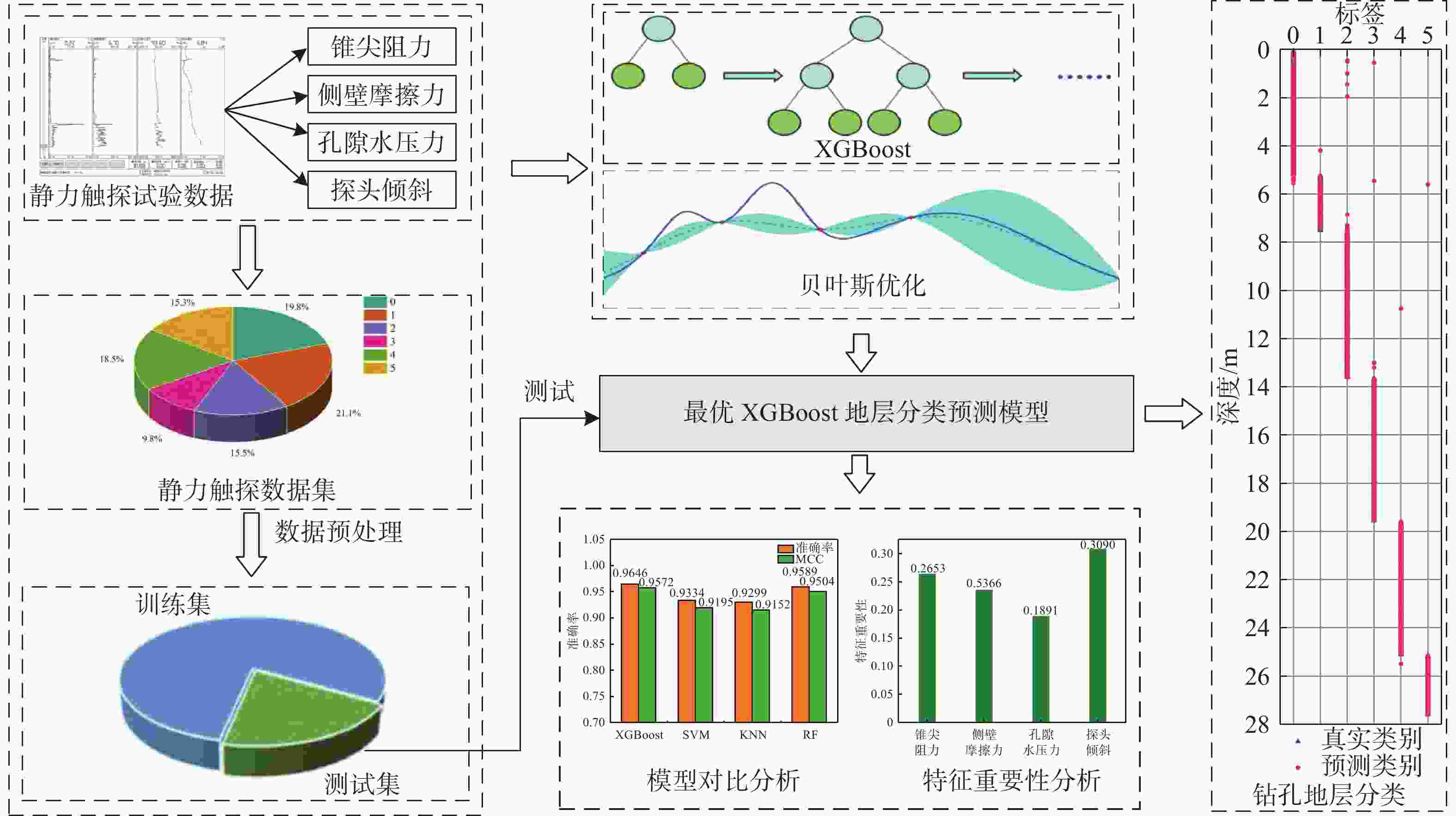
Stratigraphic classification prediction method for static cone penetrate test based on XGBoost and Bayesian optimization
-
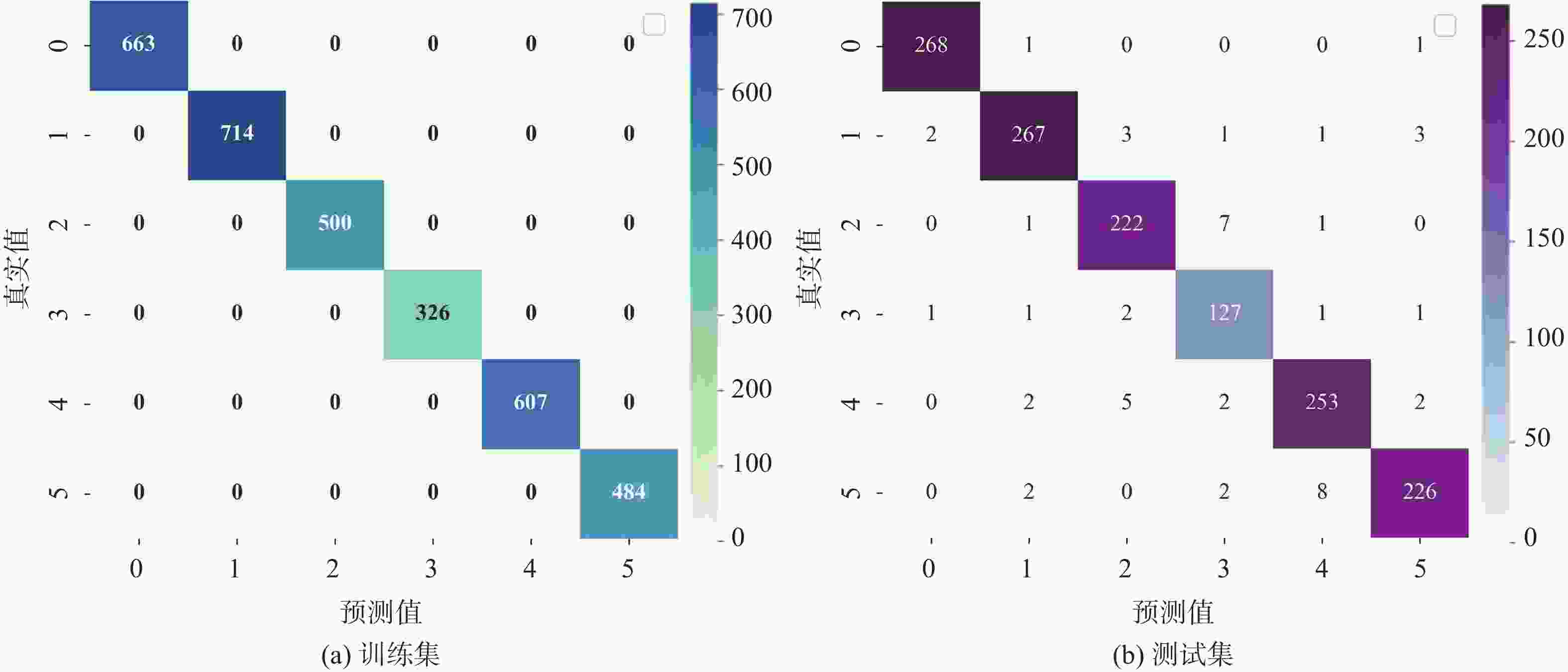
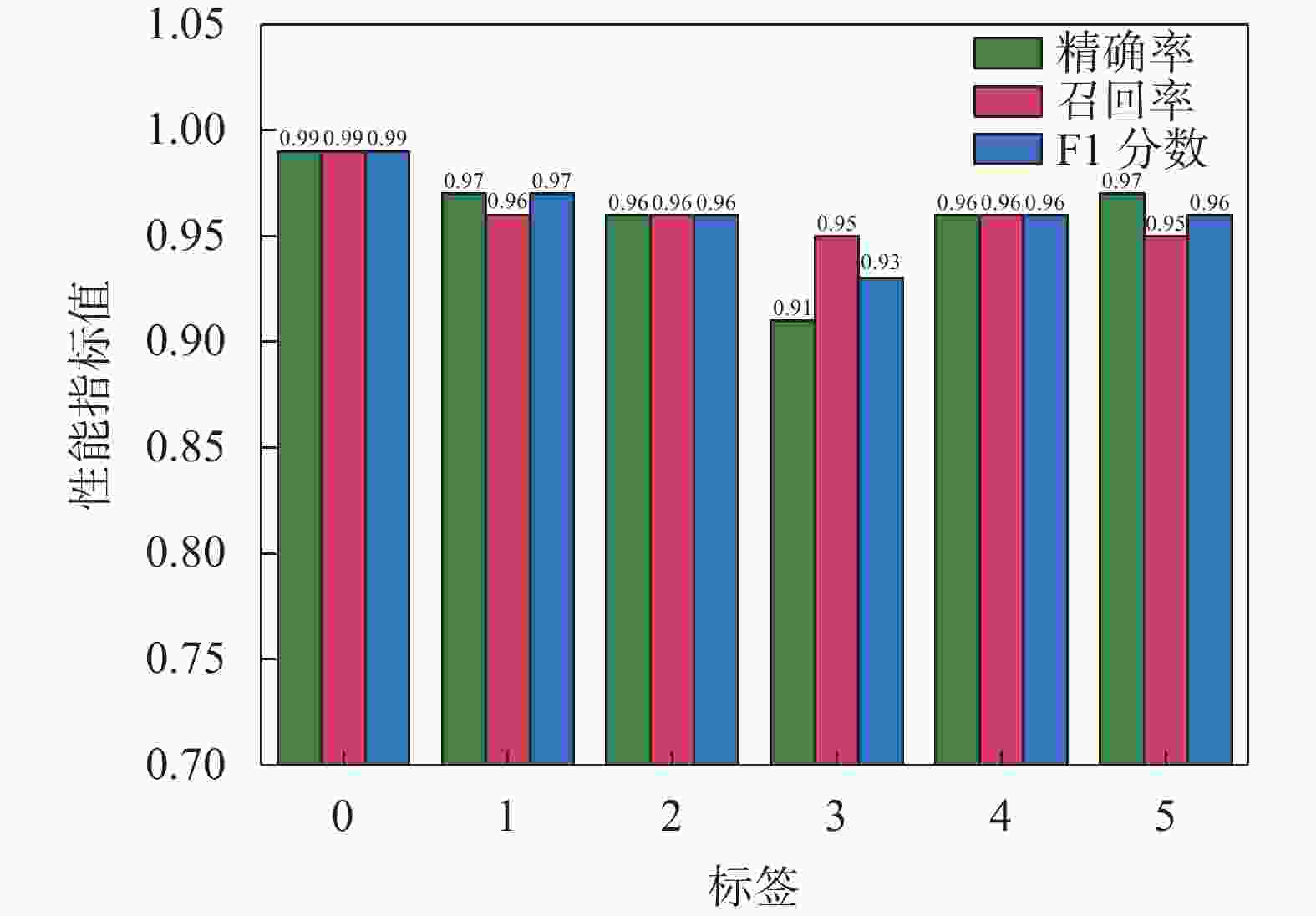
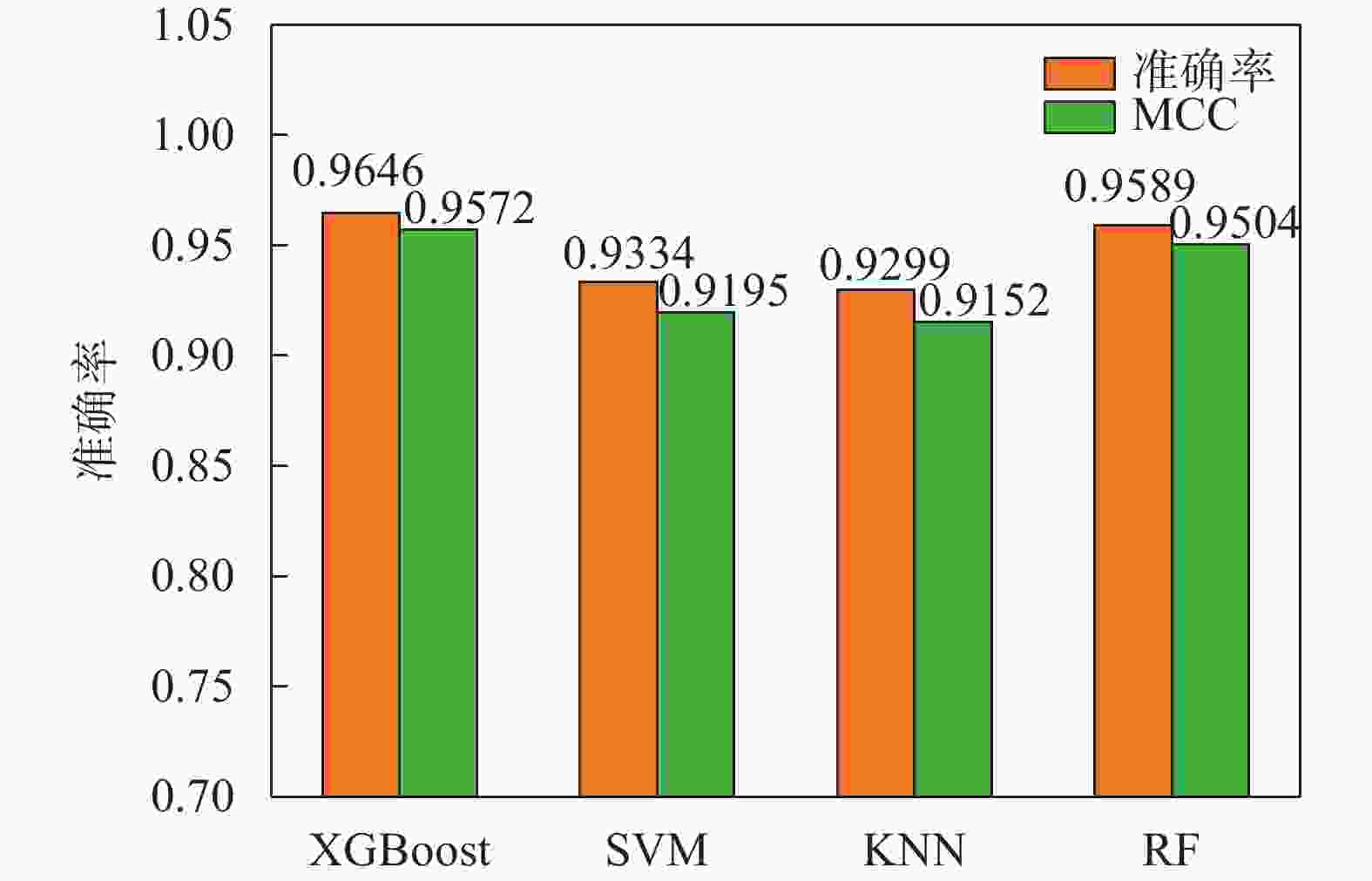
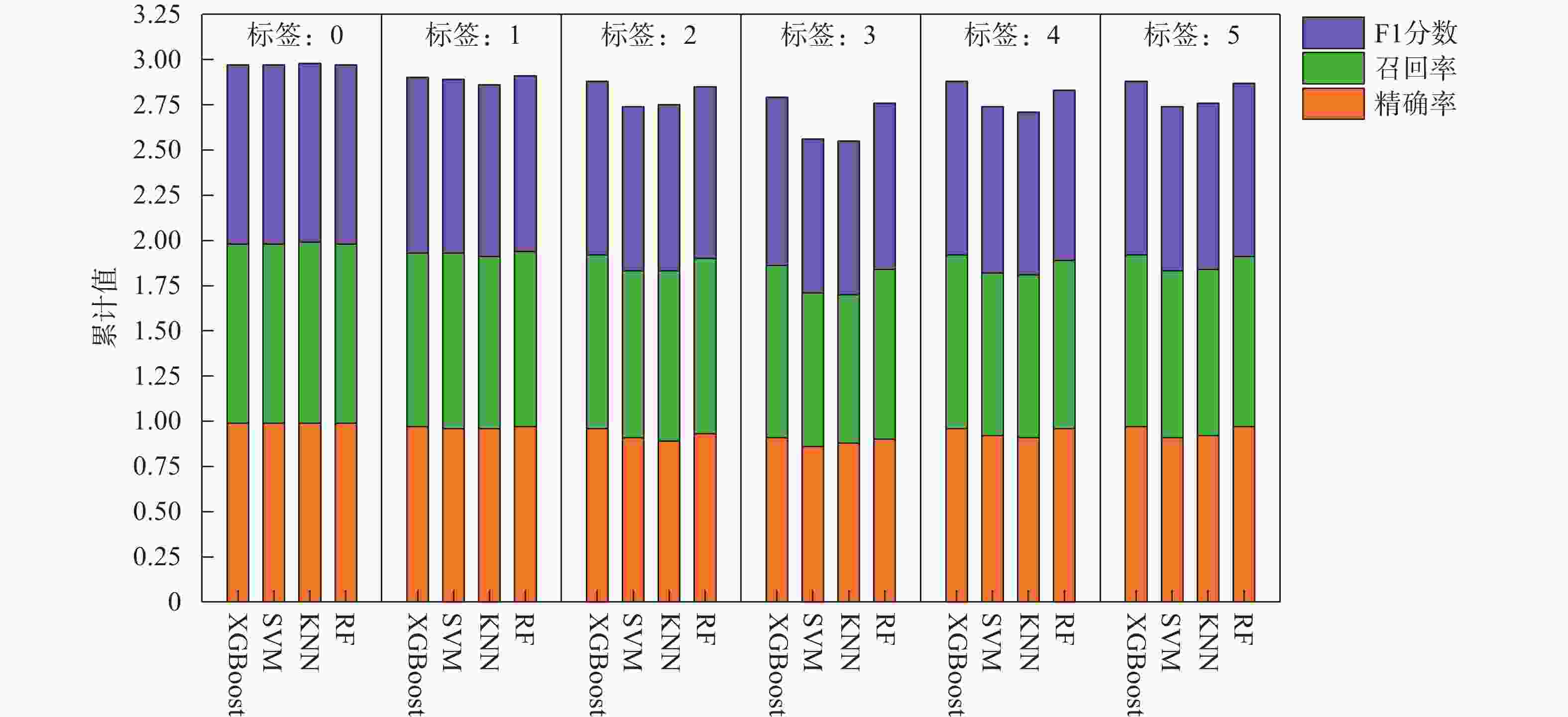
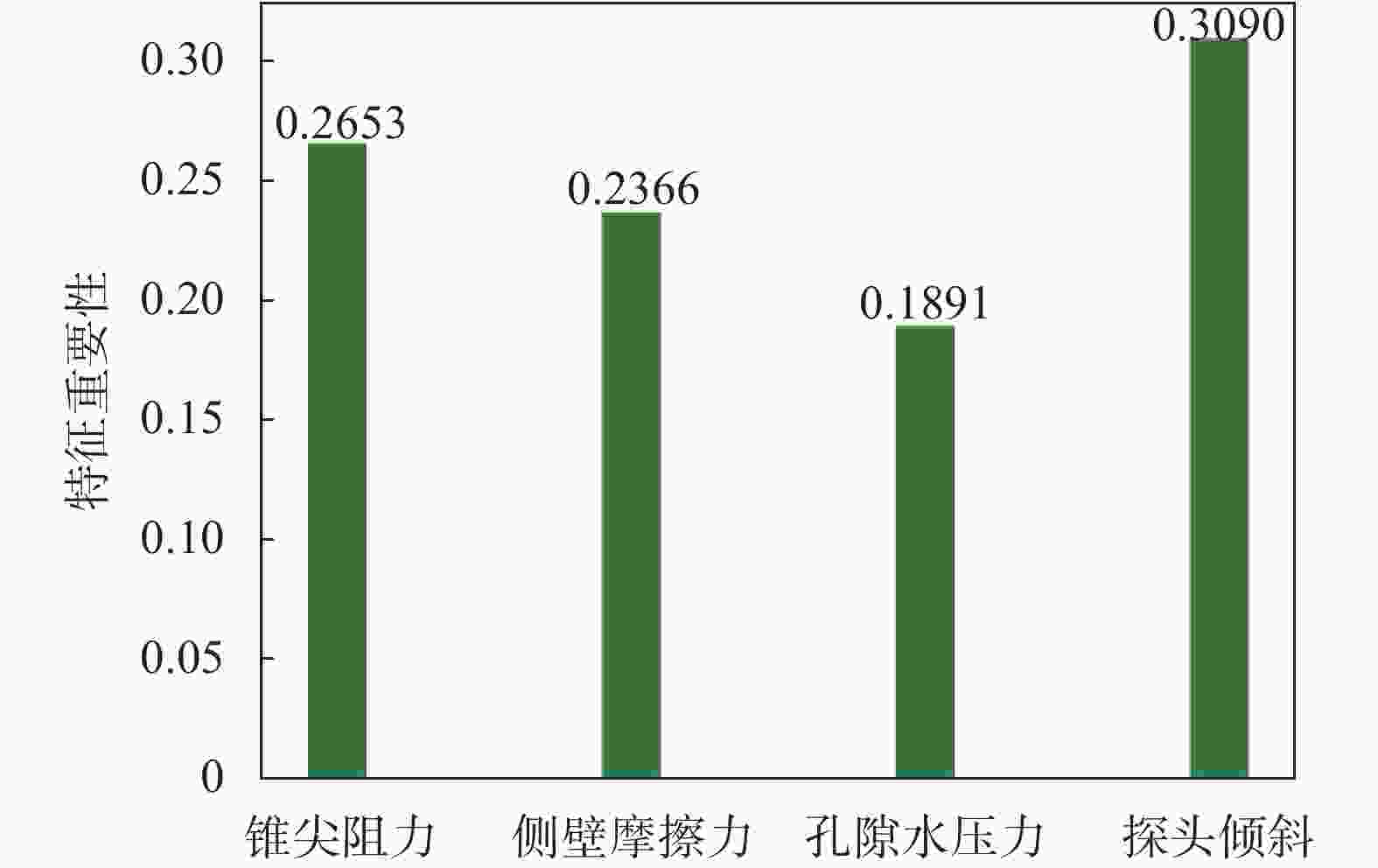
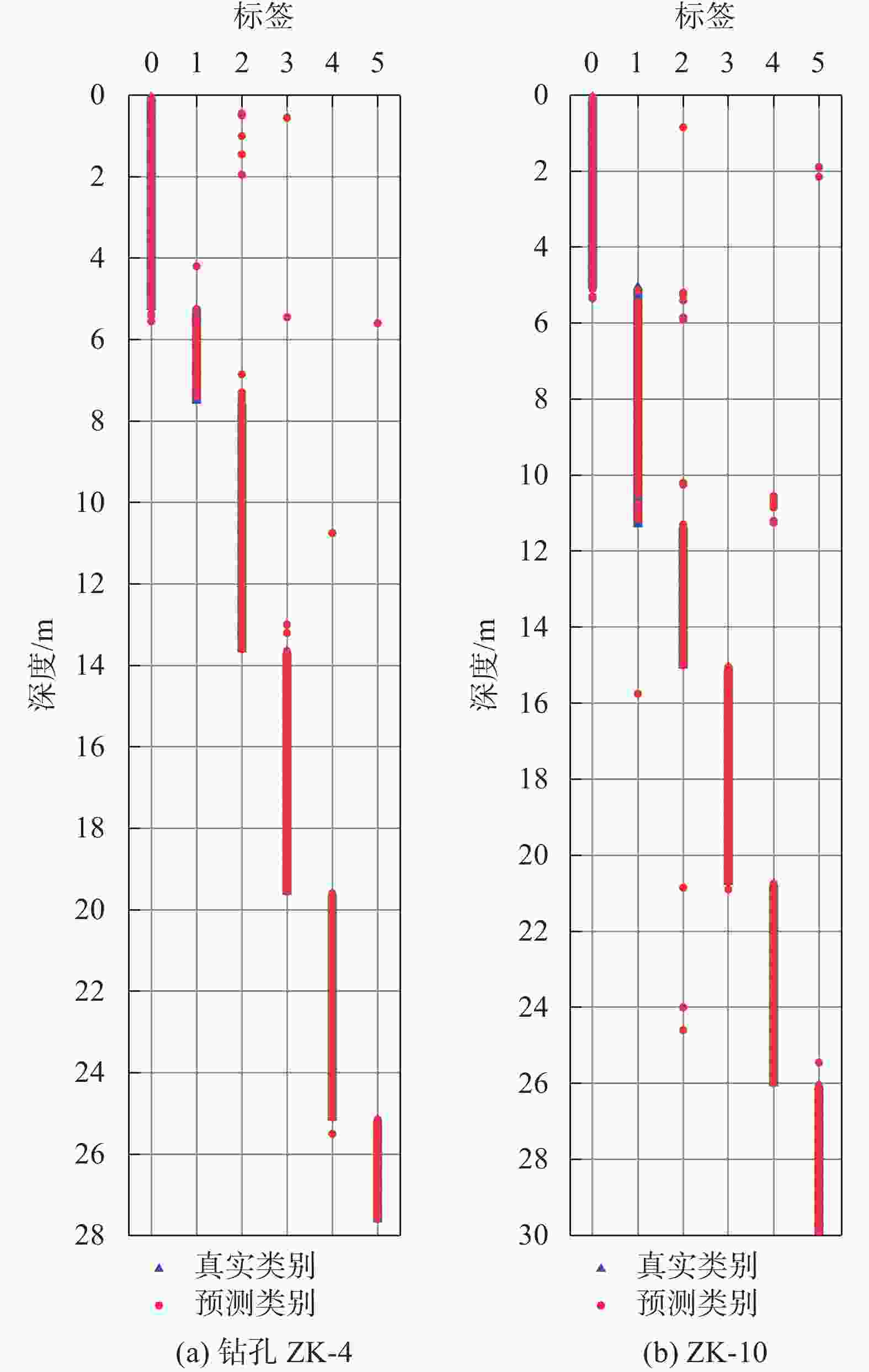
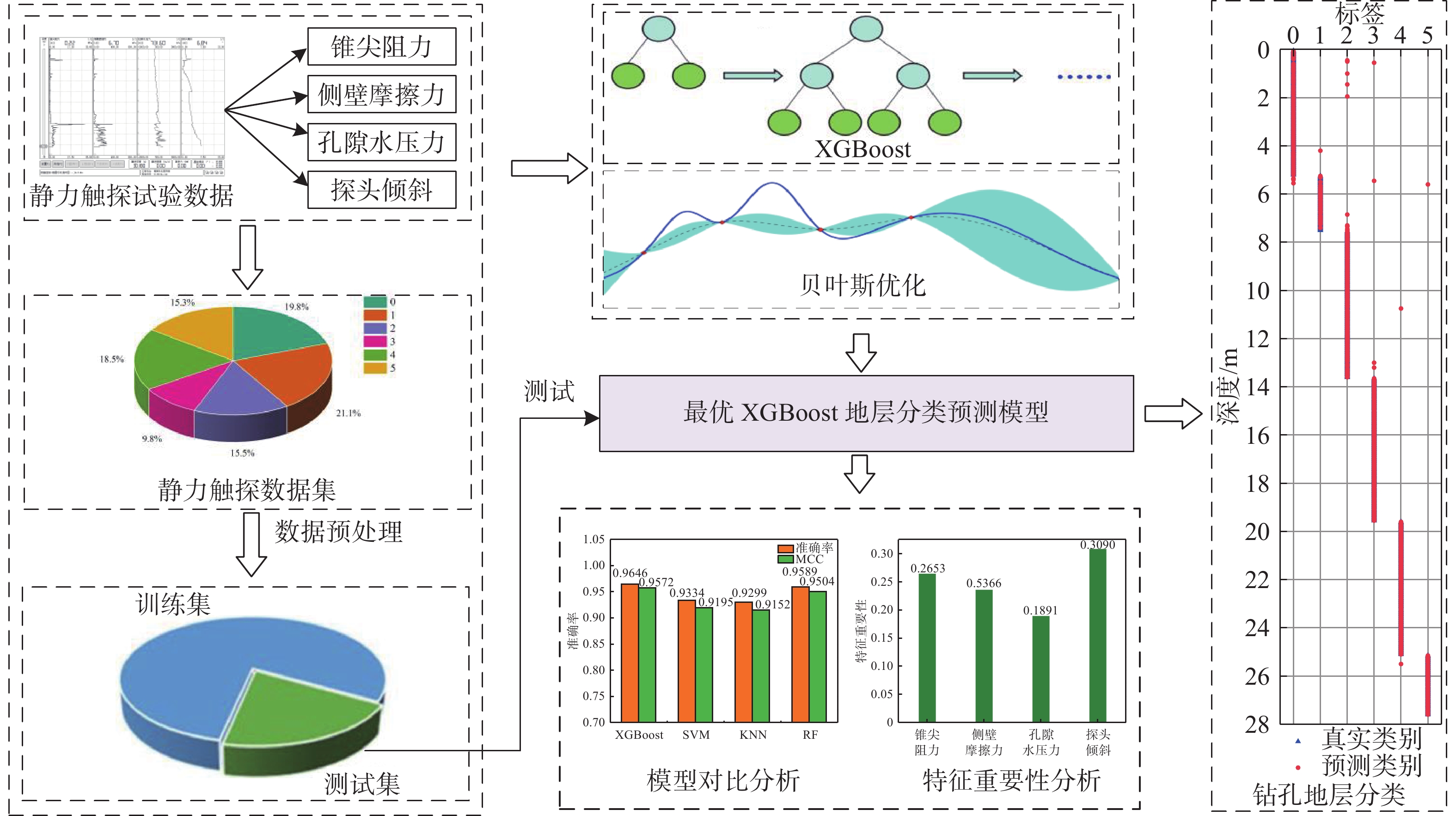
摘要: 地层划分和土类识别是静力触探试验成果应用的基础。为了实现基于静力触探试验数据的地层准确分类,提出了一种基于极限梯度提升(eXtreme Gradient Boosting,XGBoost)和贝叶斯优化(Bayesian Optimization, BO)的静力触探土层分类预测方法。采用XGBoost方法,基于华南地区某岩土工程勘察项目的静力触探试验数据构建数据集,采用贝叶斯优化方法对XGBoost模型超参数进行优化,并构建了最优XGBoost模型对地层类别进行分类预测。所构建的XGBoost模型在训练集和测试集上的分类预测准确率分别为100%和96.46%。经过贝叶斯优化的支持向量机模型、K近邻模型和随机森林模型在测试集上的预测准确率分别为93.34%,92.99%和95.89%,均低于XGBoost模型的准确率,证明了XGBoost模型的地层分类预测性能的优越性。将所构建的XGBoost模型用于华南地区某岩土工程勘察项目的两个钻孔的地层分类预测,预测准确率均达到了95%以上,表明该模型对于实际岩土工程勘察实践中的静力触探地层分类工作具有可靠的应用价值。Abstract: Stratigraphic classification and soil type identification are the basis for the application of static cone penetrate test results. To achieve accurate stratigraphic classification based on static cone penetrate test data, a prediction method based on eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) and Bayesian optimization (BO) was proposed. Using the XGBoost method, a dataset is constructed based on the static cone penetrate test data of a project in South China, the hyperparameters of the XGBoost model were optimised using Bayesian optimisation, and the optimal XGBoost model was constructed to classify and predict the stratigraphic categories. The classification prediction accuracies of the constructed XGBoost model on the training set and the test set are 100% and 96.46%, respectively. The prediction accuracies of the Bayesian-optimised support vector machine (SVM), k-nearest neighbor (KNN) and random forest (RF) models on the test set are 93.34%, 92.99% and 95.89%, respectively, which are lower than those of the XGBoost, proving the superior prediction performances of the XGBoost model. The constructed XGBoost model was used to predict the stratigraphic classification of two boreholes in a geotechnical engineering exploration project in South China, and the prediction accuracy reaches more than 95%, which indicates that the model has a very reliable application value for the stratigraphic classification of static cone penetrate test in the actual geotechnical engineering exploration practice.
-
表 1 岩土层性质
岩土层名称 岩土层特征描述 静力触探数值范围 锥尖阻力/MPa 侧壁摩擦力/kPa 孔隙水压力/kPa 探头倾斜/(°) 1-1杂填土 杂色,松散,稍湿,主要以黏性土为主,
充填砖块、碎石、瓦砾等,工程性质极差[0.0, 10.8] [0.0, 199.0] [−87.0, 253.2] [0.4, 10.9] 2-1淤泥质土 灰黑色,饱和,流塑,主要以粉、黏粒为主,
有腥臭味,韧性差,局部夹少量粉细砂[0.1, 23.2] [0.1, 637.2] [−3.1, 814.5] [1.4, 9.1] 3-1粉质黏土 灰褐色,稍湿,可塑,主要以粉、黏粒为主,
干强度高,刀切面光滑,局部夹少量粉细砂[0.4, 28.5] [0, 459.7] [−67.0, 694.2] [2.2, 7.4] 3-2中砂 灰白色、黄褐色,稍密,饱和,主要为石英颗粒,
分选性好,局部含少量黏性土[0.7, 28.9] [4.5, 429.9] [−71.0, 1039.2] [3.5, 7.5] 4-1砂质黏性土 灰褐色,稍湿,硬塑−坚硬,由花岗岩风化残积而成,
原岩结构全部破坏,遇水易软化崩解[0.0, 19.0] [0.5, 568.1] [−36.3, 923.2] [3.2, 8.6] 5-1全风化花岗岩 红褐色,原岩结构破坏,局部尚可分辨,
岩质软手捏易碎,岩心多呈土柱状[0.2, 13.7] [3.8, 637.4] [−61.7, 1302.1] [4.5, 8.9] 表 2 静力触探数据集统计特征表
锥尖阻
力/MPa侧壁摩
擦力/kPa孔隙水
压力/kPa探头
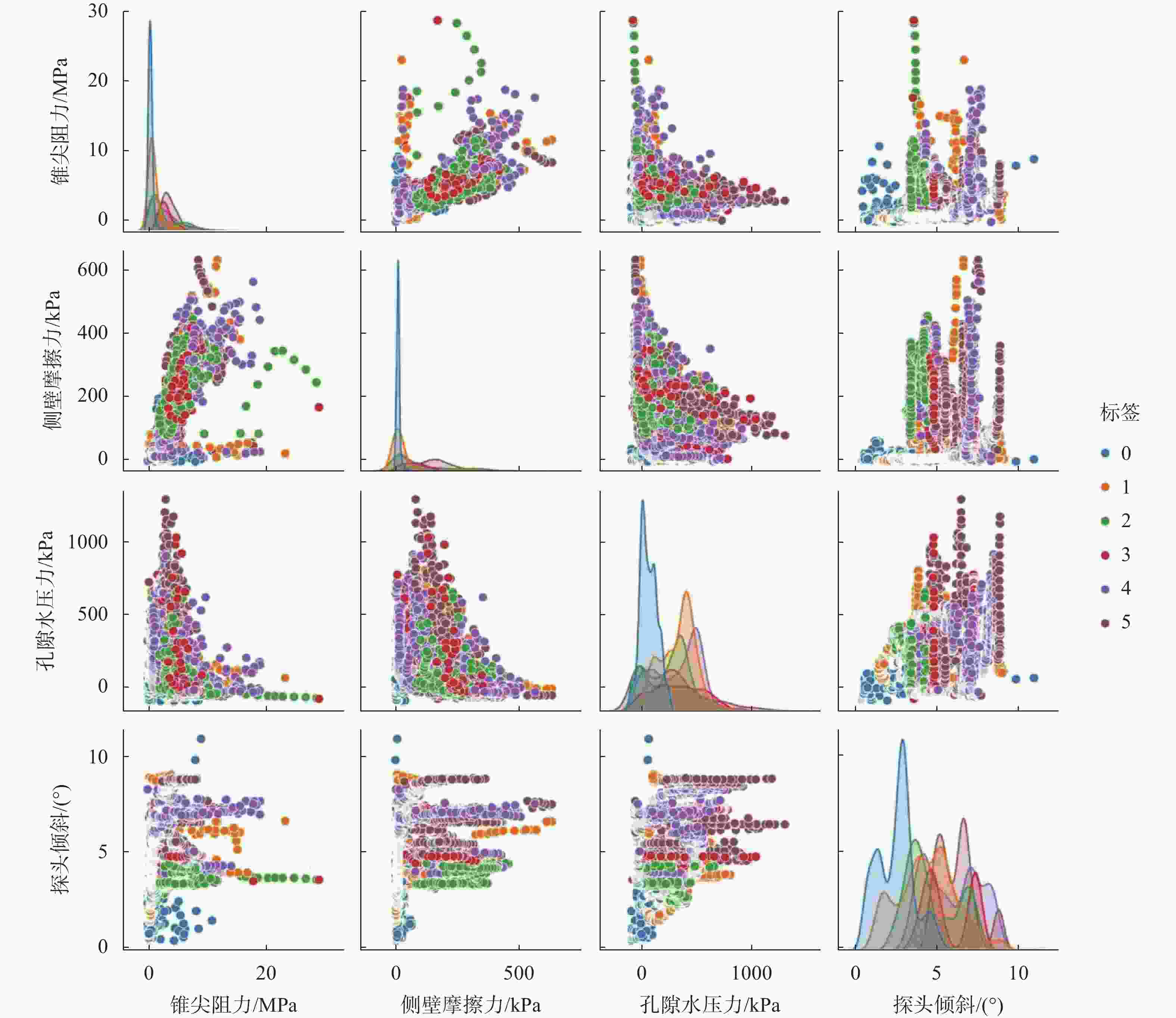
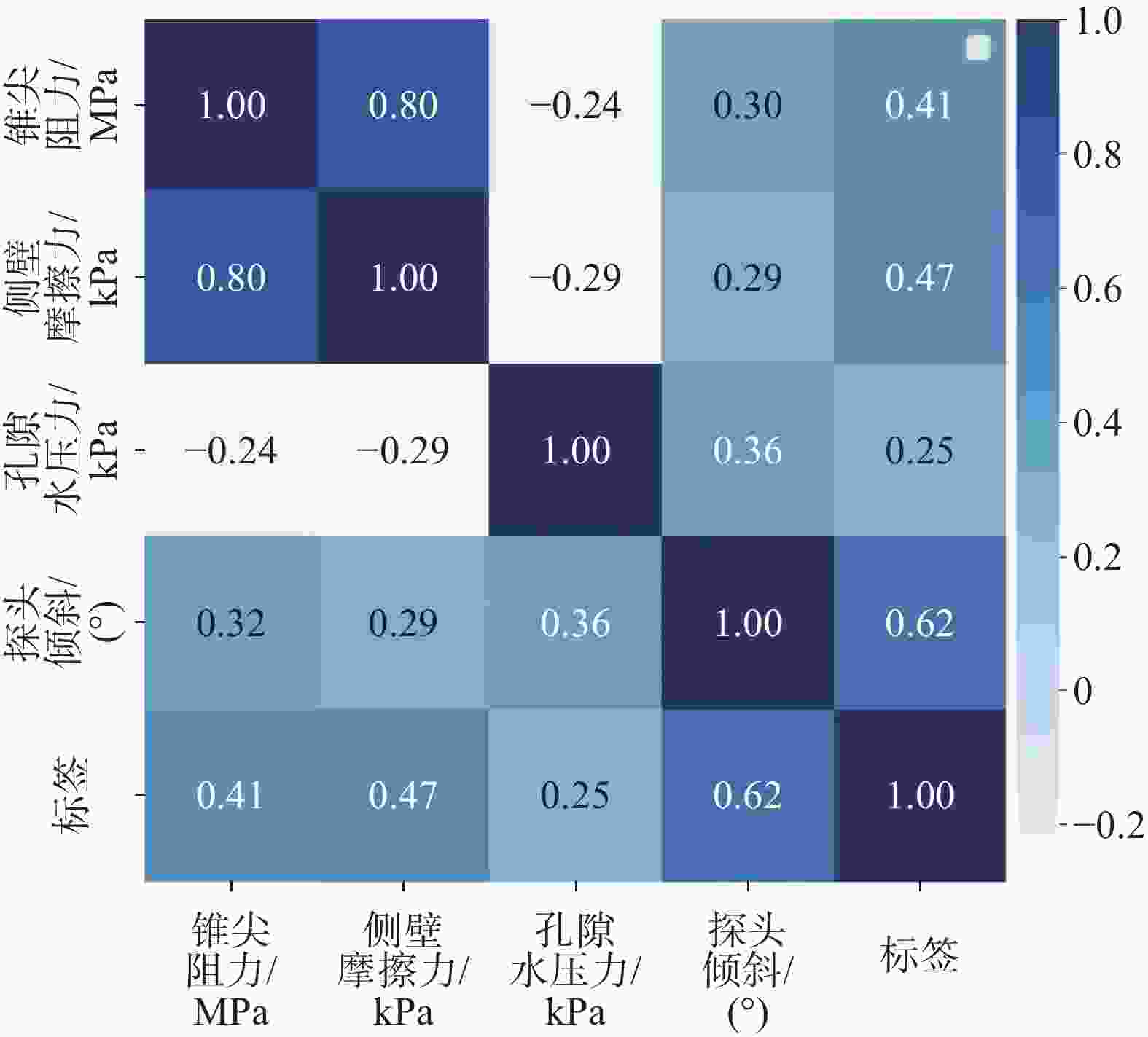
倾斜/(°)总数 4706 4706 4706 4706 平均值 2.54 84.74 261.27 4.79 标准差 2.87 111.56 216.85 1.97 最小值 0 0 −87 0.44 25%分位值 0.63 10 74.60 3.38 中位数 1.33 19.05 247.85 4.69 75%分位值 3.46 136.1 421.37 6.57 最大值 28.92 637.46 1302.1 10.96 表 3 地层标签
地层名称 标签 样本数量 杂填土 0 932 淤泥质土 1 991 粉质黏土 2 731 中砂 3 459 砂质黏性土 4 871 全风化花岗岩 5 722 表 4 XGBoost模型超参数优化结果表
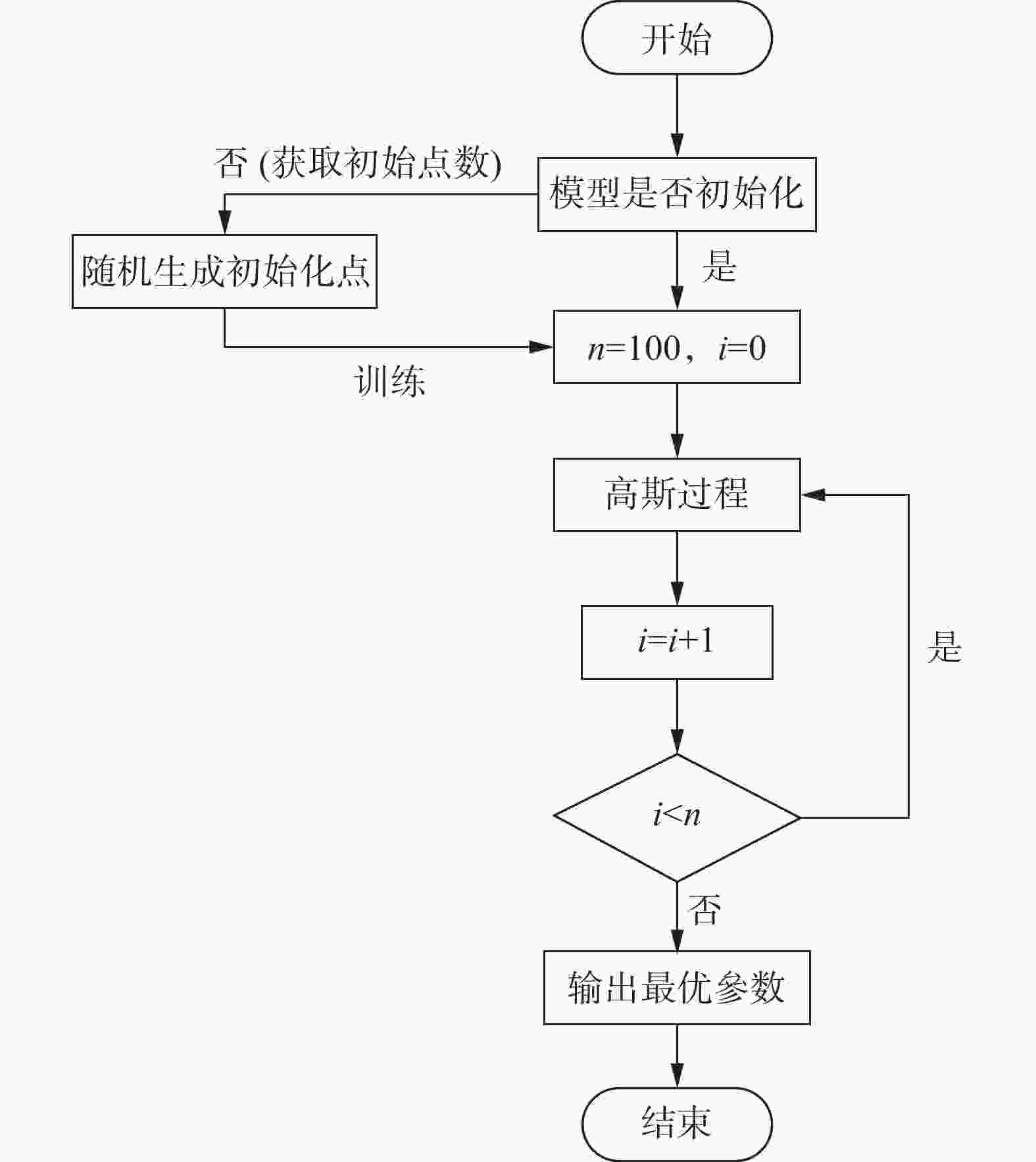
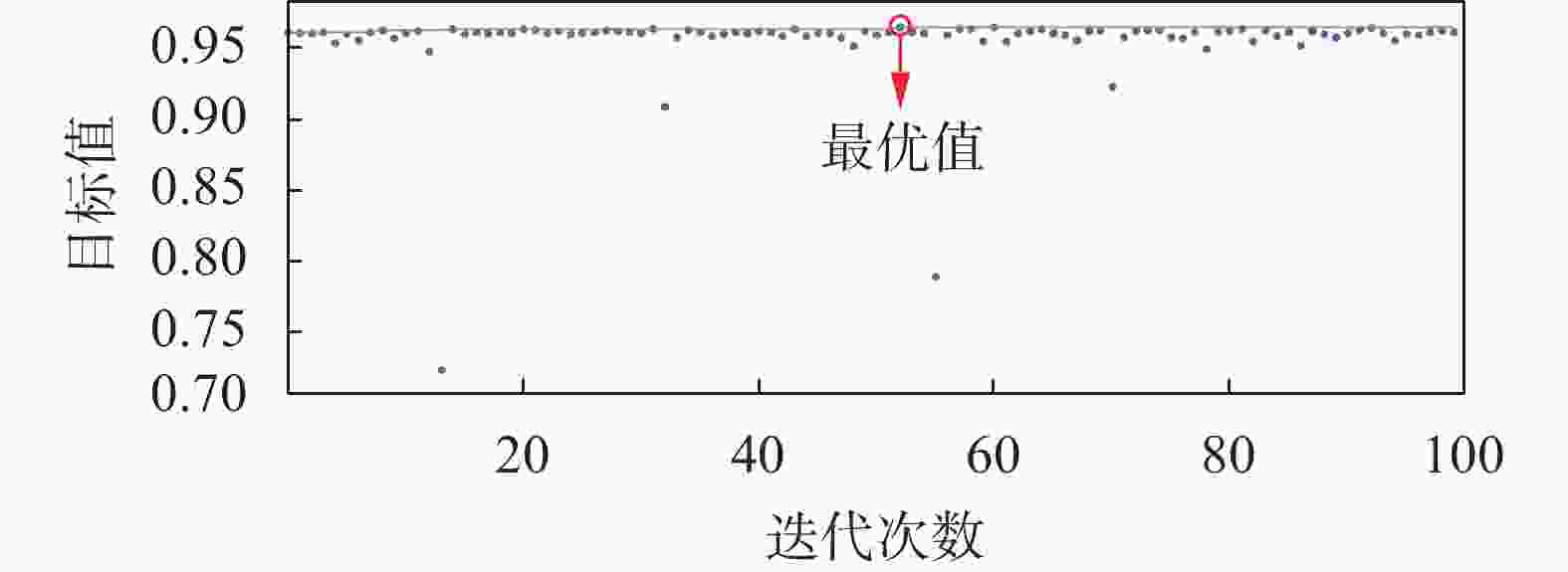
搜索范围 最优参数值 迭代次数 最优值 n_estimators [10, 500] 314 100 0.9646 max_depth [1, 50] 8 learning_rate [0.001, 0.2] 0.1679 subsample [0.6, 0.9] 0.8707 表 5 XGBoost模型预测错误数量统计表
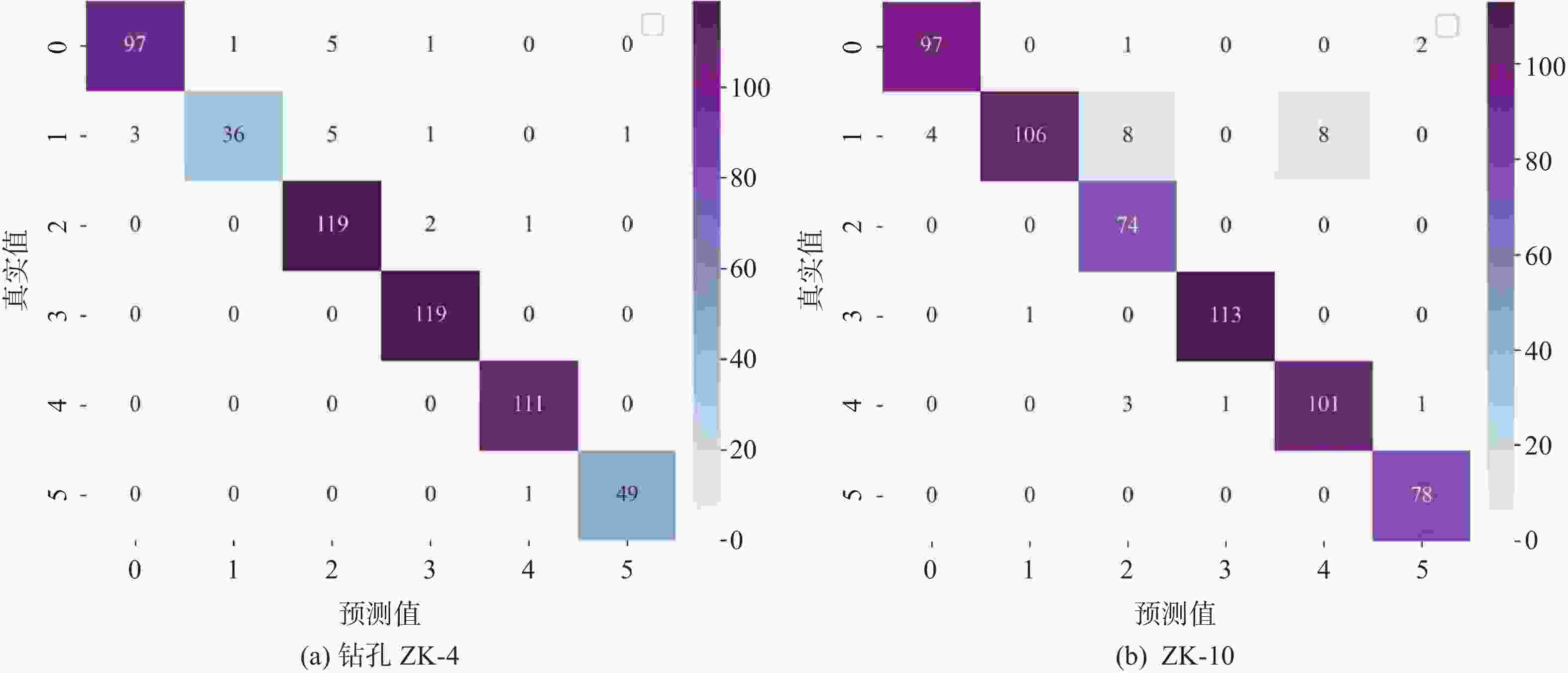
地层名称 ZK-4 ZK-10 杂填土 7 3 淤泥质土 10 20 粉质黏土 3 0 中砂 0 1 砂质黏性土 0 5 全风化花岗岩 1 0 -
[1] 吴波鸿, 王贵和, 刘宝林, 等. 静力触探在海底土层工程性质评价中的应用研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2016, 16(23): 123-128. (WU B H, WANG G H, LIU B L, et al. The application of cone penetration test in subsea soil geotechnical properties evaluation[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2016, 16(23): 123-128. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2016.23.023WU B H, WANG G H, LIU B L, et al. The application of cone penetration test in subsea soil geotechnical properties evaluation[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2016, 16(23): 123-128. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2016.23.023 [2] 王 波, 李建强, 冯 涛, 等. 超深孔压静力触探在工程勘察的应用[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2016, 33(8): 44-49. (WANG B, LI J Q, FENG T, et al. Application of super-deep piezocone penetration tests in engineering investigation[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2016, 33(8): 44-49. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2016.08.010WANG B, LI J Q, FENG T, et al. Application of super-deep piezocone penetration tests in engineering investigation[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2016, 33(8): 44-49. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2016.08.010 [3] 林 军, 蔡国军, 刘松玉, 等. 基于孔压静力触探力学分层的土体边界识别方法研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2017, 38(5): 1413-1423. (LIN J, CAI G J, LIU S Y, et al. Identification of soil layer boundaries using mechanical layered method base on piezocone penetration test data[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(5): 1413-1423. (in Chinese)LIN J, CAI G J, LIU S Y, et al. Identification of soil layer boundaries using mechanical layered method base on piezocone penetration test data[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(5): 1413-1423. (in Chinese) [4] 曹子君, 郑 硕, 李典庆, 等. 基于静力触探的土层自动划分方法与不确定性表征[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2018, 40(2): 336-345. (CAO Z J, ZHENG S, LI D Q, et al. Probabilistic characterization of underground stratigraphy and its uncertainty based on cone penetration test[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 40(2): 336-345. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201802015CAO Z J, ZHENG S, LI D Q, et al. Probabilistic characterization of underground stratigraphy and its uncertainty based on cone penetration test[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 40(2): 336-345. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201802015 [5] 苗永红, 柏国龙. 基于概率神经网络的孔压静力触探的土层界面识别[J]. 济南大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 31(4): 279-284. (MIAO Y H, BAI G L. Soil layer interface identification using piezocone penetration test based on probabilistic neural network[J]. Journal of University of Jinan (Science and Technology), 2017, 31(4): 279-284. (in Chinese)MIAO Y H, BAI G L. Soil layer interface identification using piezocone penetration test based on probabilistic neural network[J]. Journal of University of Jinan (Science and Technology), 2017, 31(4): 279-284. (in Chinese) [6] 吕树胜, 陈培帅, 邱 敏, 等. 基于层次聚类算法的静力触探试验土体分类方法及试验研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(7): 2609-2615. (LÜ S S, CHEN P S, QIU M, et al. Soil classification method and experimental research from CPT based on hierarchical clustering algorithm[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(7): 2609-2615. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.07.007LÜ S S, CHEN P S, QIU M, et al. Soil classification method and experimental research from CPT based on hierarchical clustering algorithm[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(7): 2609-2615. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.07.007 [7] 刘松玉, 蔡国军, 邹海峰. 基于CPTU的中国实用土分类方法研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2013, 35(10): 1765-1776. (LIU S Y, CAI G J, ZOU H F. Practical soil classification methods in China based on piezocone penetration tests[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(10): 1765-1776. (in Chinese)LIU S Y, CAI G J, ZOU H F. Practical soil classification methods in China based on piezocone penetration tests[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(10): 1765-1776. (in Chinese) [8] 蔡国军, 刘松玉, 童立元, 等. 基于聚类分析理论的CPTU土分类方法研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2009, 31(3): 416-424. (CAI G J, LIU S Y, TONG L Y, et al. Soil classification using CPTU data based upon cluster analysis theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2009, 31(3): 416-424. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2009.03.018CAI G J, LIU S Y, TONG L Y, et al. Soil classification using CPTU data based upon cluster analysis theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2009, 31(3): 416-424. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2009.03.018 [9] ZHU W Y, SONG T R, WANG M C, et al. Stratigraphic subdivision-based logging curves generation using neural random forests[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 219: 111086. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2022.111086 [10] ZHANG W G, PHOON K K. Editorial for advances and applications of deep learning and soft computing in geotechnical underground engineering[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 14(3): 671-673. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.01.001 [11] 邱 敏, 宋友建, 丛 璐, 等. 基于层次聚类算法的孔压静力触探土体分类方法及试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2019, 46(3): 117-123. (QIU M, SONG Y J, CONG L, et al. Soil classification method and experimental research on CPTU based on the hierarchical clustering algorithm[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(3): 117-123. (in Chinese)QIU M, SONG Y J, CONG L, et al. Soil classification method and experimental research on CPTU based on the hierarchical clustering algorithm[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(3): 117-123. (in Chinese) [12] 徐黎明. 基于支持向量机的双桥静力触探地层自动划分方法[J]. 铁道勘察, 2023, 49(4): 90-95. (XU L M. Automatic method of soil layers division using double bridge static cone penetration test data based on support vector machine[J]. Railway Investigation and Surveying, 2023, 49(4): 90-95. (in Chinese)XU L M. Automatic method of soil layers division using double bridge static cone penetration test data based on support vector machine[J]. Railway Investigation and Surveying, 2023, 49(4): 90-95. (in Chinese) [13] 陈振新, 何旭涛, 袁舟龙, 等. 基于自编码神经网络的孔压静力触探海底土层划分方法改进[J]. 工程勘察, 2019, 47(6): 23-28. (CHEN Z X, HE X T, YUAN Z L, et al. Improvement of division method for seabed strata base on piezocone penetration test data with autoencoders[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2019, 47(6): 23-28. (in Chinese)CHEN Z X, HE X T, YUAN Z L, et al. Improvement of division method for seabed strata base on piezocone penetration test data with autoencoders[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2019, 47(6): 23-28. (in Chinese) [14] WOOD D A. Predicting porosity, permeability and water saturation applying an optimized nearest-neighbour, machine-learning and data-mining network of well-log data[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 184: 106587. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106587 [15] LI S L, ZHANG X J. Research on orthopedic auxiliary classification and prediction model based on XGBoost algorithm[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2020, 32(7): 1971-1979. doi: 10.1007/s00521-019-04378-4 [16] CHEN T Q, GUESTRIN C. XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. San Francisco: Association for Computing Machinery, 2016: 785-794. [17] WANG T T, BIAN Y J, ZHANG Y X, et al. Classification of earthquakes, explosions and mining-induced earthquakes based on XGBoost algorithm[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2023, 170: 105242. [18] GENG X J, WU S C, ZHANG Y J, et al. Developing hybrid XGBoost model integrated with entropy weight and Bayesian optimization for predicting tunnel squeezing intensity[J]. Natural Hazards, 2023, 119(1): 751-771. doi: 10.1007/s11069-023-06137-0 [19] ZHANG W G, WU C Z, ZHONG H Y, et al. Prediction of undrained shear strength using extreme gradient boosting and random forest based on Bayesian optimization[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2021, 12(1): 469-477. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2020.03.007 [20] PANTELEEV A V, LOBANOV A V. Mini-batch adaptive random search method for the parametric identification of dynamic systems[J]. Automation and Remote Control, 2020, 81(11): 2026-2045. doi: 10.1134/S0005117920110065 [21] BHAT P C, PROSPER H B, SEKMEN S, et al. Optimizing event selection with the random grid search[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2018, 228: 245-257. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2018.02.018 [22] GHAHRAMANI Z. Probabilistic machine learning and artificial intelligence[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 452-459. doi: 10.1038/nature14541 [23] XIA Y F, LIU C Z, LI Y Y, et al. A boosted decision tree approach using Bayesian hyper-parameter optimization for credit scoring[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2017, 78: 225-241. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2017.02.017 [24] QIU Y G, ZHOU J, KHANDELWAL M, et al. Performance evaluation of hybrid WOA-XGBoost, GWO-XGBoost and BO-XGBoost models to predict blast-induced ground vibration[J]. Engineering with Computers, 2022, 38(S5): 4145-4162. doi: 10.1007/s00366-021-01393-9 -





 下载:
下载: