Calculation methods of water-soil pressure for silty clay in Tianjin area
-
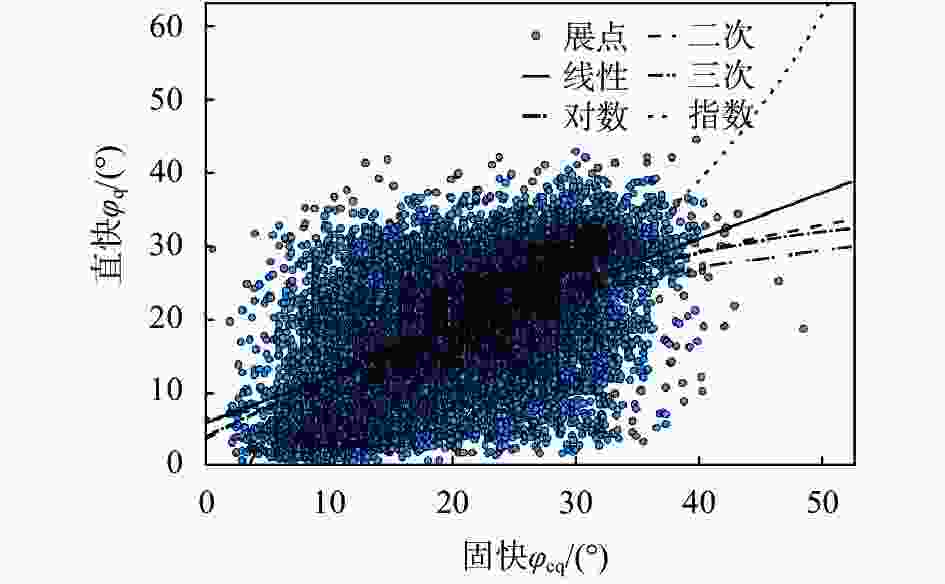
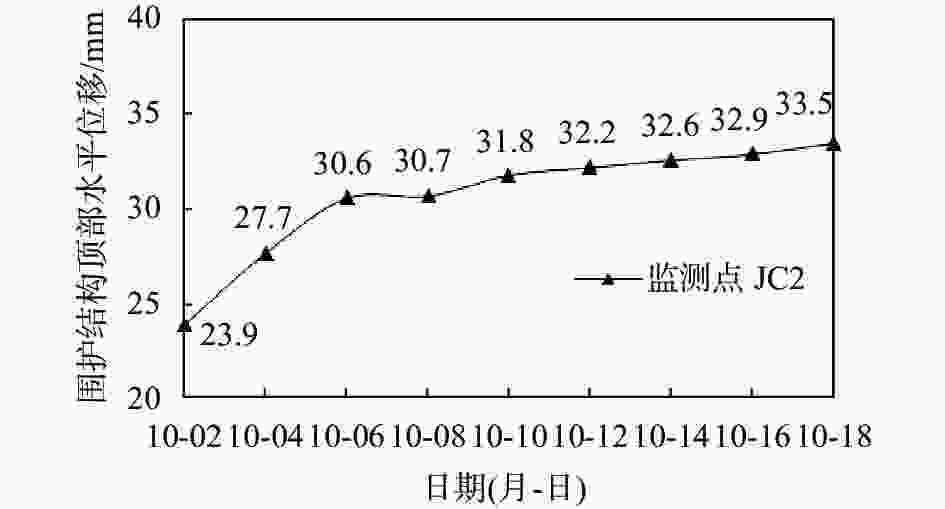
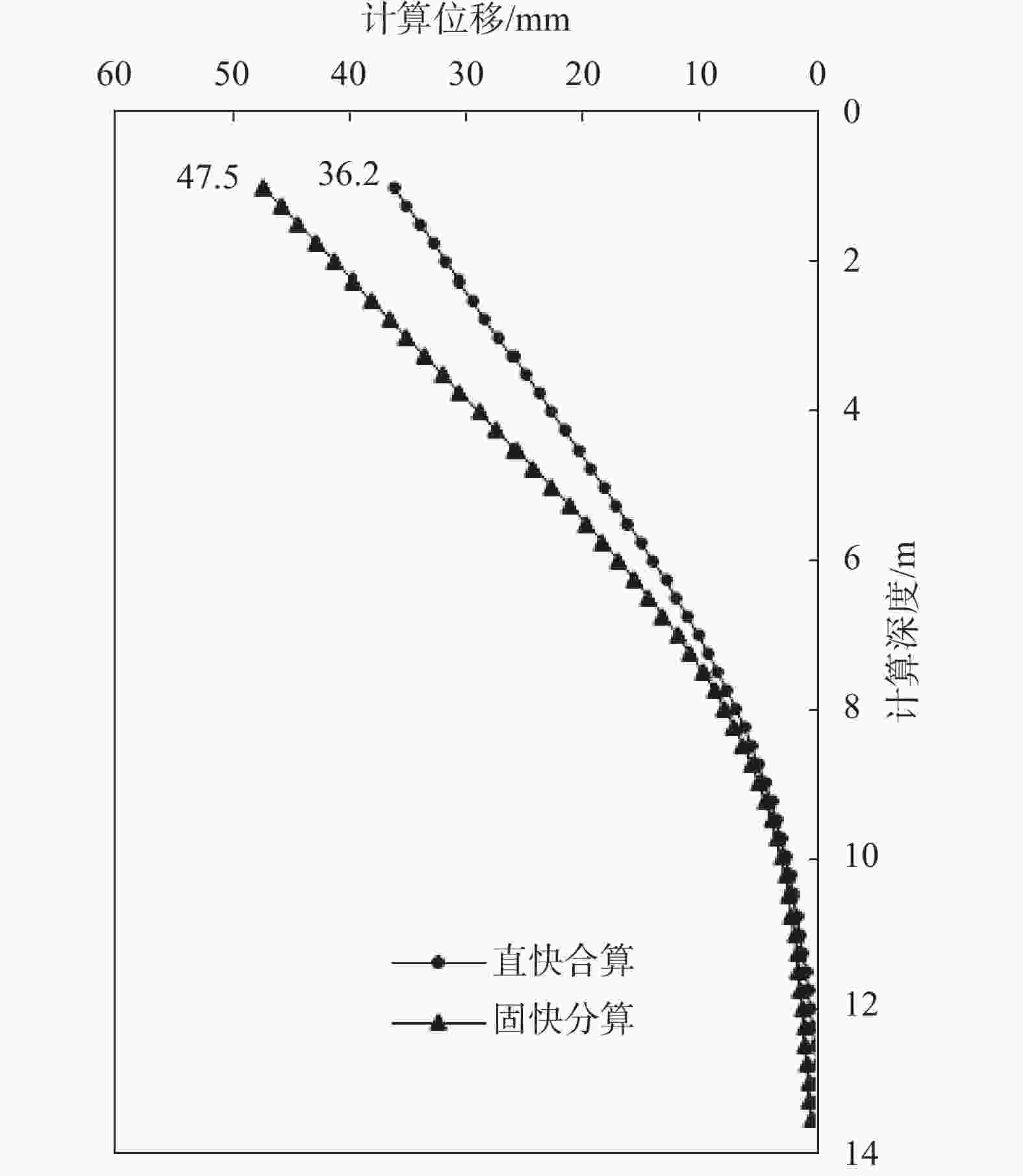
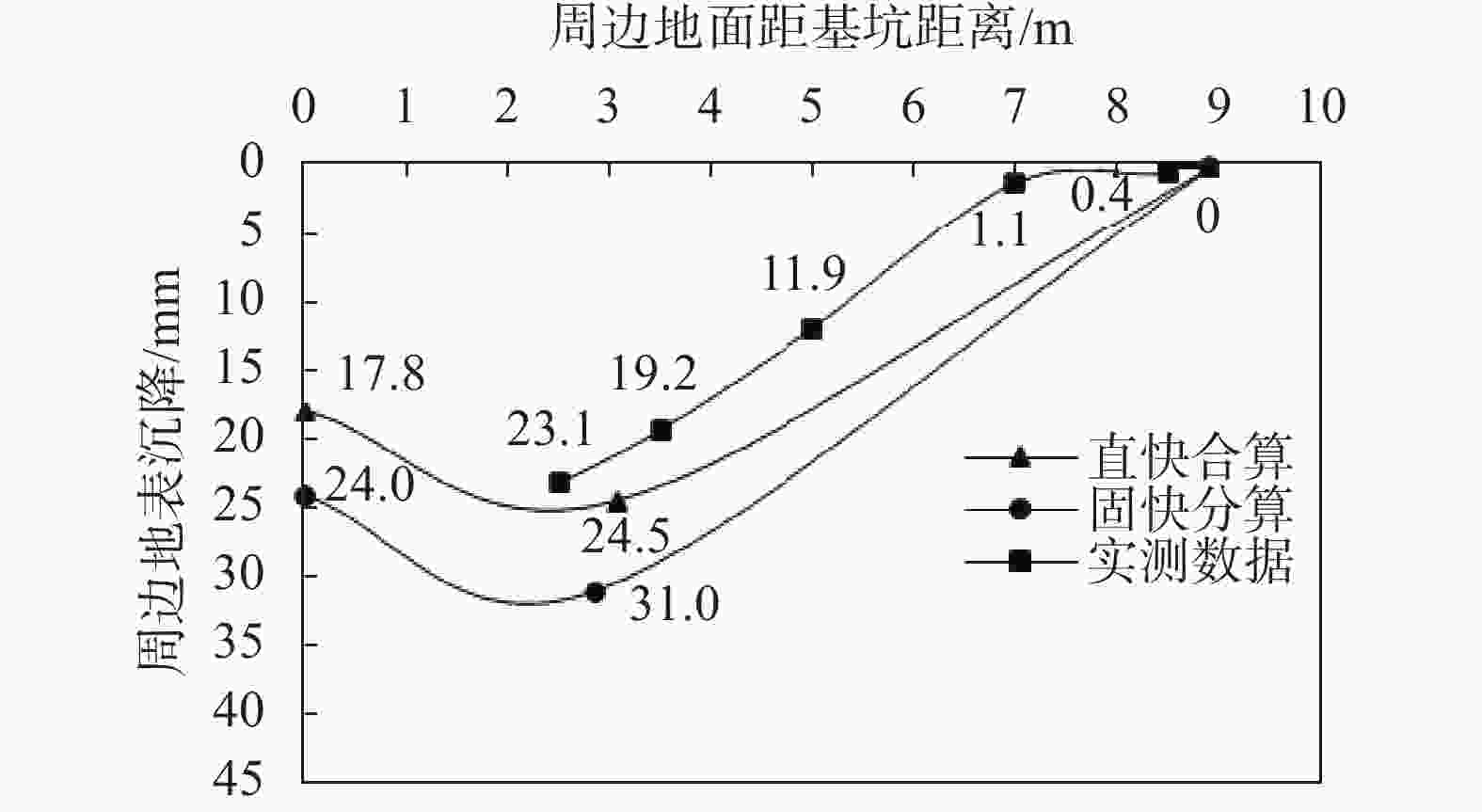
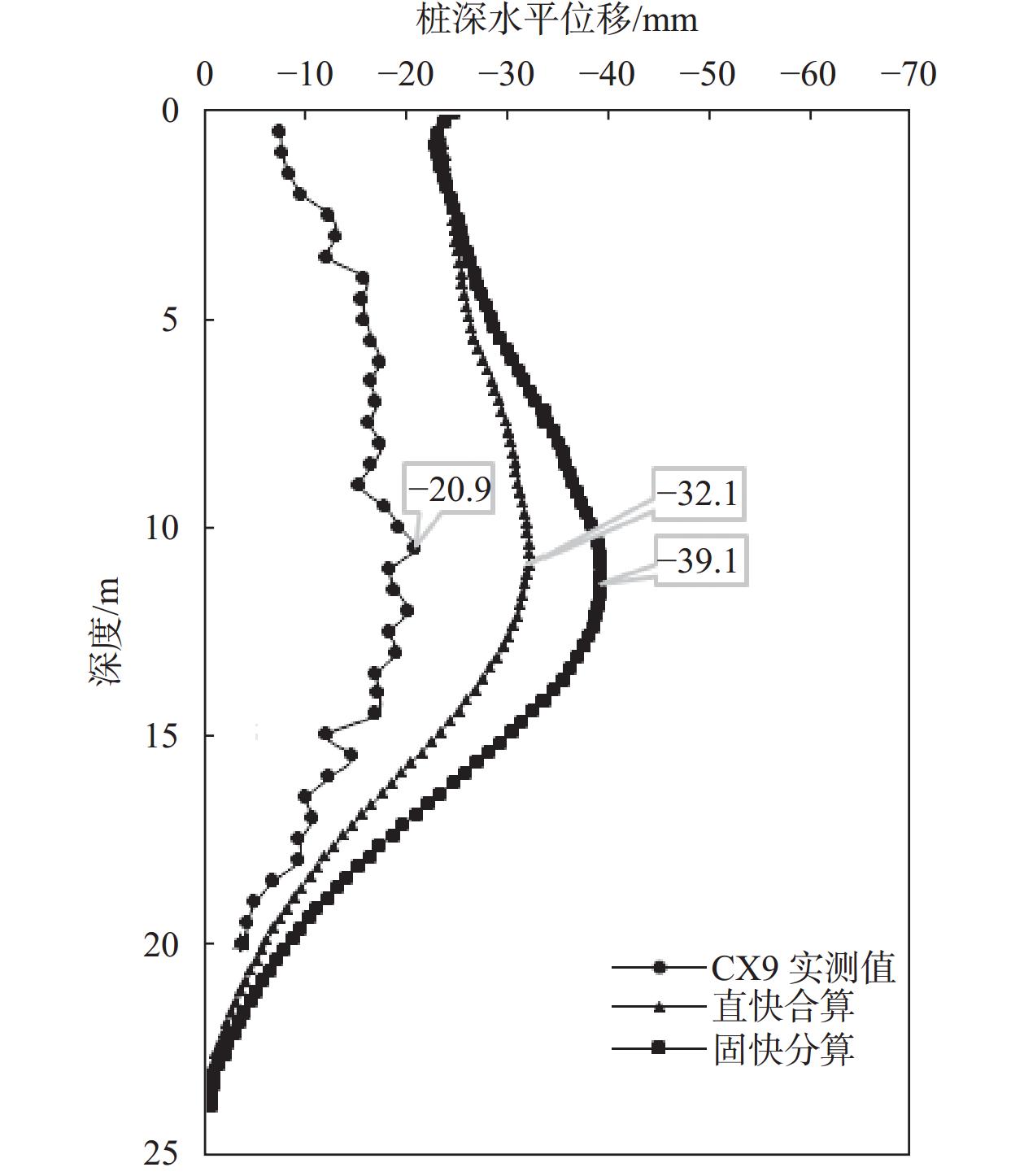
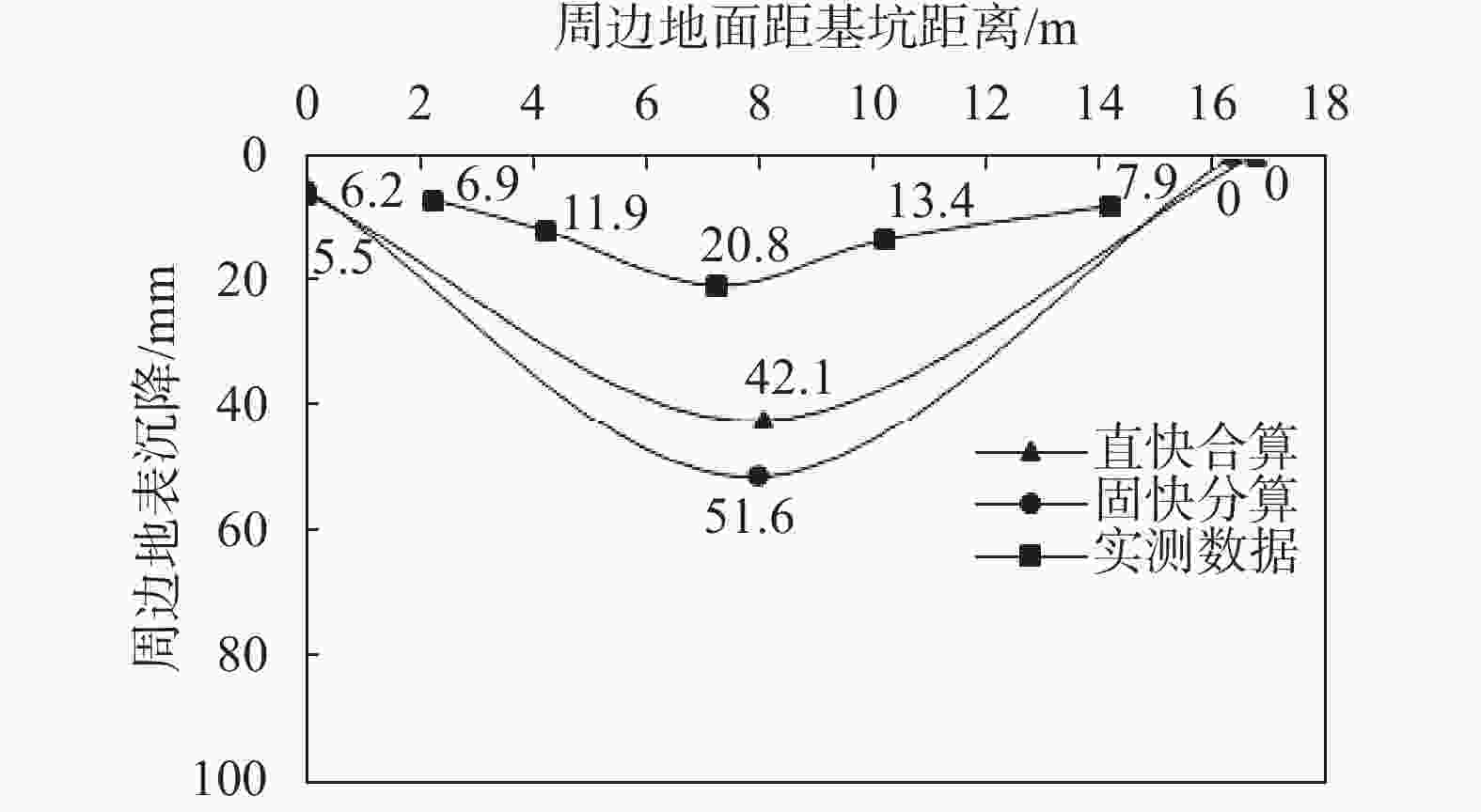
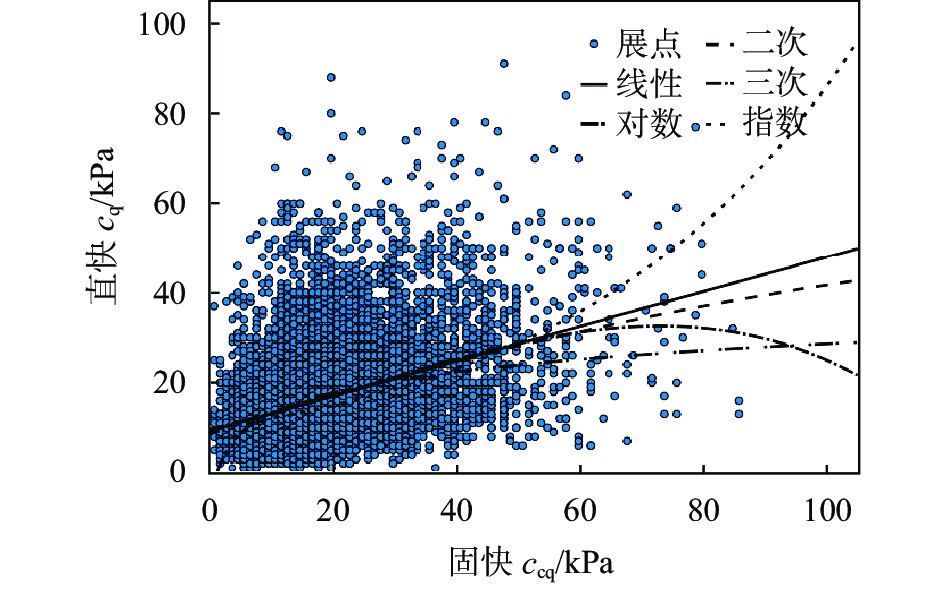
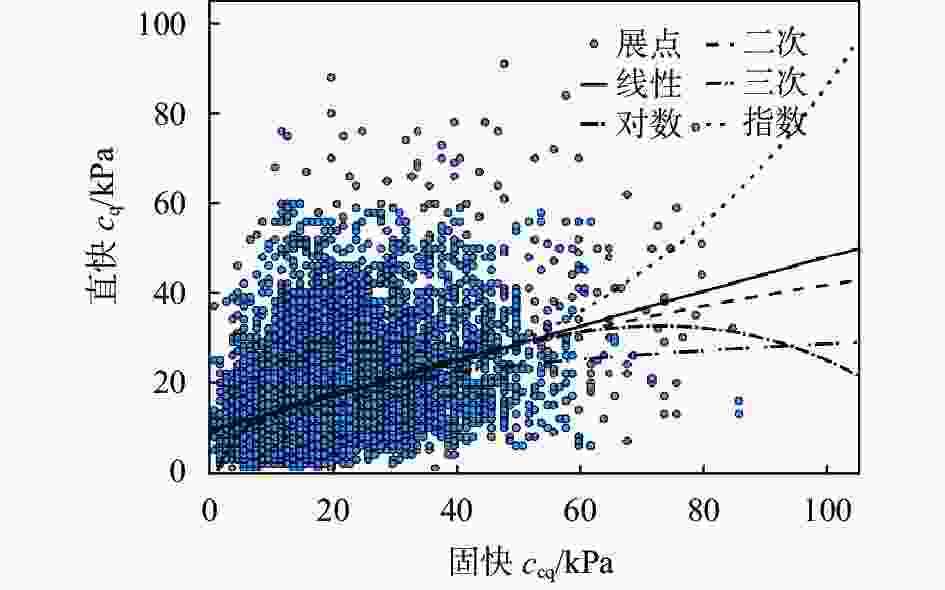
摘要: 对天津地区粉质黏土发育分布特征及其工程特性进行了详细介绍,针对天津地区基坑工程影响范围内的5个主要粉质黏土层的剪切指标相关关系开展研究,给出了各粉质黏土标准层的抗剪强度一元线性回归方程公式及剪切指标统计结果;结合天津地区多个典型工程案例,分析粉质黏土水土分算、水土合算的安全性、经济性,并通过基坑实测变形对比分析,探讨了天津地区粉质黏土直快水土合算、固快水土分算的适用性。研究结果表明:(1)天津地区粉质黏土层剪切指标cq与ccq、φq与φcq的关系曲线特征不具典型性,拟合优度检验统计量R2为0.2~0.3;(2)相比于粉质黏土直快水土合算,天津地区粉质黏土固快水土分算安全性较差;(3)无论是悬臂结构还是带支撑的围护结构,整体上粉质黏土直快水土合算计算的围护结构弯矩及剪力结果较水土分算小,经济性好;(4)实测变形分析表明,相比于粉质黏土固快水土分算,各项目围护结构计算的深层水平位移及周边地表沉降现场实测值与采用直快合算计算的结果更为接近。Abstract: This research takes the Tianjin area as an example to analyze the development, distribution, and engineering characteristics of silty clay in the region. A correlation study of the shear indices within the five silty clay layers affected by the foundation pit was conducted. The univariate linear regression equations and statistical results of shear indices for each standard layer of silty clay were provided. In conjunction with multiple typical engineering cases in the Tianjin area, the safety and economic analyses of silty clay water-soil separate accounting and combined accounting methods were carried out. Additionally, through comparative analysis of measured deformations of foundation pits, the applicability of direct quick water-soil combined accounting and fixed quick water-soil separate accounting methods for silty clay in the Tianjin area was discussed. The research findings are as follows: (1) In the Tianjin area, the relationships between the shear indices cq and ccq, as well as φq and φcq of the silty clay layer are not significant, with the coefficient of determination R2 ranging between 0.2 and 0.3. (2) Compared to the direct quick water-soil combined accounting method, the safety of the fixed quick water-soil separate accounting method for silty clay in the Tianjin area is relatively poor. (3) Regardless of whether it is a cantilever structure or a supported retaining structure, the calculated bending moments and shear forces of the retaining structures using the direct quick water-soil combined accounting method are generally smaller than those using the water-soil separate accounting method, resulting in better economic efficiency. (4) Analysis of measured deformations indicates that the on-site measured values of deep horizontal displacement and surrounding surface settlement of the retaining structures for various projects are more closely aligned with the results calculated using the direct quick combined accounting method than with the fixed quick water-soil separate accounting method.
-
Key words:
- silty clay /
- shear strength /
- water-soil pressure /
- foundation pit support
-
表 1 直快与固快指标拟合优度检验R2统计结果
序号 方程 φq,φcq拟合R2 cq,ccq拟合R2 1 线性 0.27 0.30 2 对数 0.24 0.29 3 二次 0.16 0.26 4 三次 0.20 0.24 5 指数 0.25 0.25 表 2 直快指标与固快指标拟合结果
序号 地层 线性回归公式 R2 1 4-1 φcq = 0.37·φq+13.43 0.41 ccq = 0.23·cq+15.88 0.23 2 6-1 φcq = 0.35·φq+15.15 0.42 ccq = 0.13·cq+14.23 0.21 3 6-4 φcq = 0.35·φq+14.68 0.41 ccq = 0.22·cq+14.10 0.29 4 7-1 φcq = 0.21·φq+17.32 0.24 ccq = 0.15·cq+16.18 0.34 5 8-1 φcq = 0.25·φq+17.21 0.26 ccq = 0.25·cq+15.38 0.23 表 3 天津地区粉质黏土层剪切指标统计结果
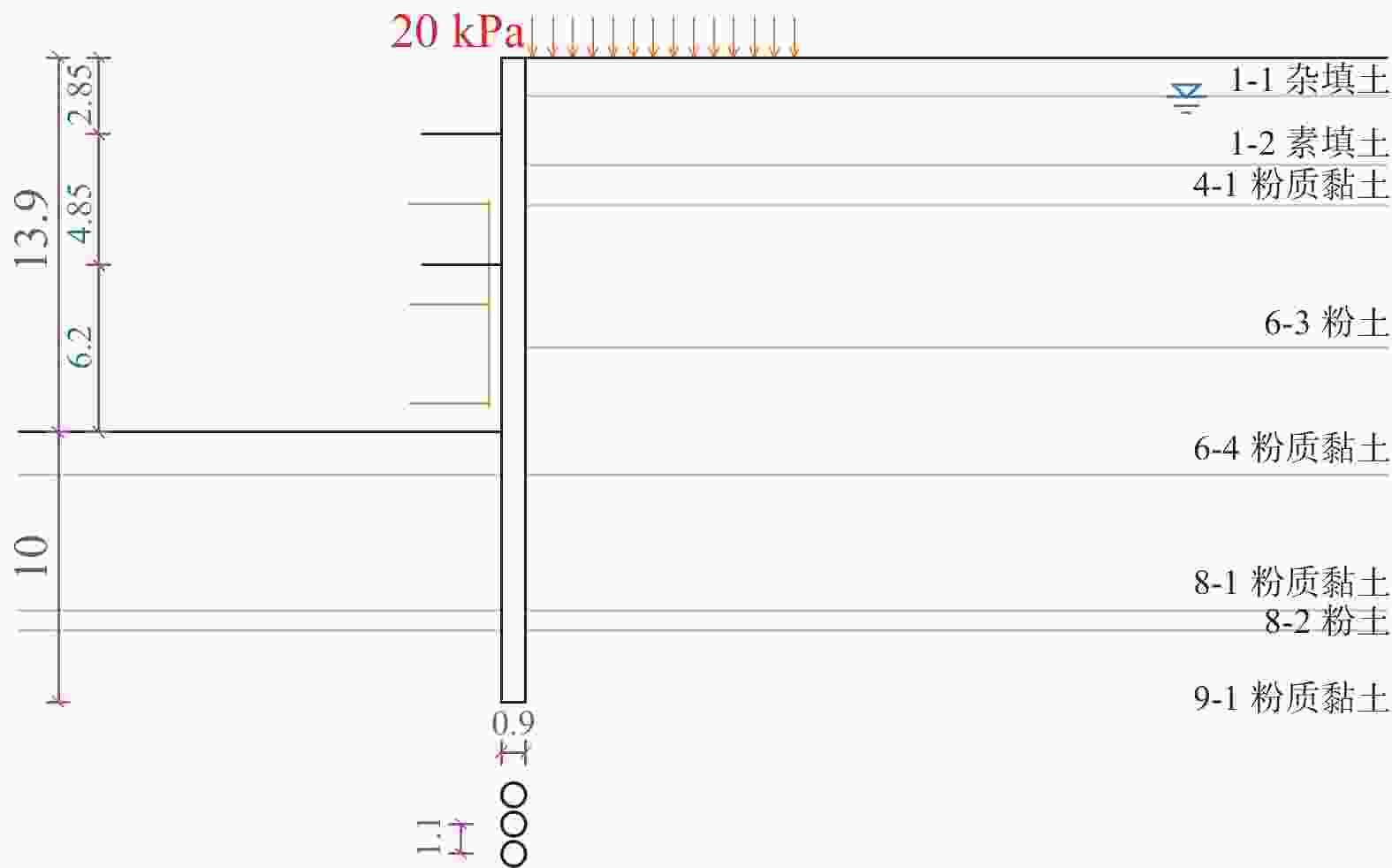
层号 统计项目 cq/kPa φq/(°) ccq/kPa φcq/(°) 4-1 最小值 8.00 10.30 9.00 11.80 最大值 20 22 22 24 标准值 13.69 15.81 15.04 18.08 变异系数 0.224 0.179 0.234 0.174 子样数 2875 2875 3966 3966 6-1 最小值 8 12 9 15.1 最大值 17 26.4 20.5 28.5 标准值 12.54 19.36 13.82 22.08 变异系数 0.204 0.195 0.209 0.159 子样数 2770 2770 3837 3837 6-4 最小值 6 12.5 9 13 最大值 22 25 24 27 标准值 12.91 19.48 14.65 20.99 变异系数 0.281 0.161 0.244 0.153 子样数 2515 2515 3447 3447 7-1 最小值 6 11.6 9 14.0 最大值 21 26.1 24 28.0 标准值 14.17 15.92 15.23 21.16 变异系数 0.266 0.183 0.249 0.169 子样数 948 948 1575 1575 8-1 最小值 8 12.60 10 14.5 最大值 22 24.70 26 28.0 标准值 14.04 17.69 15.56 20.85 变异系数 0.233 0.192 0.244 0.177 子样数 2625 2625 5521 5521 表 4 典型工程案例粉质黏土水土分算、水土合算计算结果
序号 计算指标 南开区某工程
(悬臂)北辰区某工程
(悬臂)河北区某工程
(一道撑)和平区某工程
(一道撑)河东区某工程
(一道撑)红桥区某工程
(二道撑)固快
分算直快
合算固快
分算直快
合算固快
分算直快
合算固快
分算直快
合算固快
分算直快
合算固快
分算直快
合算1 Ea/kN 612.8 597.8 1476.6 1137.4 1892.7 1676.1 1962.3 1869.5 1867.7 1855.9 2808.0 2336.6 2 Ep/kN 1527.3 1878.5 2353.6 1961.6 1320.7 1634.1 1842.7 1818.5 1732.4 1894.7 1780.5 2319.0 3 K整稳 3.2 2.8 3.0 2.3 1.6 1.5 2.3 2.1 2.2 1.8 1.7 1.5 4 F抗倾覆 2.1 2.6 1.2 1.6 1.0 1.5 1.3 1.3 1.2 1.3 0.9 1.4 表 5 典型工程案例计算弯矩、剪力统计
序号 计算值 南开区某工程
(悬臂)北辰区某工程
(悬臂)河北区某工程
(一道撑)和平区某工程
(一道撑)河东区某工程
(一道撑)红桥区某工程
(二道撑)固快
分算直快
合算固快
分算直快
合算固快
分算直快
合算固快
分算直快
合算固快
分算直快
合算固快
分算直快
合算1 最大弯矩
/(kN·m)−215.3 −145.3 −594.7 −585.6 959.1 938.8 1084.5 832.4 953.8 889.7 1323.4 986.1 2 最大剪力
/kN73.6 54.6 152.3 153.2 −365.6 −335.7 −354.4 −299.6 280.7 262.7 −576.4 −463.3 -
[1] 顾宝和. 基坑工程的土水压力计算[J]. 岩土工程技术, 1997, 11(4): 4-10. (GU B H. Calculation of soil and water pressure in foundation pit engineering[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique, 1997, 11(4): 4-10. (in Chinese)GU B H. Calculation of soil and water pressure in foundation pit engineering[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique, 1997, 11(4): 4-10. (in Chinese) [2] 李广信. 基坑支护结构上水土压力的分算与合算[J]. 岩土工程学报,2000,22(3):348-352. (LI G X. Estimating the water and earth pressures on the supporting structure around a foundation pit separately and together[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2000,22(3):348-352. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2000.03.018LI G X. Estimating the water and earth pressures on the supporting structure around a foundation pit separately and together[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2000, 22(3): 348-352. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2000.03.018 [3] 李广信, 吕 禾. 土强度试验的排水条件与强度指标的应用[J]. 工程勘察,2006(3):11-14,49. (LI G X, LYU H. Drainage conditions for tests of soil strength and the application of strength indices[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2006(3):11-14,49. (in Chinese)LI G X, LYU H. Drainage conditions for tests of soil strength and the application of strength indices[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2006(3): 11-14,49. (in Chinese) [4] 魏汝龙. 再论总应力法及水和土压力——与陈愈炯教授商榷[J]. 岩土工程学报,1999,21(4):509-510. (WEI R L. Discussion on total stress method and earth and water pressure(No. 1)[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1999,21(4):509-510. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1999.04.025WEI R L. Discussion on total stress method and earth and water pressure(No. 1)[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1999, 21(4): 509-510. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1999.04.025 [5] 沈珠江. 关于固结理论和有效应力的讨论[J]. 岩土工程学报, 1995, 17(6): 118-119. (SHEN Z J. Discussion on consolidation theory and effective stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1995, 17(6): 118-119. (in Chinese)SHEN Z J. Discussion on consolidation theory and effective stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1995, 17(6): 118-119. (in Chinese) [6] 陈愈炯, 温彦锋. 对“基坑支护结构上的水和土压力”讨论的答复[J]. 岩土工程学报, 1999, 21(4): 512-513. (CHEN Y J, WEN Y F. Reply to the discussion on "water and earth pressures on foundation pit support structures"[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1999, 21(4): 512-513. (in Chinese)CHEN Y J, WEN Y F. Reply to the discussion on "water and earth pressures on foundation pit support structures"[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1999, 21(4): 512-513. (in Chinese) [7] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑基坑支护技术规程: JGJ 120–2012[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2012. (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Technical specification for retaining and protection of building foundation excavations: JGJ 120–2012[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2012. (in Chinese)Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Technical specification for retaining and protection of building foundation excavations: JGJ 120–2012[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2012. (in Chinese) [8] 上海市住房和城乡建设管理委员会. 基坑工程技术标准: DG/TJ 08–61–2018[S]. 上海: 同济大学出版社, 2018. (Shanghai Housing and Urban-Rural Construction Commision. Technical code for excavation engineering: DG/TJ 08–61–2018[S]. Shanghai: Tongji University Press, 2018. (in Chinese)Shanghai Housing and Urban-Rural Construction Commision. Technical code for excavation engineering: DG/TJ 08–61–2018[S]. Shanghai: Tongji University Press, 2018. (in Chinese) [9] 天津市住房和城乡建设委员会. 天津市建筑基坑工程技术规程: DB/T 29–202–2022[S]. 天津: 天津市住房和城乡建设委员会, 2022. (Tianjin Housing and Urban-Rural Construction Commission. Tianjin technical specification for retaining and protection of building foundation excavation: DB/T 29–202–2022[S]. Tianjin: Tianjin Housing and Urban-Rural Construction Commission, 2022. (in Chinese)Tianjin Housing and Urban-Rural Construction Commission. Tianjin technical specification for retaining and protection of building foundation excavation: DB/T 29–202–2022[S]. Tianjin: Tianjin Housing and Urban-Rural Construction Commission, 2022. (in Chinese) [10] 天津市住房和城乡建设委员会. 天津市岩土工程技术规范: DB/T 29–20–2017[S]. 天津: 天津市住房和城乡建设委员会, 2017. (Tianjin Housing and Urban-Rural Construction Commission. Tianjin technical code for geotechnical engineering: DB/T 29–20–2017[S]. Tianjin: Tianjin Housing and Urban-Rural Construction Commission, 2017. (in Chinese)Tianjin Housing and Urban-Rural Construction Commission. Tianjin technical code for geotechnical engineering: DB/T 29–20–2017[S]. Tianjin: Tianjin Housing and Urban-Rural Construction Commission, 2017. (in Chinese) [11] 李广信. 论土骨架与渗透力[J]. 岩土工程学报,2016,38(8):1522-1528. (LI G X. On soil skeleton and seepage force[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2016,38(8):1522-1528. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201608021LI G X. On soil skeleton and seepage force[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2016, 38(8): 1522-1528. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201608021 [12] 罗嗣海, 谭昌明, 李 志. 水土合算法土压力计算时的强度指标[J]. 岩土工程技术,1998,12(1):3-7. (LUO S H, TAN C M, LI Z. The strength index of earth pressure calculation considering soil-water jointly calculation[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique,1998,12(1):3-7. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.1998.01.001LUO S H, TAN C M, LI Z. The strength index of earth pressure calculation considering soil-water jointly calculation[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique, 1998, 12(1): 3-7. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.1998.01.001 [13] 任 君, 许 超, 尹文彪. 黏土地层中桩锚支护结构土压力分布研究[J]. 岩土工程技术,2017,31(1):21-25. (REN J, XU C, YIN W B. Research on the soil pressure distribution of the pile-anchor supporting structure in clay[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique,2017,31(1):21-25. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2017.01.006REN J, XU C, YIN W B. Research on the soil pressure distribution of the pile-anchor supporting structure in clay[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique, 2017, 31(1): 21-25. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2017.01.006 [14] 天津市住房和城乡建设委员会. 天津市地基土层序划分技术规程: DB/T 29–191–2021[S]. 天津: 天津市住房和城乡建设委员会, 2022. (Tianjin Housing and Urban-Rural Construction Commission. Technical specification for division of subsoil sequence in Tianjin: DB/T 29–191–2021[S]. Tianjin: Tianjin Housing and Urban-Rural Construction Administration Committee, 2022. (in Chinese)Tianjin Housing and Urban-Rural Construction Commission. Technical specification for division of subsoil sequence in Tianjin: DB/T 29–191–2021[S]. Tianjin: Tianjin Housing and Urban-Rural Construction Administration Committee, 2022. (in Chinese) [15] 李金德, 秦 晶, 欧贤才, 等. SPSS统计分析与应用[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社出版, 2019. (LI J D, QIN J, OU X C, et al. SPSS statistical analysis and application[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2019. (in Chinese)LI J D, QIN J, OU X C, et al. SPSS statistical analysis and application[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2019. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: