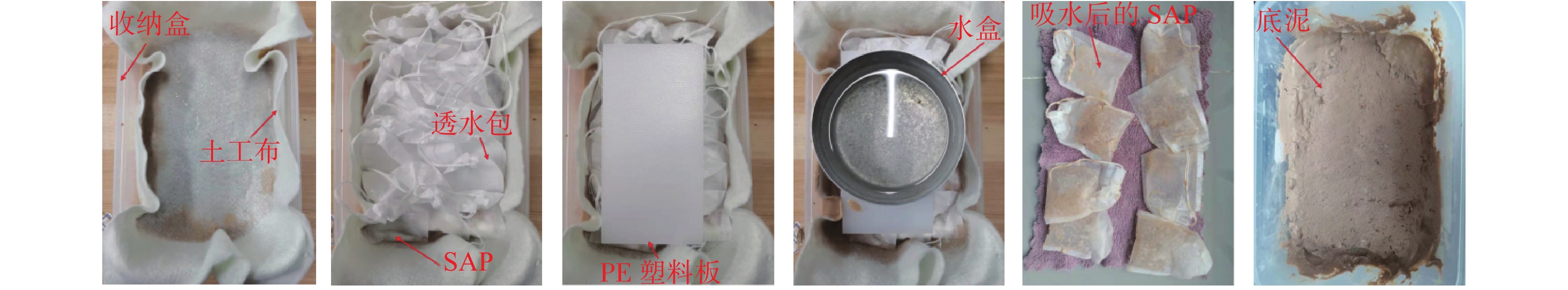
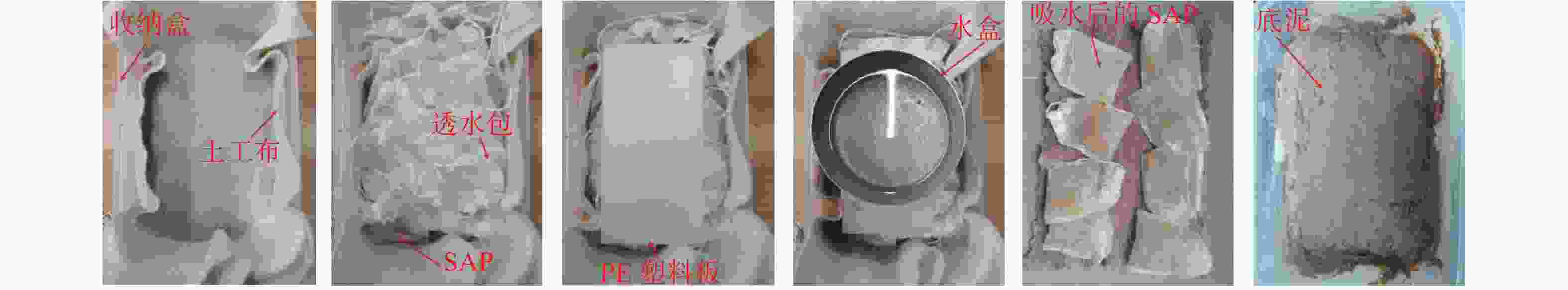
Dewatering of high water content subsoil under the action of water absorber
-
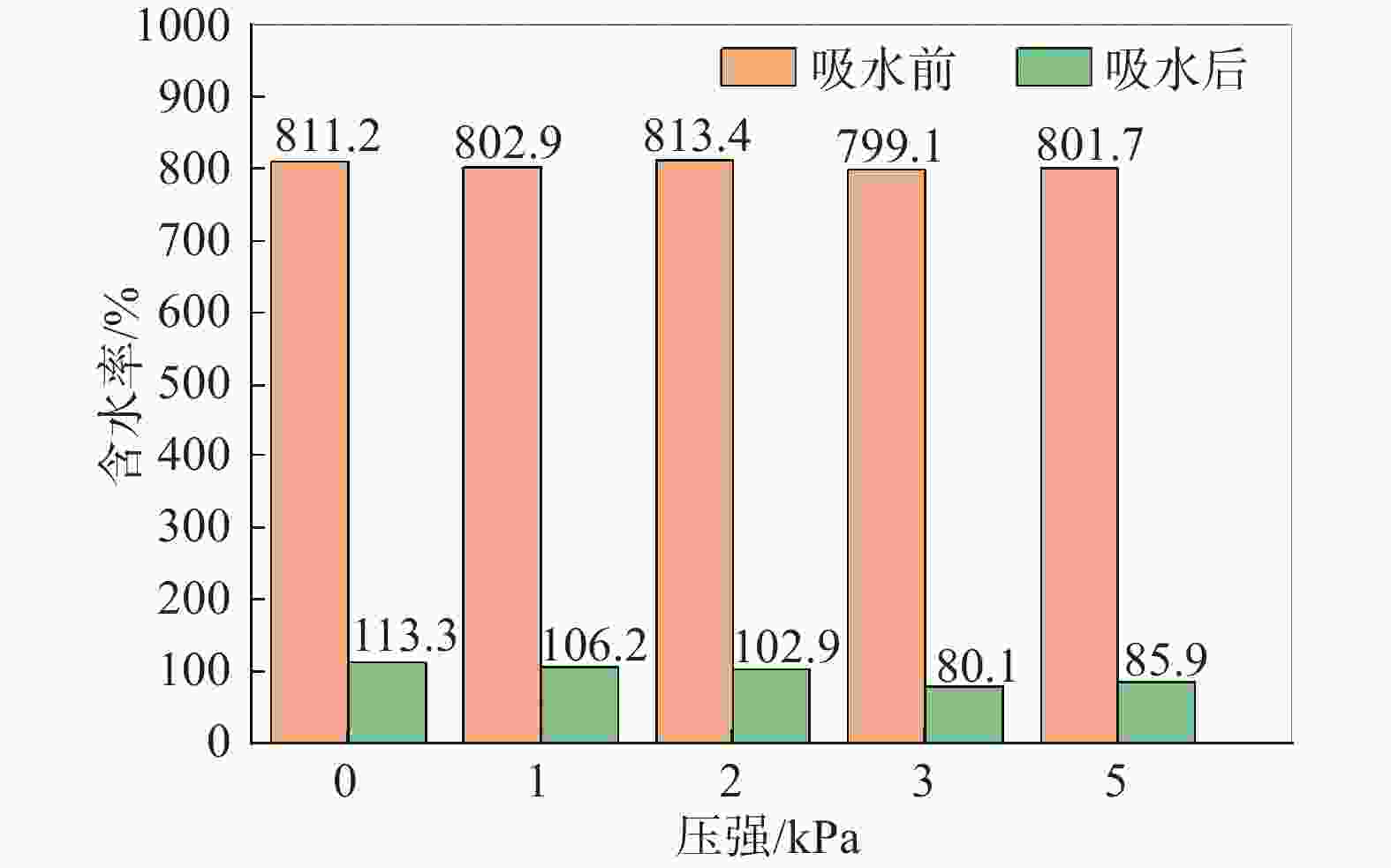
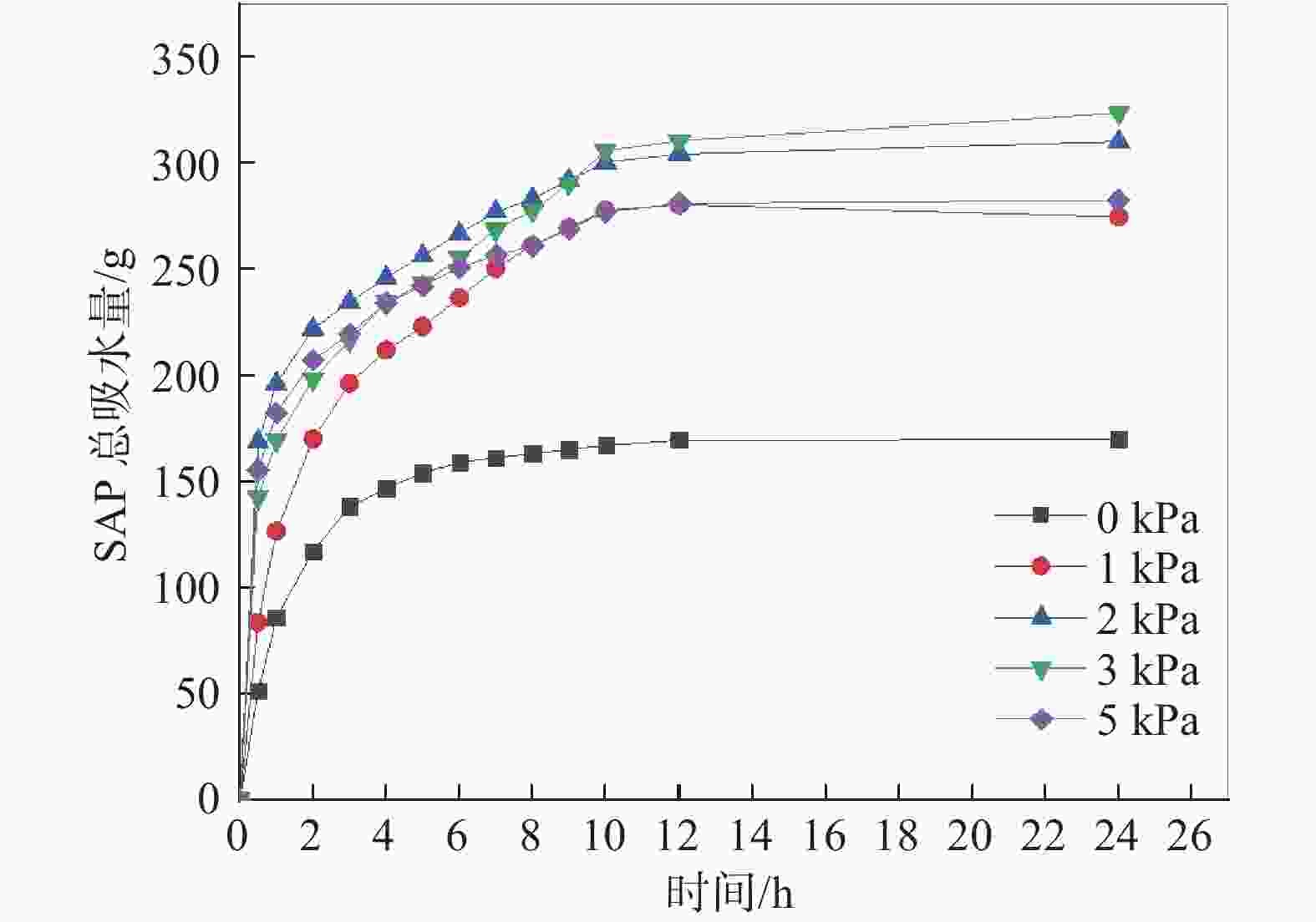
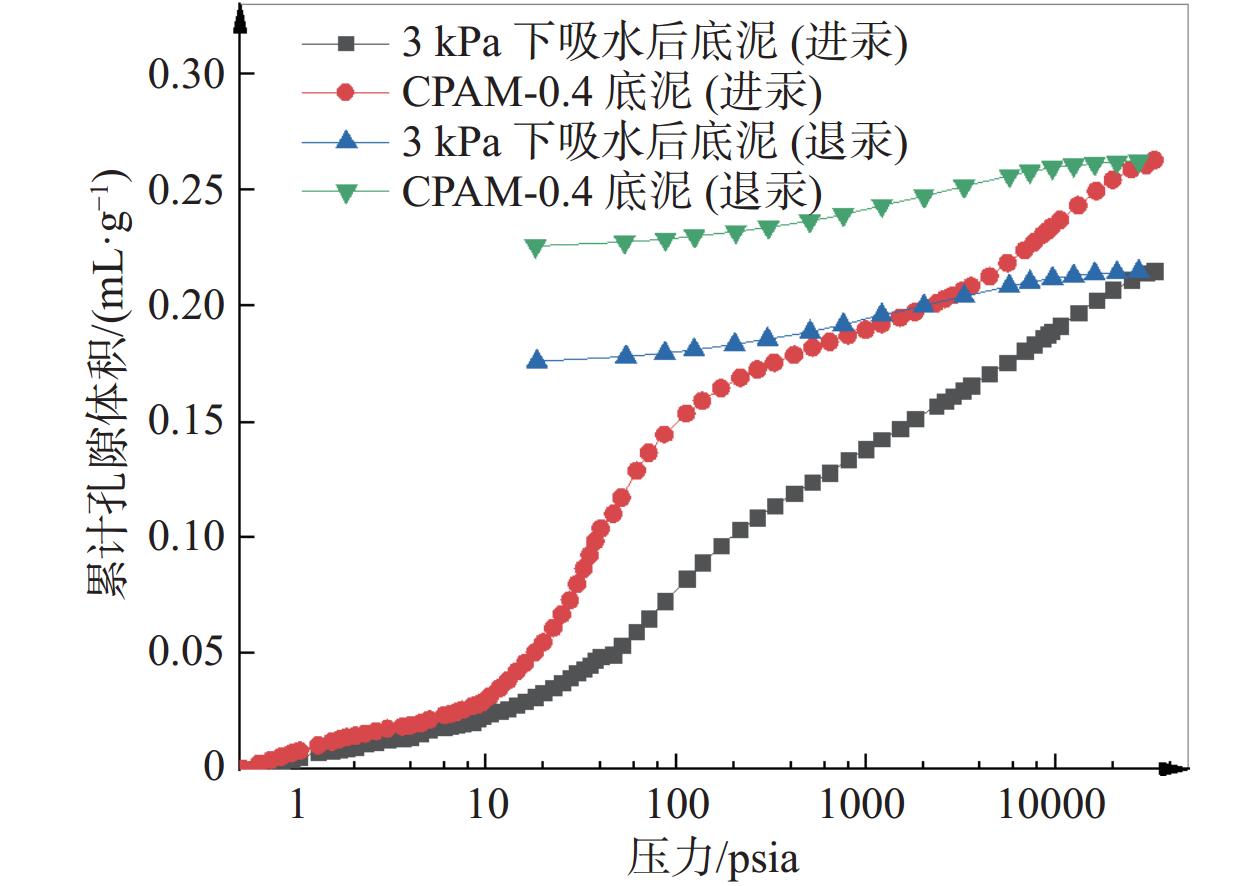
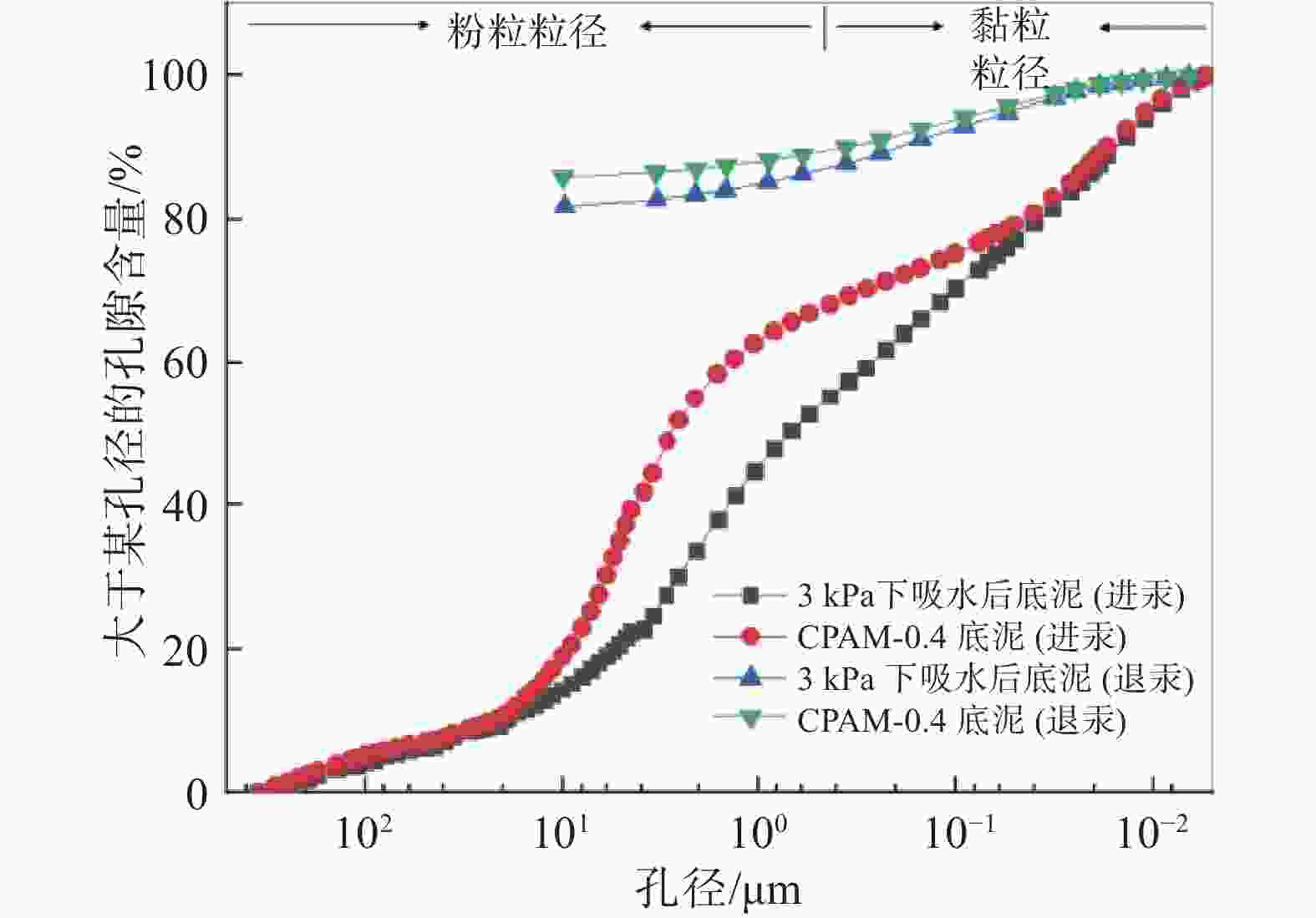
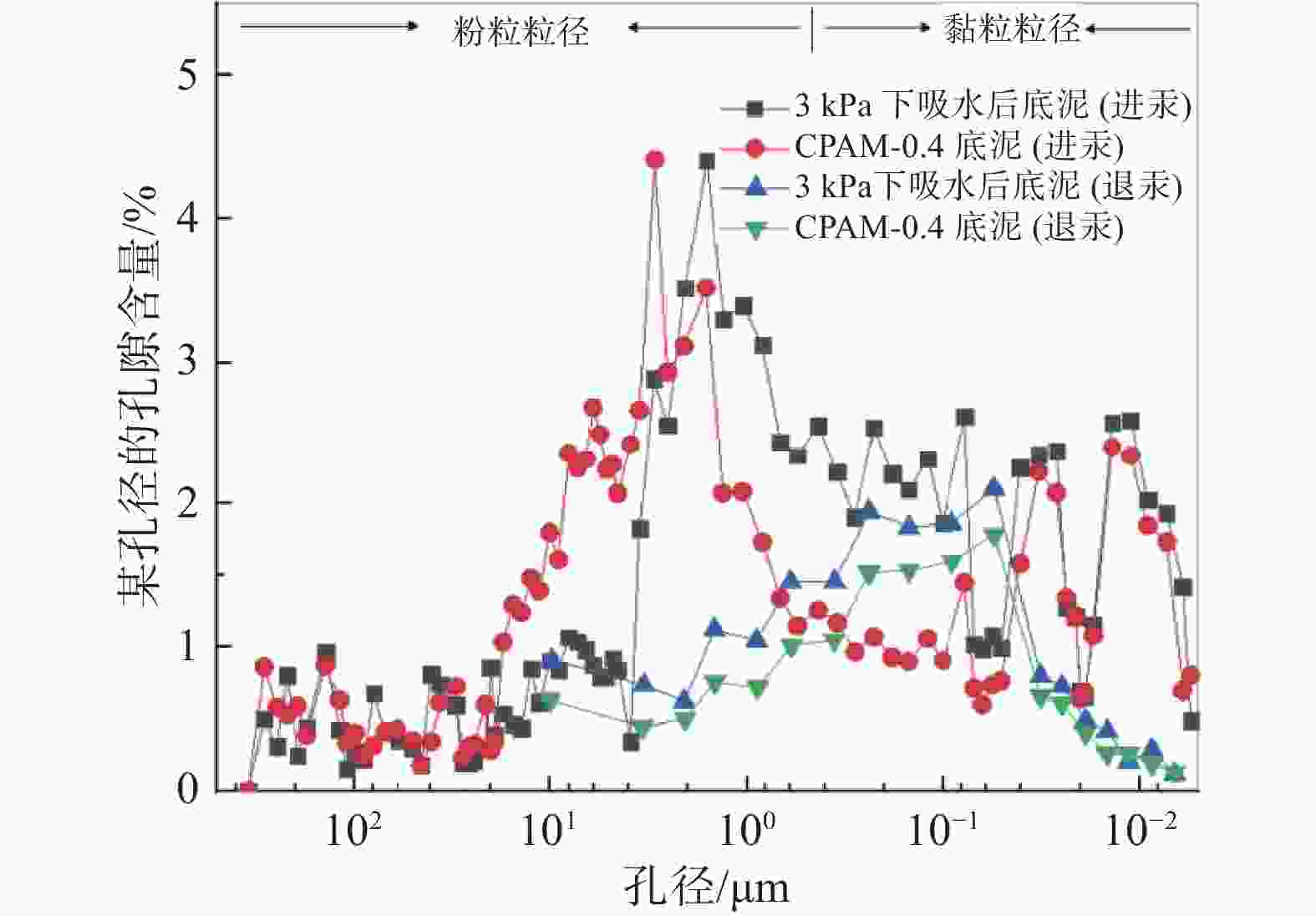
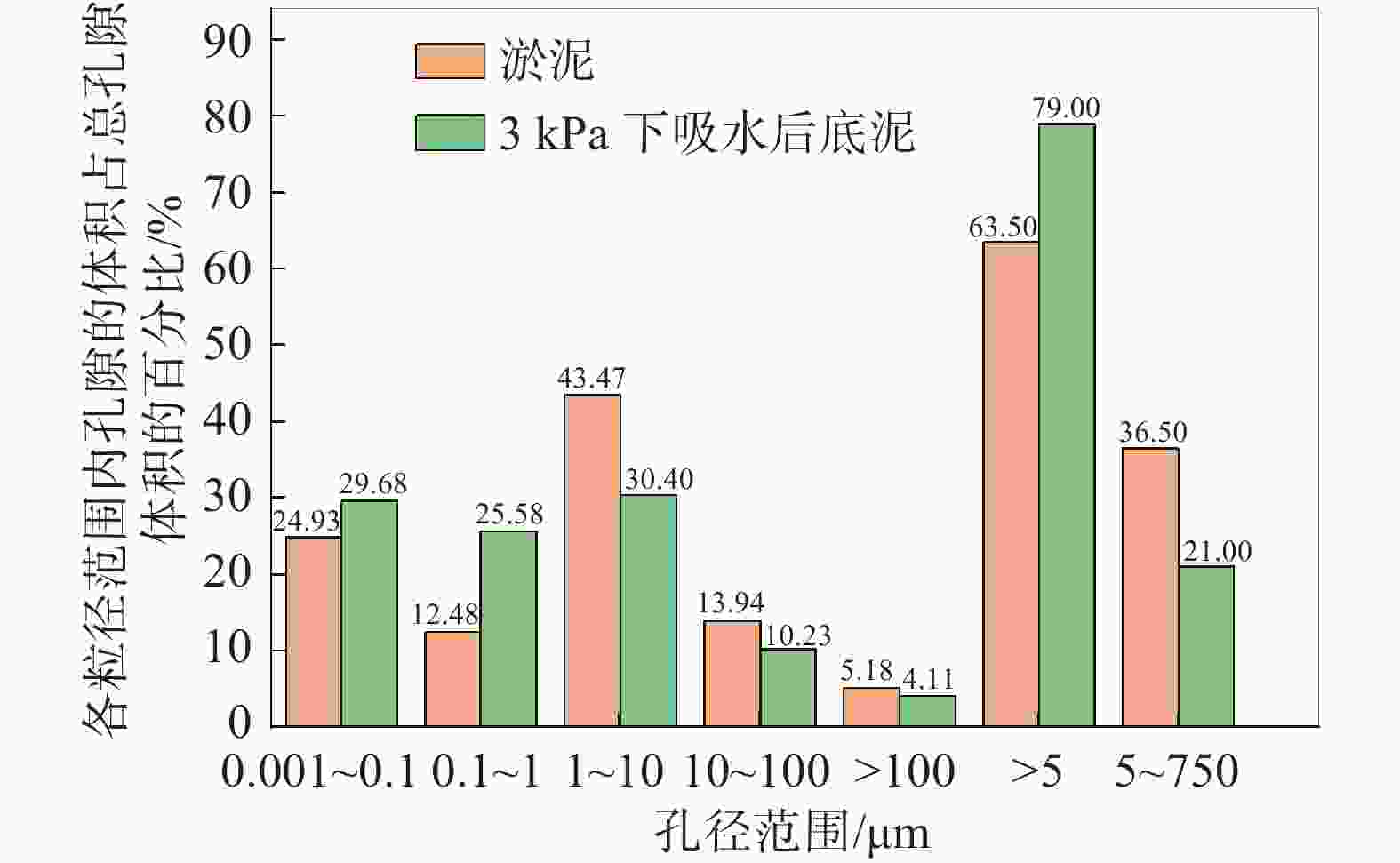
摘要: 目前大多数高含水率底泥脱水处理采用添加絮凝剂方法来提高脱水性能,碱药剂处理后土样无法利用。为此,提出了一种通过高分子吸水树脂SAP处理高含水率底泥的物理方法,并且通过室内吸水试验和压汞试验,对高含水率底泥在吸水剂作用下的失水变形机理进行研究。试验研究表明:在3 kPa的上覆压强下用高分子吸水树脂SAP对底泥吸水所得的底泥含水率最低;吸水后底泥的孔隙体积和尺寸变小,孔隙结构变得更加复杂和不规则;在高分子吸水树脂SAP的作用下,底泥中的自由水通过内部渗透通道被吸收,颗粒在自重的作用下重新排列,颗粒间的渗透通道逐渐减小,底泥产生收缩变形。Abstract: Most of the high water content subsoil dewatering treatment use methods such as adding flocculants to improve the dewatering performance, and the soil samples cannot be utilized after alkaline agent treatment. For this reason, a physical method of treating high water content subsoil was proposed using polymer water-absorbent resin SAP, and through the indoor water absorption test and mercury intrusion test, the mechanism of dewatering and deformation of high water content subsoil under the action of water-absorbent agent was studied, and the results show that: the water content of subsoil obtained by water-absorbing with polymer water-absorbent resin SAP reached the lowest under the overlaying pressure of 3 kPa. After water absorption, the pore volume and size of the subsoil reduced, and the pore structure became more complex and irregular. Under the action of polymer water-absorbing resin SAP, the free water in the mud was absorbed through the internal permeable channels, the particles were rearranged under the action of self-weight, the permeable channels between the particles were gradually reduced, and the subsoil shrinks and deforms.
-
表 1 吸水试验方案
编号 泥浆质量/g SAP质量/g 压强/kPa 1 540.00 4.80 0 2 1 3 2 4 3 5 5 表 2 膨润土泥浆的物理特性参数
初始含水率/% 密度/(g·cm−3) 黏度/s 液限/% 塑限/% 1500.0 1.02 16.8 85.0 29.0 表 3 高分子吸水树脂SAP部分性质及物理参数
外观 主要化学成分 目数 pH值 堆积密度/
(g·cm−3)0.9%盐水
吸收倍率/
(g·g−1)纯白粉末 低交联型
聚丙烯酸钠88%,
水8%~10%,
交联剂0.5%~1.0%200~400 6.2 0.84 52 表 4 泥浆与3 kPa条件下脱水后底泥主要孔隙参数对比
比较项目 泥浆 3 kPa下脱水后底泥 样品质量/g 0.8587 0.9531 33000 psia时汞总侵入量/(mL·g–1) 0.2629 0.2153 33000 psia时总孔隙面积(m2·g–1) 15.8430 15.0450 平均孔径大小(按d=4 V/A计算)/nm 66.3900 57.2300 体积密度/(g·mL–1) 1.4852 1.6470 表观骨骼密度/(g·mL–1) 2.4368 2.5517 孔隙率/% 39.0516 35.4549 门槛压力/psia 0.8000 0.9400 特征长度/nm 224852.3700 191989.6300 曲折系数 1.7890 1.8290 弯曲度 3.5099 3.6663 渗透分形维数 2.8880 2.8680 骨分形维数 2.4430 2.5030 -
[1] 宋 闯, 李 冰, 邱艳茹. 河道淤泥处理及资源化应用[J]. 中国水利,2018(23):35-37. (SONG C, LI B, QIU Y R. River sludge treatment and resourcing application[J]. China Water Resources,2018(23):35-37. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2018.23.016SONG C, LI B, QIU Y R. River sludge treatment and resourcing application[J]. China Water Resources, 2018(23): 35-37. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2018.23.016 [2] 麻 杰. 中小河道淤泥处理技术及资源化利用研究[J]. 水利建设与管理,2016,36(9):64-67,55. (MA J. Research on medium and small river silt disposal technology and resource utilization[J]. Water Conservancy Construction and Management,2016,36(9):64-67,55. (in Chinese)MA J. Research on medium and small river silt disposal technology and resource utilization[J]. Water Conservancy Construction and Management, 2016, 36(9): 64-67,55. (in Chinese) [3] 高 扬, 孙 科, 谭一军, 等. 多种疏浚淤泥脱水技术的典型应用及分析[J]. 江苏水利,2020(9):51-54. (GAO Y, SUN K, TAN Y J, et al. Typical application and analysis of various dredged silt dehydration technology[J]. Jiangsu Water Resources,2020(9):51-54. (in Chinese)GAO Y, SUN K, TAN Y J, et al. Typical application and analysis of various dredged silt dehydration technology[J]. Jiangsu Water Resources, 2020(9): 51-54. (in Chinese) [4] 梁 波, 陈海琴, 关 杰. 超声波预处理城市剩余污泥脱水性能研究进展[J]. 工业用水与废水,2017,48(4):1-6. (LIANG B, CHEN H Q, GUAN J. Research progress on dewatering performance of municipal excess sludge pretreated by ultrasonic[J]. Industrial Water & Wastewater,2017,48(4):1-6. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2455.2017.04.001LIANG B, CHEN H Q, GUAN J. Research progress on dewatering performance of municipal excess sludge pretreated by ultrasonic[J]. Industrial Water & Wastewater, 2017, 48(4): 1-6. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2455.2017.04.001 [5] 谭林立, 许 航, 刘 珊, 等. 真空电渗给水污泥脱水机理的研究[J]. 环境科技,2017,30(1):1-4. (TAN L L, XU H, LIU S, et al. Mechanism research of water treatment residual sludge dewatering by vacuum electro-osmosis[J]. Environmental Science and Technology,2017,30(1):1-4. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4829.2017.01.002TAN L L, XU H, LIU S, et al. Mechanism research of water treatment residual sludge dewatering by vacuum electro-osmosis[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2017, 30(1): 1-4. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4829.2017.01.002 [6] 纪文栋, 张宇亭, 颜容涛, 等. 高吸水材料改善高含水率淤泥流动性的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(S1):281-286. (JI W D, ZHANG Y T, YAN R T, et al. An experimental study of decreasing fluidity of silt with high moisture content by high water absorbent material[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2015,36(S1):281-286. (in Chinese)JI W D, ZHANG Y T, YAN R T, et al. An experimental study of decreasing fluidity of silt with high moisture content by high water absorbent material[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(S1): 281-286. (in Chinese) [7] 韦文珍, 张 玲, 李炳奇. 高分子吸水树脂的合成与应用[J]. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版),2000,4(4):338-343. (WEI W Z, ZHANG L, LI B Q. The synthetic and use of macromolecule resin of absorbing moisture[J]. Journal of Shihezi University (Natural Science),2000,4(4):338-343. (in Chinese)WEI W Z, ZHANG L, LI B Q. The synthetic and use of macromolecule resin of absorbing moisture[J]. Journal of Shihezi University (Natural Science), 2000, 4(4): 338-343. (in Chinese) [8] 石星丽, 张亚娟, 冯 潇. 浅谈高分子吸水树脂的合成与应用[J]. 石化技术,2017,24(10):85. (SHI X L, ZHANG Y J, FENG X. Synthesis and application of macromolecular water absorbent resin[J]. Petrochemical Industry Technology,2017,24(10):85. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0235.2017.10.060SHI X L, ZHANG Y J, FENG X. Synthesis and application of macromolecular water absorbent resin[J]. Petrochemical Industry Technology, 2017, 24(10): 85. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0235.2017.10.060 [9] BIAN X, ZENG L L, DENG Y F, et al. The role of superabsorbent polymer on strength and microstructure development in cemented dredged clay with high water content[J]. Polymers,2018,10(10):1069. doi: 10.3390/polym10101069 [10] BIAN X, DING G Q, WANG Z F, et al. Compression and strength behavior of cement–lime–polymer-solidified dredged material at high water content[J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology,2017,35(6):840-846. [11] BIAN X, CAO Y P, WANG Z F, et al. Effect of super-absorbent polymer on the undrained shear behavior of cemented dredged clay with high water content[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering,2017,29(7):04017023. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0001849 [12] BIAN X, WANG Z F, DING G Q, et al. Compressibility of cemented dredged clay at high water content with super-absorbent polymer[J]. Engineering Geology,2016,208:198-205. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.04.036 -






 下载:
下载: