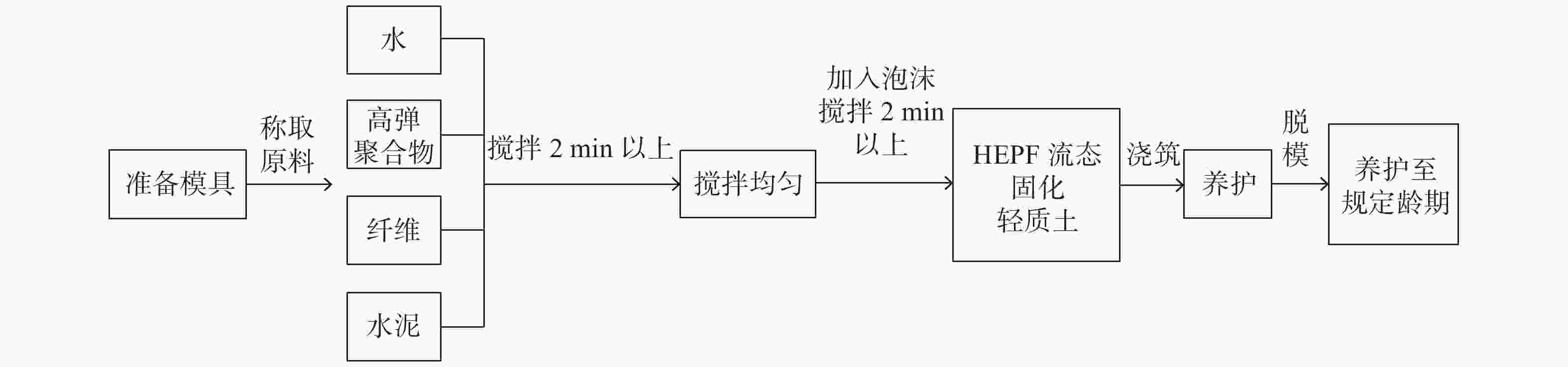
Durability of HEPF fluid-solidified lightweight soil
-
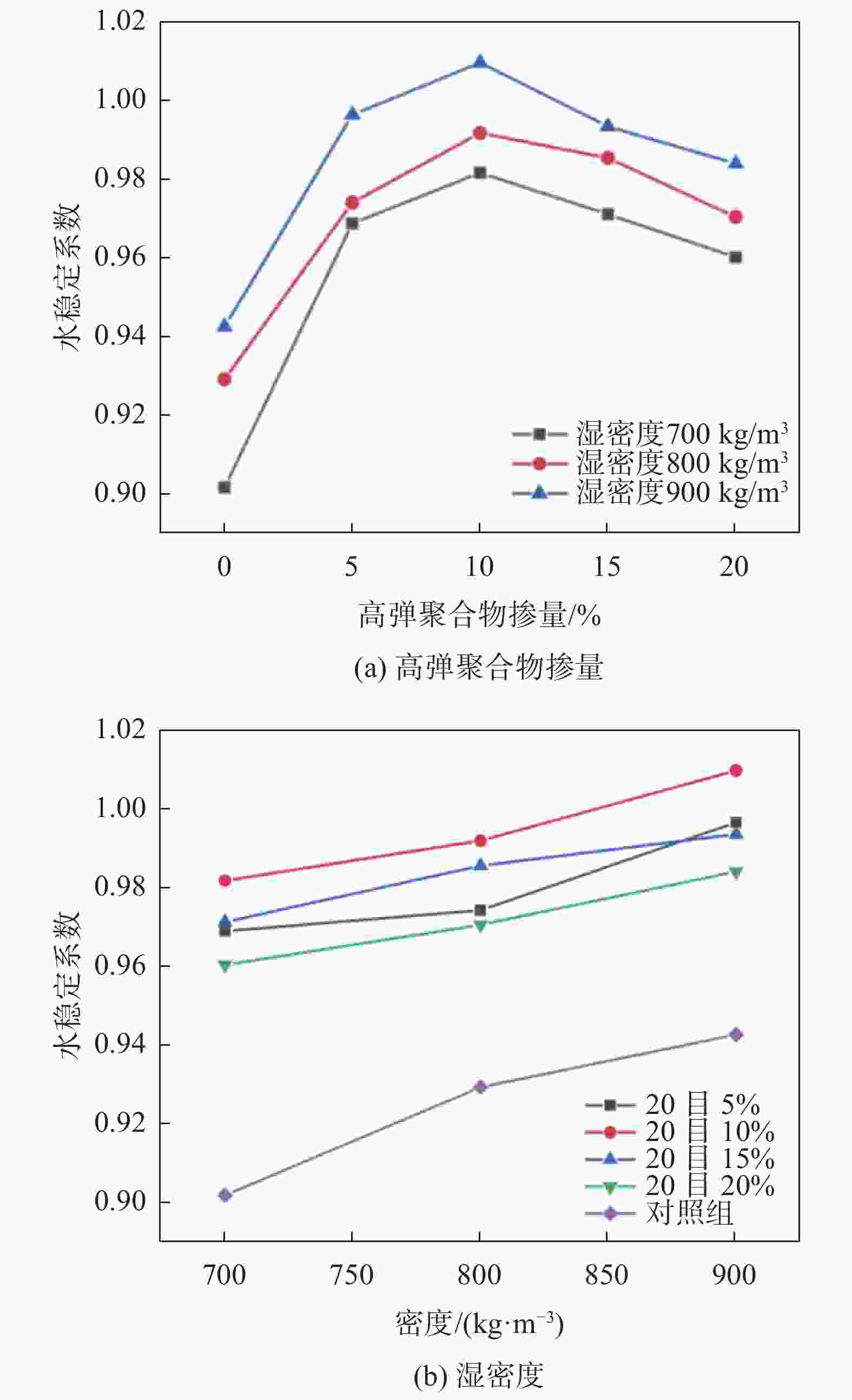
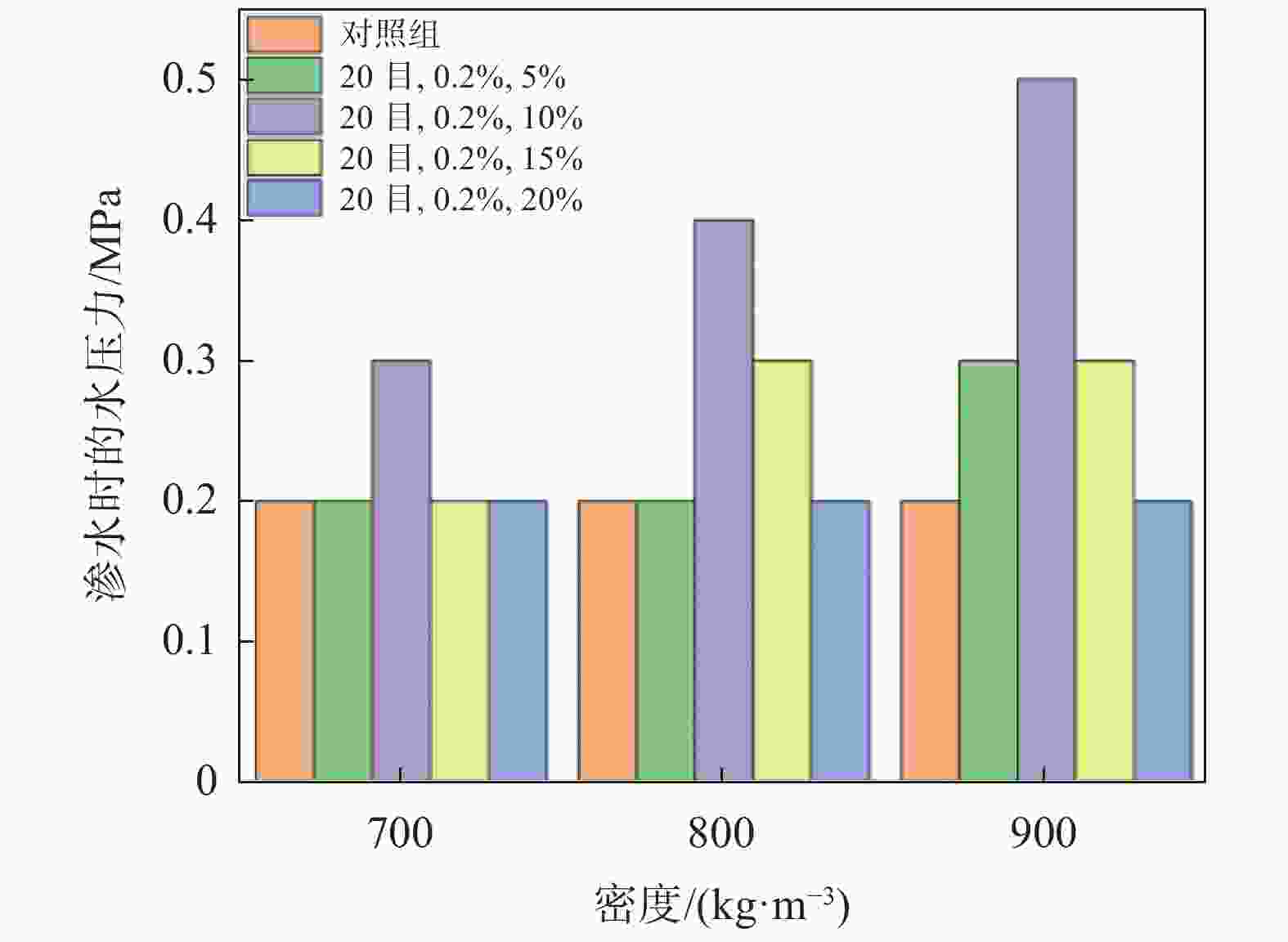
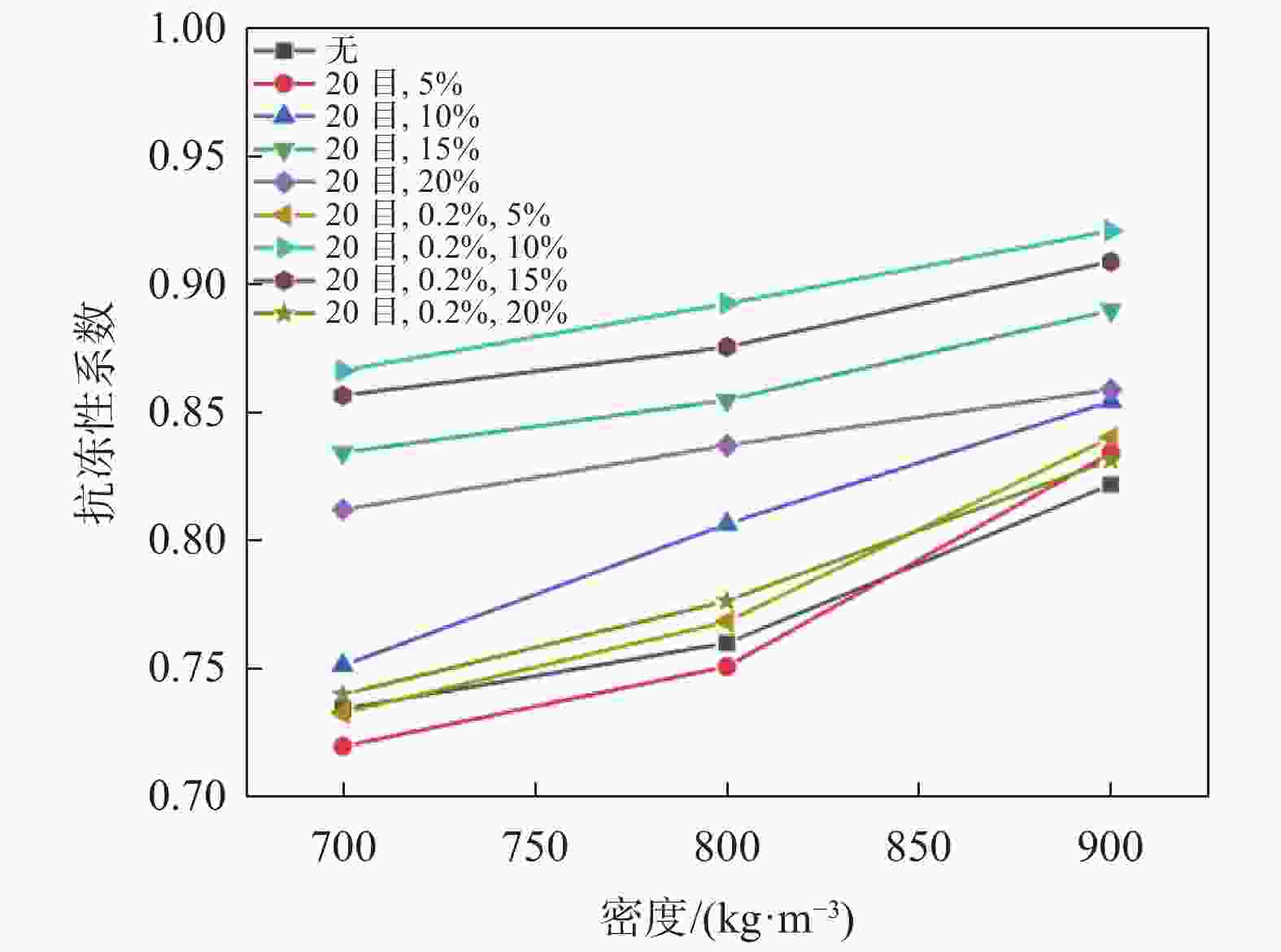
摘要: 为进一步提高泡沫轻质土的吸能减震效果和工程安全性,制备了新型高弹聚合物纤维(Highly Elastic Polymers Fiber,简称HEPF)流态固化轻质土材料,并通过试验分析了其水稳定性、抗渗性、抗冻融性和疲劳加载特性。试验结果表明,掺入高弹聚合物和纤维的HEPF流态固化轻质土较普通泡沫轻质土在材料的水稳定性、抗水渗透性和抗冻性能方面表现出显著优势。当高弹聚合物掺量10%、纤维掺量0.2%时,材料的水稳定系数均达到0.98以上,渗水压力较对照组提升了50%~150%,抗冻性系数显著提高。此外,材料在疲劳加载试验中展现出良好的耐久性和抗裂性能,有效地延长了其使用寿命。研究结果验证了HEPF流态固化轻质土在工程应用中的优越性能,证明其在交通荷载循环振动等恶劣条件下,具有良好的耐久性和环境适应性。Abstract: To further improve the energy absorption and shock absorption effects of foam light soil and enhance engineering safety, a novel Highly Elastic Polymer Fiber (HEPF) fluid-solidified lightweight soil material was developed. A series of tests were conducted to analyze its water stability, impermeability, freeze-thaw resistance, and fatigue loading characteristics. The test results show that HEPF fluid-solidified light soil, containing high elastic polymer and fiber, offers significant advantages in improving water stability, water permeability resistance, and frost resistance compared to common foam light soil. When the content of high-elastic polymer is 10% and the fiber content is 0.2%, the water stability coefficient exceeds 0.98, the seepage pressure increases by 50% to 150% compared to the control group, and the frost resistance coefficient significantly improves. Additionally, the material demonstrated good durability and crack resistance in fatigue loading tests, effectively extending its service life. The research findings validate the superior performance of HEPF fluid-solidified light soil in engineering applications, confirming its good durability and environmental adaptability under harsh conditions, such as traffic loads and cyclic vibrations.
-
Key words:
- fluid-solidified lightweight soil /
- high elastic polymer /
- durability /
- fatigue loading
-
表 1 P.O 42.5水泥物理力学性能
密度 /(kg∙m−³) 标准稠度/% 凝结时间/min 3 d抗压强度 /MPa 3 d抗折强度 /MPa 28 d抗压强度 /MPa 28 d抗折强度 /MPa 初凝 终凝 3100 28.5 173 201 21.2 6.9 54.3 10.1 表 2 水泥的化学成分及性能
成分 CaO SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 MgO SO3 总碱量 烧失量 含量 /% 64.3 21.6 4.73 3.68 2.59 0.3 0.63 2.89 表 3 高弹聚合物颗粒主要技术参数
密度
/(kg∙m−³)加热
减量 /%灰分
/%含铁量
/%纤维
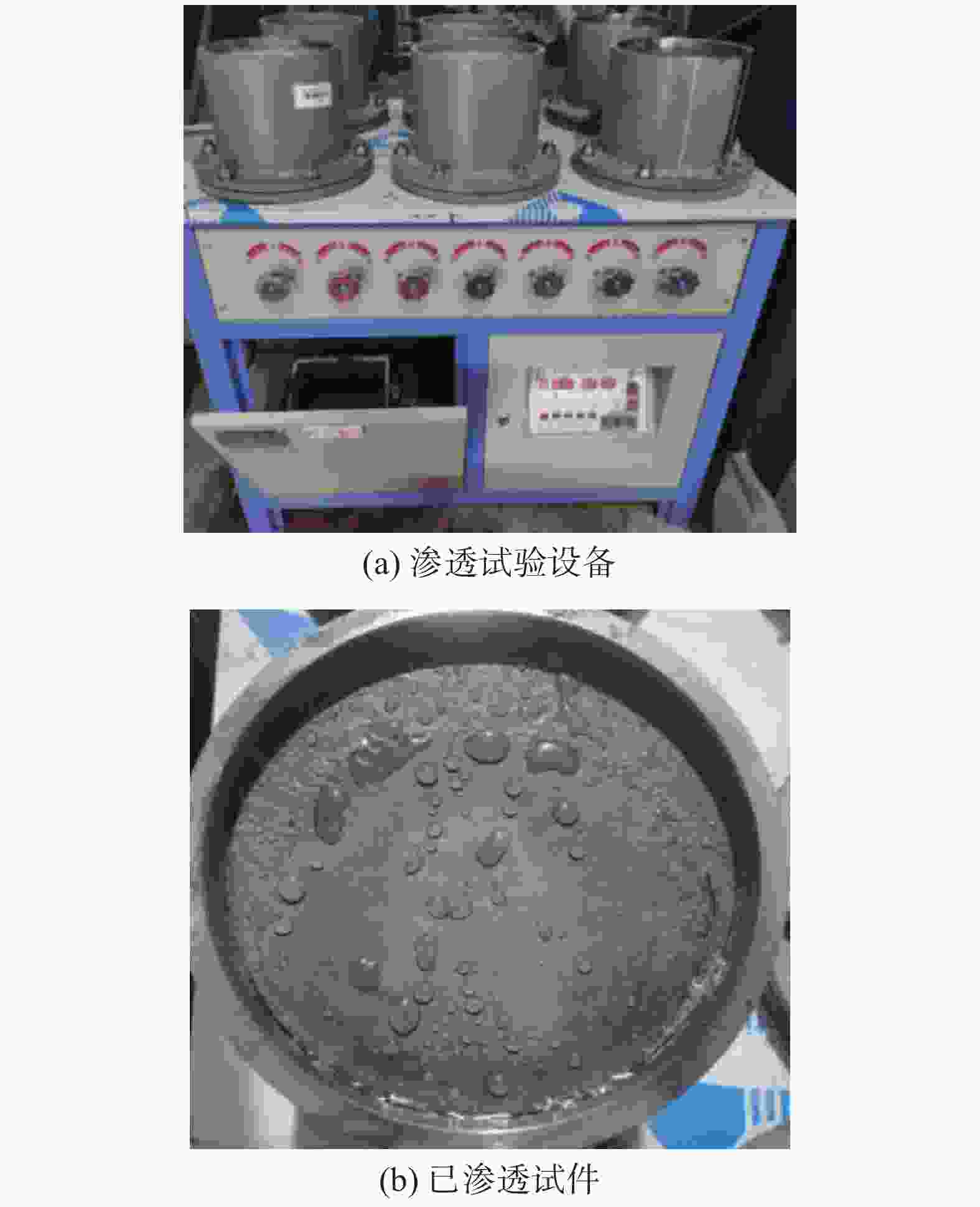
掺量/%筛余物
/%750 0.62 8.75 0.029 0 0.014 表 4 聚丙烯纤维主要技术参数
抗拉强度
/MPa弹性模量
/GPa拉伸
极限/%纤维直径
/μm比重 吸水
性抗低
温性抗酸
碱性导热
性>486 >4.8 >15 18~48 0.91 无 强 高 低 表 5 试验参数表
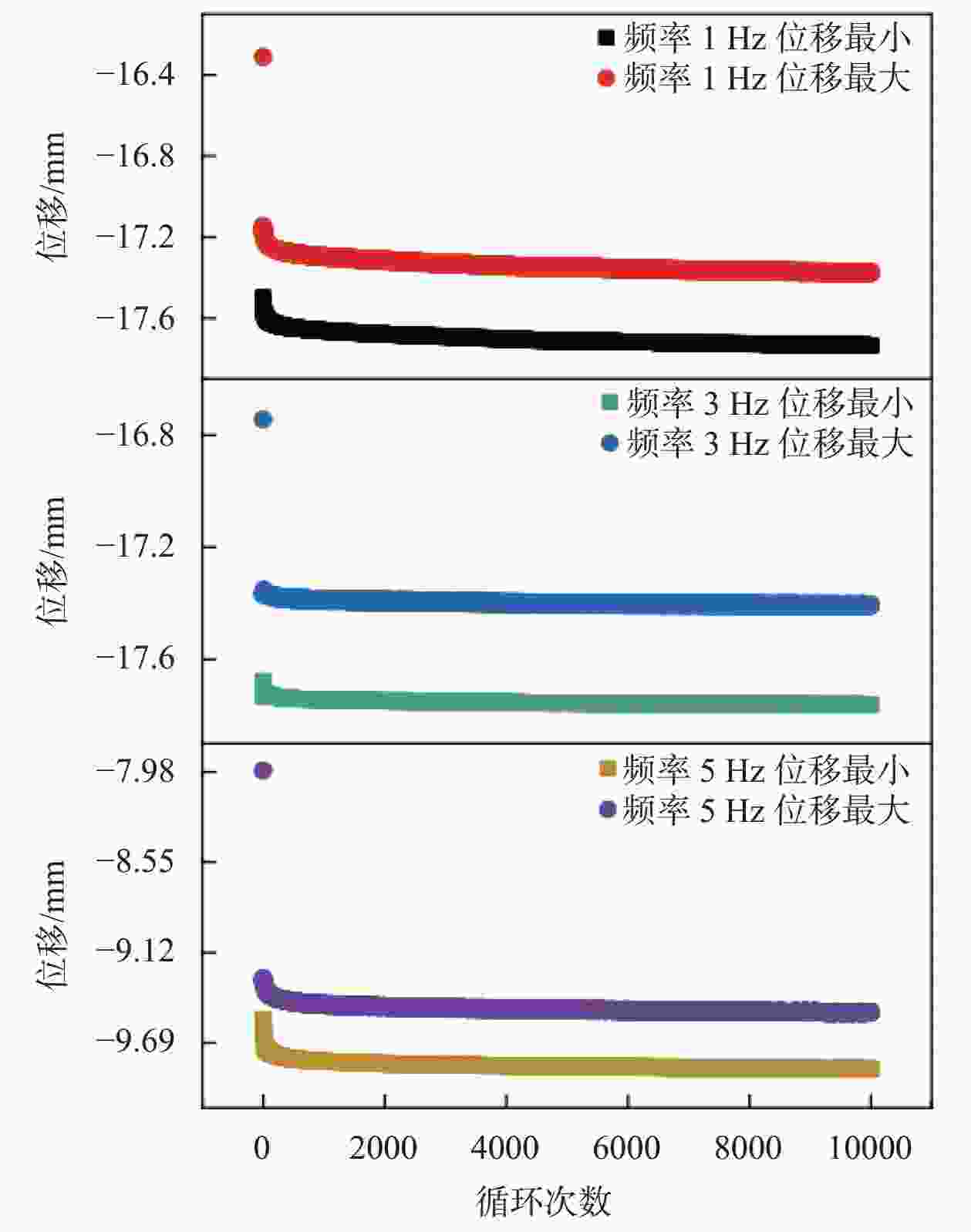
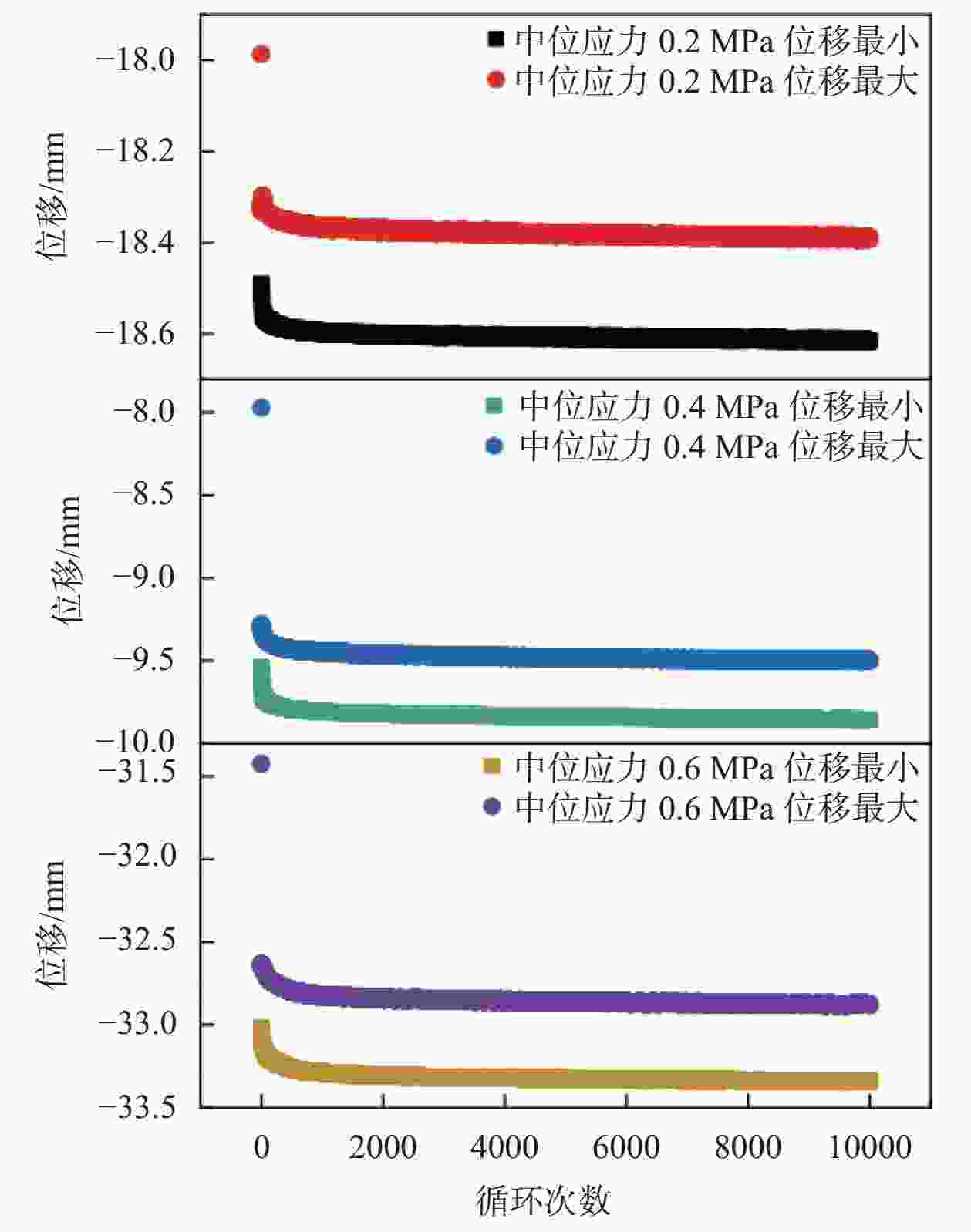
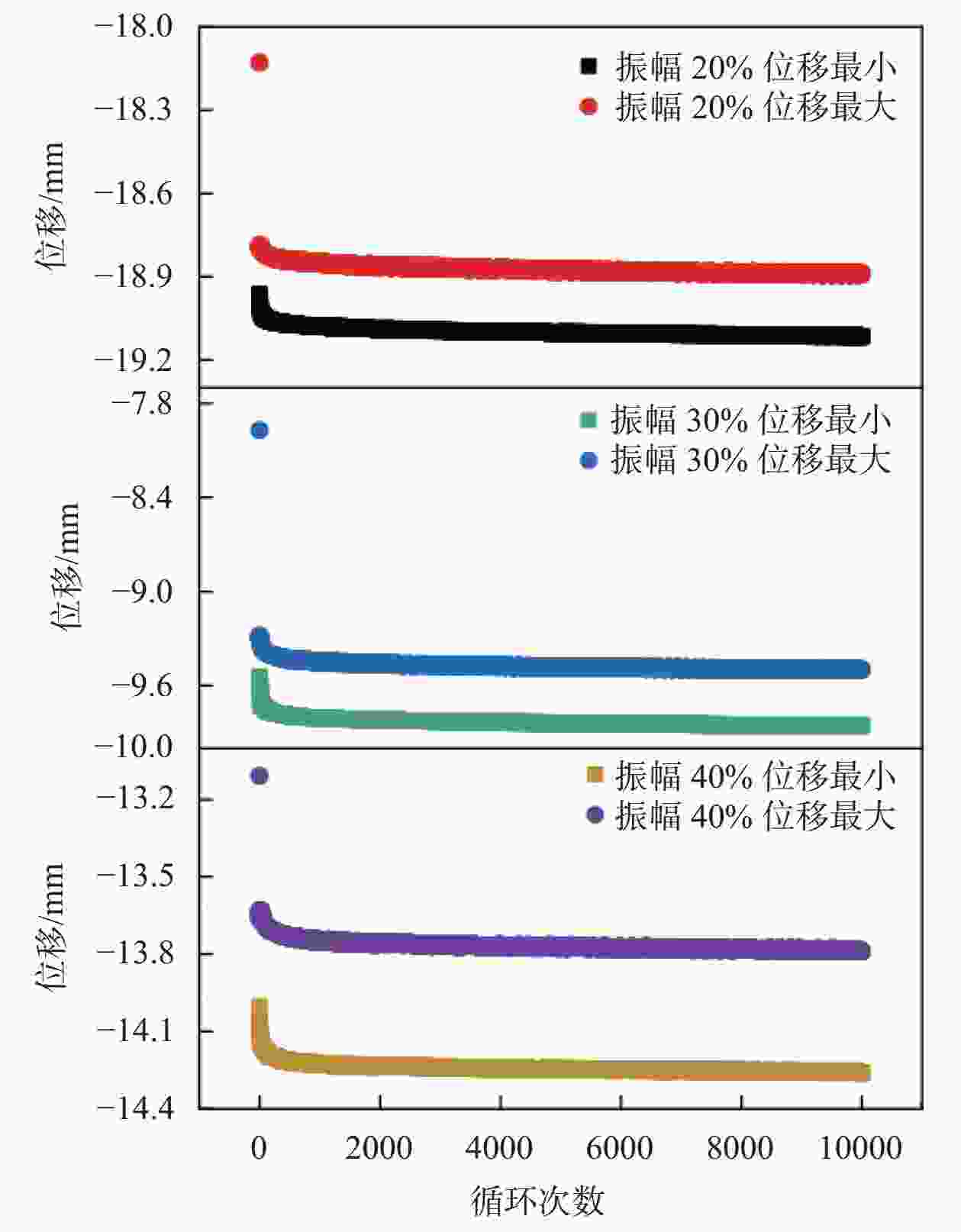
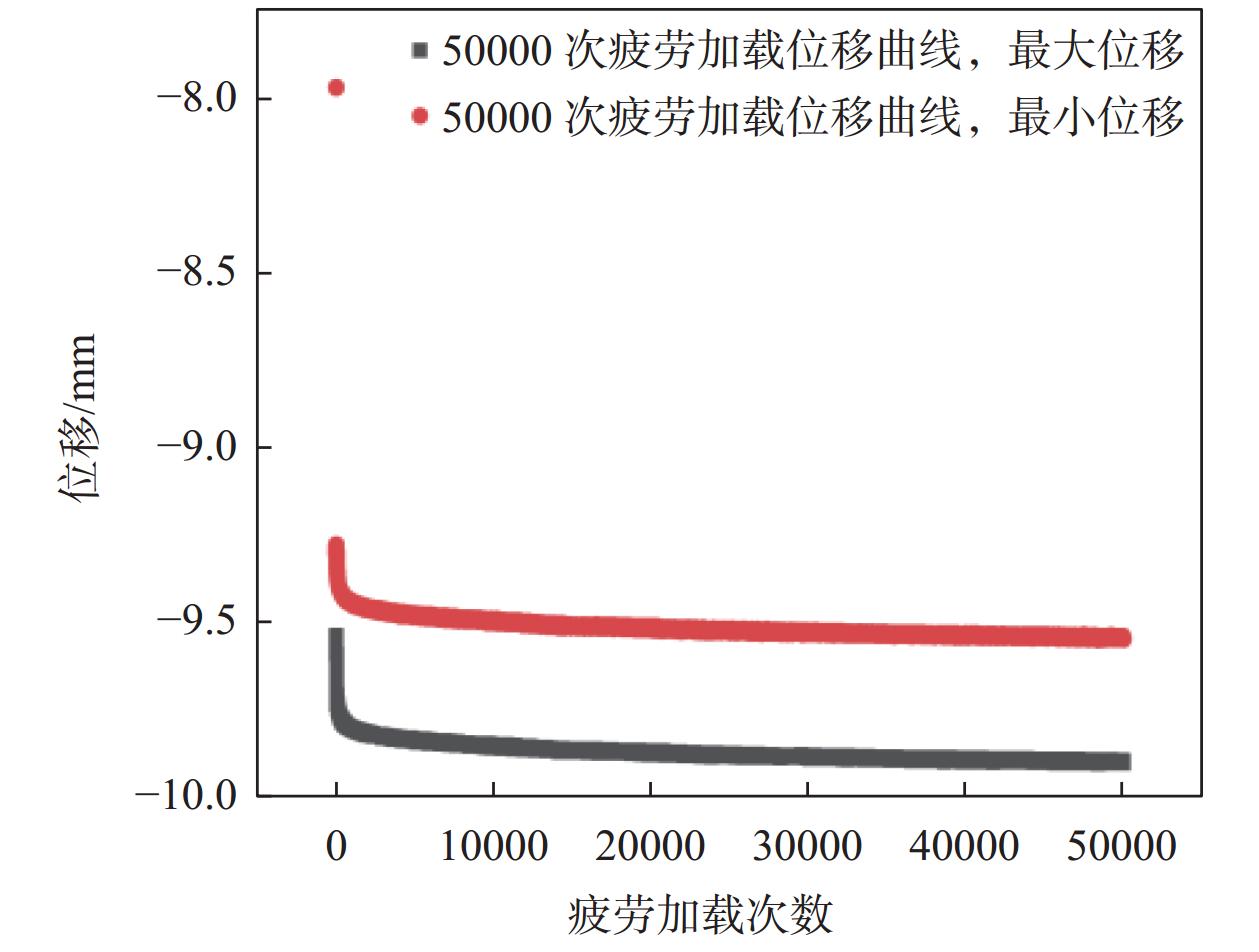
试验 频率/Hz 中位应力
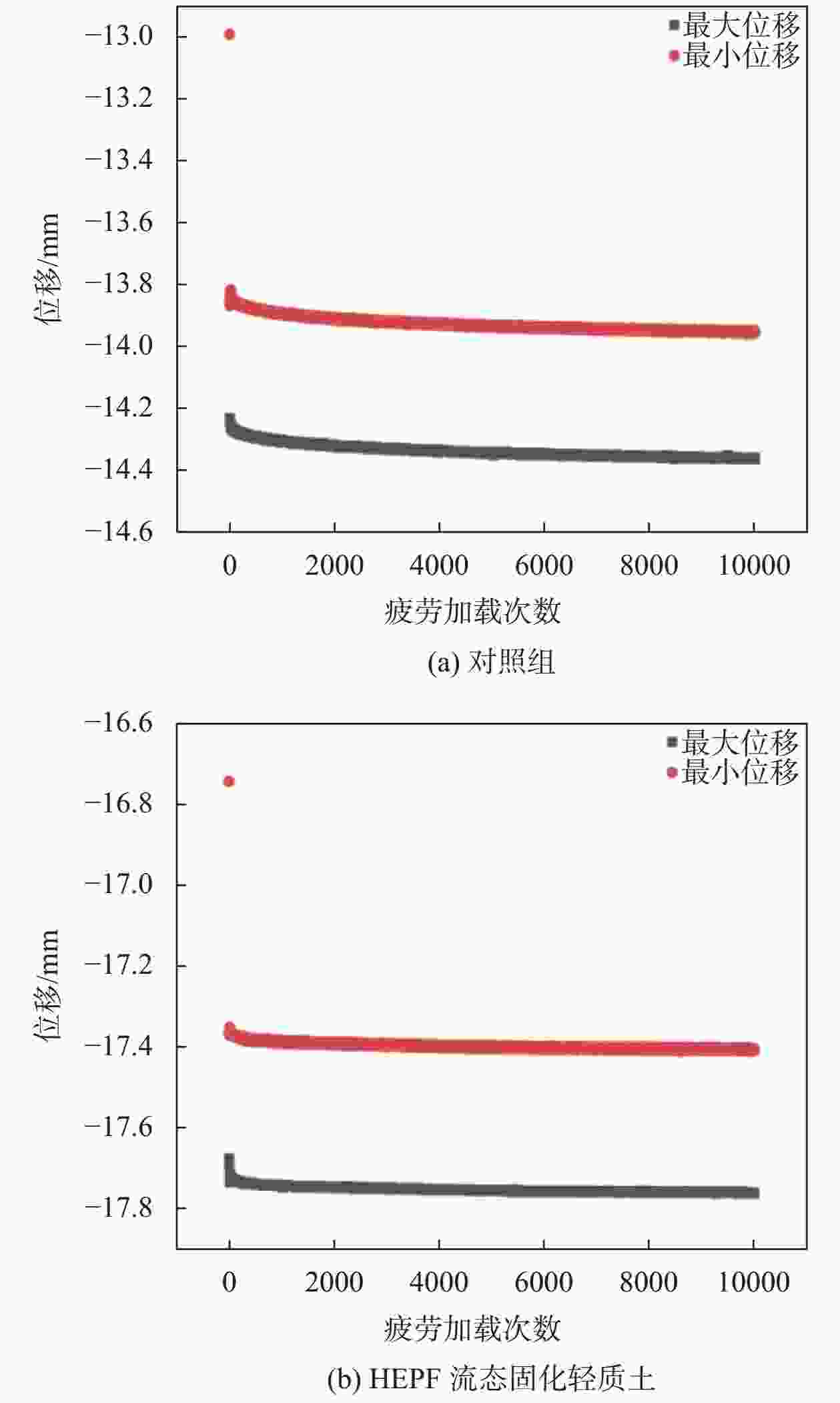
/MPa振幅/% 次数 频率试验 1, 3, 5 0.4 30 10000 振幅试验 5 0.4 20, 30, 40 10000 中位应力试验 5 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 30 10000 次数试验 5 0.4 30 10000, 30000, 50000 表 6 两种工况下疲劳加载试验的位移变化量
对照组 HEPF流态固化轻质土 位移最小 位移最大 位移最小 位移最大 0.659% 0.765% 0.441% 0.483% 注:中位应力:0.4MPa ;频率:3Hz ;振幅:30% ;次数:10000次。 -
[1] ZHANG H B, WANG J, WANG C, et al. Using foamed concrete layer to optimize the design of pavement and subgrade structures: from the perspectives economy and durability[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2023, 48(10): 12859-12874. doi: 10.1007/s13369-023-07606-1 [2] LIU M P, WANG J, WANG C, et al. Stress-solid materials-voids interaction of foamed concrete in isotropic compression[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 358: 129468. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.129468 [3] 牛金龙, 施卫星. 房屋建筑顶层采用橡胶支承的消能减震[J]. 建筑结构, 2002, 32(6): 63-65. (NIU J L, SHI W X. Reduction vibration with rubber shock absorber under top storey in the building[J]. Building Structure, 2002, 32(6): 63-65. (in Chinese)NIU J L, SHI W X. Reduction vibration with rubber shock absorber under top storey in the building[J]. Building Structure, 2002, 32(6): 63-65. (in Chinese) [4] SHI M H, YIN G S, ZHANG W Q, et al. Study on key parameters and design methods for the density-mix proportion of rubber-foamed concrete[J]. Buildings, 2024, 14(8): 2468. doi: 10.3390/buildings14082468 [5] DAMIANI R M, SONG Y, LANGE D A. Effect of waste rubber inclusion on the microstructure and mechanical performance of low-density foam concrete[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2024, 36(7): 04024168. doi: 10.1061/JMCEE7.MTENG-16750 [6] WANG R, GAO P W, TIAN M H, et al. Experimental study on mechanical and waterproof performance of lightweight foamed concrete mixed with crumb rubber[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 209: 655-664. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.03.157 [7] BENAZZOUK A, DOUZANE O, MEZREB K, et al. Physico-mechanical properties of aerated cement composites containing shredded rubber waste[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2006, 28(7): 650-657. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2006.05.006 [8] 王亚威. 轻质混凝土耐久性及其提升技术试验研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2017. (WANG Y W. Experimental study on durability and improvement techniques for the lightweight concrete[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017. (in Chinese)WANG Y W. Experimental study on durability and improvement techniques for the lightweight concrete[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017. (in Chinese) [9] BATOOL F, BINDIGANAVILE V. Evaluation of thermal conductivity of cement-based foam reinforced with polypropylene fibers[J]. Materials and Structures, 2020, 53(1): 13. doi: 10.1617/s11527-020-1445-7 [10] JAFFAL A N, HILAL A A, MAHMOUD A S, et al. Investigating the possibility of producing fiber reinforced foamed concrete for structural applications[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2024, 3009(1): 030088. [11] BAYRAKTAR O Y, KAPLAN G, GENCEL O, et al. Physico-mechanical, durability and thermal properties of basalt fiber reinforced foamed concrete containing waste marble powder and slag[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 288: 123128. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123128 [12] KAZMI S M S, MUNIR M J, WU Y F, et al. Effect of different aggregate treatment techniques on the freeze-thaw and sulfate resistance of recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2020, 178: 103126. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2020.103126 [13] 王立新, 范飞飞, 汪 珂, 等. 地铁车站不同减震层的减震机理及性能分析[J]. 铁道标准设计, 2022, 66(5): 131-139. (WANG L X, FAN F F, WANG K, et al. Damping mechanism and performance analysis of different shock absorption layers in metro station[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2022, 66(5): 131-139. (in Chinese)WANG L X, FAN F F, WANG K, et al. Damping mechanism and performance analysis of different shock absorption layers in metro station[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2022, 66(5): 131-139. (in Chinese) [14] ELTAYEB E, MA X, ZHUGE Y, et al. Influence of rubber particles on the properties of foam concrete[J]. Journal of Building Engineering, 2020, 30: 101217. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101217 [15] 米天煜. 废胶粉泡沫混凝土设计及疲劳性能研究[D]. 赣州: 江西理工大学, 2023. (MI T Y. Design and fatigue properties of waste rubber powder foamconcrete[D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2023. (in Chinese)MI T Y. Design and fatigue properties of waste rubber powder foamconcrete[D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2023. (in Chinese) [16] 吴 昊, 龙广成, 杨 恺, 等. PE纤维与细橡胶颗粒对泡沫混凝土弯曲韧性的影响[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2024, 27(3): 206-214. (WU H, LONG G C, YANG K, et al. Effects of PE fiber and fine rubber particles on flexural toughness of foam concrete[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2024, 27(3): 206-214. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2024.03.003WU H, LONG G C, YANG K, et al. Effects of PE fiber and fine rubber particles on flexural toughness of foam concrete[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2024, 27(3): 206-214. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2024.03.003 [17] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 蒸压加气混凝土性能试验方法: GB/T 11969—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009. (General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, China National Standardization Administration. Test methods of autoclaved aerated concrete: GB/T 11969—2008[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2009. (in Chinese)General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, China National Standardization Administration. Test methods of autoclaved aerated concrete: GB/T 11969—2008[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2009. (in Chinese) [18] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 普通混凝土长期性能和耐久性能试验方法标准: GB/T 50082—2024[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社. (Ministry of Housing and Urban Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for test methods of long-term performance and durability of ordinary concrete: GB/T 50082—2024[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press. (in Chinese)Ministry of Housing and Urban Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for test methods of long-term performance and durability of ordinary concrete: GB/T 50082—2024[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press. (in Chinese) [19] 姚义胜. 基于泡沫轻质土复合路基的半刚性路面结构优化及动力响应研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2021. (YAO Y S. Semi-rigid pavement structure optimization and dynamic response study based on foam lightweight soil composite subgrade[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2021. (in Chinese)YAO Y S. Semi-rigid pavement structure optimization and dynamic response study based on foam lightweight soil composite subgrade[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2021. (in Chinese) -






 下载:
下载: