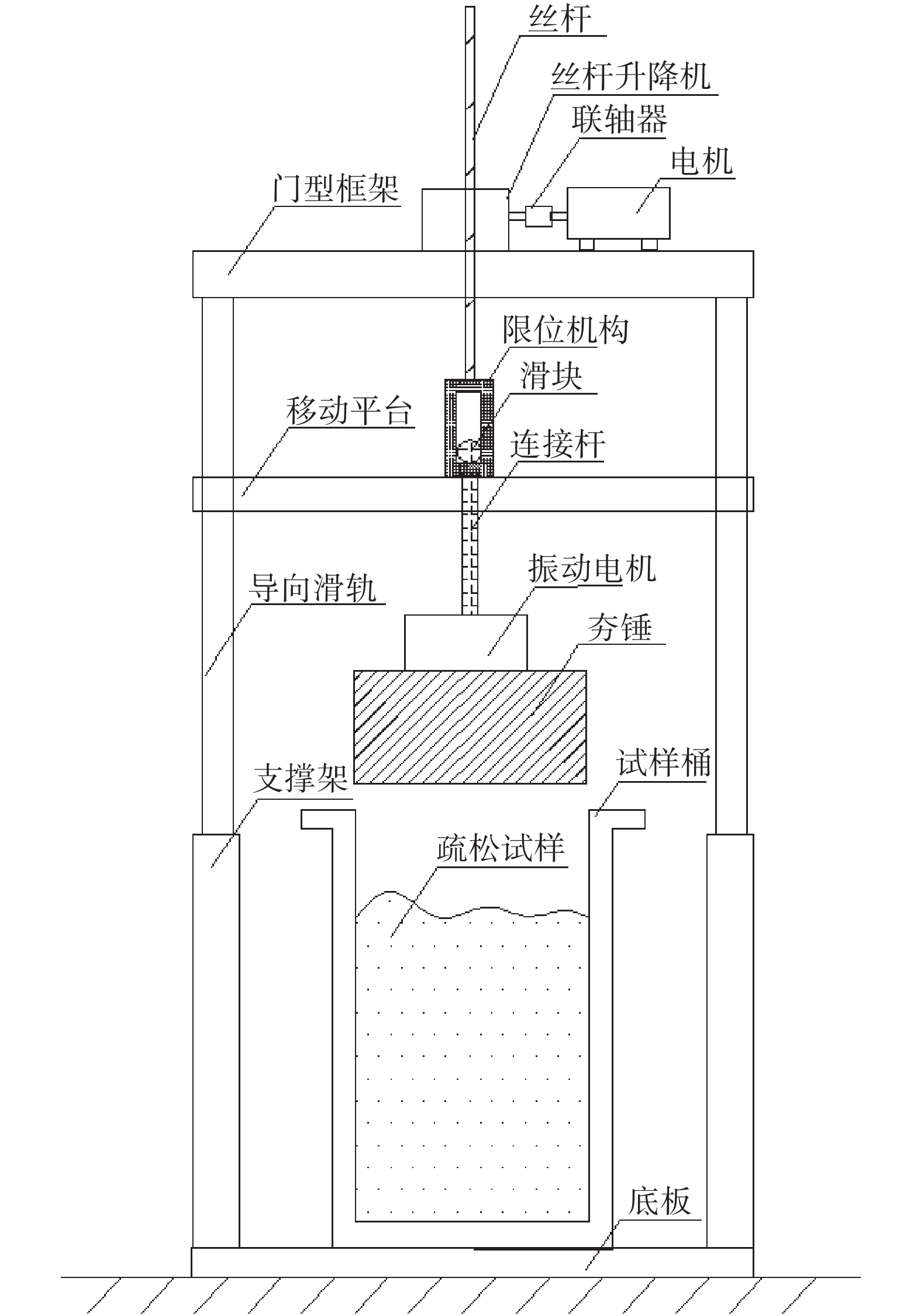
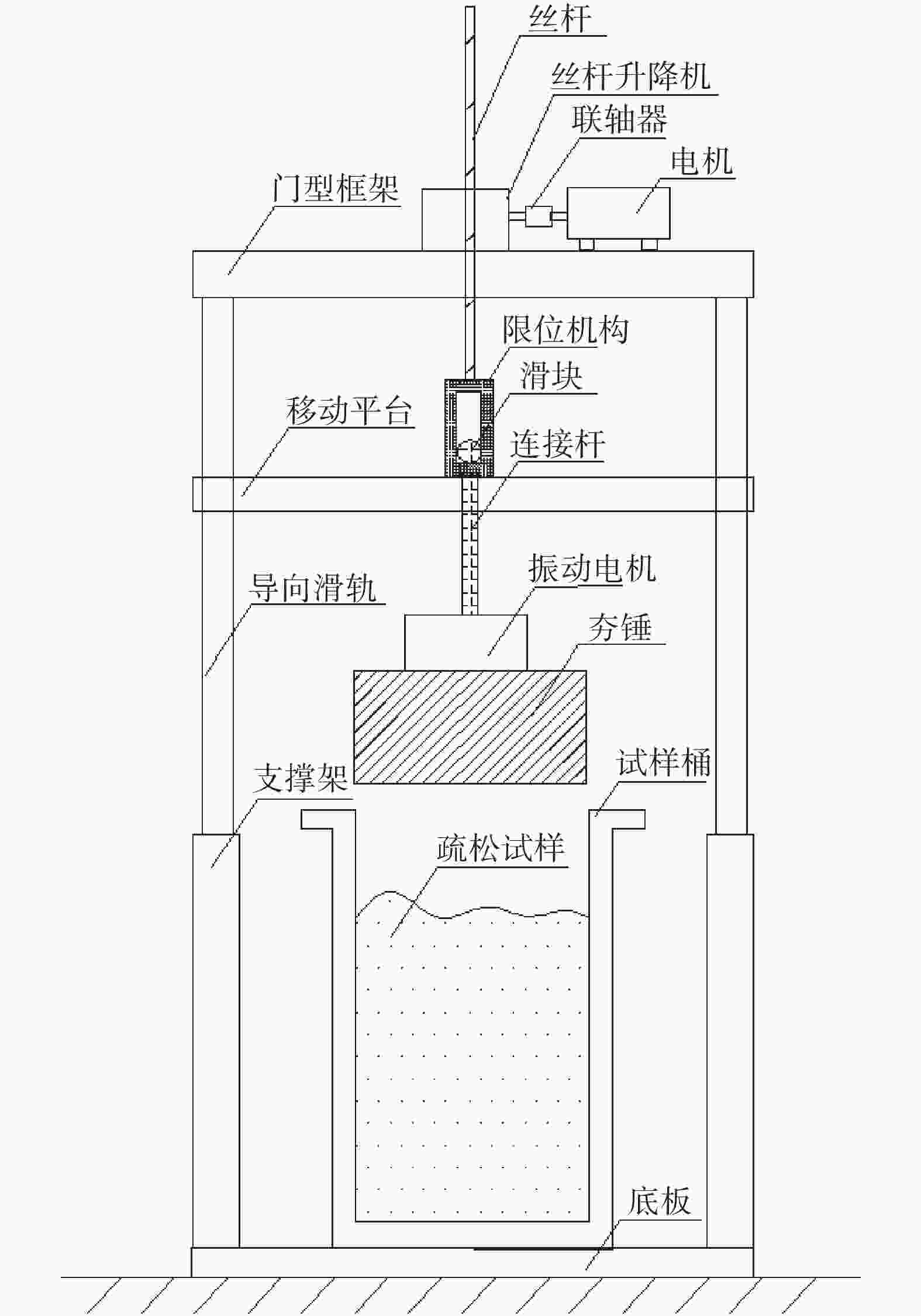
Development of high-precision drilling model test platform for sand and gravel formations
-
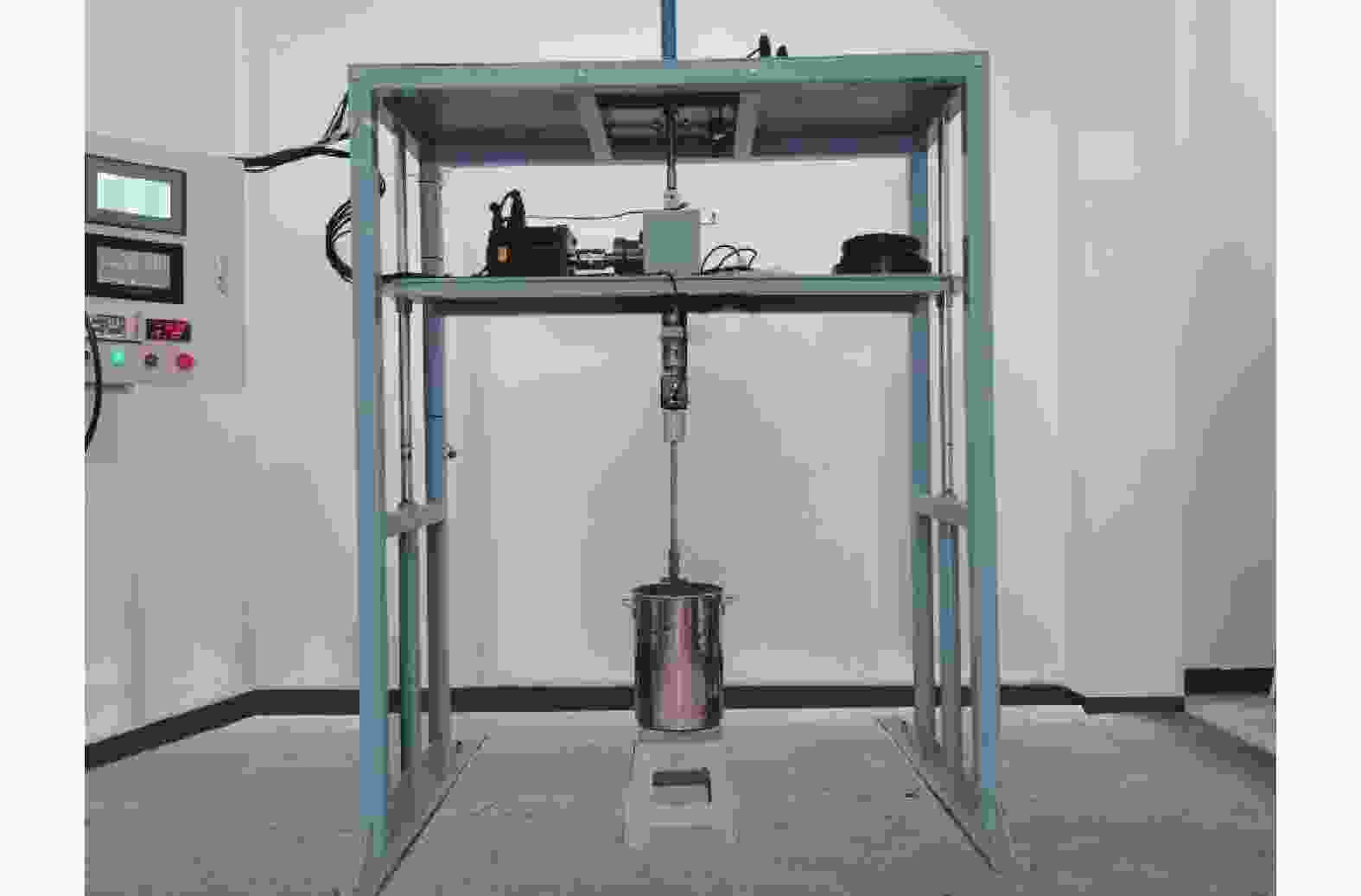
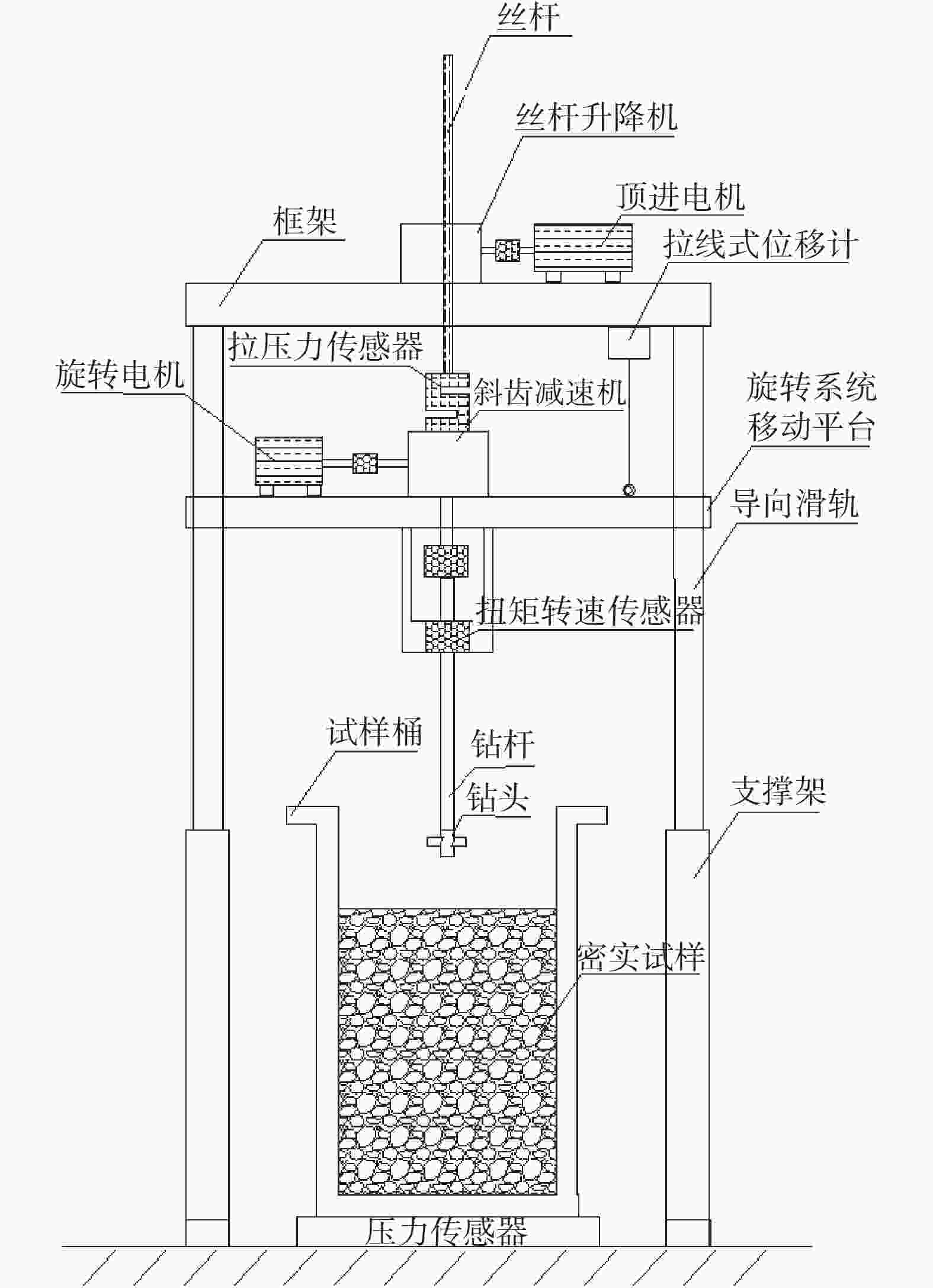
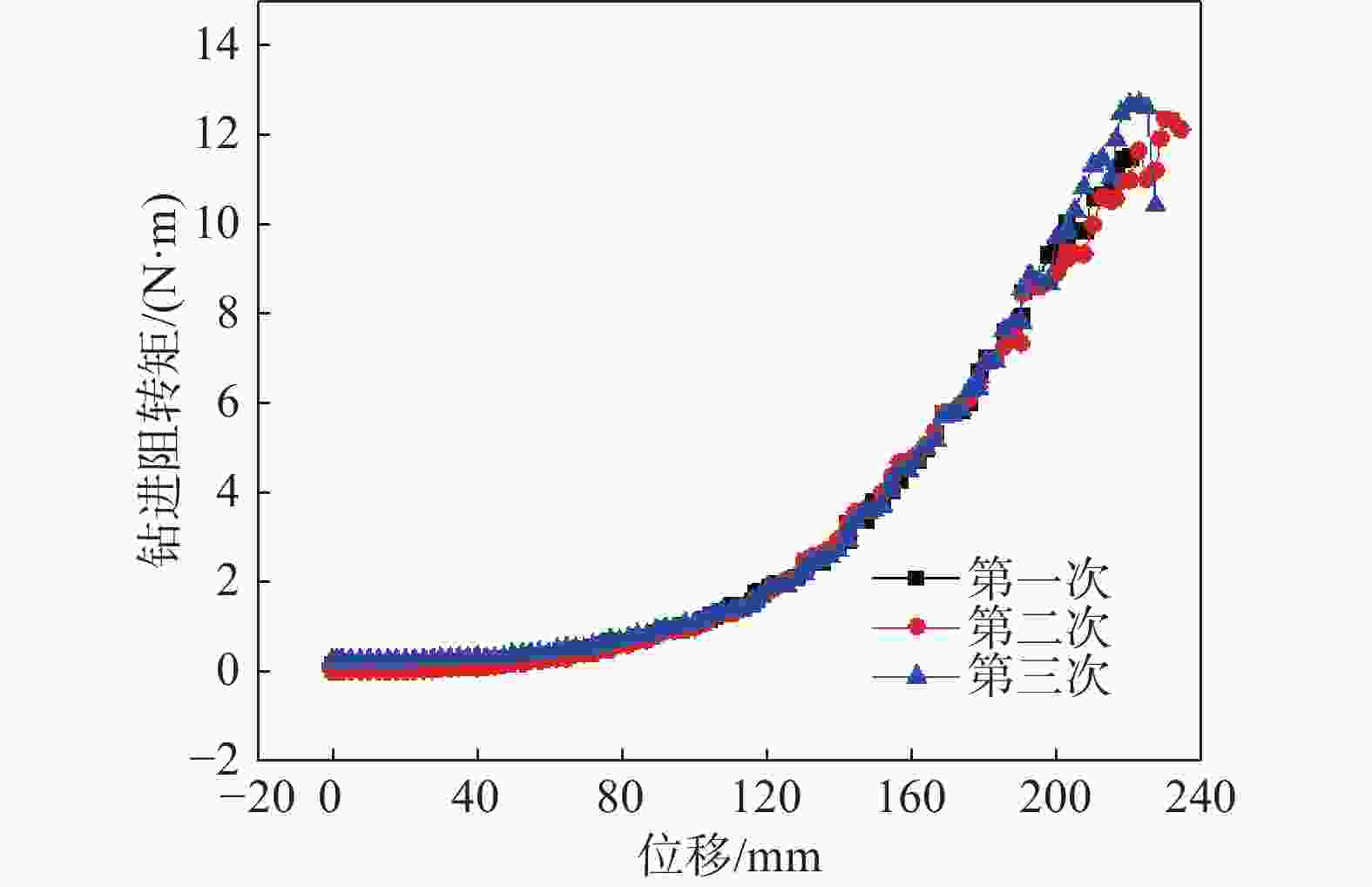
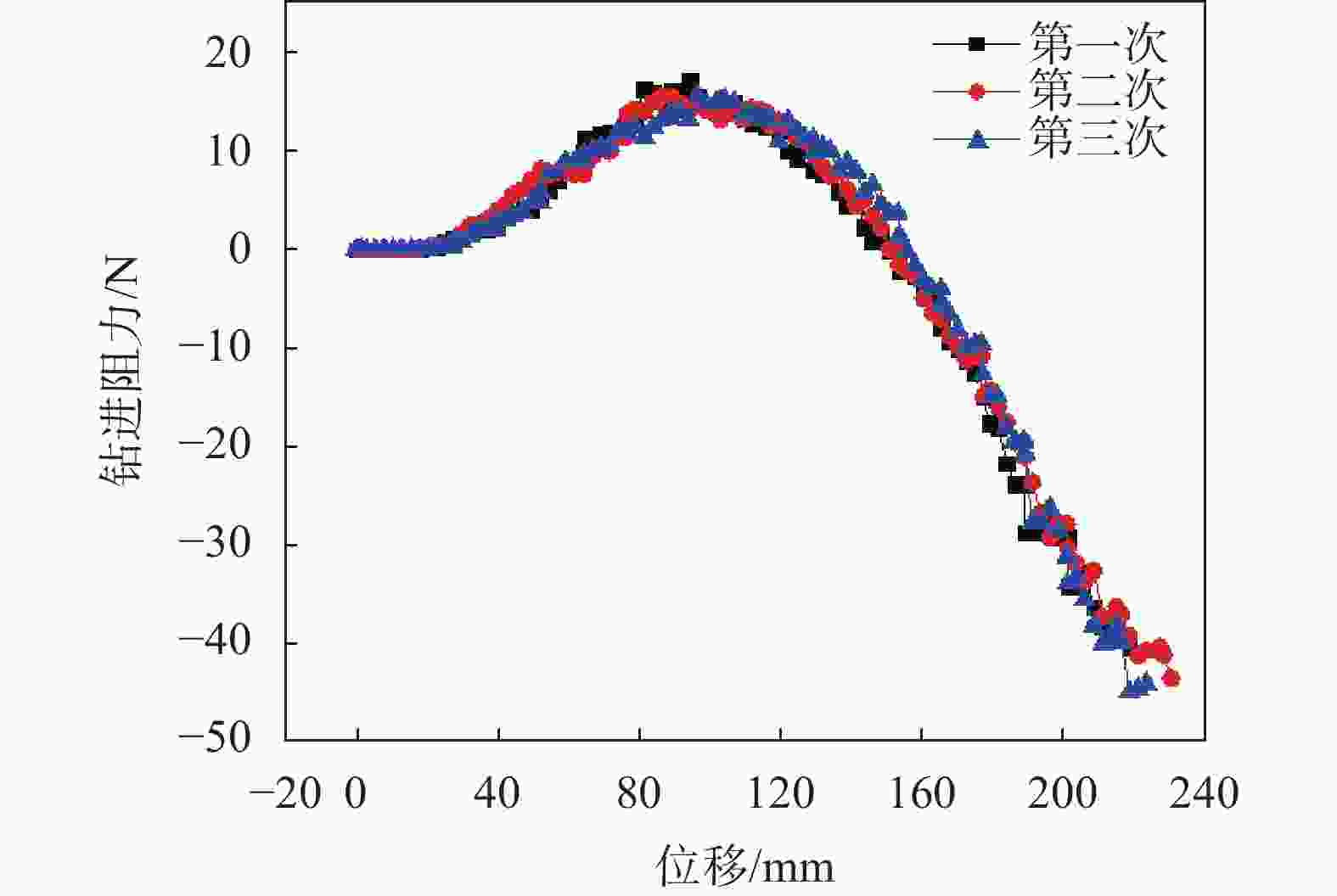
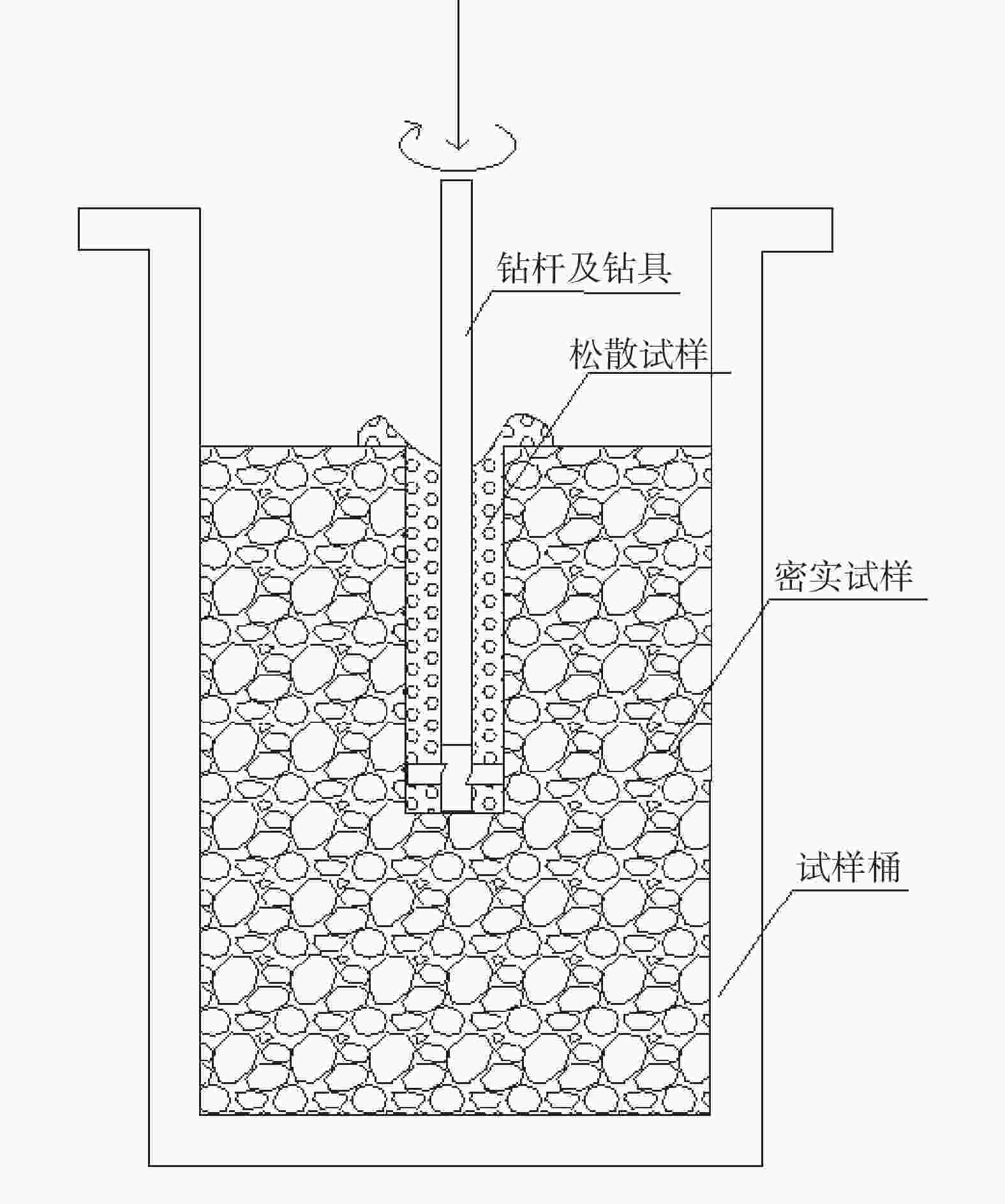
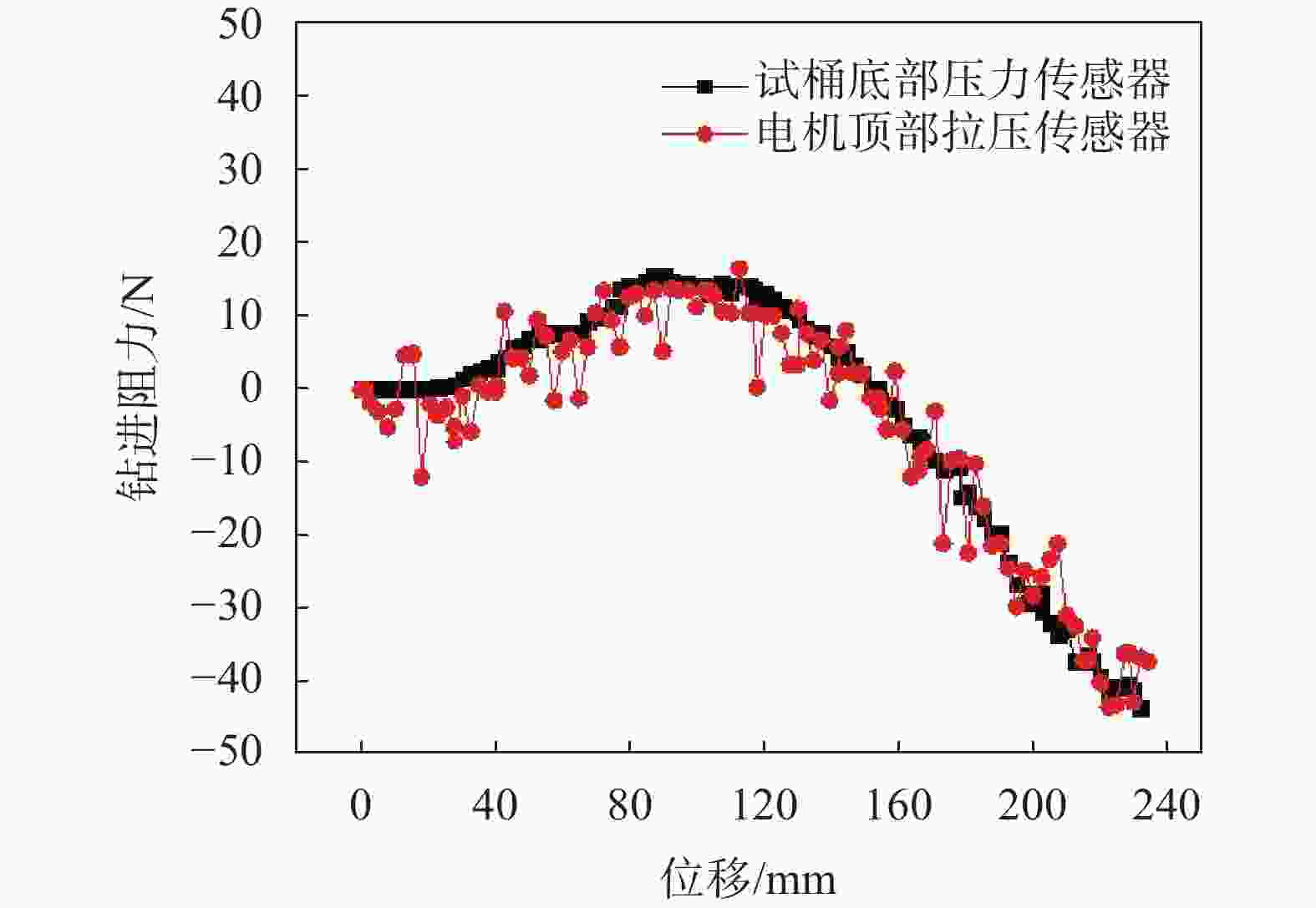
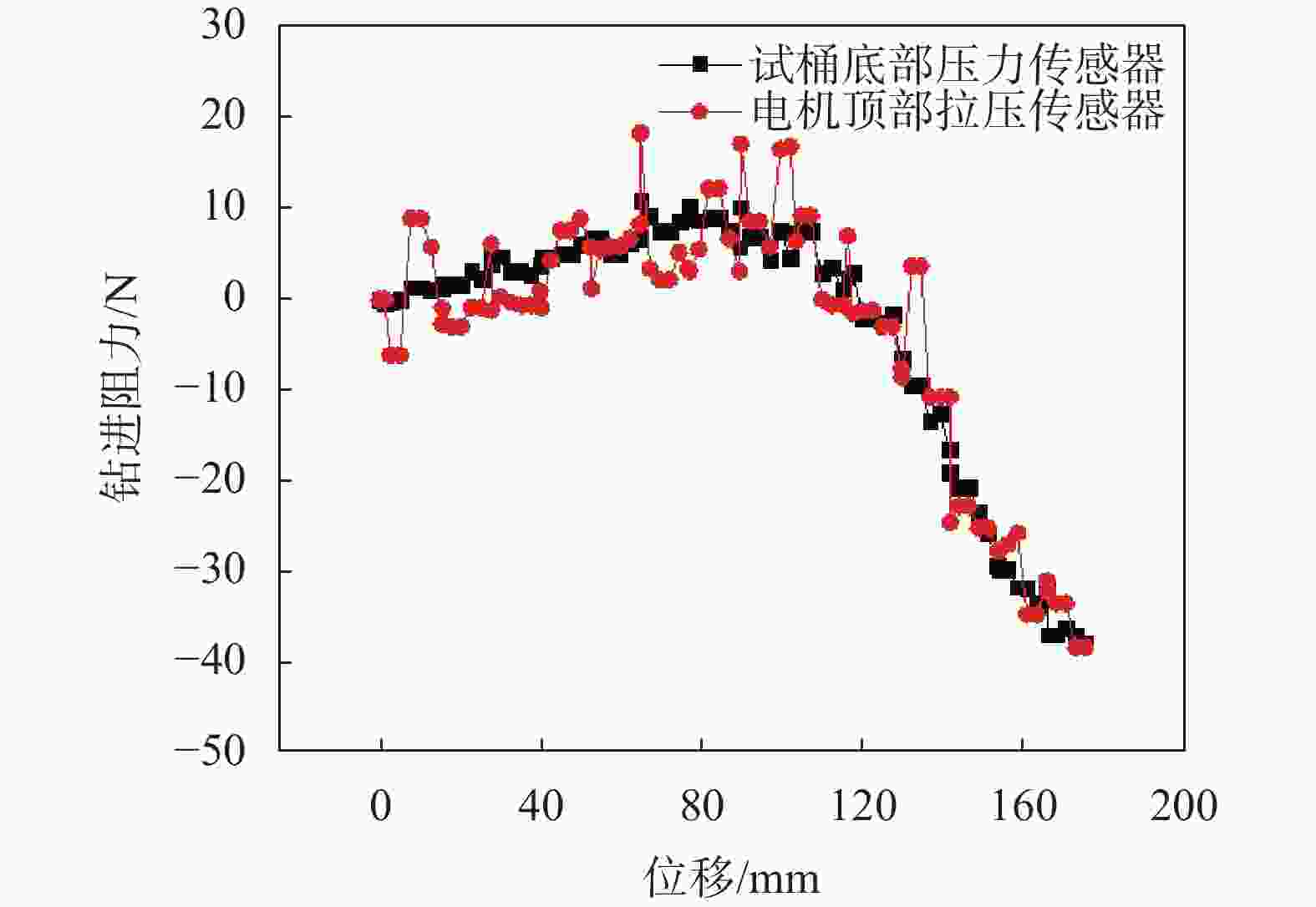
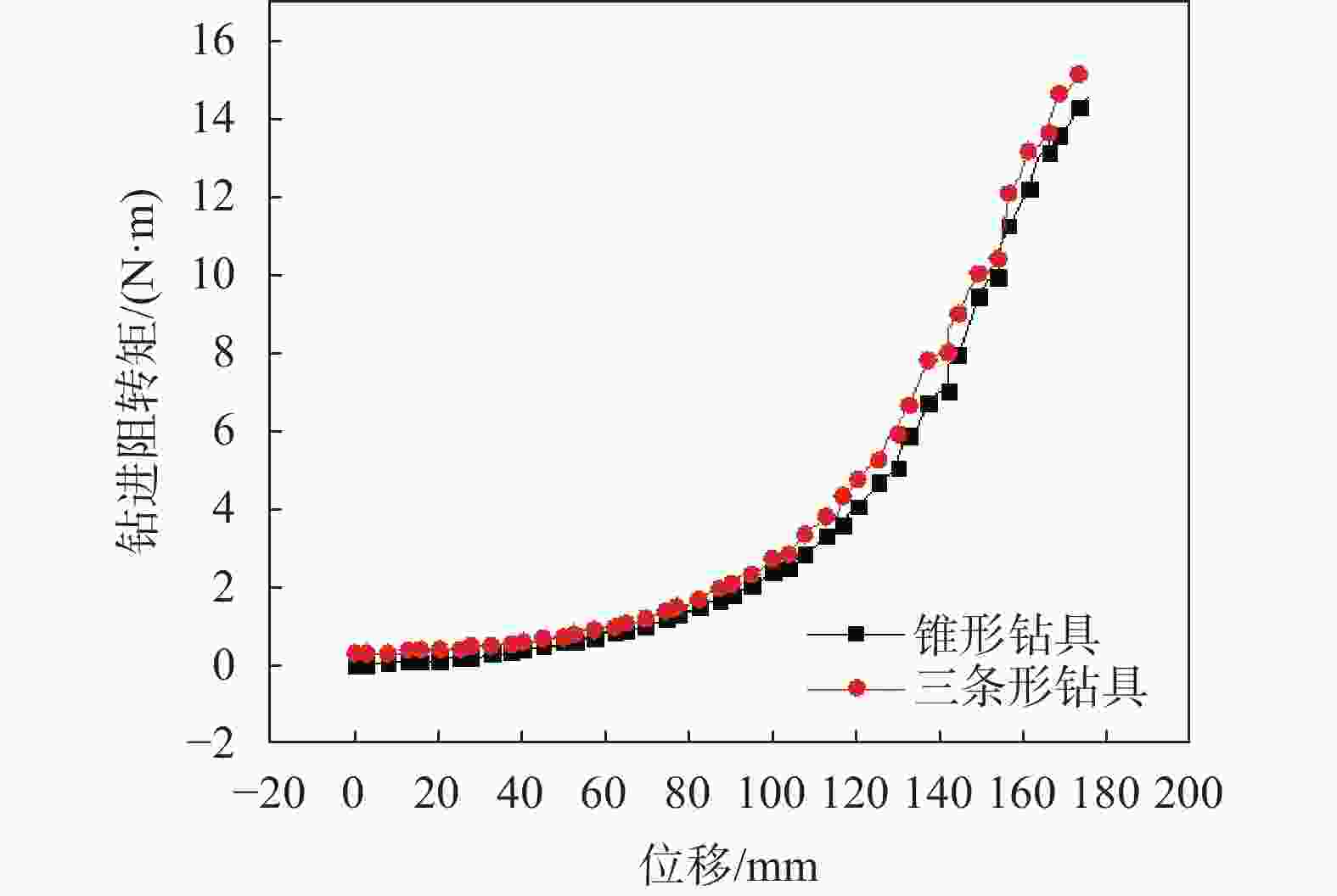
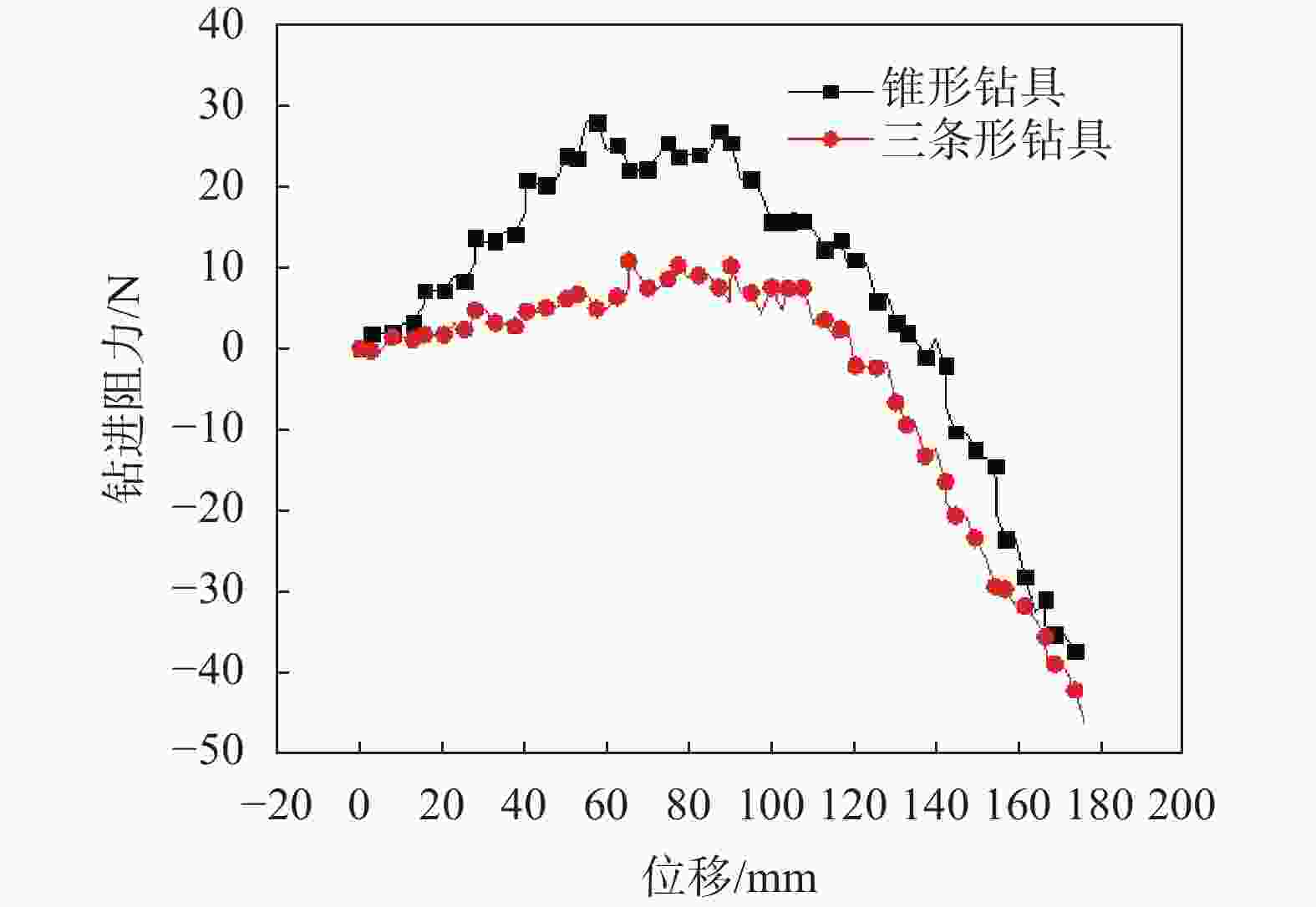
摘要: 相比一般静力学模型试验,钻进类模型试验需考虑动力学问题,试验理论复杂,控制条件严格。在静力学相似比判据的基础上,推导了钻进类模型试验的动力学相似比判据,并研制了匹配的模型试验平台。该平台采用表面振动压实法制备试样,通过精细控制振动条件,克服传统落雨法、人工夯实法的不足,使试样达到最大干密度,密实度与均匀性更高。针对监测数据稳定性要求高的问题,试验在试样桶底部设压力监测传感器监测钻进阻力,消除导向滑轨与旋转钻机平台滑动摩擦力的影响。新方法监测值更稳定,残差平方和约为传统方法的 1/3。试验表明,新型模型试验平台及方法能克服现有技术不足,分辨细微试验条件变化对钻进效率的影响,可用于成桩钻具适应性及钻具选型等研究。Abstract: Compared to general static model tests, drilling type model tests require consideration of dynamic issues. The test theories are complex and the test control conditions are strict. On the basis of the static similarity ratio criterion, this article derives the dynamic similarity ratio criterion for drilling model tests and develops a matching model test platform. The platform uses surface vibration compaction method to prepare samples. By finely controlling the vibration conditions, it overcomes the shortcomings of traditional rain method and manual compaction method, and achieves the maximum dry density, higher density and uniformity of the samples. To address the issue of high stability requirements for monitoring data, a pressure monitoring sensor was installed at the bottom of the sample barrel to monitor drilling resistance and eliminate the influence of sliding friction between the guide rail and the rotary drilling platform. The new method provides more stable monitoring values, with residual squared values approximately one-third that of traditional methods. The experiment shows that the new model experimental platform and method can overcome the shortcomings of existing technology, distinguish the influence of subtle changes in experimental conditions on drilling efficiency, and can be used for research on the adaptability of pile drilling tools and tool selection.
-
Key words:
- drilling /
- sand and gravel stratum /
- model test /
- similarity ratio
-
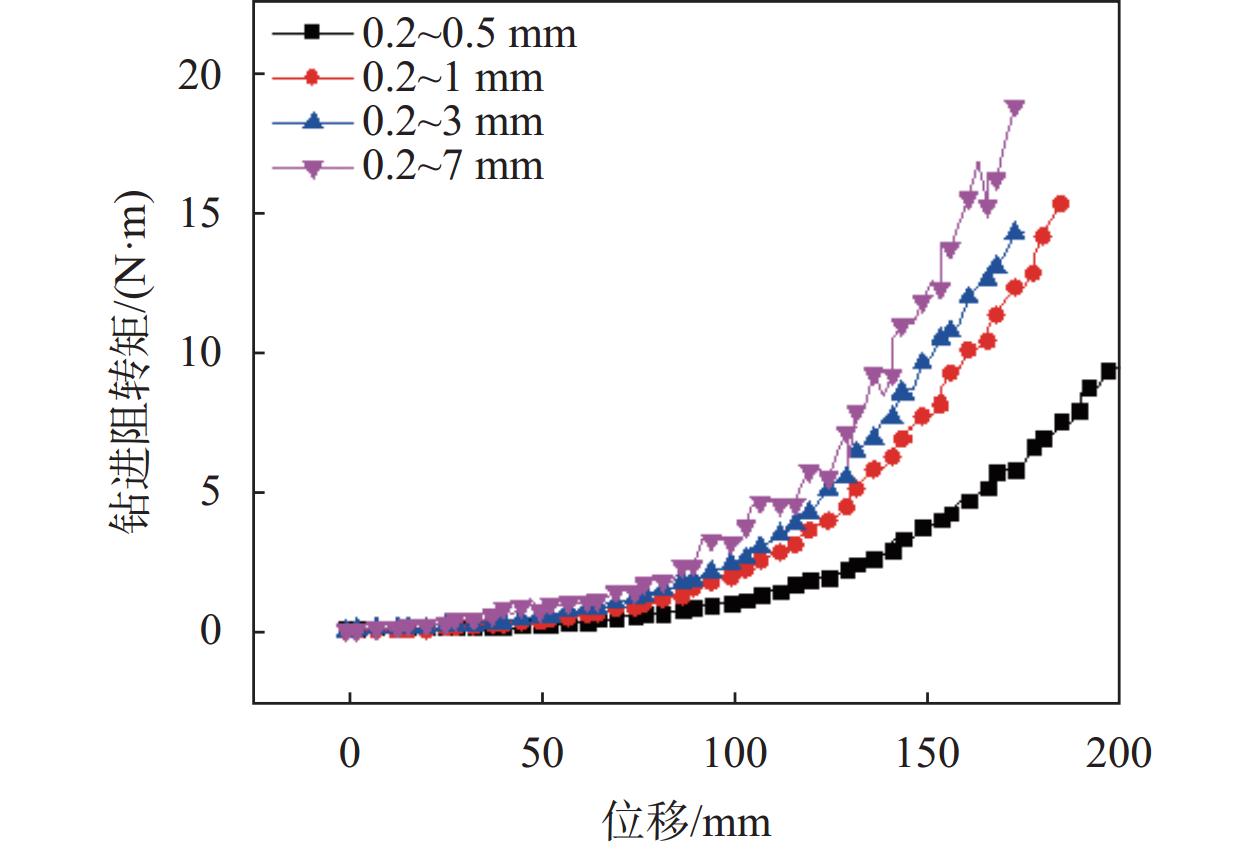
表 1 试验用颗粒材料的各粒径范围颗粒所占体积分数
Table 1. volume fraction of particles in each particle size range of granular materials for test
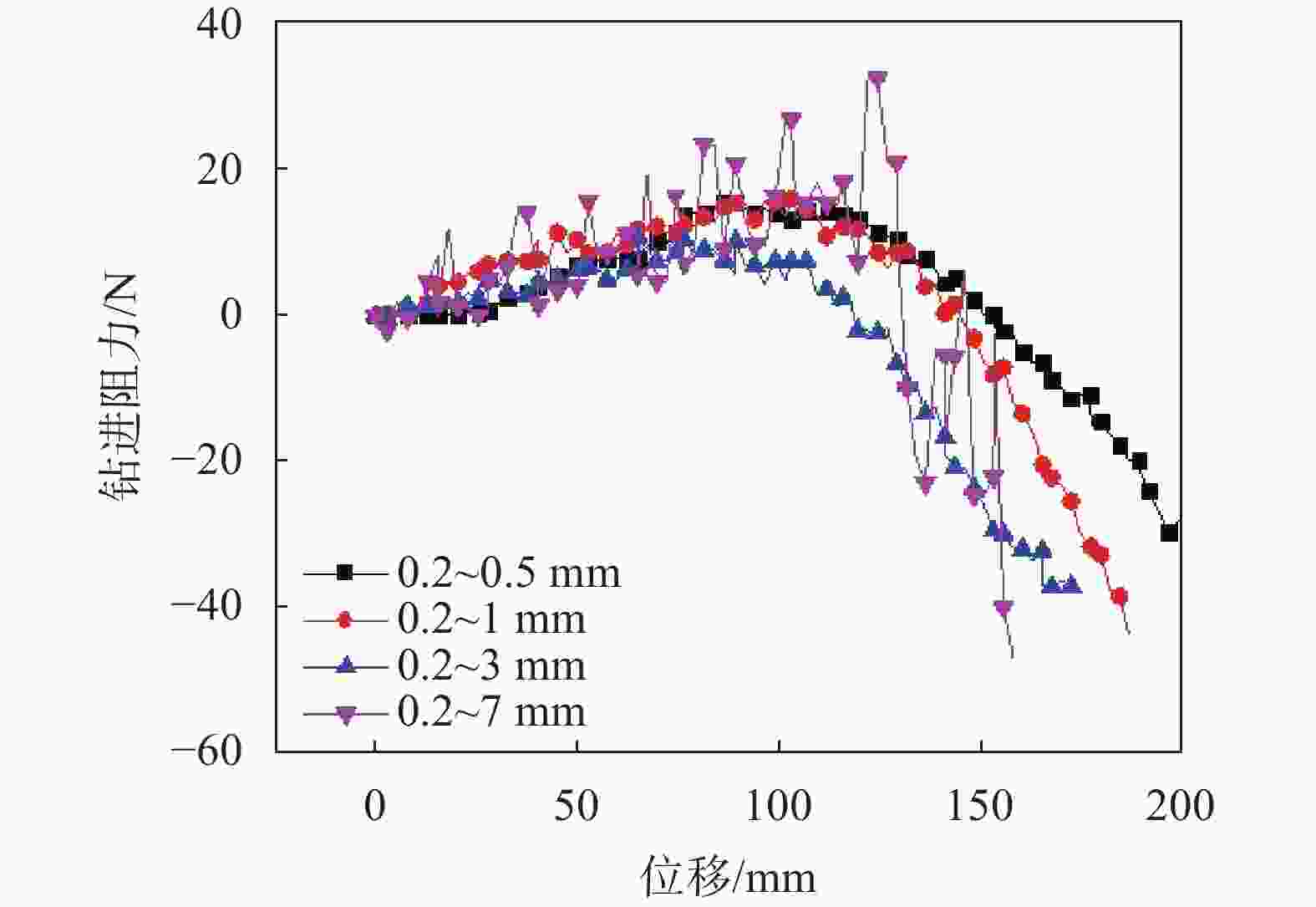
粒径组 体积分数/% 不均匀系数 0.2~0.5 mm 0.5~1.0 mm 1.0~2.0 mm 2.0~3.0 mm 3.0~4.0 mm 4.0~5.0 mm 5.0~6.0 mm 6.0~7.0 mm 0.2~0.5 mm粒径组 100 1.6 0.2~1.0 mm粒径组 50 50 2.5 0.2~3.0 mm粒径组 25 25 25 25 4.6 0.2~7.0 mm粒径组 12.5 12.5 12.5 12.5 12.5 12.5 12.5 12.5 8.4 -
[1] WEI Y J, YANG Y Y, TAO M J. Effects of gravel content and particle size on abrasivity of sandy gravel mixtures[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,243:26-35. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.06.009 [2] 申玉生, 陈先智, 卢治仁, 等. 富水圆砾地层地铁车站超深基坑施工关键技术[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社有限公司, 2019. (SHEN Y S, CHEN X Z, LU Z R, et al. Key technology for ultra deep foundation pit construction of water-rich round gravel formation subway station[M]. Beijing: Publishing House, 2019. (in Chinese)SHEN Y S, CHEN X Z, LU Z R, et al. Key technology for ultra deep foundation pit construction of water-rich round gravel formation subway station[M]. Beijing: Publishing House, 2019. (in Chinese) [3] 李长清, 叶万军, 胡双平, 等. 高富水卵砾石地层热物理参数试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(3):510-519. (LI C Q, YE W J, HU S P, et al. Experimental study on thermophysical parameters of high water gravel formation for freezing construction[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(3):510-519. (in Chinese)LI C Q, YE W J, HU S P, et al. Experimental study on thermophysical parameters of high water gravel formation for freezing construction[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(3): 510-519. (in Chinese) [4] MA S K, DUAN Z B, HUANG Z, et al. Study on the stability of shield tunnel face in clay and clay-gravel stratum through large-scale physical model tests with transparent soil[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2022,119:104199. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2021.104199 [5] ZHEN Z, GE X S, ZHANG J. Soil conditioning tests on sandy and cobbly soil for shield tunneling[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering,2021,25(4):1229-1238. doi: 10.1007/s12205-021-0921-0 [6] LIU X R, XIONG F, ZHOU X H, et al. Physical model test on the influence of the cutter head opening ratio on slurry shield tunnelling in a cobble layer[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2022,120:104264. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2021.104264 [7] 史旦达, 杨彦骋, 邓益兵, 等. 考虑转速比影响的砂土中螺旋挤扩钻具成孔特性宏细观模型试验[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(6):1981-1990,1998. (SHI D D, YANG Y C, DENG Y B, et al. Experimental study of the effect of drilling velocity ratio on the behavior of auger piling in sand[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2018,39(6):1981-1990,1998. (in Chinese)SHI D D, YANG Y C, DENG Y B, et al. Experimental study of the effect of drilling velocity ratio on the behavior of auger piling in sand[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(6): 1981-1990,1998. (in Chinese) [8] 邓益兵, 周 健, 刘 钟, 等. 砂土中螺旋挤扩钻具下旋成孔过程的模型试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2011,30(12):2558-2566. (DENG Y B, ZHOU J, LIU Z, et al. Model test study of augered piling of screw displacement auger in sand[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2011,30(12):2558-2566. (in Chinese)DENG Y B, ZHOU J, LIU Z, et al. Model test study of augered piling of screw displacement auger in sand[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2011, 30(12): 2558-2566. (in Chinese) [9] 张 林, 陈建叶. 水工大坝与地基模型试验及工程应用[M]. 成都: 四川大学出版社, 2009. (ZHANG L, CHEN J Y. Hydraulic dam and foundation model test and engineering application[M]. Chengdu: Sichuan University Press, 2009. (in Chinese)ZHANG L, CHEN J Y. Hydraulic dam and foundation model test and engineering application[M]. Chengdu: Sichuan University Press, 2009. (in Chinese) [10] 张强勇, 李术才, 李 勇, 等. 地下工程模型试验新方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012. (ZHANG Q Y, LI S C, LI Y, et al. New method for underground engineering model testing[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012. (in Chinese)ZHANG Q Y, LI S C, LI Y, et al. New method for underground engineering model testing[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012. (in Chinese) [11] 中华人民共和国交通运输部. 公路土工试验规程: JTG 3430−2020[S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2020. (Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China. Test methods of soils for highway engineering: JTG 3430−2020[S]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2020. (in Chinese)Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China. Test methods of soils for highway engineering: JTG 3430−2020[S]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2020. (in Chinese) [12] DENIES N, HUYBRECHTS N. Deep mixing method: equipment and field of applications[M]//INDRARATNA B, CHU J, RUJIKIATKAMJORN C. Ground Improvement Case Histories. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2015: 311-350. [13] KITAZUME M, TERASHI M. The deep mixing method[M]. London: CRC Press, 2013. [14] 何清华. 工程机械手册: 桩工机械[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2018. (HE Q H. Handbook of construction machinery: piling machinery [M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2018. (in Chinese)HE Q H. Handbook of construction machinery: piling machinery [M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2018. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: