Dehydration model test of high moisture content mud
-
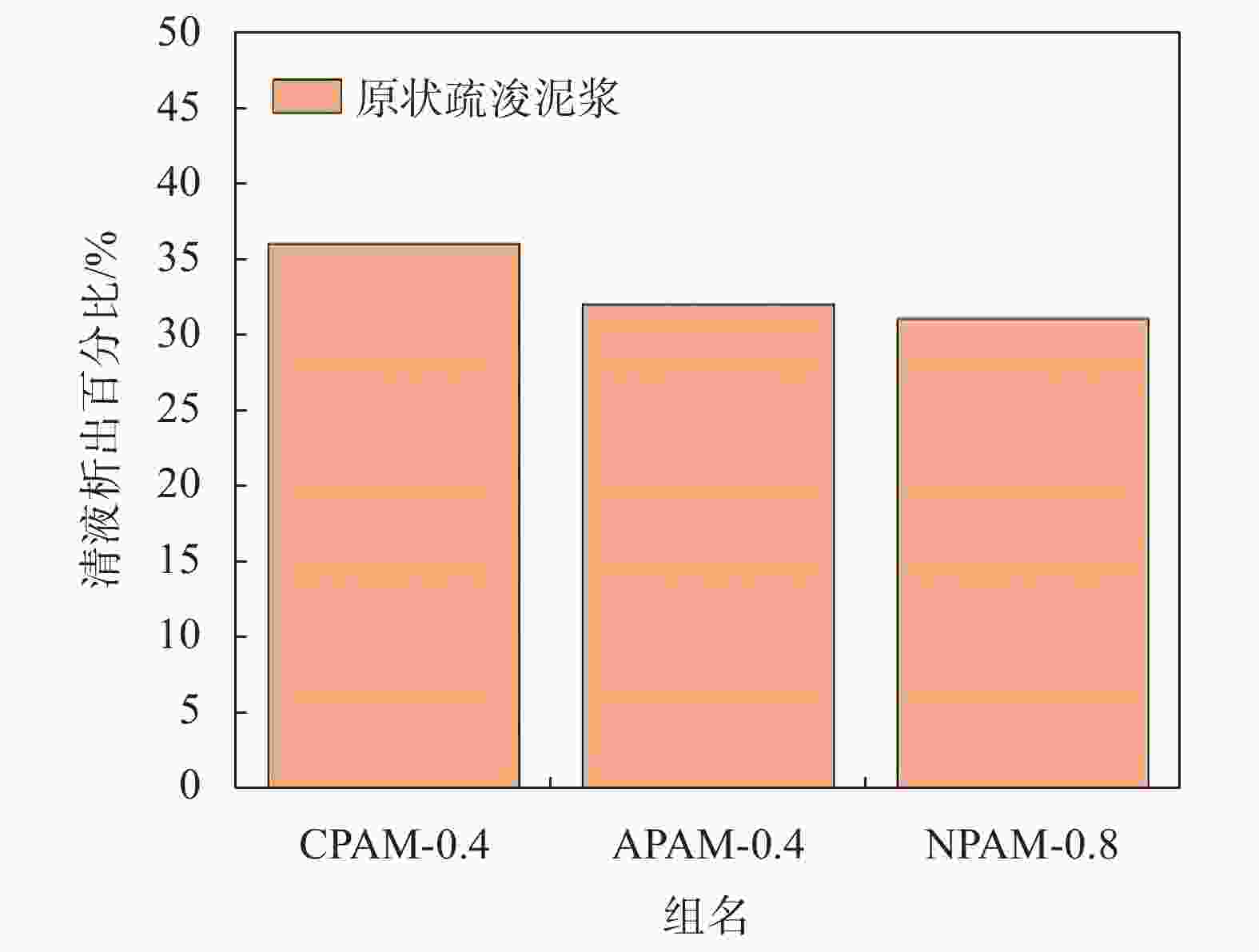
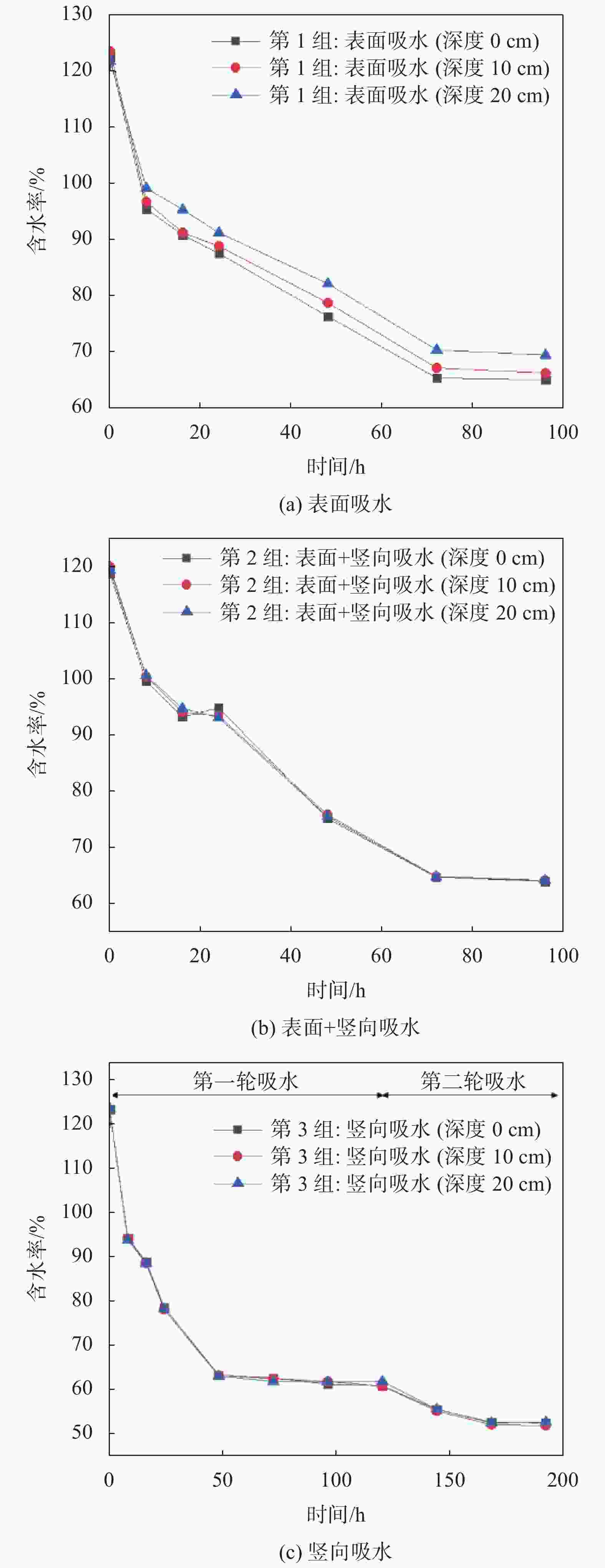
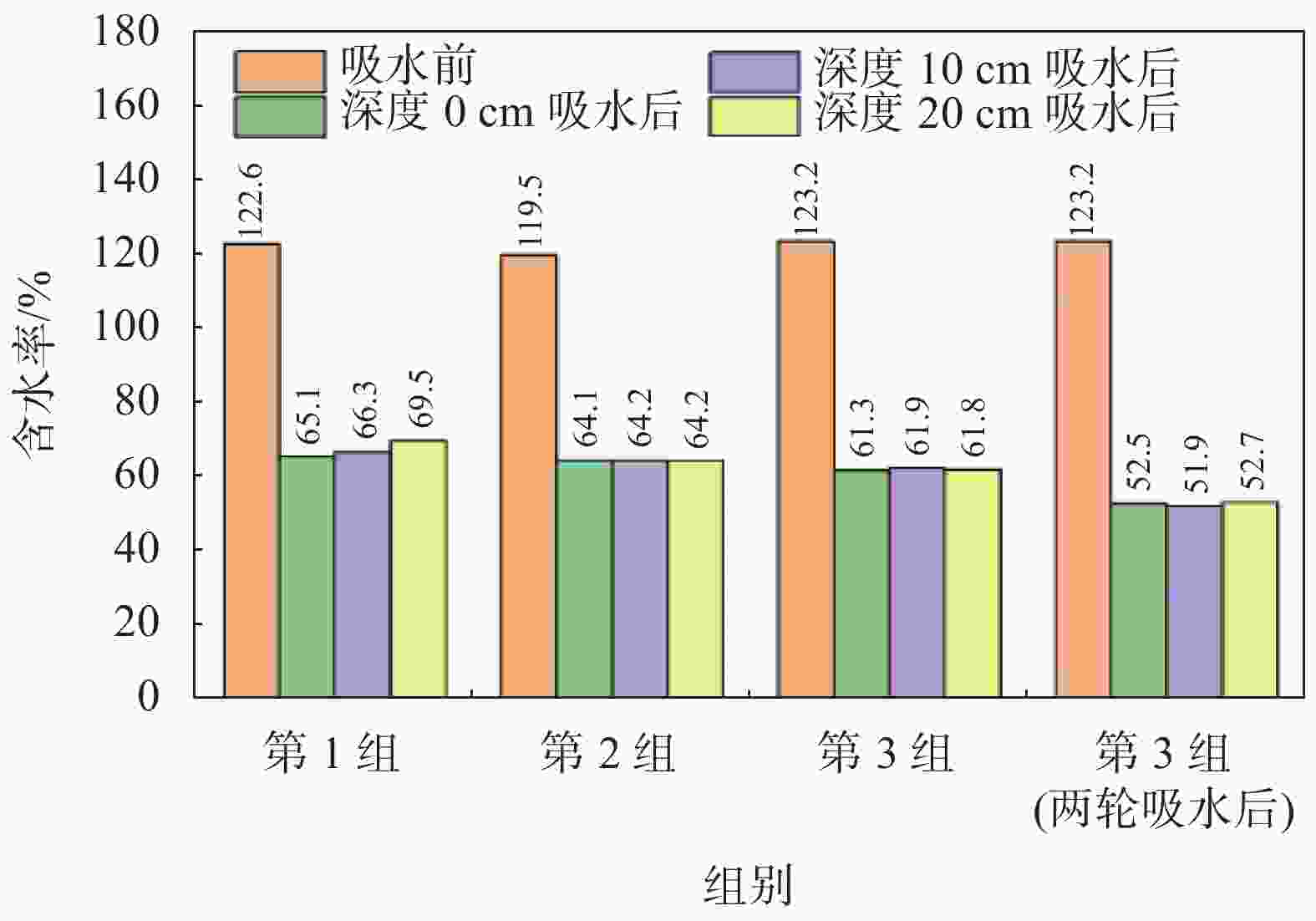
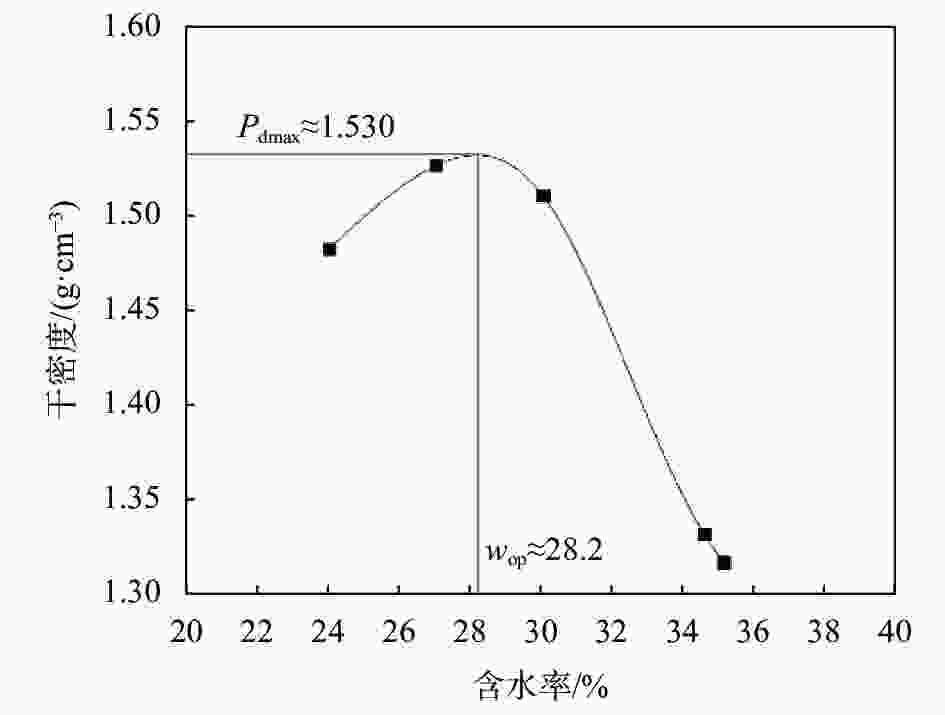
摘要: 针对实际工程中的大量疏浚淤泥和废弃泥浆,提出了一种新的絮凝–吸水联合处理方法,有效解决传统泥浆处理方法处理缓慢且成本高的难题。通过絮凝试验验证了最佳絮凝剂种类对原状疏浚淤泥的适应性,通过室内模型试验分析了不同吸水方式对絮凝后泥浆的脱水效果。结果表明:对于原状疏浚泥浆,阳离子型聚丙烯酰胺(CPAM)、阴离子型聚丙烯酰胺(APAM)和非离子型聚丙烯酰胺(NPAM)均可以获得较高的絮凝效果,可以选择0.4%的阳离子型聚丙烯酰胺(CPAM)作为最佳絮凝剂种类;竖向吸水方式在降低底泥含水率方面最为有效,能将含水率降至52%,略低于泥浆的液限53%;竖向吸水方式和竖向+表面吸水方式均可以在不同的深度获得较为均匀的干化效果;泥浆含水率降至其最优含水率的1.8~1.9倍标志着吸水过程已经完成,为实际工程中判断吸水过程是否完成提供了依据。Abstract: A new flocculation-absorption combined treatment method is proposed for a large amount of dredged mud and waste mud in actual projects, effectively solving the problem of slow treatment and the high cost of traditional mud treatment methods. The suitability of the optimal flocculant type for the original state dredged sediment was verified through flocculation tests. The dewatering effect of different water absorption methods on the flocculated mud through an indoor modeling test was analyzed. The results show that: for the primary dredged mud, cationic polyacrylamide (CPAM), anionic polyacrylamide (APAM), and nonionic polyacrylamide (NPAM) can achieve a high flocculation effect, and the best flocculant type can be 0.4% of cationic polyacrylamide (CPAM); vertical water absorption is the most effective way to reduce the water content of the mud, which can reduce the water content to 52%, slightly lower than the liquid limit of 53% of the mud; vertical water absorption and vertical + surface water absorption can be used to obtain a more uniform drying effect at different depths; the water content of the mud was reduced to 1.8~1.9 times of the optimal water content to mark the completion of the absorption process, which provides a basis for the judgment of the completion of the absorption process in the actual project.
-
Key words:
- mud /
- flocculate /
- absorb water /
- moisture content /
- treatment effect
-
表 1 原状疏浚泥浆絮凝试验方案
编号 絮凝剂类型 絮凝剂分子量
(×104)絮凝剂掺量
/%CPAM-0.4 阳离子型聚丙烯酰胺 1200 0.04 APAM-0.4 阴离子型聚丙烯酰胺 0.04 NPAM-0.8 非离子型聚丙烯酰胺 0.08 注:絮凝剂掺量为相对于泥浆的质量分数。 表 2 吸水方式试验方案
组别编号 过滤袋
(内部装有SAP)
布置方式初始泥浆
深度/m所用SAP
总质量/kg所用
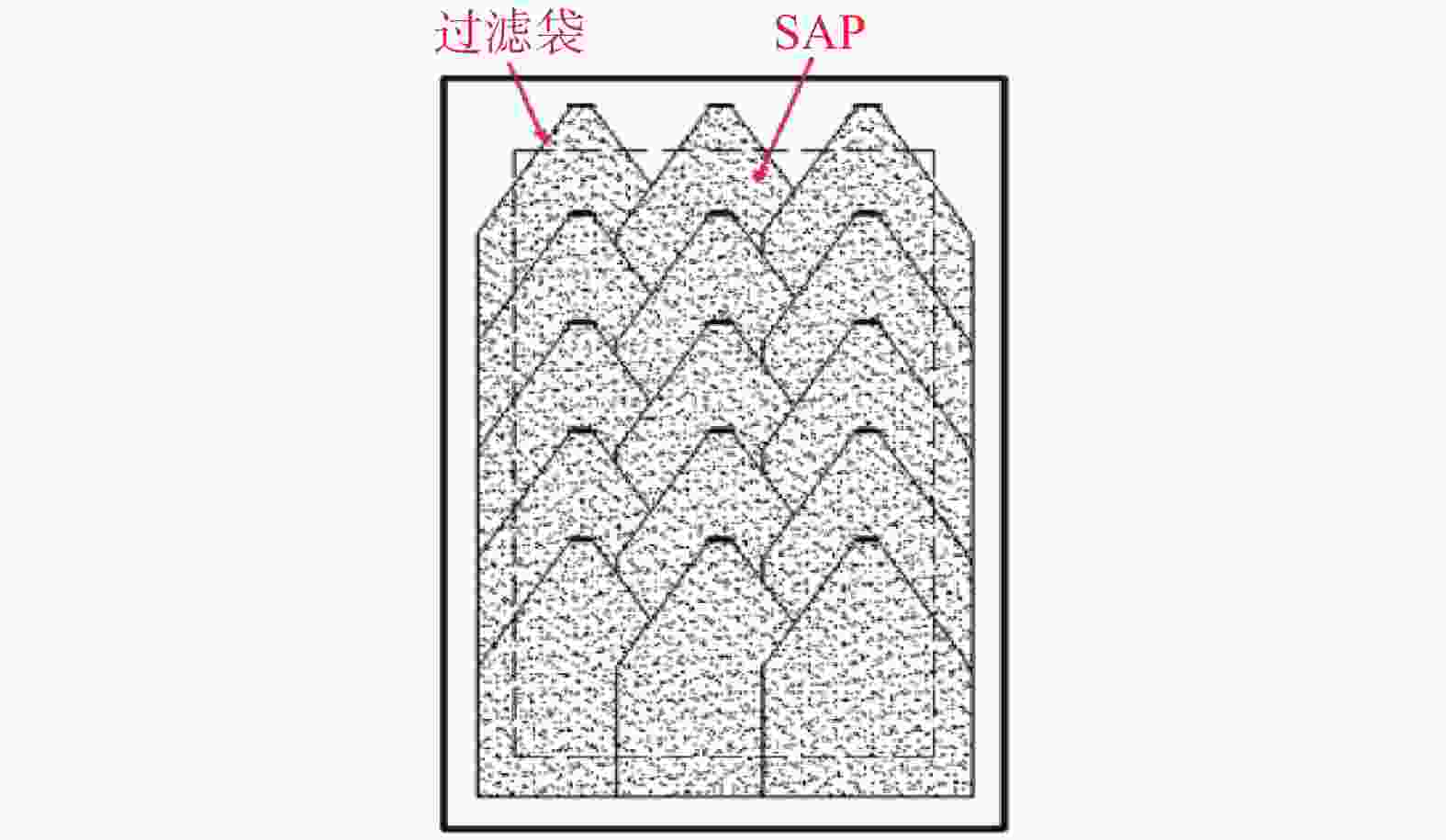
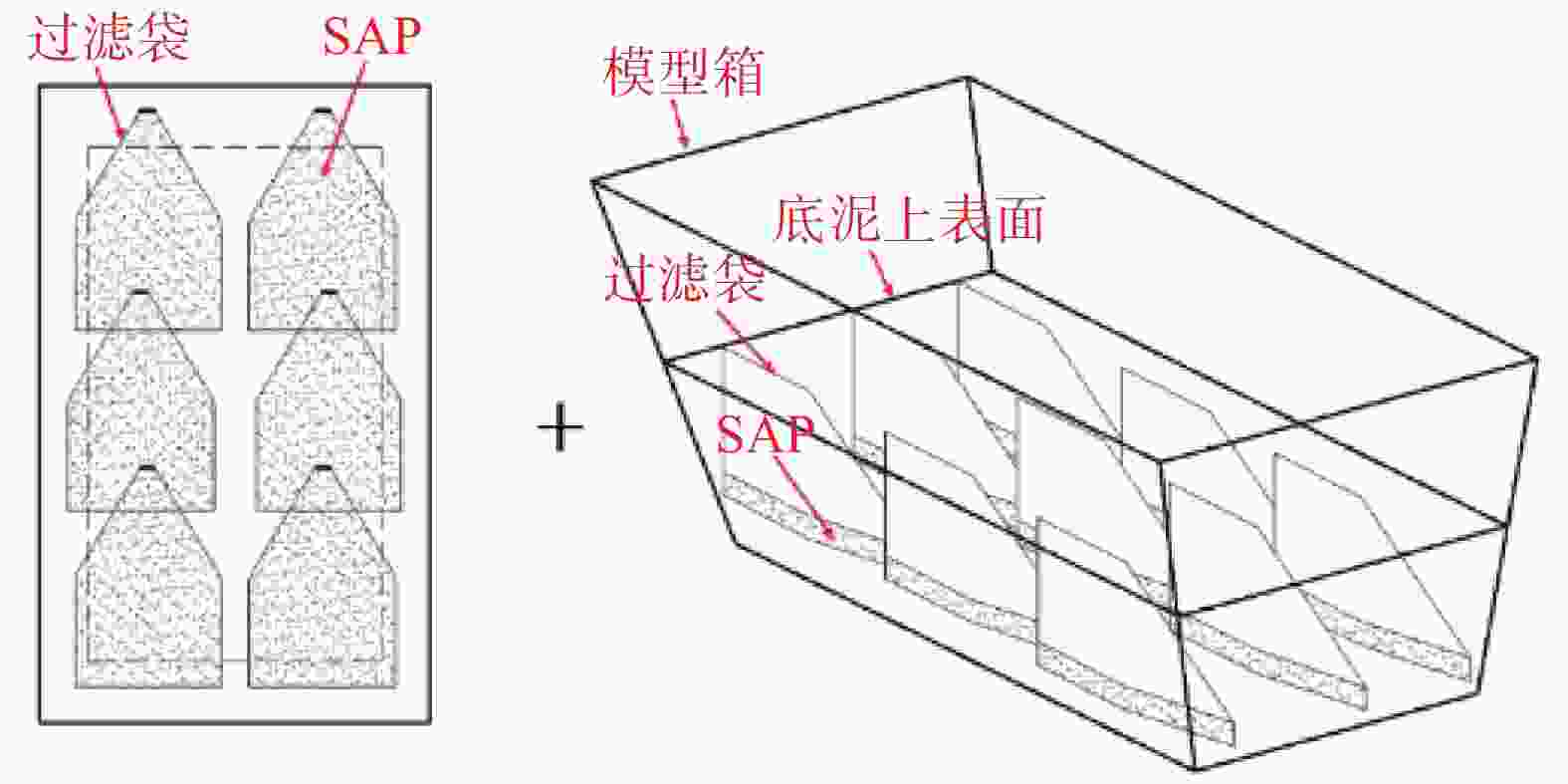
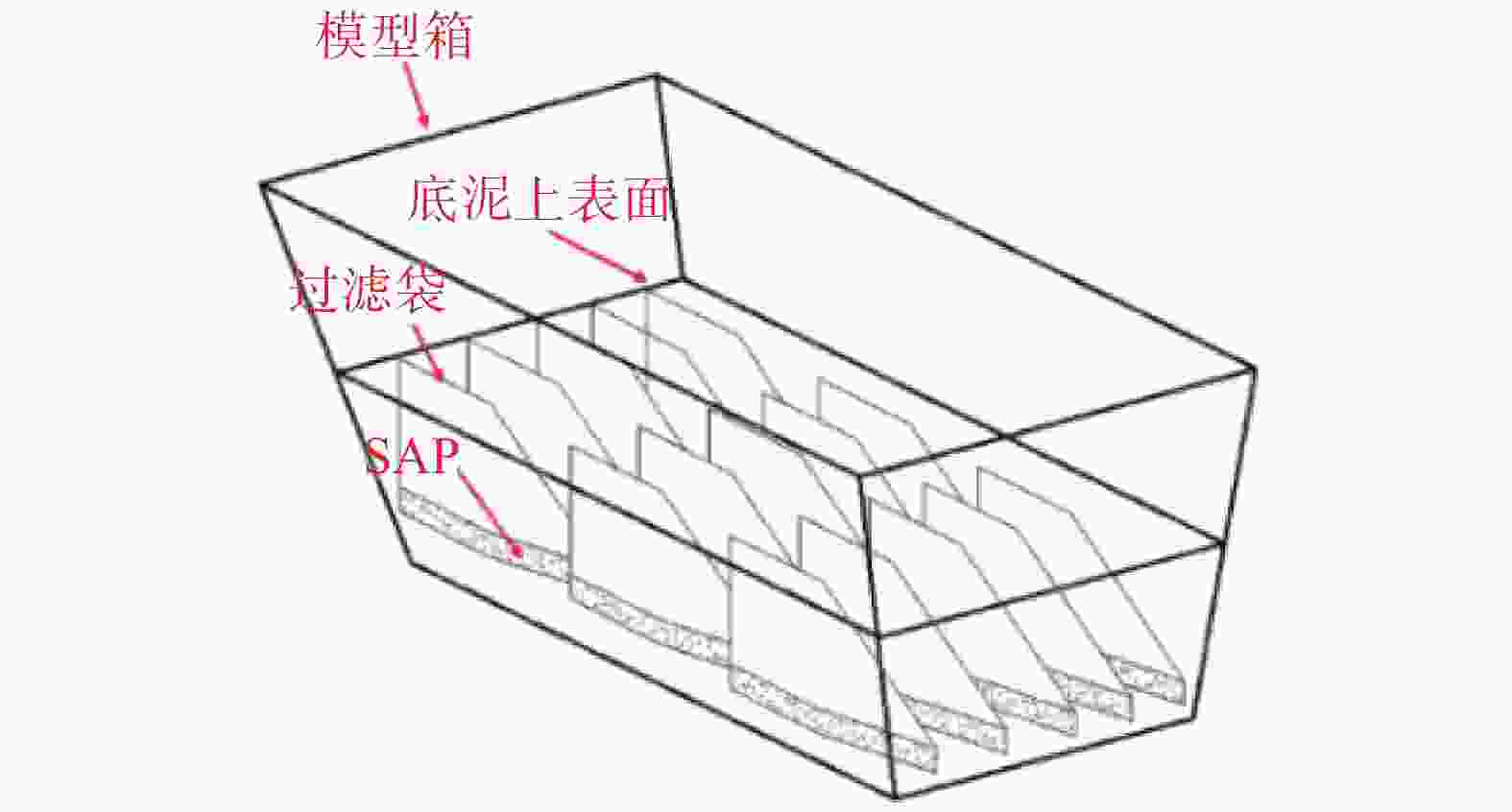
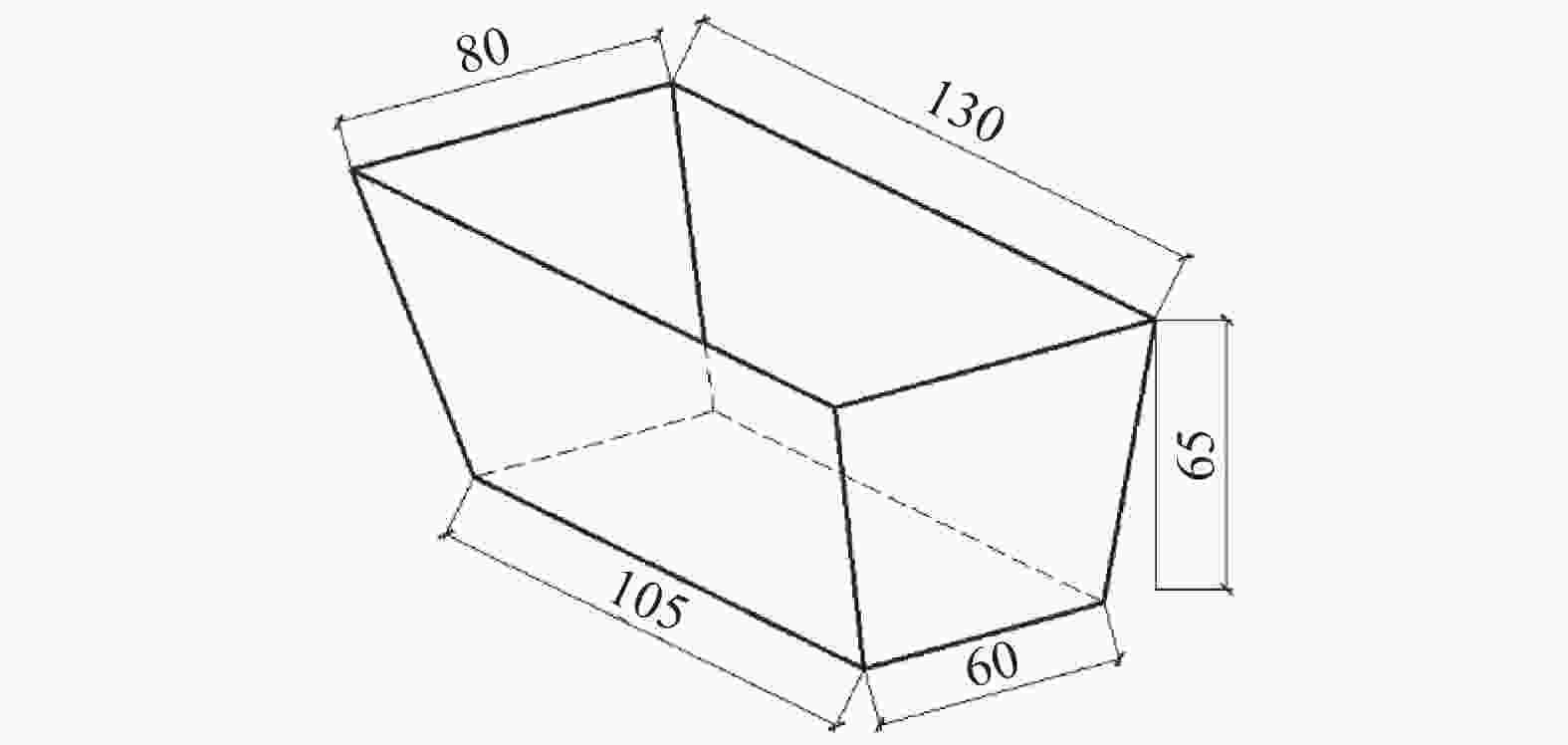
过滤袋/个1 上表面 0.6 3 15 2 上表面+竖向 3 竖向 注:1.由苏凡[15]的研究可知最优加载压强取3 kPa;2.对于第一轮吸水后底泥含水率最低的组别重新更换SAP和过滤袋,开展第二轮试验。 -
[1] 田文斌. 高含水率疏浚泥沉积固结联合试验研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2016. (TIAN W B. Experimental study on sedimentation-consolidation behavior of dredged clays at high water contents[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2016. (in Chinese)TIAN W B. Experimental study on sedimentation-consolidation behavior of dredged clays at high water contents[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2016. (in Chinese) [2] 宋 闯, 李 冰, 邱艳茹. 河道淤泥处理及资源化应用[J]. 中国水利,2018(23):35-37. (SONG C, LI B, QIU Y R. River sludge treatment and resourcing application[J]. China Water Resources,2018(23):35-37. (in Chinese)SONG C, LI B, QIU Y R. River sludge treatment and resourcing application[J]. China Water Resources, 2018(23): 35-37. (in Chinese) [3] 麻 杰. 中小河道淤泥处理技术及资源化利用研究[J]. 水利建设与管理,2016,36(9):64-67,55. (MA J. Research on medium and small river silt disposal technology and resource utilization[J]. Water Conservancy Construction and Management,2016,36(9):64-67,55. (in Chinese)MA J. Research on medium and small river silt disposal technology and resource utilization[J]. Water Conservancy Construction and Management, 2016, 36(9): 64-67,55. (in Chinese) [4] 高 扬, 孙 科, 谭一军, 等. 多种疏浚淤泥脱水技术的典型应用及分析[J]. 江苏水利,2020,36(9):51-54. (GAO Y, SUN K, TAN Y J, et al. Typical application and analysis of various dredged silt dehydration technology[J]. Jiangsu Water Resources,2020,36(9):51-54. (in Chinese)GAO Y, SUN K, TAN Y J, et al. Typical application and analysis of various dredged silt dehydration technology[J]. Jiangsu Water Resources, 2020, 36(9): 51-54. (in Chinese) [5] 杨 宾, 李银月, 董明坤, 等. 不同絮凝剂对钻井泥浆的处理效果及絮凝机理[J]. 无机盐工业,2024,56(4):34-41. (YANG B, LI Y Y, DONG M K, et al. Treatment effect and flocculation mechanism of abandoned drilling mud by different flocculants[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2024,56(4):34-41. (in Chinese)YANG B, LI Y Y, DONG M K, et al. Treatment effect and flocculation mechanism of abandoned drilling mud by different flocculants[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2024, 56(4): 34-41. (in Chinese) [6] 唐雨卉, 程润喜, 徐 杨. 河湖生态清淤及淤泥固化一体化技术应用研究[J]. 广西水利水电,2023(5):58-62. (TANG Y H, CHENG R X, XU Y. Research on the application of integrated technology for ecological dredging and sludge solidification in rivers and lakes[J]. Guangxi Water Resources & Hydropower Engineering,2023(5):58-62. (in Chinese)TANG Y H, CHENG R X, XU Y. Research on the application of integrated technology for ecological dredging and sludge solidification in rivers and lakes[J]. Guangxi Water Resources & Hydropower Engineering, 2023(5): 58-62. (in Chinese) [7] 吴绍凯, 祝建中, 何敏霞, 等. 高含水率淤泥的流动电渗透脱水实验研究[J]. 科学技术与工程,2018,18(16):154-160. (WU S K, ZHU J Z, HE M X, et al. Experimental study on electro-osmotic dewatering of high moisture-content of sediment in the state of flow[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2018,18(16):154-160. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.16.024WU S K, ZHU J Z, HE M X, et al. Experimental study on electro-osmotic dewatering of high moisture-content of sediment in the state of flow[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2018, 18(16): 154-160. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.16.024 [8] 冯兴国, 刘 宁, 卢向雨. 复合地聚物固化高含水率泥浆的回填性能及微观机理研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2023,42(10):3643-3651. (FENG X G, LIU N, LU X Y. Backfilling performance and microscopic mechanism of high moisture content slurry solidified by composite geopolymer[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2023,42(10):3643-3651. (in Chinese)FENG X G, LIU N, LU X Y. Backfilling performance and microscopic mechanism of high moisture content slurry solidified by composite geopolymer[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2023, 42(10): 3643-3651. (in Chinese) [9] 宋 浩, 孙 伟, 王 蓉, 等. 水玻璃-固化剂固化地表冰碛物试验研究[J]. 有色金属工程,2023,13(10):118-125. (SONG H, SUN W, WANG R, et al. Experimental study on surface moraine solidified by sodium silicate-curing agent[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering,2023,13(10):118-125. (in Chinese)SONG H, SUN W, WANG R, et al. Experimental study on surface moraine solidified by sodium silicate-curing agent[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2023, 13(10): 118-125. (in Chinese) [10] 刘智峰, 崔剑峰, 蒋勇兵, 等. 絮凝剂对打桩废弃泥浆的处理研究[J]. 山西建筑,2015,41(22):181-183. (LIU Z F, CUI J F, JIANG Y B, et al. The study on the disposal of waste drilling mud by flocculation[J]. Shanxi Architecture,2015,41(22):181-183. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2015.22.102LIU Z F, CUI J F, JIANG Y B, et al. The study on the disposal of waste drilling mud by flocculation[J]. Shanxi Architecture, 2015, 41(22): 181-183. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2015.22.102 [11] 梁止水, 杨才千, 高海鹰, 等. 建筑工程废弃泥浆快速泥水分离试验研究[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版),2016,46(2):427-433. (LIANG Z S, YANG C Q, GAO H Y, et al. Experimental study on rapid separation between water and slurry from construction engineering[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition),2016,46(2):427-433. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0505.2016.02.031LIANG Z S, YANG C Q, GAO H Y, et al. Experimental study on rapid separation between water and slurry from construction engineering[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 46(2): 427-433. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0505.2016.02.031 [12] 张钦喜, 陶 韬, 王晓杰, 等. 钻孔灌注桩废弃泥浆处理的试验研究[J]. 水利学报,2015,46(S1):40-45. (ZHANG Q X, TAO T, WANG X J, et al. Experimental study on treatment of waste slurry in cast-in-situ bored pile[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2015,46(S1):40-45. (in Chinese)ZHANG Q X, TAO T, WANG X J, et al. Experimental study on treatment of waste slurry in cast-in-situ bored pile[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2015, 46(S1): 40-45. (in Chinese) [13] 成金康. 絮凝调理对淤泥(浆)沉积规律与固结特性的影响研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2019. (CHENG J K. Effect of chemical conditioning on sedimentation and consolidation behavior of mud slurry[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science & Technology, 2019. (in Chinese)CHENG J K. Effect of chemical conditioning on sedimentation and consolidation behavior of mud slurry[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science & Technology, 2019. (in Chinese) [14] 张跃军, 黄娟凤, 周 莉, 等. 不同离子性质絮凝剂在淤泥脱水中的脱水作用特征[J]. 精细化工,2007,24(9):903-909. (ZHANG Y J, HUANG J F, ZHOU L, et al. Dehydration characteristics of flocculants with different ionic properties and molecular weights in the processes of sludge dehydration[J]. Fine Chemicals,2007,24(9):903-909. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5214.2007.09.019ZHANG Y J, HUANG J F, ZHOU L, et al. Dehydration characteristics of flocculants with different ionic properties and molecular weights in the processes of sludge dehydration[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2007, 24(9): 903-909. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5214.2007.09.019 [15] 苏 凡. 极高含水率泥浆的絮凝吸水联合处理效果研究[D]. 南京: 河海大学, 2021. (SU F. Study on the combined treatment effect and dehydration mechanism of flocculation and water absorption for extremely high water content slurry[D]. Nanjing: Hohai University, 2021. (in Chinese)SU F. Study on the combined treatment effect and dehydration mechanism of flocculation and water absorption for extremely high water content slurry[D]. Nanjing: Hohai University, 2021. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: