Analysis Conversion Method of Self-balanced Test Pile and Engineering Application
-
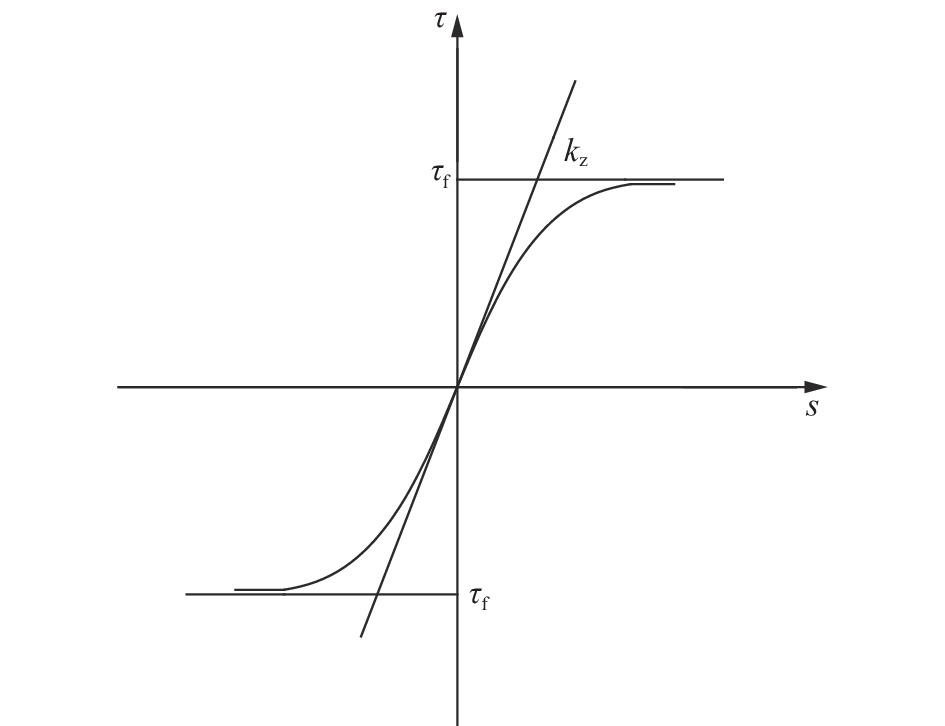
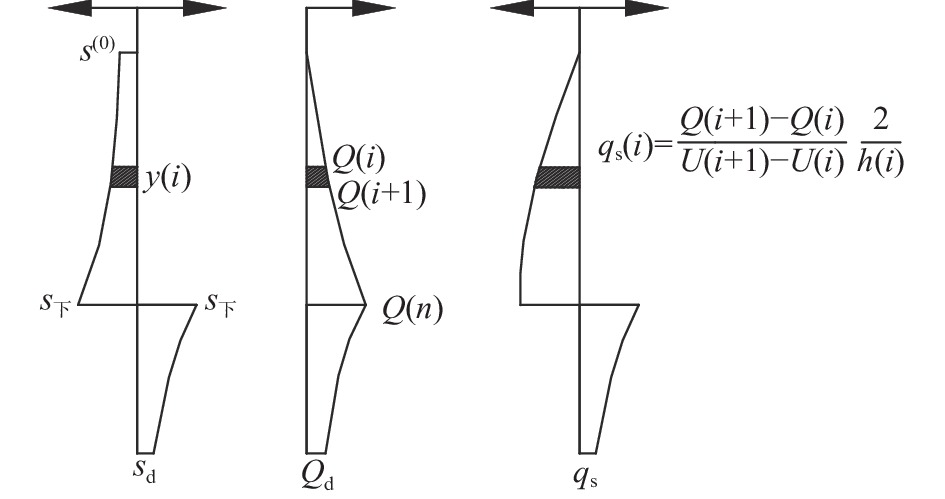
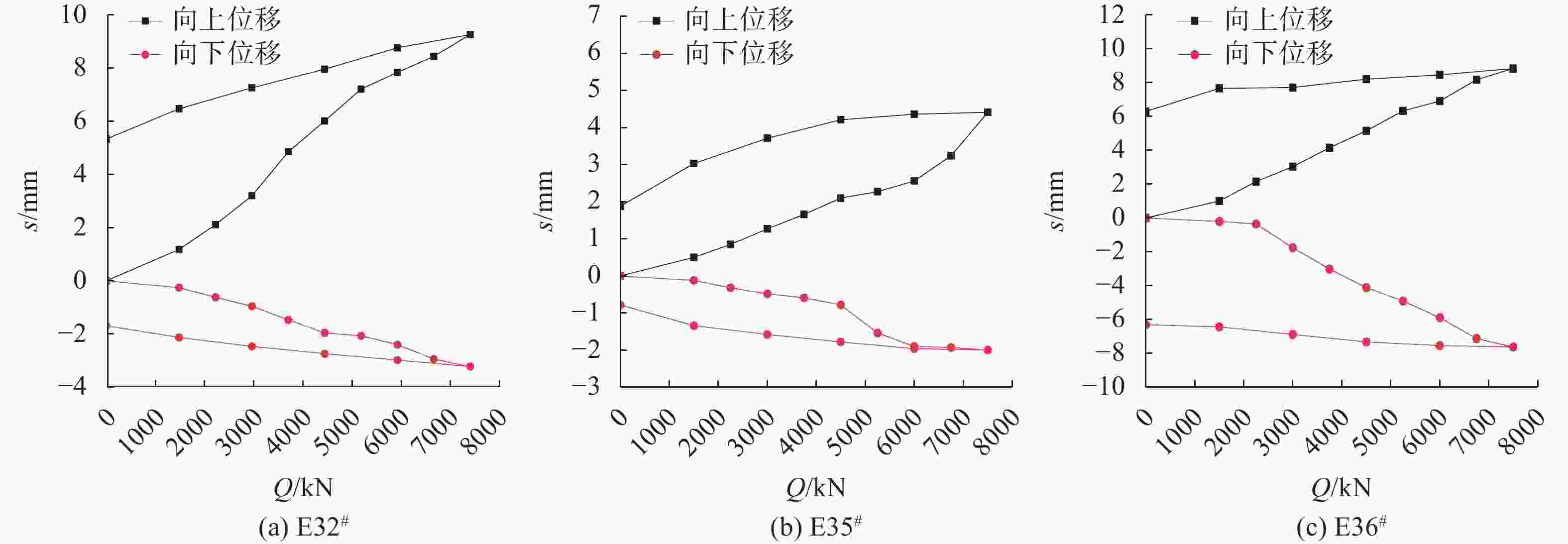
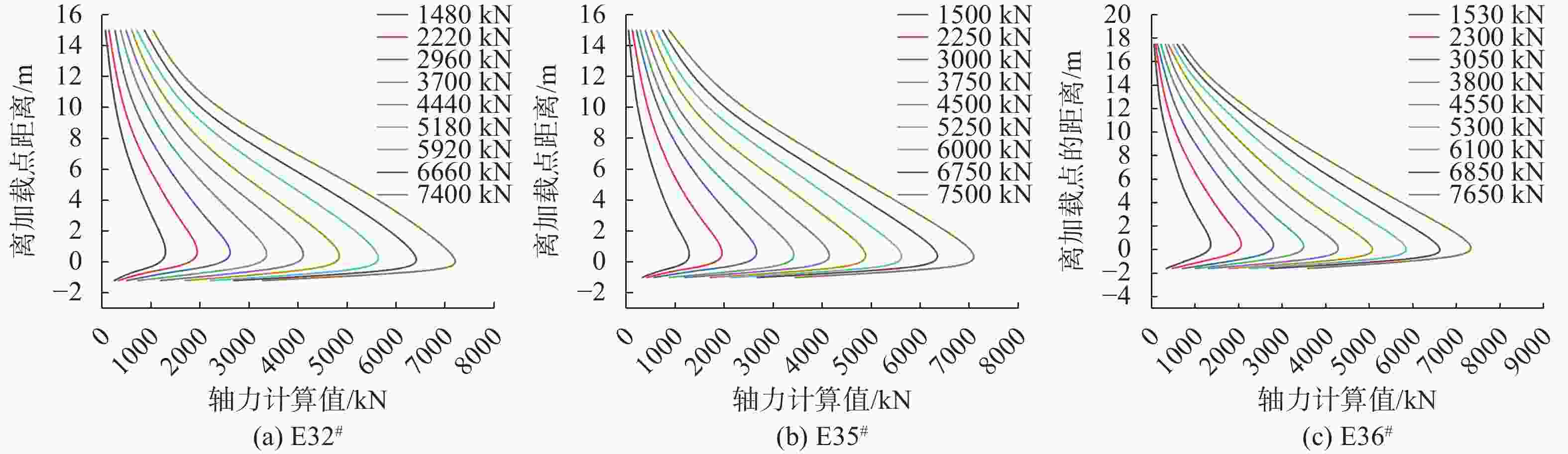
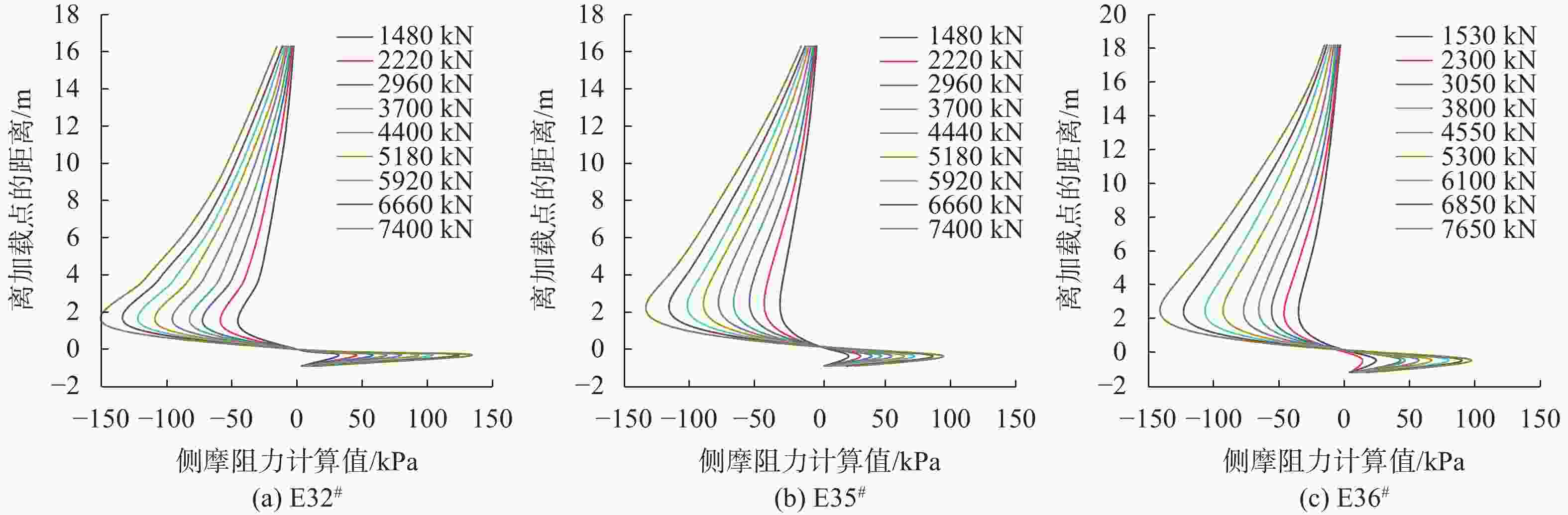
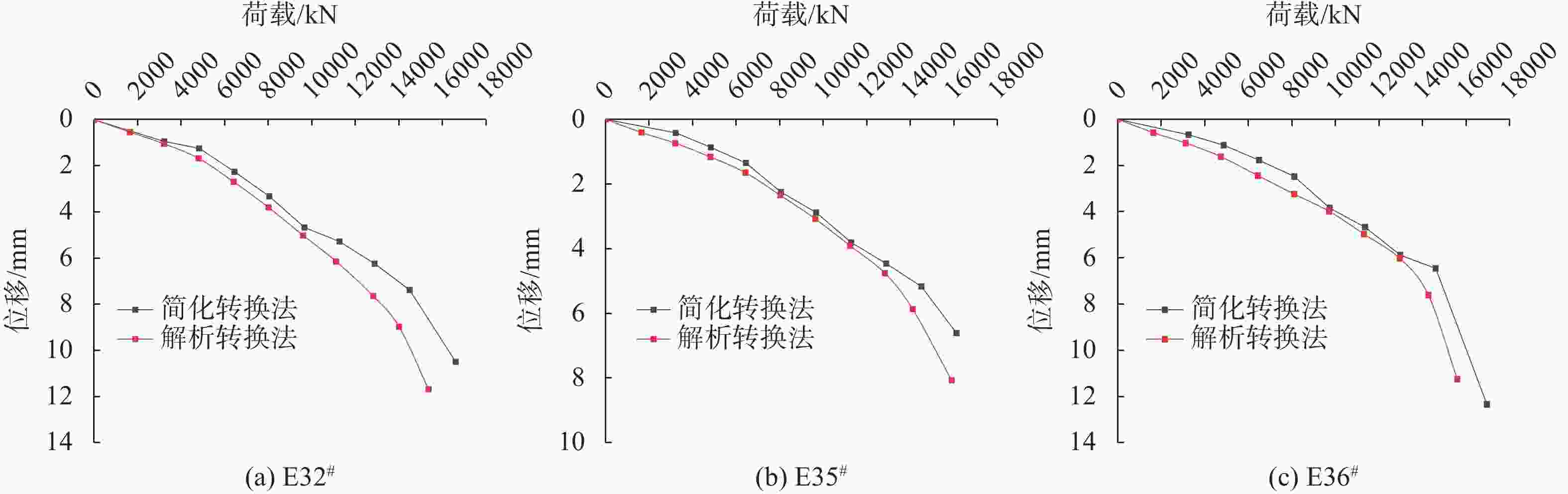
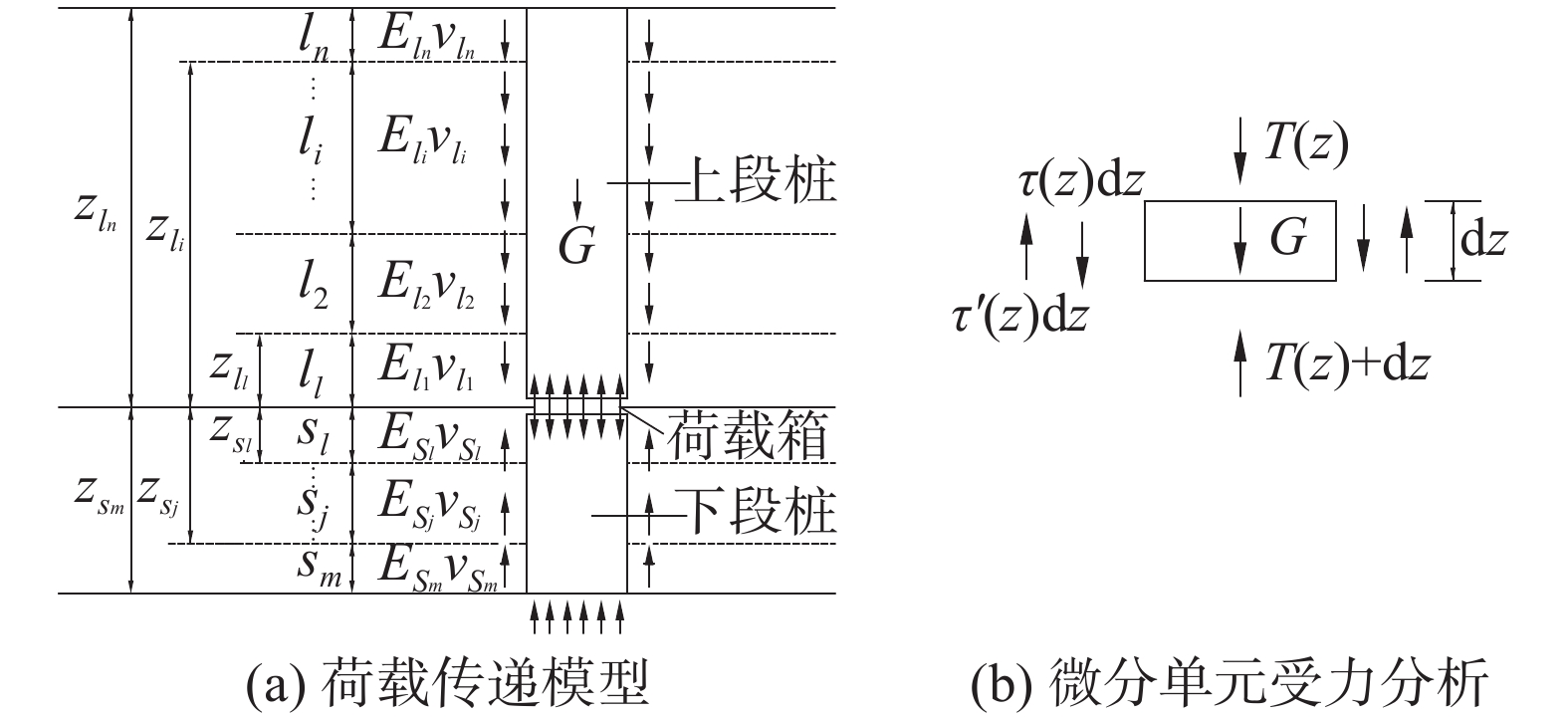
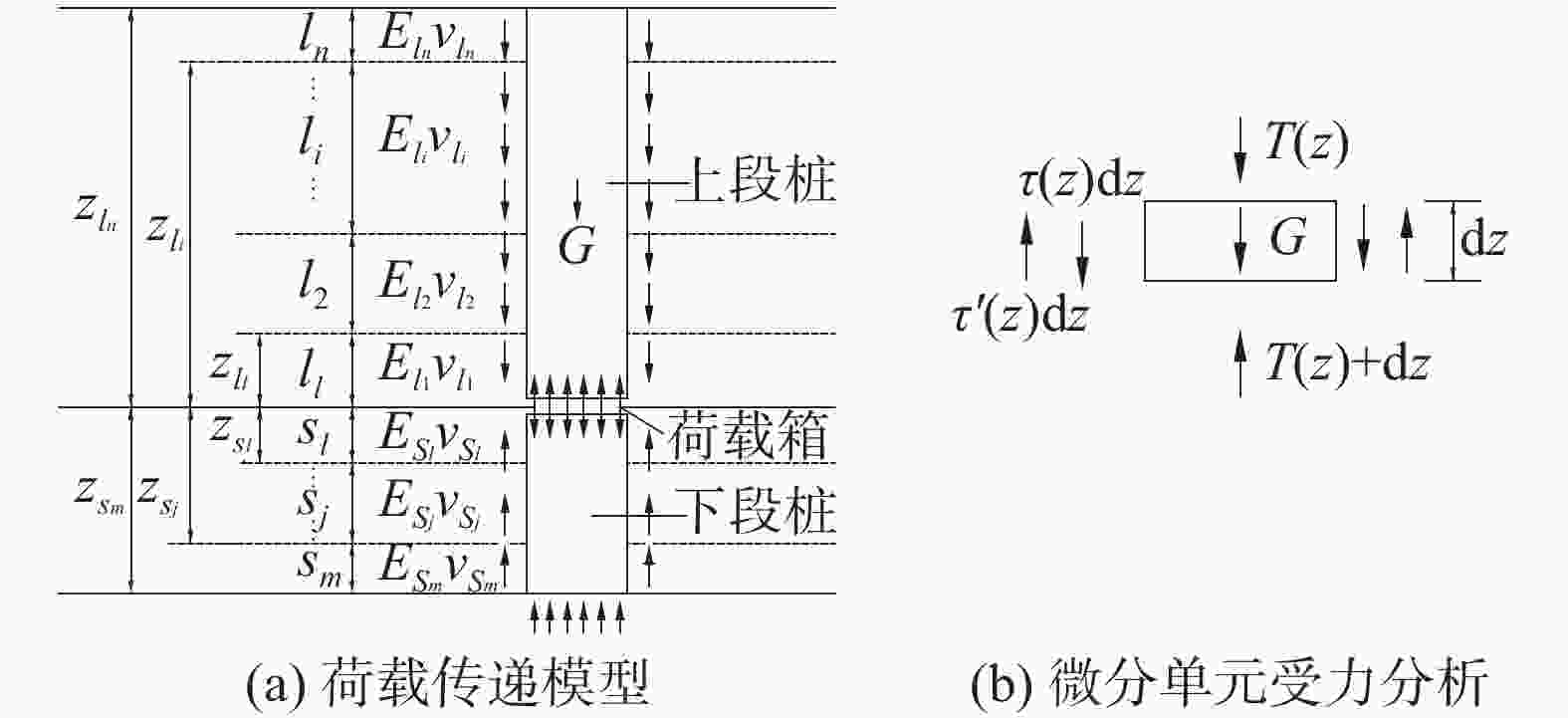
摘要: 提出一种基桩承载力自平衡测试的解析转换方法,采用有限差分法建立上、下段桩各微段控制方程,通过编程求解上、下桩身各微段处的内力及变位量,代入精确转换公式,将自平衡试桩结果转换为类似传统静载测试荷载(Q)-位移(s)曲线形式,并求解其极限承载力。结合广西来宾裕达梧桐苑3根钻孔灌注桩自平衡法测试工程,应用该解析转换方法对测试结果进行转换。研究表明,3根试桩内力均表现为离加载端较近的土层承担的荷载较大,轴力由加载端向两端衰减程度逐渐减小,且侧摩阻力变化特性呈现双曲线分布。就单桩承载力而言,简化转换方法偏于保守,而解析转换方法考虑了桩侧各层土的性质差异,相比精度可提高约12%。该解析转换方法能准确地反映出上、下段桩身内力分布规律以及桩侧土层承载特性,且可以高效准确地实现承载力的转换,在基桩承载力自平衡测试工程领域具有广泛应用前景。Abstract: An analytical conversion method for self-balanced test of foundation pile was proposed. The finite difference method was used to establish the control equations for each micro-section of the upper and lower piles, and the internal forces and displacements at each micro-section of the upper and lower piles can be obtained by programmed solution, which can be substituted into the exact conversion formula to convert the self-balanced test pile results into the form of the load (Q) - displacement (s) curves similar to those of the traditional static test and to solve the ultimate bearing capacity. This analytical conversion method was applied to convert the test results in conjunction with the test project of self-balanced method for three drilled piles in Yuda Wutong Court, Laibin, Guangxi. The internal forces of the three test piles all show that the soil layer closer to the loading end bears a larger load, the axial force gradually decreases from the loading end to both ends, and the change characteristics of the lateral resistances show a hyperbolic distribution. In terms of single pile bearing capacity, the simplified conversion method is conservative, while the analytical conversion method takes into account the differences in the characteristics of the soil layers on the pile side, and the accuracy can be improved by about 12% compared to the simplified conversion method. The analytical conversion method can accurately reflect the distribution law of internal force of upper and lower pile body and the bearing characteristics of soil layer on the pile side, and can efficiently and accurately realize the conversion of bearing capacity, which is widely used in the field of self-balanced test engineering of pile foundation bearing capacity.
-
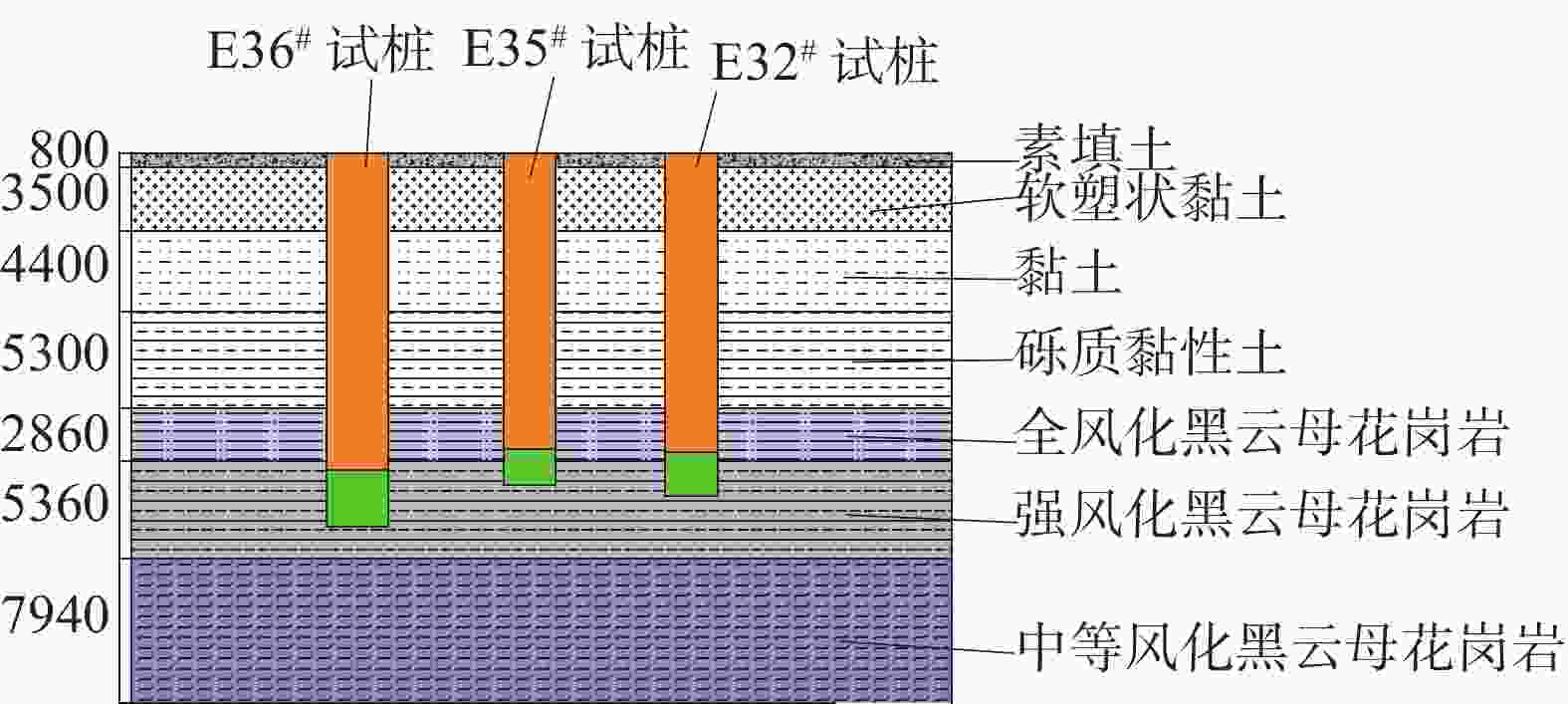
表 1 土层物理力学性质参数
自上而下
土层类别厚度
h/m黏聚力
c/kPa内摩擦角
φ/(°)重度
γ/(kN·m−3)泊松比
ν弹性模量
E/MPa软塑状黏土 3.50 38 18 19.5 0.38 5.80 黏土 4.00 40 18 19.3 0.35 6.34 砾质黏性土 5.30 38 37 23.3 0.305 6.84 全风化黑云母
花岗岩2.80 14.2 37 23.3 0.25 10.4 强风化黑云母
花岗岩5.36 16.5 37 22.5 0.24 12.3 中等风化
黑云母花岗岩7.94 16.5 36 23.1 0.19 16.1 表 2 桩体参数
桩号 桩长L/m 荷载箱距桩底距离s/m 桩径d/cm 混凝土等级 重度γ/(kN·m−3) 弹性模量E/MPa 单桩竖向抗压承载力特征值/kN E32# 18.82 1.2 120 C35 25 3.15$ \times $104 7200 E35# 18.21 1.0 120 C35 25 3.15$ \times $104 7200 E36# 20.50 1.6 120 C35 25 3.15$ \times $104 7200 表 3 自平衡法静载试验承载力检测结果
检测桩号 试验上板
最大位移/mm试验下板
最大位移
/mm最大试验
荷载
/kN加载时长
/min极限承载力计算/kN 单桩承载力特征值2倍
/kNE32# 9.26 3.23 2×7500 1170 14676.19 ≥2×7200 E35# 4.41 2.00 2×7400 1200 14566.67 ≥2×7200 E36# 8.83 7.63 2×7500 1320 14686.43 ≥2×7200 -
[1] 朱建民, 殷开成, 龚维明, 等. 中美欧自平衡静载试验标准若干问题探讨[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(10):3491-3499. [2] XING H, WU J, LUO Y. Field tests of large-diameter rock-socketed bored piles based on the self-balanced method and their resulting load bearing characteristics[J]. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering,2019,23(12):1535-1549. doi: 10.1080/19648189.2017.1359111 [3] 欧孝夺, 白 露, 吕政凡, 等. 自平衡试桩Q-s曲线理论解析方法研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2022,19(2):399-408. [4] OSTERBERG J. New device for load testing driven piles and drilled shafts separates friction and end bearing[J]. Piling and Deep Foundations,1989,1(6):421-427. [5] 龚成中, 何春林, 龚维明, 等. 基于自平衡试桩法大直径嵌岩桩尺寸效应分析[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(8):2403-2407. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.08.025 [6] JGJ/T 403—2017 建筑基桩自平衡静载试验技术规程[S]. [7] OU X, BAI L, JIANG J, et al. Research on analytical conversion method of self-balanced test pile results. [J] European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering, 2021, 26(14), 7209–7225. [8] 欧孝夺, 白 露, 吕政凡, 等. 黏土地基中自平衡试桩Q-s曲线解析转换方法与室内模型试验研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2022,53(2):631-642. [9] XI X Z, CHEN L Z, LIU W. An analytical solution to transform O-cell pile test data into conventional load-settlement curve[C]. GeoShanghai 2010 International Conference, 2010: 192-199. [10] SEOL H, JEONG S. Load-settlement behavior of rock-socketed drilled shafts using Osterberg-Cell tests[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2009, 36(7): 1134-1141. [11] SEOL H, JEONG S, KIM Y. Load transfer analysis of rock-socketed drilled shafts by coupled soil resistance[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2009, 36(3): 446-453. [12] NIAZI FAWAD S, MAYNEPAUL W. Axial pile response of bidirectional O-cell loading from modified analytical elastic solution and downhole shear wave velocity[J]. NRC Research Press, 2014, 51(11):1284-1302. [13] KIM S R, CHUNG S G. Equivalent head-down load vs. Movement relationships evaluated from bi-directional pile load tests[J]. Ksce Journal of Civil Engineering, 2012, 16(7): 1170-1177. [14] LEE J S, PARK Y H. Equivalent pile load-head settlement curve using a bi-directional pile load test[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2008, 35(2): 124-133. [15] MISSION J L C, KIM H J. Design charts for elastic pile shortening in the equivalent top-down load-settlement curve from a bidirectional load test[J]. Computers and Geotechnics,2011,38(2):167-177. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2010.11.001 [16] KRAFT L M, RAY R P, KAGAWA T. Theoretical t-z curves[J]. Journal of the Geotechnical Engineering Division, ASCE,1981,107(11):1543-1561. doi: 10.1061/AJGEB6.0001207 [17] 江 杰, 王顺苇, 欧孝夺, 等. 黏土地基中桩顶扭矩–竖向荷载加载路径下单桩承载特性分析[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(11):3573-3582. [18] 江 杰, 王顺苇, 欧孝夺, 等. 膨胀土地基中单桩受扭非线性分析[J]. 工程力学,2020,37(11):219-227. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.04.0243 [19] RANDOLPH M F, WROTH C P. Analysis of deformation of vertically loaded piles[J]. Journal of the Geotechnical Engineering Division,1978,104(12):1465-1488. doi: 10.1061/AJGEB6.0000729 -





 下载:
下载: