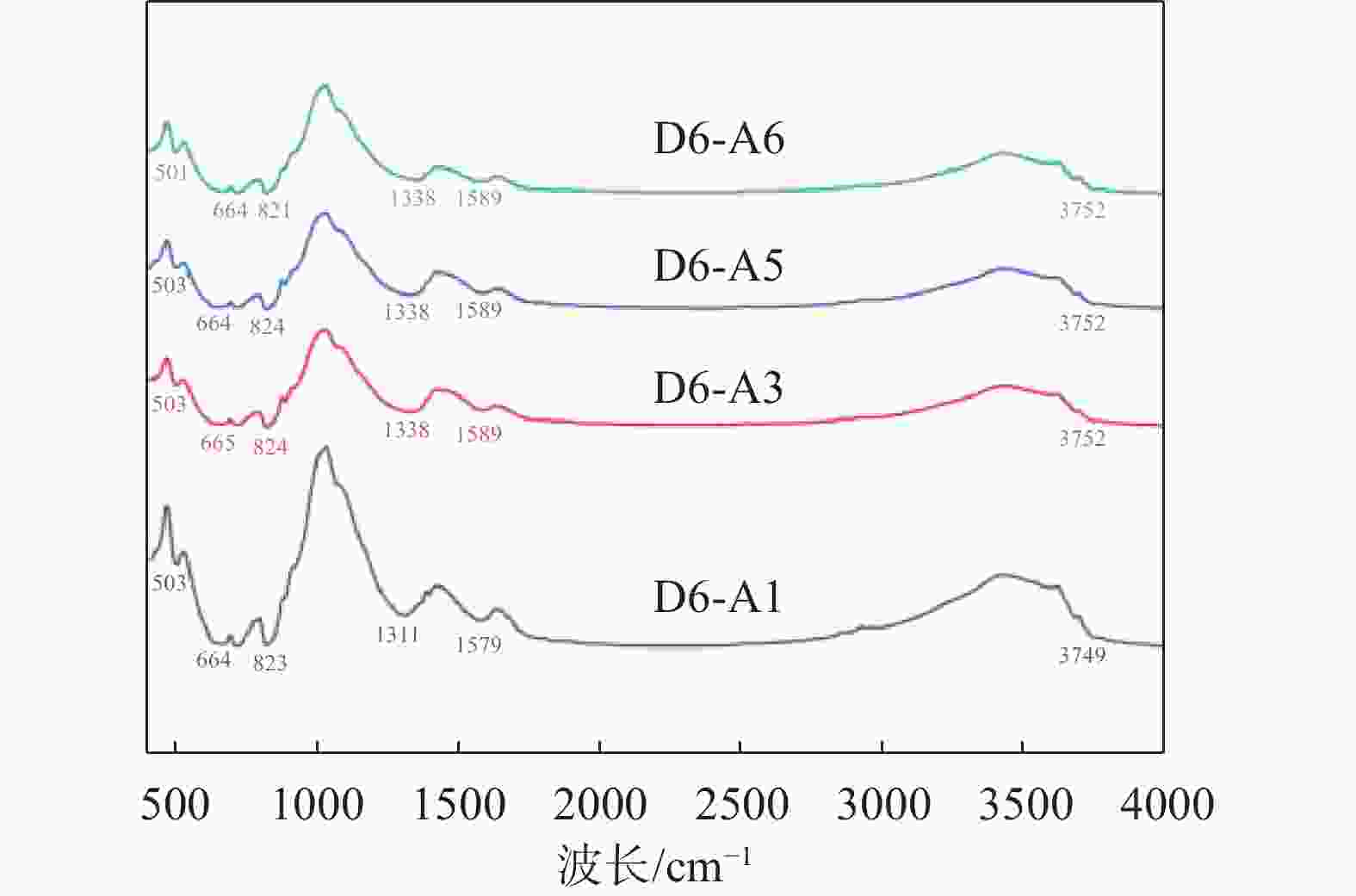
摘要: 顶管施工中会产生大量淤泥,且这些淤泥具有含水率高、稳定性差、颗粒分布不均匀等特点。淤泥固化技术是解决工程施工废弃物再利用的重要手段,为提升淤泥固结体强度,探究稳定化药剂高效配方,采用胶砂强度试验、无侧限抗压强度试验、X射线衍射分析、比表面及孔径分析试验、FTIR傅里叶红外光谱分析,检测稳定化药剂和固结体强度,探究固结体物质组成变化规律、内部孔隙度变化和微观结构中分子键的变化。结果表明:以建筑垃圾、磷石膏和矿渣作为原料,选出满足国内固废基用于道路底基层材料强度要求的配比(顶管淤泥∶建筑垃圾∶磷石膏∶矿渣=0.40∶0.55∶0.015∶0.052),养护28 d后试样的含水率为1.32%~2.89%,抗压强度为3.3~6.6 MPa。Abstract: During pipe jacking construction, a large amount of silt will be generated, which has characteristics such as high moisture content, poor stability, and uneven particle distribution. Mud solidification technology is an important means for the reuse of construction waste. To improve the strength of mud consolidation and explore the efficient formula of stabilizing agents, sand strength tests, unconfined compressive strength tests, X-ray diffraction analysis, specific surface and pore size analysis tests, FTIR Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analysis were used to detect the strength of stabilizing agents and consolidation bodies. The changes in the composition of consolidation bodies, internal porosity changes, and molecular bonds in the microstructure were studied. The results show that using construction waste, phosphogypsum, and slag as raw materials, a ratio (top pipe sludge: construction waste: phosphogypsum: slag=0.40:0.55:0.015:0.052) was selected to meet the strength requirements of domestic solid waste base materials for road subgrade. After 28 days of curing, the moisture content of the samples was 1.32%~2.89%, and the compressive strength was 3.3~6.6 MPa.
-
Key words:
- top pipe sludge /
- subbase material /
- curing and stabilization /
- compressive strength /
- pore structure
-
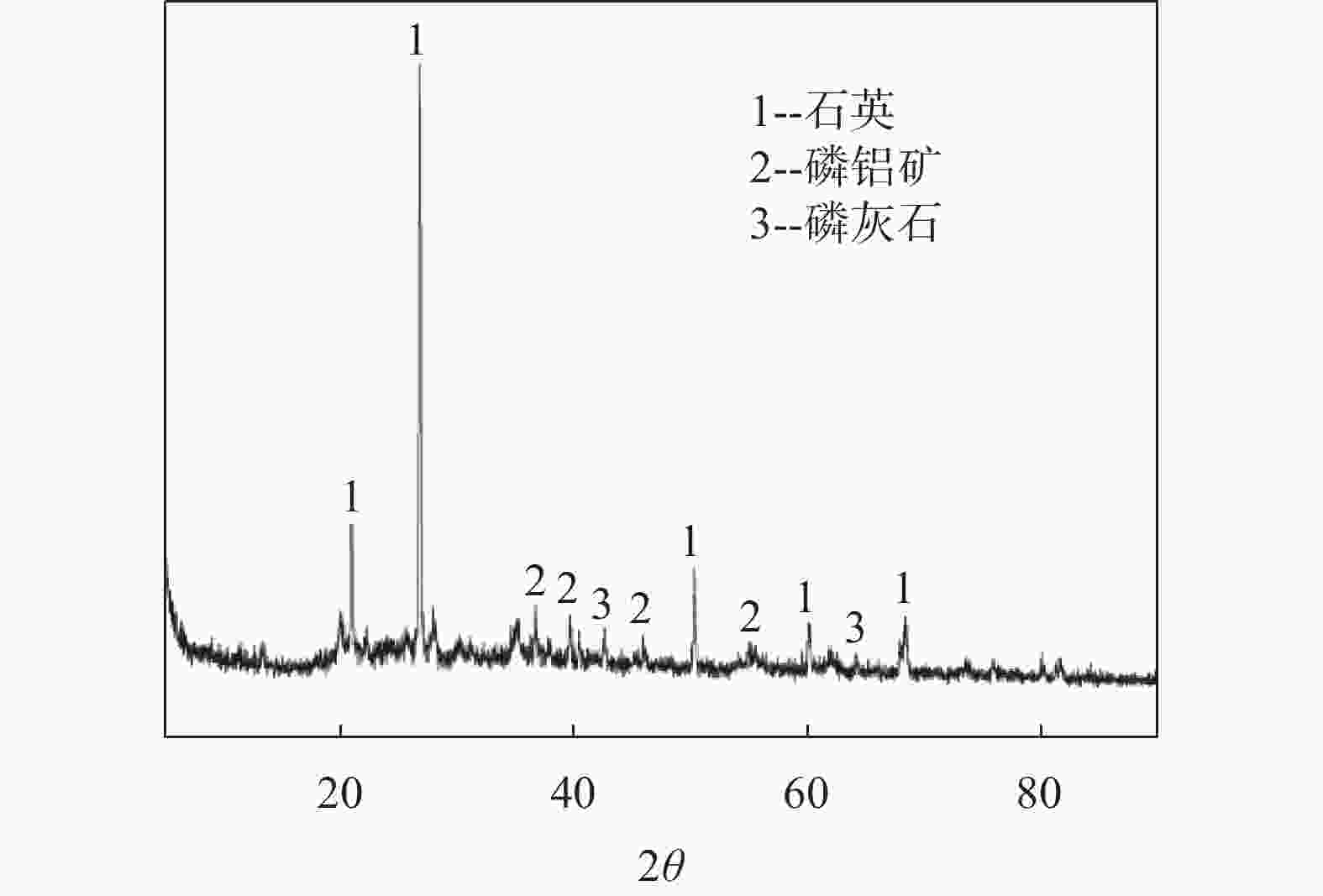
表 1 顶管淤泥化学成分组成
成分 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO P2O5 MgO 其它 占比/% 57.31 17.44 9.65 6.95 3.17 2.24 3.24 表 2 建筑垃圾化学成分组成表
成分 SiO2 CaO Al2O3 Fe2O3 SO3 其它 占比/% 39.85 35.09 8.93 6.03 3.09 7.01 表 3 顶管淤泥稳定化药剂设计配比表
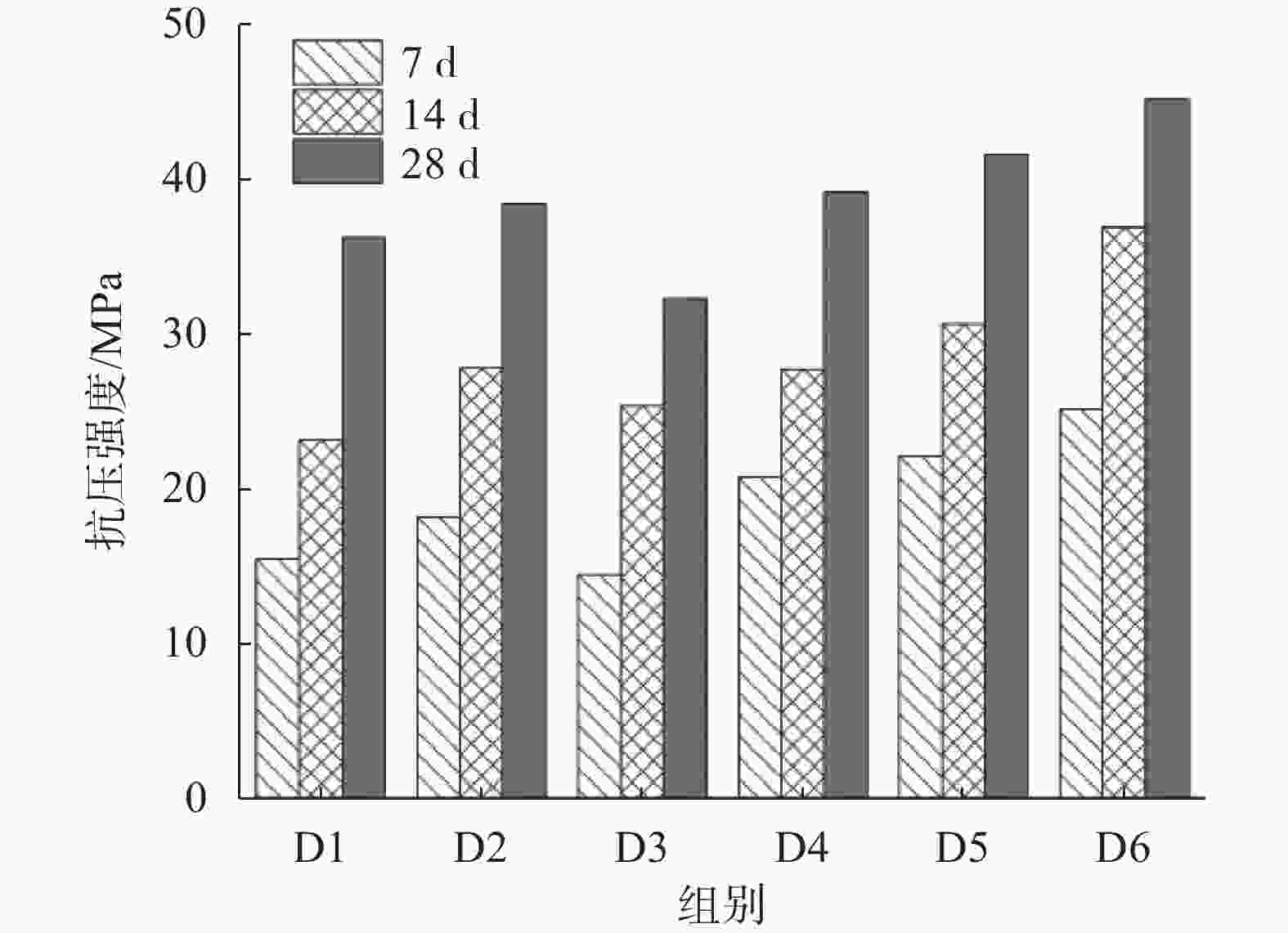
序号 成分质量占比/% 矿渣 磷石膏 激发剂 活化剂 D1 62 20 15 3 D2 57 20 20 3 D3 52 20 25 3 D4 62 15 20 3 D5 57 15 25 3 D6 52 15 30 3 表 4 道路底基层材料配比表(质量比)
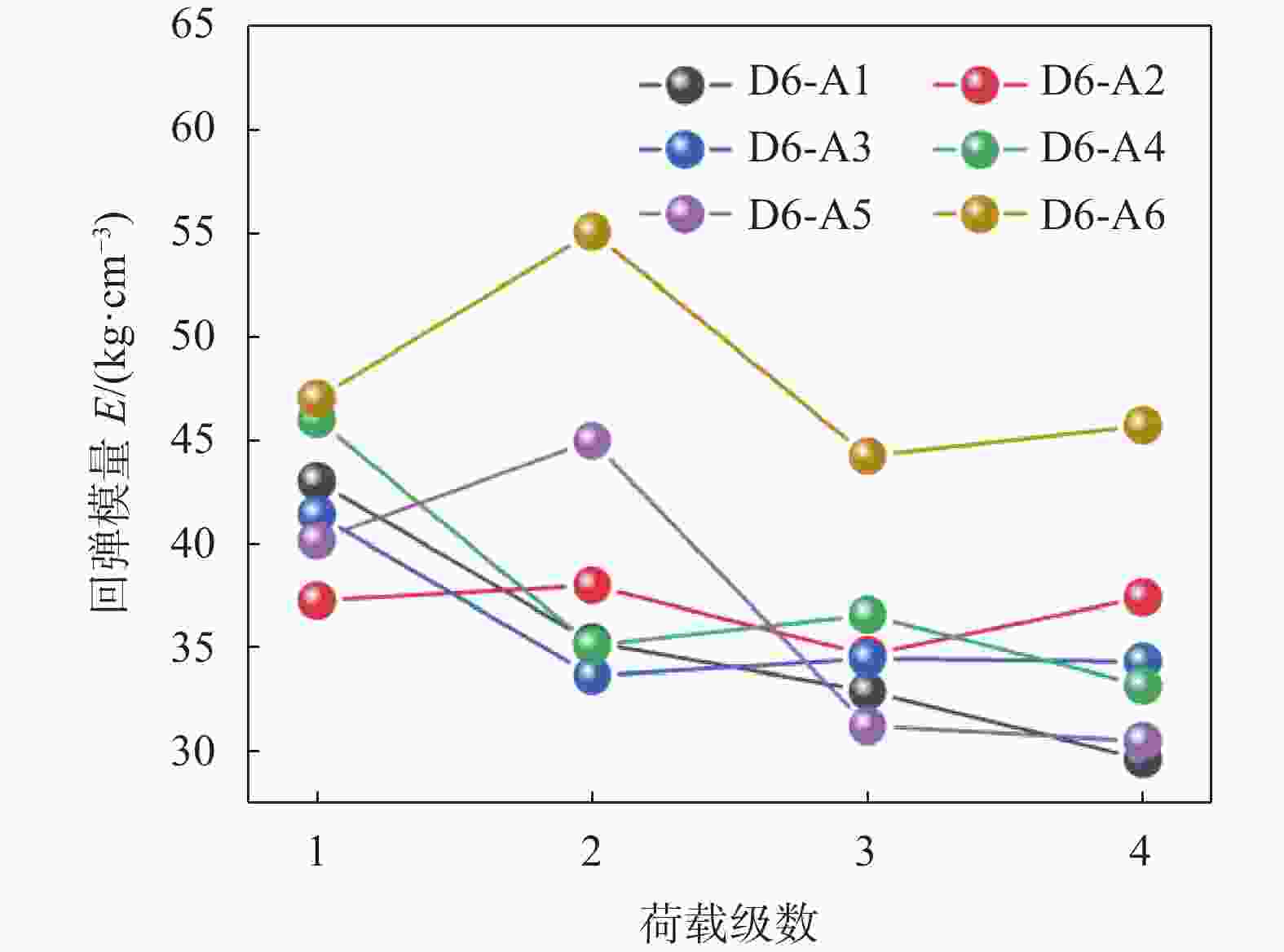
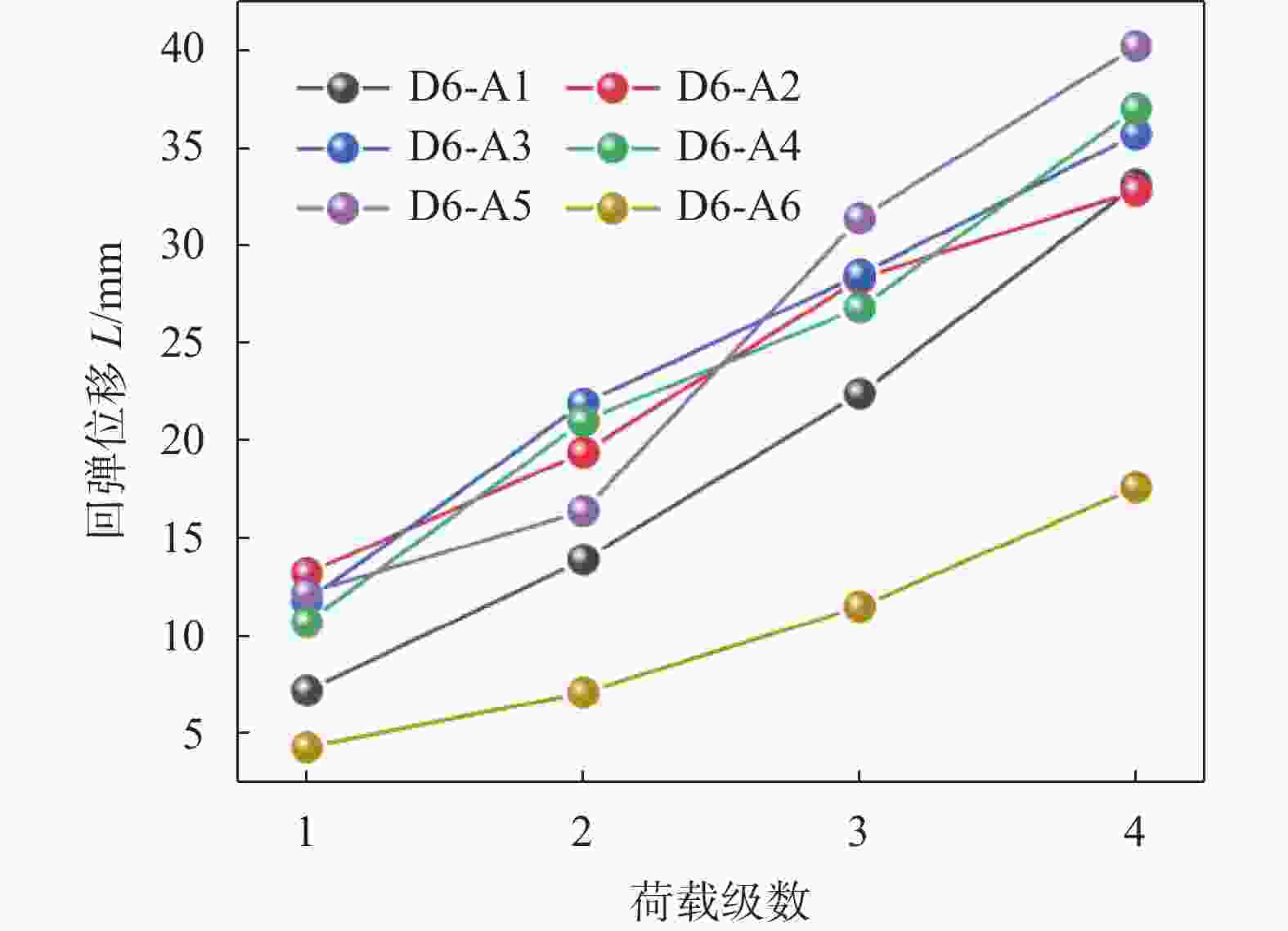
% 编号 稳定化药剂 建筑垃圾 顶管淤泥 外掺水 A1 8 61 35 9 A2 8 63 33 10 A3 10 58 37 8 A4 10 60 35 9 A5 8 66 30 8 A6 10 55 40 10 表 5 道路底基层材料孔隙结构参数
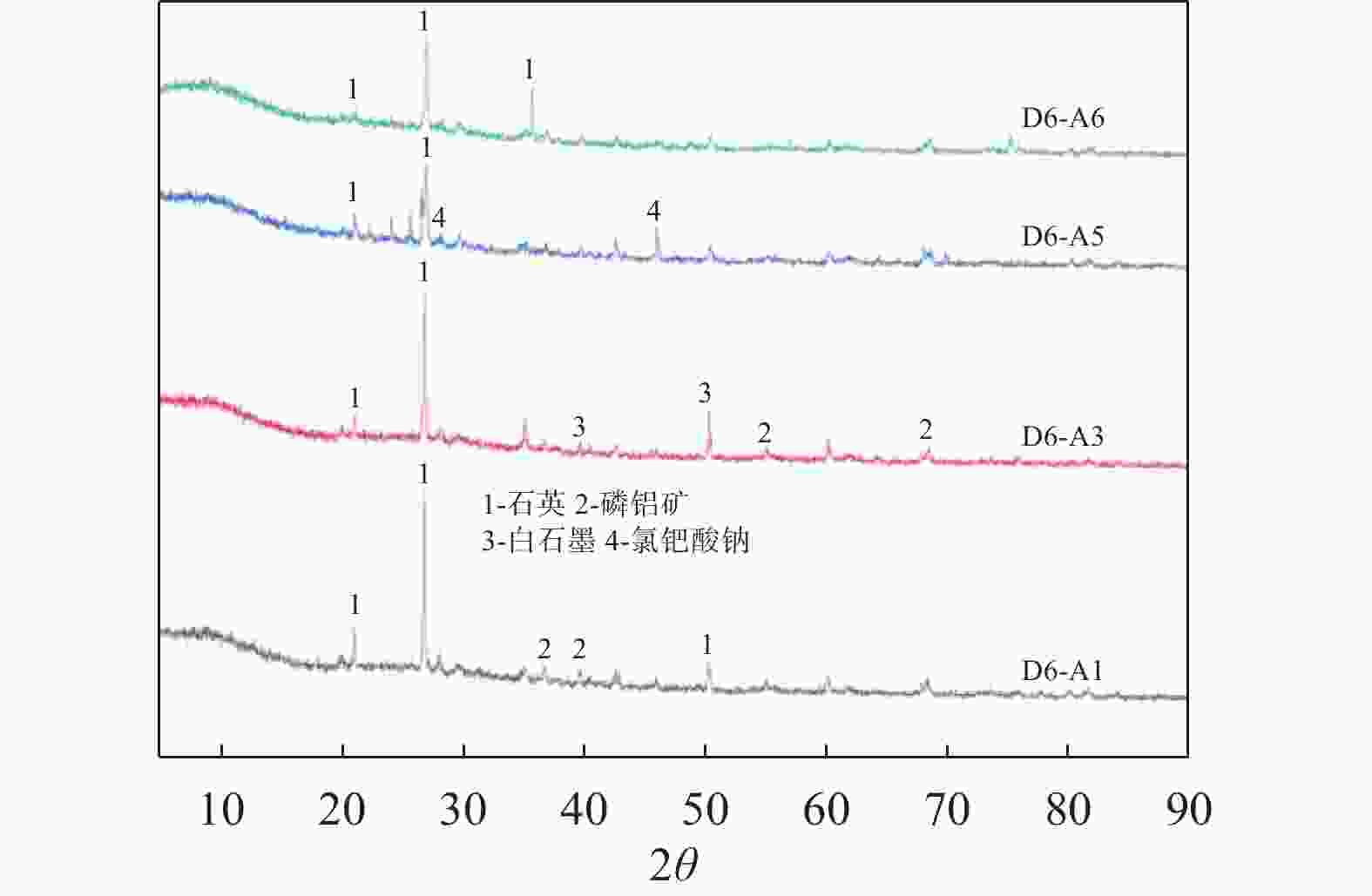
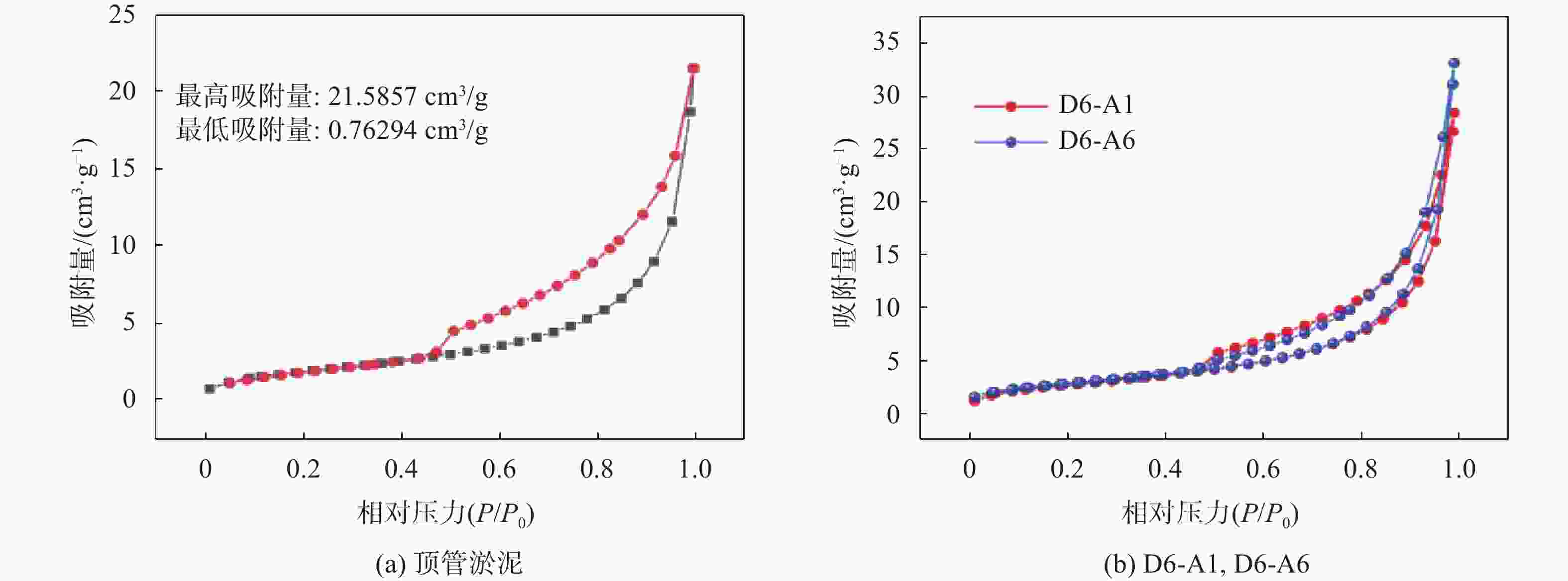
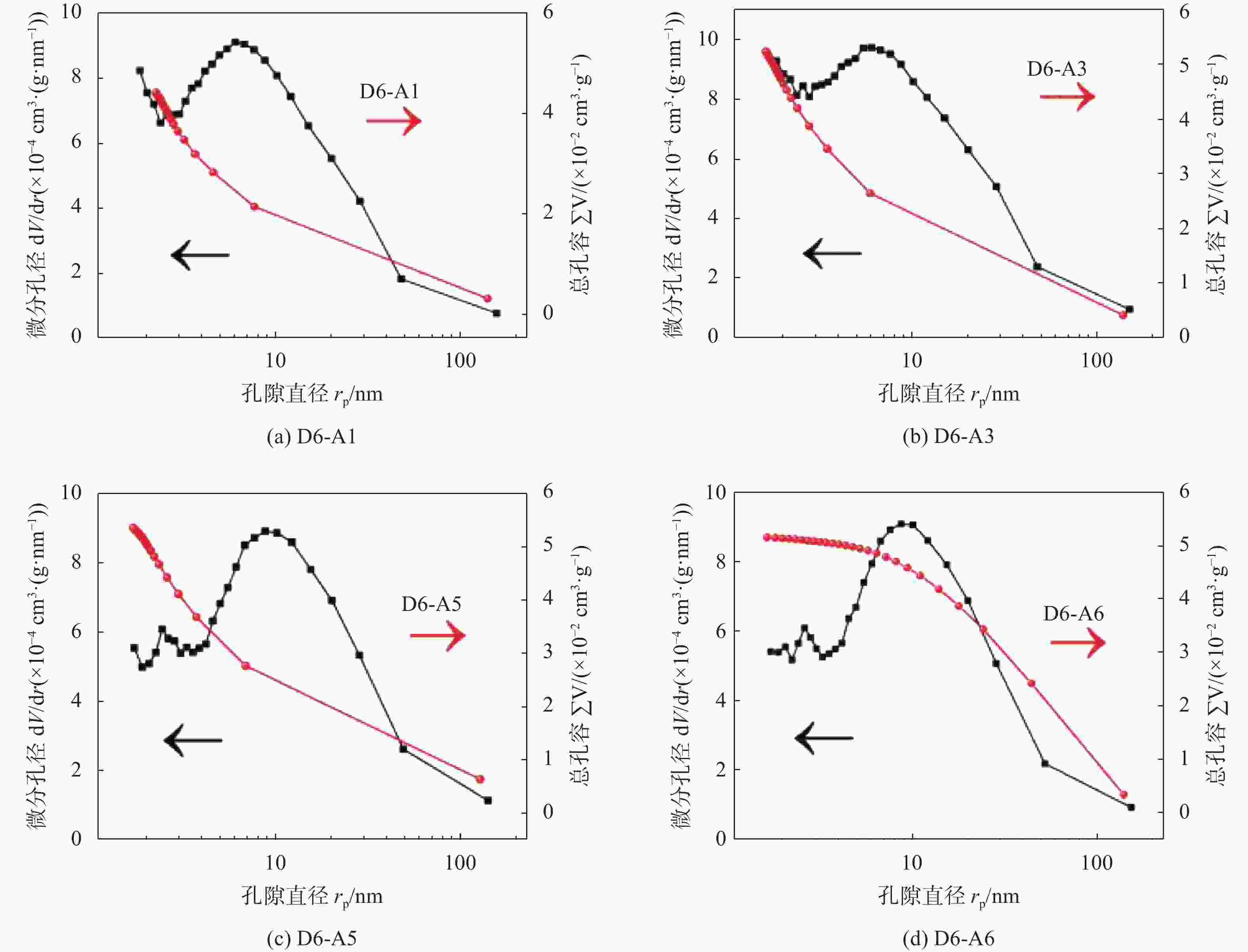
样品 比表面积 /(m2·g−1) 平均孔容 /(cm3·g−1) 平均孔径 /nm 顶管淤泥 7.2137 0.017849 9.8972 D6-A1 9.9303 0.025061 10.0949 D6-A3 11.3595 0.028743 10.1213 D6-A5 10.2498 0.028550 11.1419 D6-A6 10.2861 0.028427 11.0546 -
[1] 再 协. 2020年全国大、中城市固体废物污染环境防治年报[J]. 中国资源综合利用,2021,39(1):4. (China Resource Recycling Association. Annual report on solid waste pollution prevention and control in major and medium sized cities in China in 2020[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization,2021,39(1):4. (in Chinese)China Resource Recycling Association. Annual report on solid waste pollution prevention and control in major and medium sized cities in China in 2020[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2021, 39(1): 4. [2] WANG L, YAN D Y, XIONG Y, et al. A review of the challenges and application of public-private partnership model in Chinese garbage disposal industry[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2019,230:219-229. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.028 [3] CHETRI J K, REDDY K R. Advancements in municipal solid waste landfill cover system: A review[J]. Journal of the Indian Institute of Science,2021,101(4):557-558. doi: 10.1007/s41745-021-00229-1 [4] 程福周, 雷学文, 孟庆山, 等. 高含水率疏浚淤泥固化的力学性质试验研究[J]. 科学技术与工程,2015,15(1):295-299. (CHENG F Z, LEI X W, MENG Q S, et al. Experimental study on the mechanical properties of solidified dredging silt of high moisture content[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2015,15(1):295-299. (in Chinese)CHENG F Z, LEI X W, MENG Q S, et al. Experimental study on the mechanical properties of solidified dredging silt of high moisture content[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2015, 15(1): 295-299. (in Chinese) [5] 张志勇, 严 娟. 城市河道淤泥固化技术试验研究[J]. 人民长江,2021,52(12):210-213. (ZHANG Z Y, YAN J. Experimental study on dredged material solidification technology for urban rivers[J]. Yangtze River,2021,52(12):210-213. (in Chinese)ZHANG Z Y, YAN J. Experimental study on dredged material solidification technology for urban rivers[J]. Yangtze River, 2021, 52(12): 210-213. (in Chinese) [6] PROVIS J L, PALOMO A, SHI C J. Advances in understanding alkali-activated materials[J]. Cement & Concrete Research,2015,78:110-125. [7] WU C H, CHEN H J, CHI J H. Study on the reuse of in situ solidified reservoir sediment[C]//Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Informatics, Environment, Energy and Applications. Osaka, Japan: ACM, 2019: 11-14. [8] 邹维列, 贺 扬, 张凤德, 等. 改性淤泥固化土非饱和渗透特性试验研究[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版),2017,51(11):2182-2188. (ZOU W L, HE Y, ZHAGN F D, et al. Experimental study on unsaturated permeability characteristics of solidified sediment stabilized with cement[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science),2017,51(11):2182-2188. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2017.11.012ZOU W L, HE Y, ZHAGN F D, et al. Experimental study on unsaturated permeability characteristics of solidified sediment stabilized with cement[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2017, 51(11): 2182-2188. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2017.11.012 [9] 陈海斌, 郑世华, 钟煌亮. 湖泊疏浚淤泥固化试验研究[J]. 水运工程,2012,20(12):230-233. (CHEN H B, ZHENG S H, ZHONG H L. Solidification test investigation on lake's dredging sludge[J]. Port & Waterway Engineering,2012,20(12):230-233. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2012.12.047CHEN H B, ZHENG S H, ZHONG H L. Solidification test investigation on lake's dredging sludge[J]. Port & Waterway Engineering, 2012, 20(12): 230-233. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2012.12.047 [10] 丁 慧, 孙秀丽, 刘文化, 等. 固化疏浚淤泥作路基材料工程特性试验研究[J]. 土木建筑与环境工程, 2017, 39(2): 11-18. (DING H, SUN X L, LIU W H, et al. Experimental analysis of engineering properties of solidified sludge as roadbed filling material[J]. Journal of Civil, Architectural & Environmental Engineering, 2017, 39(2): 11-18. (in Chinese)DING H, SUN X L, LIU W H, et al. Experimental analysis of engineering properties of solidified sludge as roadbed filling material[J]. Journal of Civil, Architectural & Environmental Engineering, 2017, 39(2): 11-18. (in Chinese) [11] 王宏伟, 王东星, 贺 扬. MgO改性淤泥固化土压缩特性试验[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2017,48(8):2133-2141. (WANG H W, WANG D X, HE Y. Experimental study on compressibility behavior of solidified dredged sludge with reactive MgO[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology),2017,48(8):2133-2141. (in Chinese)WANG H W, WANG D X, HE Y. Experimental study on compressibility behavior of solidified dredged sludge with reactive MgO[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2017, 48(8): 2133-2141. (in Chinese) [12] 甘雅雄. 早强型材料淤泥固化试验研究[J]. 科学技术与工程,2015,15(2):270-274,283. (GAN Y X. Experimental study of solidification of dredged clays by adding early-strength type material[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2015,15(2):270-274,283. (in Chinese)GAN Y X. Experimental study of solidification of dredged clays by adding early-strength type material[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2015, 15(2): 270-274,283. (in Chinese) [13] 胡孝彭, 赵仲辉. 固化淤泥持水特性的微观机理研究[J]. 人民长江,2017,48(13):81-84,99. (HU X P, ZHAO Z H. Micro-mechanism of water retention property of solidified dredged material[J]. Yangtze River,2017,48(13):81-84,99. (in Chinese)HU X P, ZHAO Z H. Micro-mechanism of water retention property of solidified dredged material[J]. Yangtze River, 2017, 48(13): 81-84,99. (in Chinese) [14] 丁建文, 吴学春, 李 辉, 等. 疏浚淤泥固化土的压缩特性与结构屈服应力[J]. 工程地质学报,2012,20(4):627-632. (DING J W, WU X C, LI H, et al. Compression properties and structure yield stress for solidified soil composing of dredged clays[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2012,20(4):627-632. (in Chinese)DING J W, WU X C, LI H, et al. Compression properties and structure yield stress for solidified soil composing of dredged clays[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2012, 20(4): 627-632. (in Chinese) [15] WANG H W, ZENTAR R, WANG D X. Predicting the compaction parameters of solidified dredged fine sediments with statistical approach[J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology,2023,41(2):195-210. [16] WU X T, SUN J S, QI Y, et al. Pore and compression characteristics of clay solidified by ionic soil stabilizer[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2021,80(6):5003-5019. doi: 10.1007/s10064-021-02145-1 [17] ZHANG X F, ZHANG Y M, LIU X, et al. Shakedown behavior of yellow river alluvial silt stabilized with lignin-lime combined additive[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering,2020,32(1):04019318. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002954 [18] 王江营, 阳 滔, 张贵金, 等. 超高含水率湖相淤泥固化试验及填筑性能分析[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2020,39(8):2691-2698. (WANG J Y, YANG T, ZHANG G J, et al. Curing experiment and filling performance of ultra-high water content lacustrine sludge[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2020,39(8):2691-2698. (in Chinese)WANG J Y, YANG T, ZHANG G J, et al. Curing experiment and filling performance of ultra-high water content lacustrine sludge[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2020, 39(8): 2691-2698. (in Chinese) [19] 李世汩, 陈文峰, 夏新星, 等. 低碱性环保固化剂调理淤泥的板框压滤脱水试验研究[J]. 长江科学院院报,2023,40(3):46-51. (LI S G, CHEN W F, XIA X X, et al. Experimental study on dewatering of plate-and-frame filter press for sludge treatment with a low-alkaline environmental modifier[J]. Journal of Changjiang River Scientific Research Institute,2023,40(3):46-51. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20211150LI S G, CHEN W F, XIA X X, et al. Experimental study on dewatering of plate-and-frame filter press for sludge treatment with a low-alkaline environmental modifier[J]. Journal of Changjiang River Scientific Research Institute, 2023, 40(3): 46-51. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20211150 [20] LIU Y, LU H J, LIU M Y, et al. Microanalytical characterizations, mechanical strength and water resistance performance of solidified dredged sludge with industrial solid waste and architecture residue soil[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials,2022,17:e01492. doi: 10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e01492 [21] 黎家国, 何旭东, 沈建生, 等. 废渣型固化剂对软土固化的研究与应用[J]. 低温建筑技术,2021,43(8):119-122. (LI J G, HE X D, SHEN J S, et al. Research and application of waste residue curing agent for soft soil solidification[J]. Low Temperature Architecture Technology,2021,43(8):119-122. (in Chinese)LI J G, HE X D, SHEN J S, et al. Research and application of waste residue curing agent for soft soil solidification[J]. Low Temperature Architecture Technology, 2021, 43(8): 119-122. (in Chinese) [22] SHEN J S, XU Y D, CHEN J, et al. Study on the stabilization of a new type of waste solidifying agent for soft soil[J]. Materials,2019,12(5):826. doi: 10.3390/ma12050826 [23] SHU B A, CHEN W Z, YANG T Y, et al. Study on laboratory and engineering application of multi source solid waste based soft soil solidification materials[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials,2022,17:e01465. doi: 10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e01465 [24] LI D D, ZHOU X G, MO J B. Experimental study on the Solidification of silt by composite curing agent with fiber[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science,2020,587(1):012014. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/587/1/012014 [25] PENG L, CHEN B. Study on the basic properties and mechanism of waste sludge solidified by magnesium phosphate cement containing different active magnesium oxide[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,281:122609. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122609 -





 下载:
下载: