Distribution pattern and cause analysis of loess sinkholes along Pengyang section of Yinchuan-Kunming Expressway
-
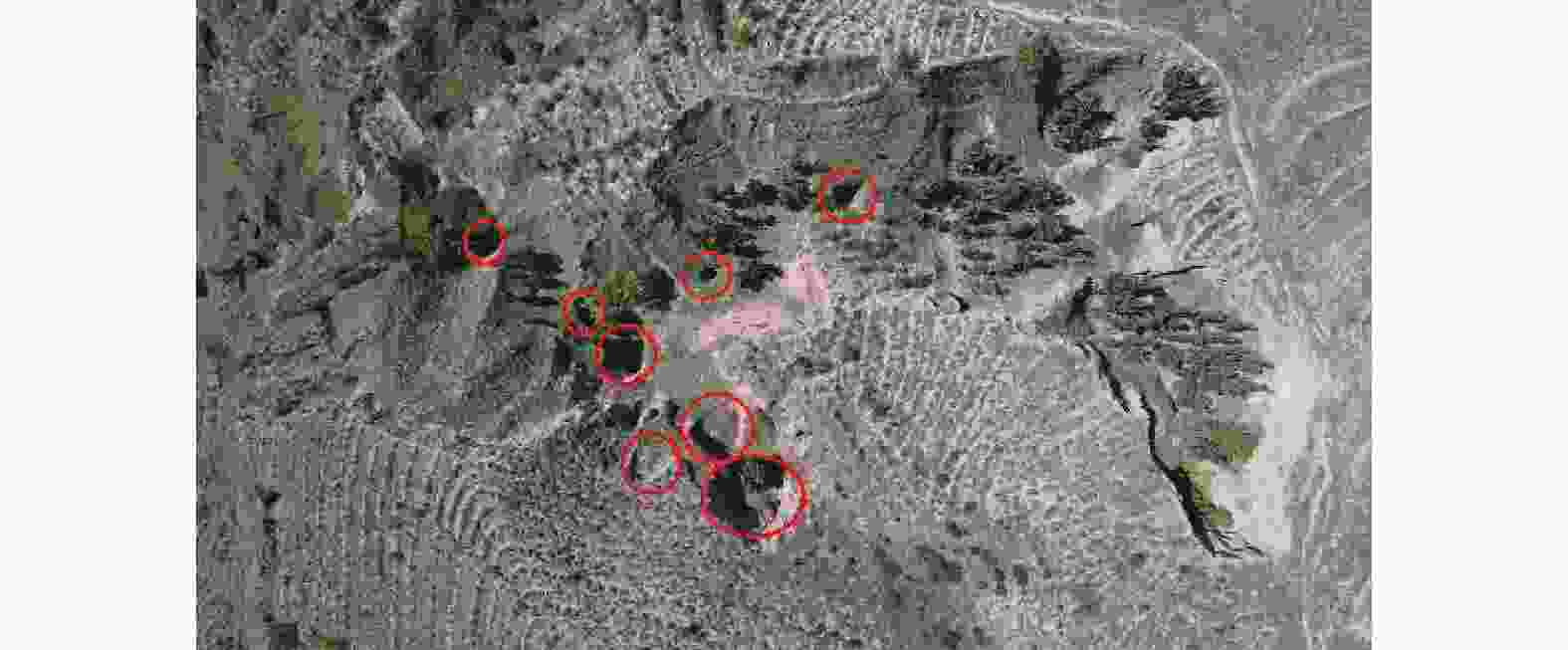
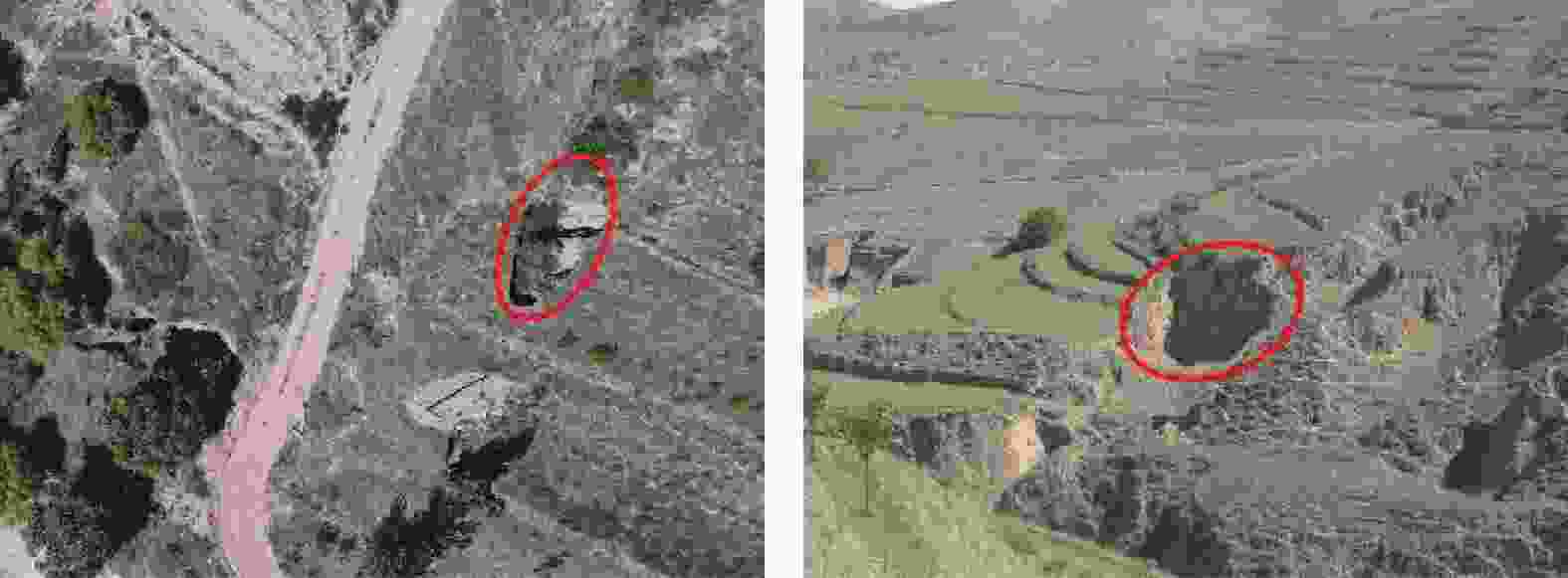
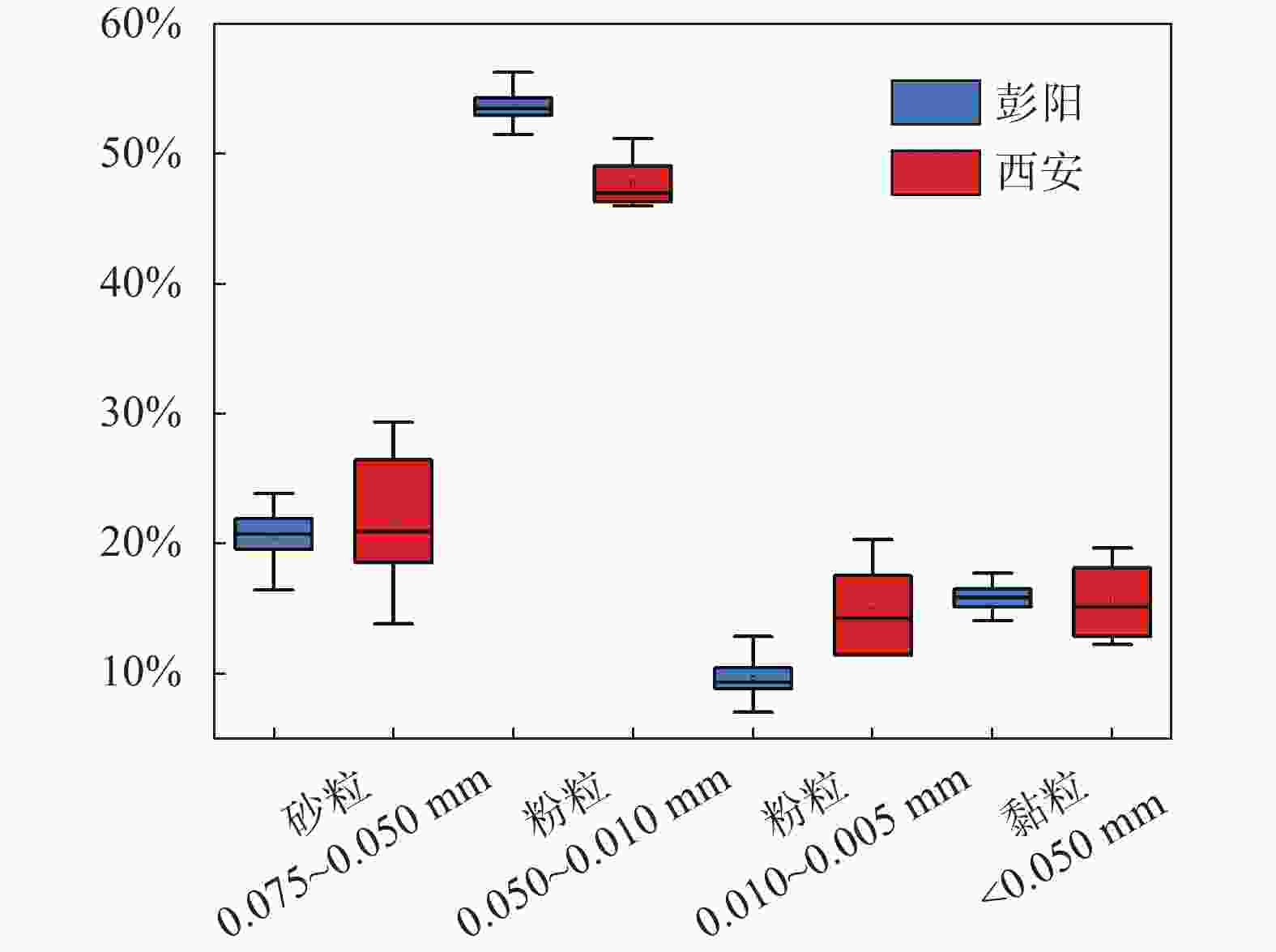
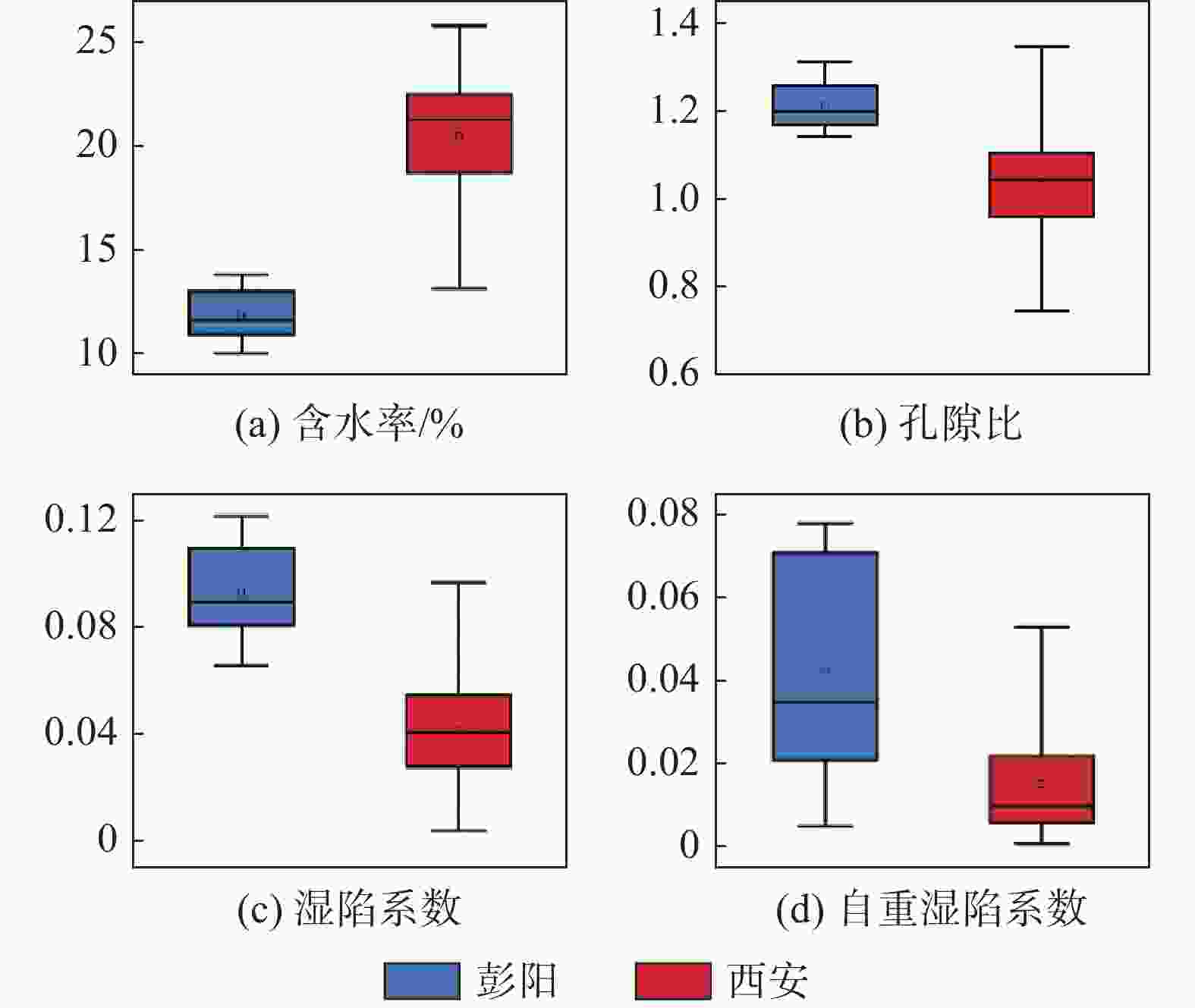
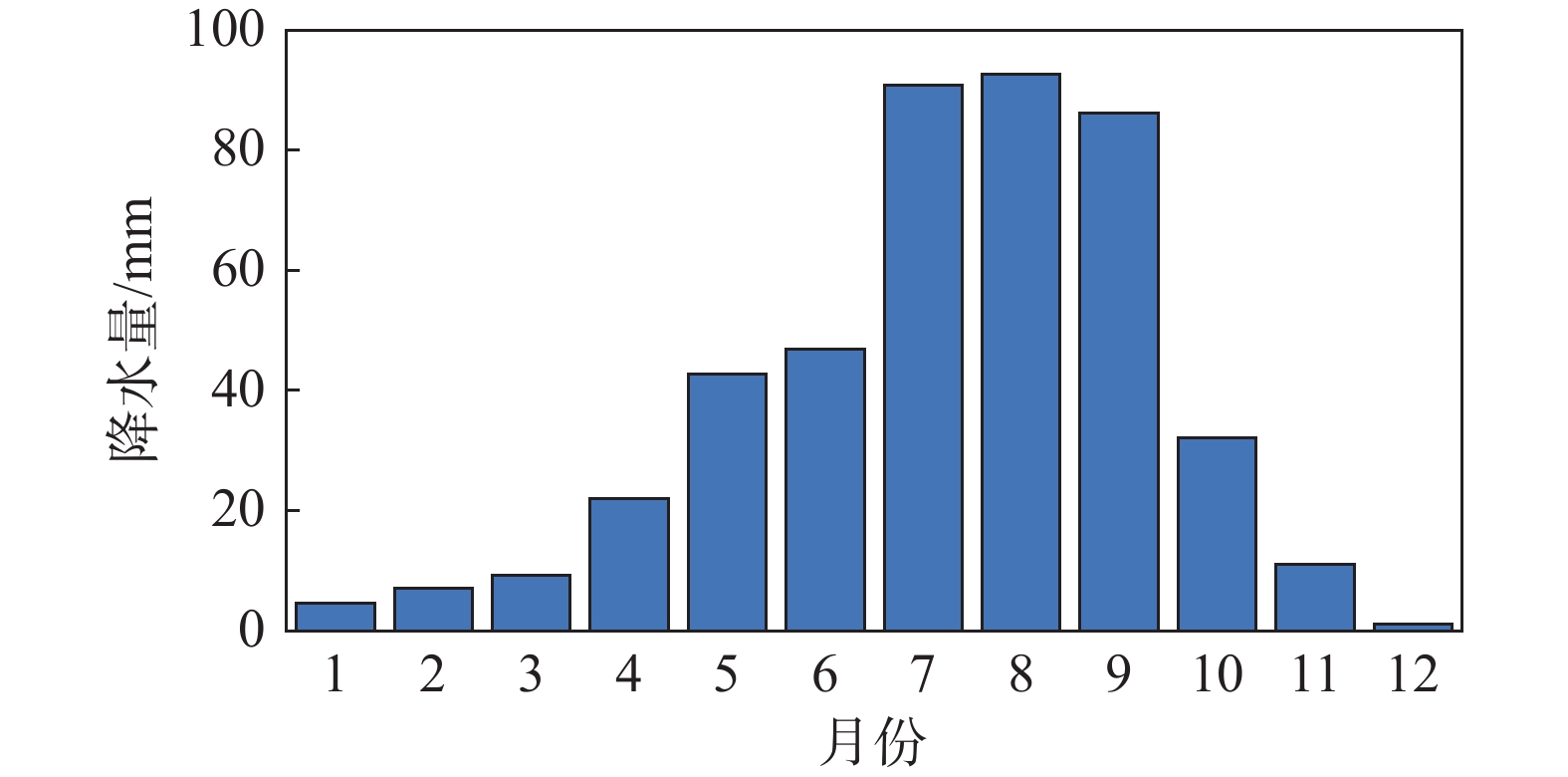
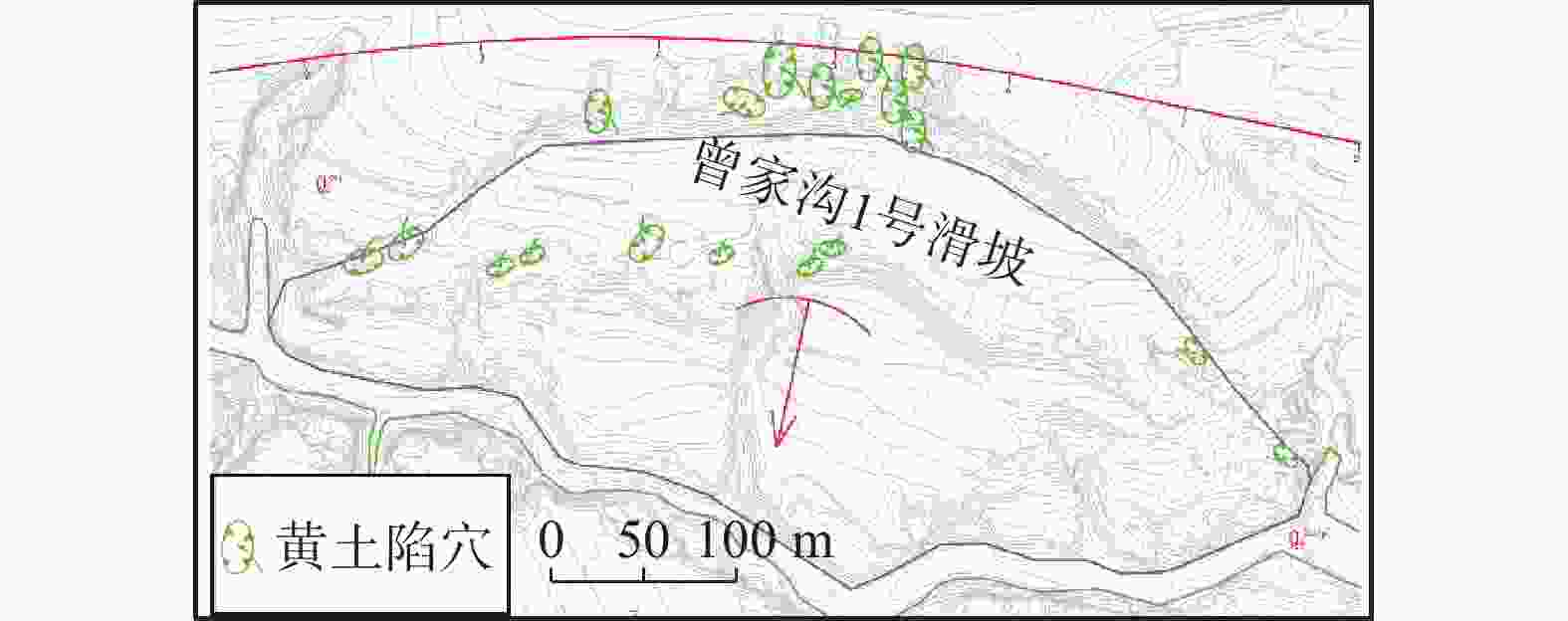
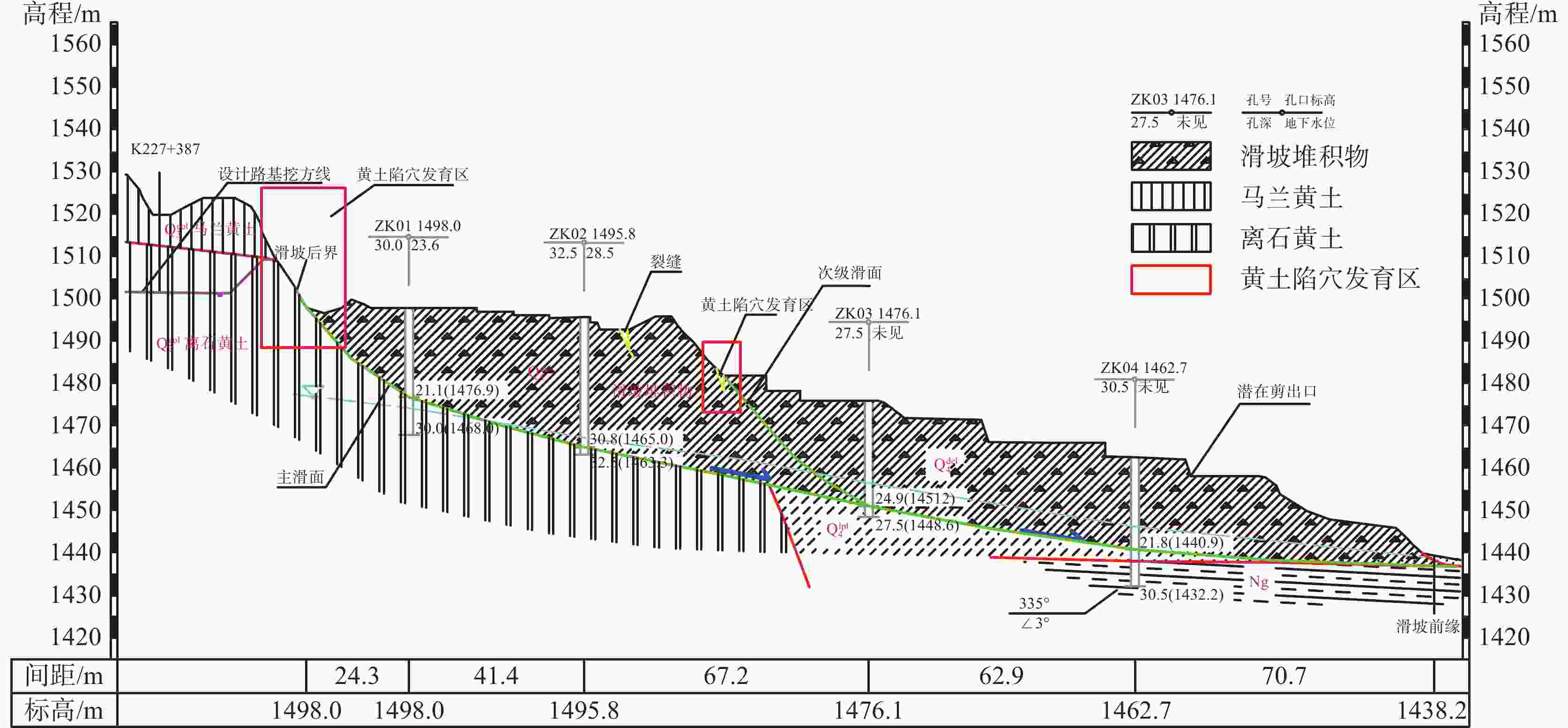
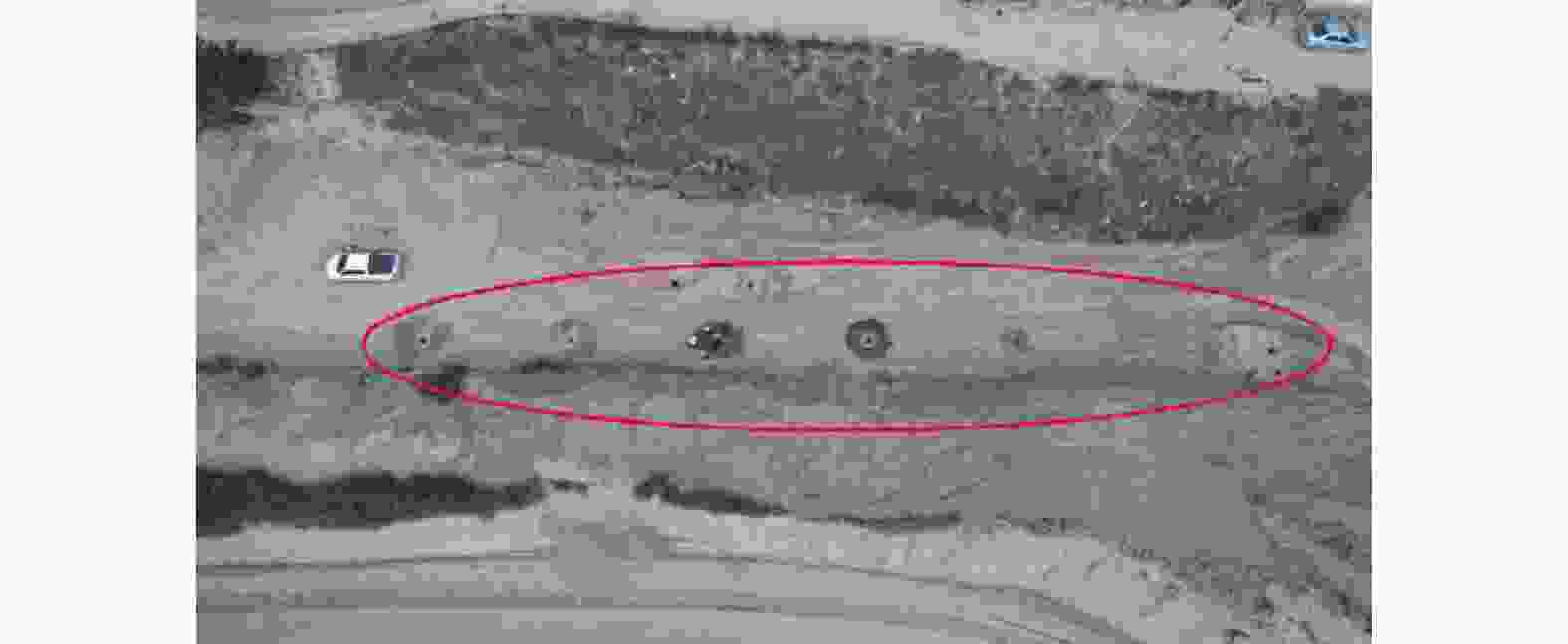
摘要: 银川至昆明高速公路彭阳段沿线黄土陷穴异常发育,黄土陷穴对路基及其他构造物的稳定性影响较大,特别是处于路基、桥台附近的黄土陷穴,易引起滑坡、崩塌,影响工程的稳定性。针对沿线黄土陷穴分布规律、成因及扩展机理进行分析,结果表明:区内陷穴多发育于塬边或冲沟两侧、冲沟沟头、滑坡或崩塌体后方,以竖井状、漏斗状、碟形、串珠状及蜂窝状为主;彭阳县湿陷性黄土具结构疏松、孔隙及垂直节理发育、湿陷强烈、易溶蚀、易冲刷的特点,是形成黄土陷穴的内在原因;区内降水集中,地形条件有利于雨水汇集下渗、冲刷坡面,水起到了搬运、溶蚀的作用,是形成黄土陷穴的外部原因;内外原因共同作用导致彭阳地区黄土陷穴异常发育。Abstract: The Yinchuan-Kunming Expressway section in Pengyang is marked by an exceptional development of loess sinkholes, which significantly compromise the stability of the roadbed and other structural elements. In particular, sinkholes near the roadbed and bridge abutments are susceptible to triggering landslides and collapse, thereby jeopardizing the integrity of the engineering project. A comprehensive analysis of the distribution patterns, causes, and expansion mechanisms of these sinkholes along the expressway was conducted. The findings indicate that sinkholes predominantly occur along the edges of plateaus, on both sides of gullies, at the heads of gullies, and behind landslide or collapse bodies, exhibiting forms such as vertical shafts, funnels, disc shapes, bead-like arrangements, and honeycomb patterns. The loess in Pengyang County, characterized by its loose structure, high porosity, well-developed vertical joints, strong collapsibility, and susceptibility to dissolution and erosion, constitutes the intrinsic factors facilitating sinkhole formation. Additionally, the region’s concentrated precipitation and terrain conditions are conducive to rainwater collection, infiltration, and erosion of slopes, and water plays a role in transportation and dissolution, representing the extrinsic factors. The synergistic effect of these intrinsic and extrinsic factors leads to the exceptional development of loess sinkholes in the Pengyang area.
-
Key words:
- collapsible loess /
- loess sinkhole /
- distribution pattern /
- formation mechanism
-
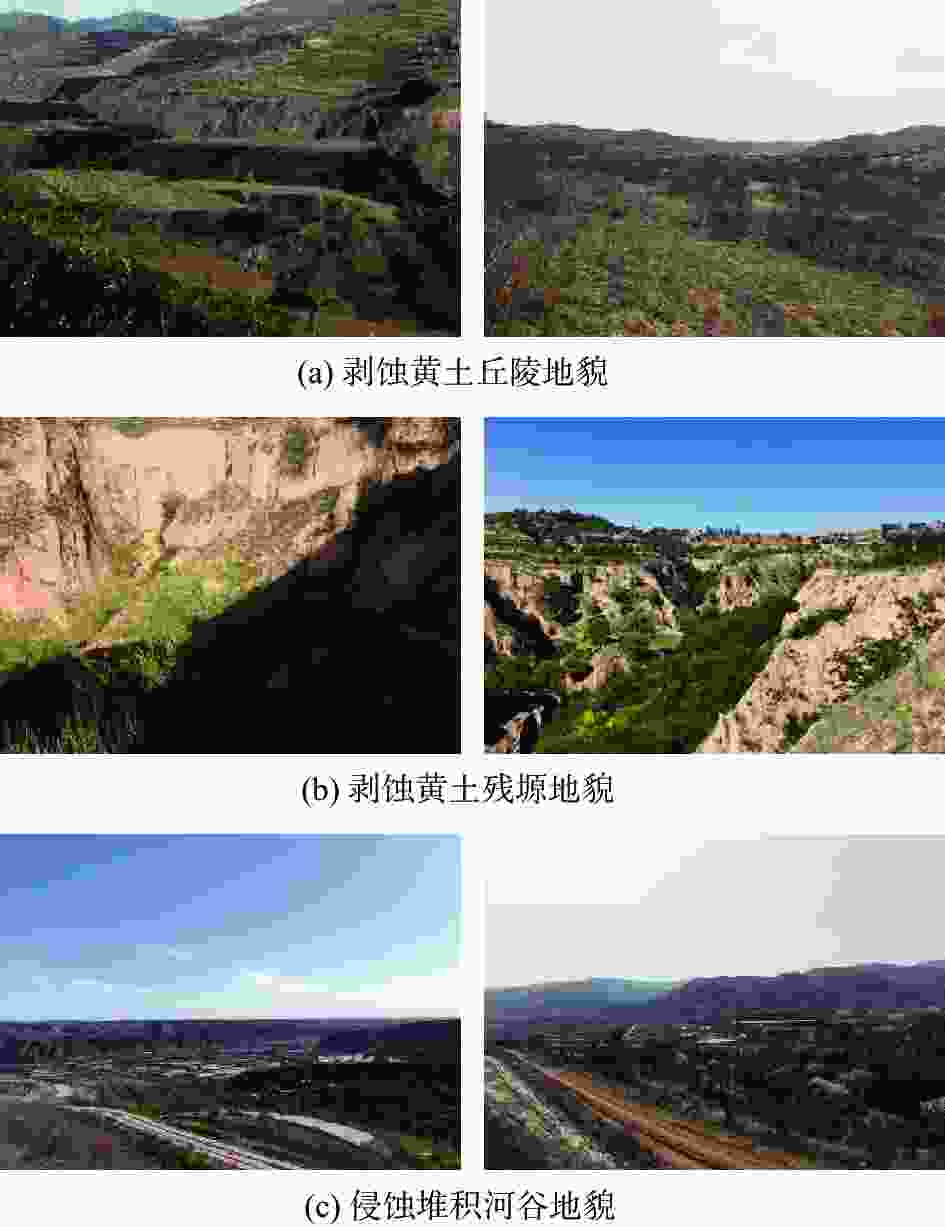
表 1 各地貌单元主要黄土及成因
地貌单元 黄土名称 地质年代及成因 剥蚀黄土丘陵地貌 马兰黄土 $ {\text{Q}}_{\text{3}}^{\text{eol}} $ 离石黄土 $ {\text{Q}}_{\text{2}}^{\text{eol}} $ 剥蚀黄土残塬地貌 马兰黄土 $ {\text{Q}}_{\text{3}}^{\text{eol}} $ 离石黄土 $ {\text{Q}}_{\text{2}}^{\text{eol}} $ 侵蚀堆积河谷地貌 黄土状土 $ {\text{Q}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{al+pl}}{\text{/Q}}_{\text{3}}^{\text{al+pl}} $ 表 2 沿线黄土陷穴分类
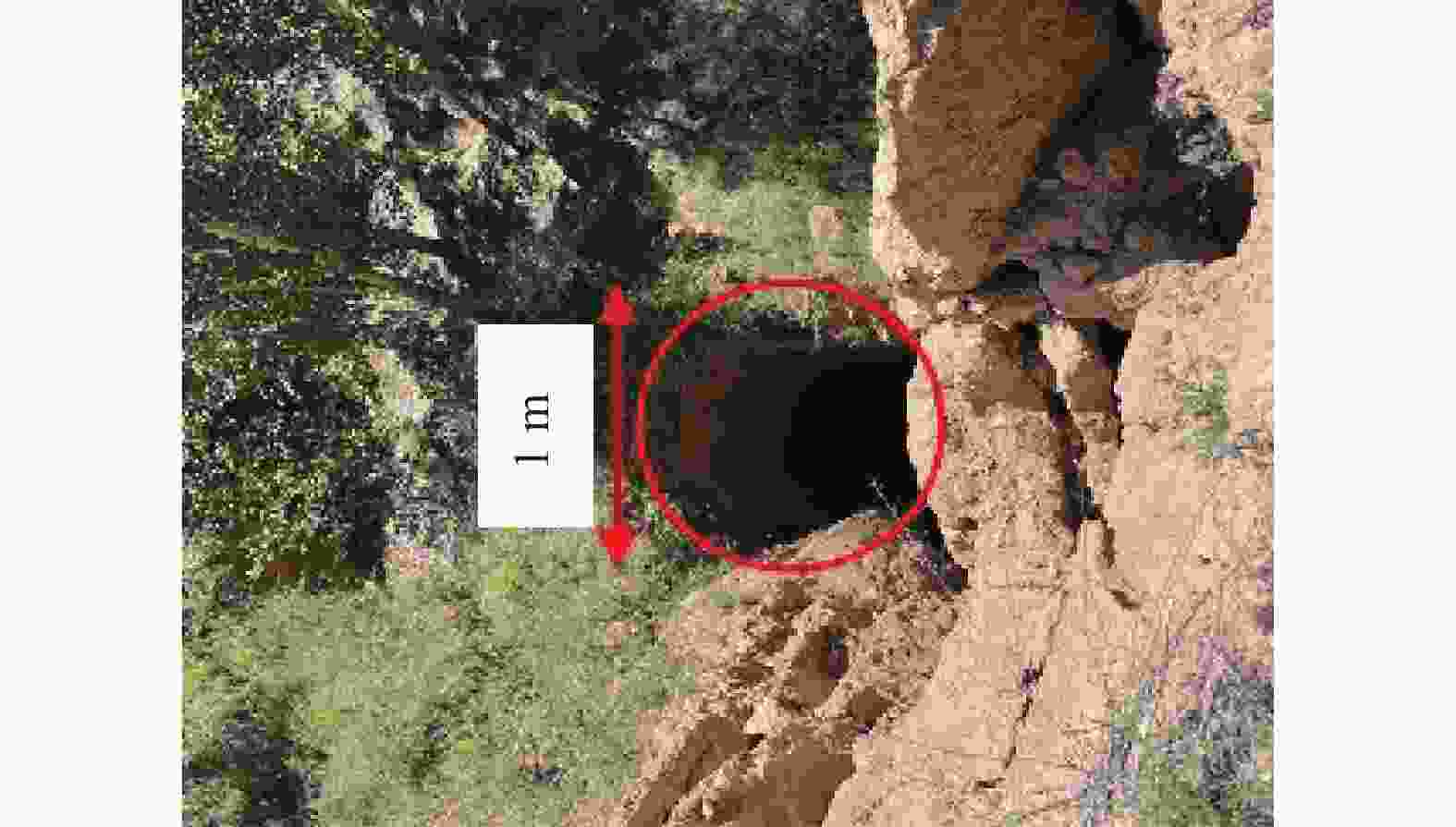
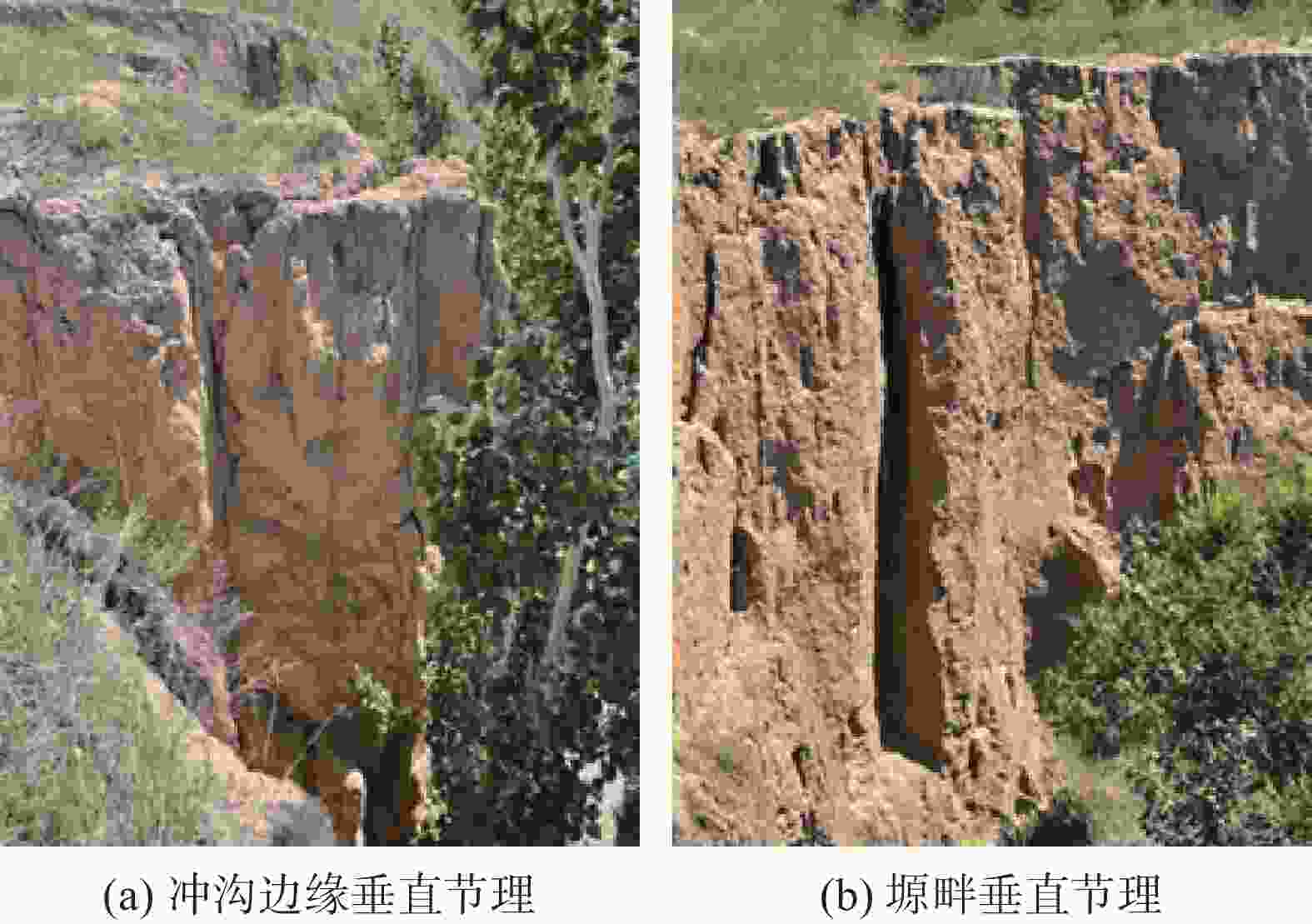
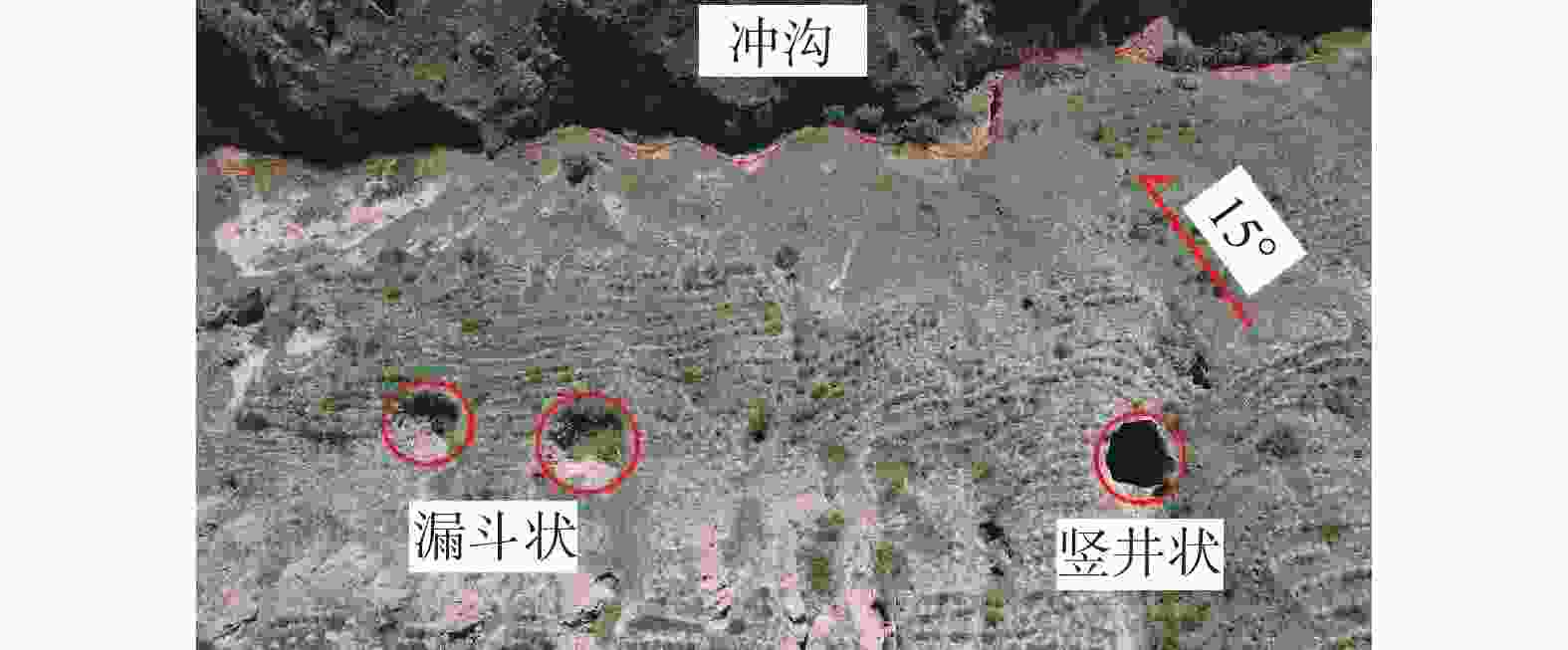
形态 尺寸 特征 竖井状 口径一般1~5 m,深度可达10 m左右 井壁垂直,并沿沟侧处往往坍塌形成半圆形,底部堆积有崩塌下来的
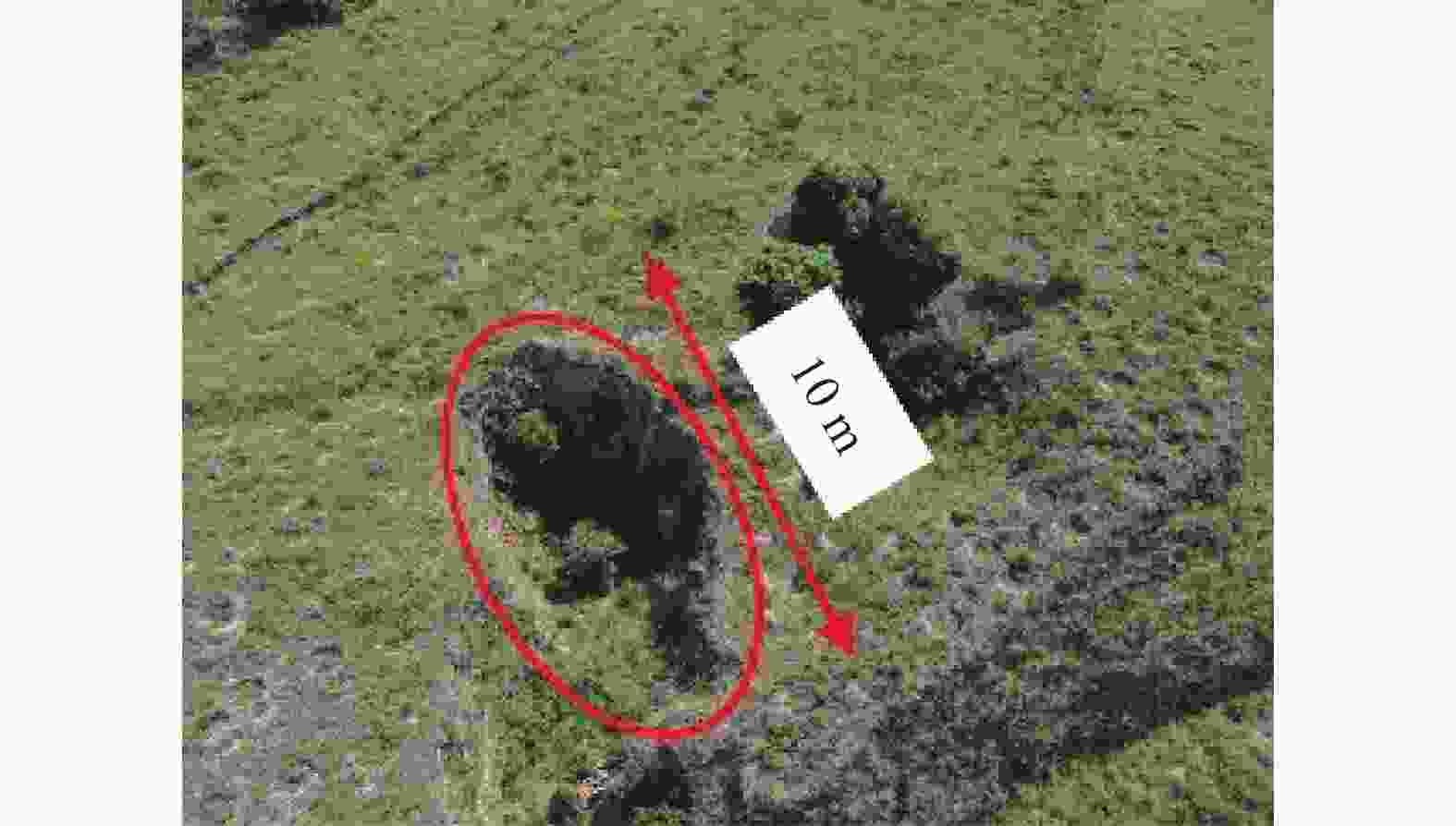
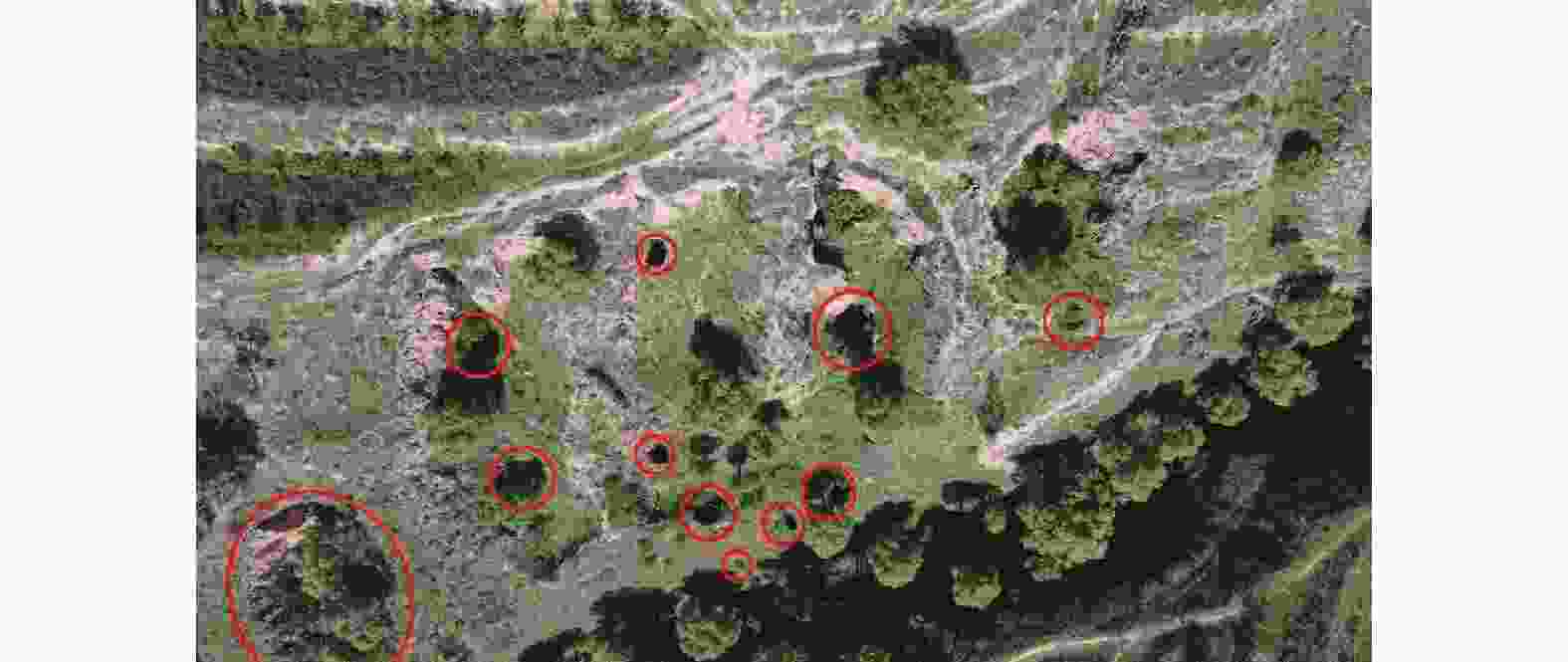
土块,底部沿沟侧处有数个小的排泄通道漏斗状 口径不一,数米至十多米 上大下小,形似漏斗 串珠状 口径0.5~3 m 形态各异,串珠状 碟形 口径相对较大,最大可达数十米,深度一般在0.5~3 m 为圆型或椭圆型,形似菜碟 蜂窝状 大小、深浅不一 由数个至数十个竖井状、漏斗状陷穴组成 暗穴 地表无出露 -
[1] 舒良树. 普通地质学[M]. 4版. 北京: 地质出版社, 2020: 261-262. (SHU L S. Physical geology[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2020: 261-262. (in Chinese)SHU L S. Physical geology[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2020: 261-262. (in Chinese) [2] DERBYSHIRE E. Geological hazards in loess terrain, with particular reference to the loess regions of China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2001,54(1/3):231-260. [3] LI X A, LI L C. Quantification of the pore structures of Malan loess and the effects on loess permeability and environmental significance, Shaanxi Province, China: an experimental study[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2017,76(15):523, doi: 10.1007/s12665-017-6855-7 [4] PENG J B, SUN P, IGWE O, et al. Loess caves, a special kind of geo-hazard on loess plateau, northwestern China[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,236:79-88. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.08.012 [5] WANG L, LI X A, LI L C, et al. Characterization of the collapsible mechanisms of Malan loess on the Chinese Loess Plateau and their effects on eroded loess landforms[J]. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal,2020,26(9):2541-2566, doi: 10.1080/10807039.2020.1721265 [6] 许 强, 彭大雷, 亓 星, 等. 2015年4.29甘肃黑方台党川2#滑坡基本特征与成因机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2016,24(2):167-180. (XU Q, PENG D L, QI X, et al. Dangchuan 2# landslide of April 29, 2015 in Heifangtai area of Gansu province: characteristices and failure mechanism[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2016,24(2):167-180. (in Chinese)XU Q, PENG D L, QI X, et al. Dangchuan 2# landslide of April 29, 2015 in Heifangtai area of Gansu province: characteristices and failure mechanism[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2016, 24(2): 167-180. (in Chinese) [7] 蔡柏松, 朱建华, 杨晓宁. 黄土陷穴对陕京输气管道的危害及处理[J]. 油气储运,2002,21(4):35-36. (CAI B S, ZHU J H, YANG X N. The methodology to protect the loess sinking in Shaanxi Beijing gas transmission pipeline[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation,2002,21(4):35-36. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8241-D.2002.04.011CAI B S, ZHU J H, YANG X N. The methodology to protect the loess sinking in Shaanxi Beijing gas transmission pipeline[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2002, 21(4): 35-36. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8241-D.2002.04.011 [8] 王克俊. 黄土陷穴工程灾害特征及处治技术研究[J]. 公路交通科技(应用技术版), 2019, 15(6): 346-348. (WANG K J. Research on the characteristics and treatment techniques of loess sinkhole engineering disasters[J]. Highway Transportation Technology (Applied Technology Edition), 2019, 15(6): 346-348. (in Chinese)WANG K J. Research on the characteristics and treatment techniques of loess sinkhole engineering disasters[J]. Highway Transportation Technology (Applied Technology Edition), 2019, 15(6): 346-348. (in Chinese) [9] DELAGE P, CUI Y J, ANTOINE P. Geotechnical problems related with loess deposits in Northern France[C]//Proceedings of International Conference on Problematic Soils. N. Cyprus, 2005. [10] 楚华栋, 裴章勤, 马周全, 等. 黄土的工程特性、筑路技术和病害处理[J]. 铁道工程学报,2005(S1):340-347. (CHU H D, PEI Z Q, MA Z Q, et al. Engineering characteristics, railway construction technique and disaster treatment of loess[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society,2005(S1):340-347. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2005.z1.048CHU H D, PEI Z Q, MA Z Q, et al. Engineering characteristics, railway construction technique and disaster treatment of loess[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2005(S1): 340-347. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2005.z1.048 [11] 沈世科, 赵天宇, 安 亮. 甘肃定西公路建设中的工程地质问题分析[J]. 地震工程学报,2023,45(5):1046-1056. (SHEN S K, ZHAO T Y, AN L. Engineering geological problems of highway construction in Dingxi City, Gansu Province[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2023,45(5):1046-1056. (in Chinese)SHEN S K, ZHAO T Y, AN L. Engineering geological problems of highway construction in Dingxi City, Gansu Province[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2023, 45(5): 1046-1056. (in Chinese) [12] 胡永占. 陇西地区黄土陷穴成因分析及形成机理[J]. 铁道工程学报,2013,30(3):1-4. (HU Y Z. Analysis of cause and formation mechanisms for loess sinking hole in Longxi region[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society,2013,30(3):1-4. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2013.03.001HU Y Z. Analysis of cause and formation mechanisms for loess sinking hole in Longxi region[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2013, 30(3): 1-4. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2013.03.001 [13] 丁建强. 甘肃黄土陷穴的形成因素及分布规律研究[J]. 甘肃科技纵横, 2009, 38(1): 148-149. (DING J Q. Study on formation and distribution law of loess sinkhole in Gansu[J]. Scientific & Technical Information of Gansu, 2009, 38(1): 148-149. (in Chinese)DING J Q. Study on formation and distribution law of loess sinkhole in Gansu[J]. Scientific & Technical Information of Gansu, 2009, 38(1): 148-149. (in Chinese) [14] 郑炜珊, 耿豪鹏, 潘保田. 兰州青水村黄土陷穴的侵蚀临界研究[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2020,56(3):326-332. (ZHENG W S, GENG H P, PAN B T. The erosion threshold of loess sinkholes at Qingshui Valley in Lanzhou[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),2020,56(3):326-332. (in Chinese)ZHENG W S, GENG H P, PAN B T. The erosion threshold of loess sinkholes at Qingshui Valley in Lanzhou[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2020, 56(3): 326-332. (in Chinese) [15] REN J L, GONG W, XUE C, et al. Formation and evolution of a loess sinkhole in the southern Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. CATENA,2023,233:107519. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2023.107519 [16] LUKIC T, MARKOVIC S, GAVRILOV M B, et al. Geomorphic diversity of the loess-paleosol sequences in SE parts of the Banat region (Vojvodina, Serbia)[C]//Proceedings of the 2nd Serbian Geographer’s Congress-Towards Europe. Novi Sad, 2010. [17] 付攀升, 刘 高, 刘从友, 等. 湿陷性黄土区某长输管道黄土陷穴灾害研究[J]. 西部探矿工程,2010,22(2):21-24,27. (FU P S, LIU G, LIU C Y, et al. The study on the loess sinkhole hazard along a long-distance pipeline in the collapsible loess area[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering,2010,22(2):21-24,27. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2010.02.008FU P S, LIU G, LIU C Y, et al. The study on the loess sinkhole hazard along a long-distance pipeline in the collapsible loess area[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2010, 22(2): 21-24,27. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2010.02.008 [18] VERACHTERT E, VAN DEN EECKHAUT M, POESEN J, et al. Factors controlling the spatial distribution of soil piping erosion on loess-derived soils: a case study from central Belgium[J]. Geomorphology,2010,118(3/4):339-348. [19] 《工程地质手册》编委会. 工程地质手册[M]. 5版. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2018: 494-496. (Editorial Board of Engineering Geology Manual. Geological engineering handbook[M]. 5th ed. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2018: 494-496. (in Chinese)Editorial Board of Engineering Geology Manual. Geological engineering handbook[M]. 5th ed. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2018: 494-496. (in Chinese) [20] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 国家市场监督管理总局. 湿陷性黄土地区建筑标准: GB 50025–2018[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2019. (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, State Administration of Market Supervision and Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for building construction in collapsible loess regions: GB 50025–2018[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2019. (in Chinese)Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, State Administration of Market Supervision and Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for building construction in collapsible loess regions: GB 50025–2018[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2019. (in Chinese) -






 下载:
下载: