Slump-based soil conditioning of EPB shield in gravelly sand and its prediction study
-
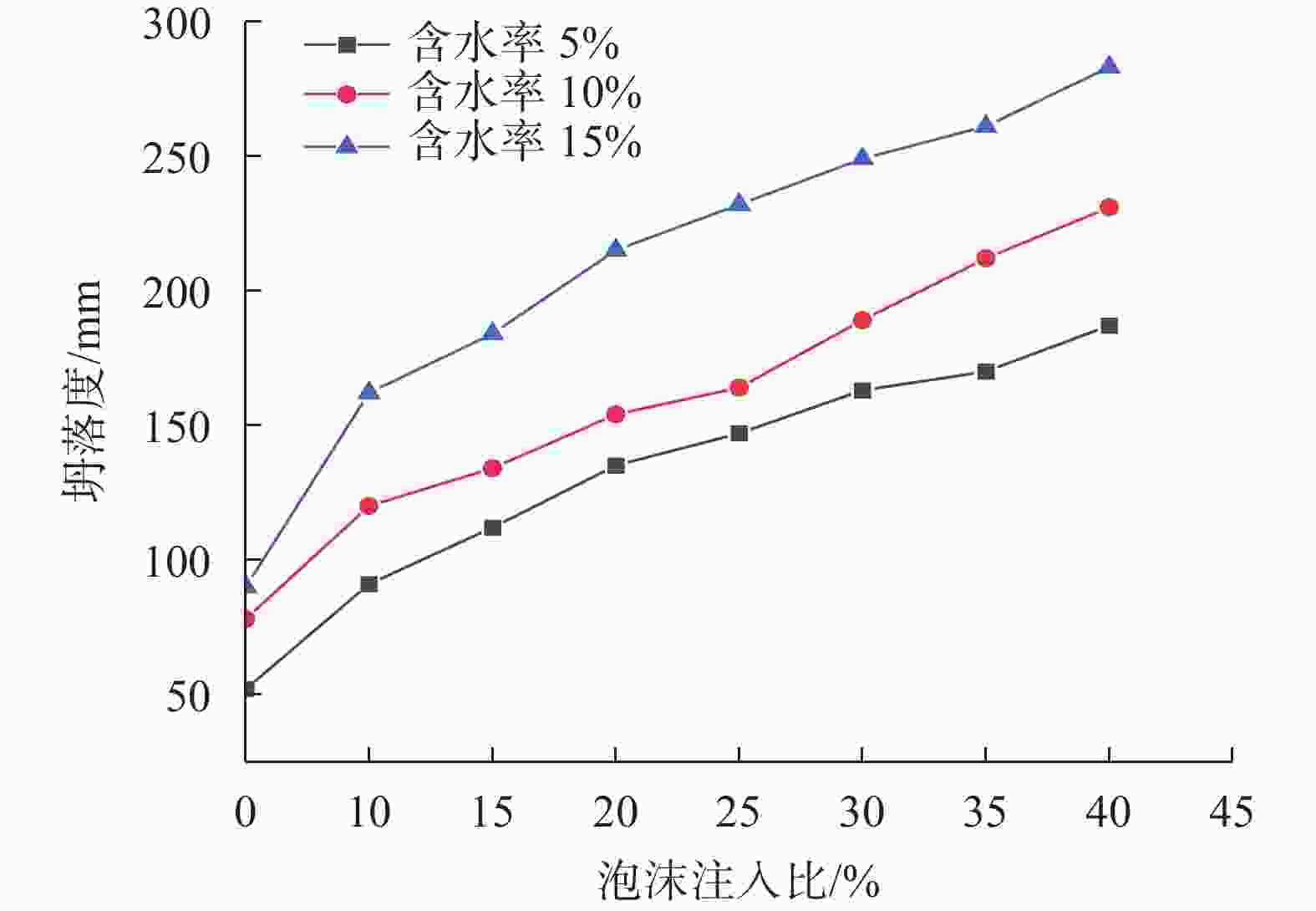
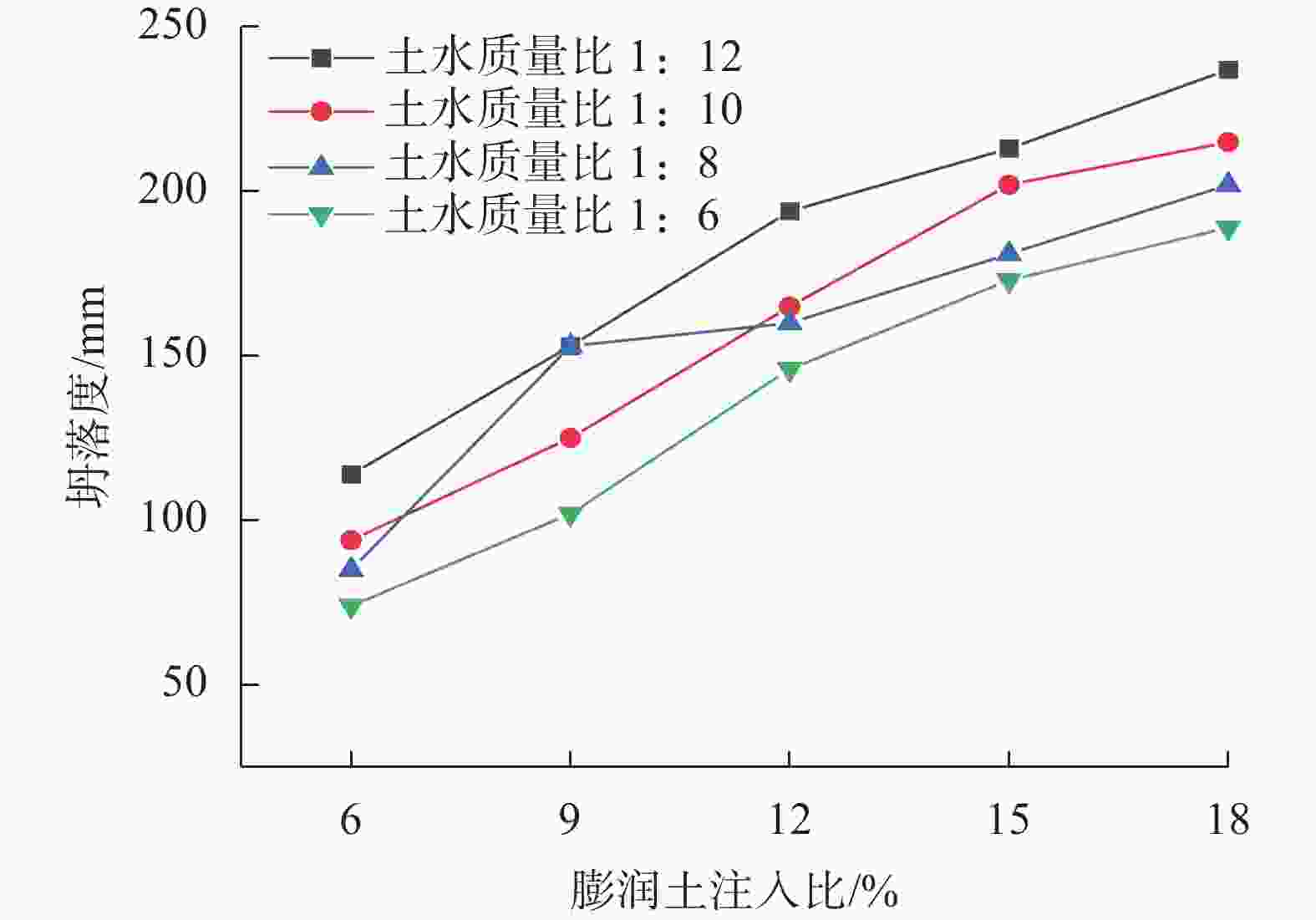
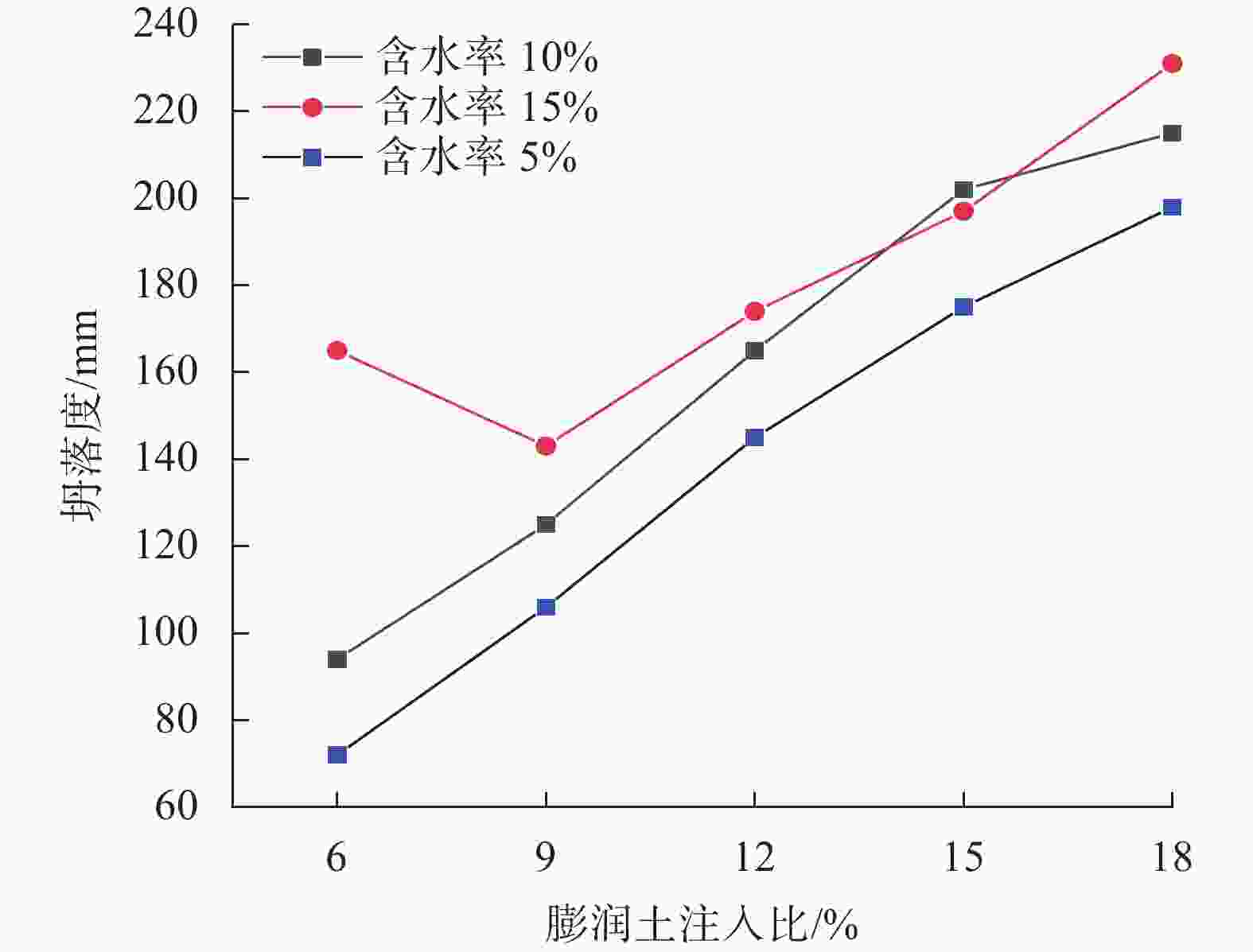
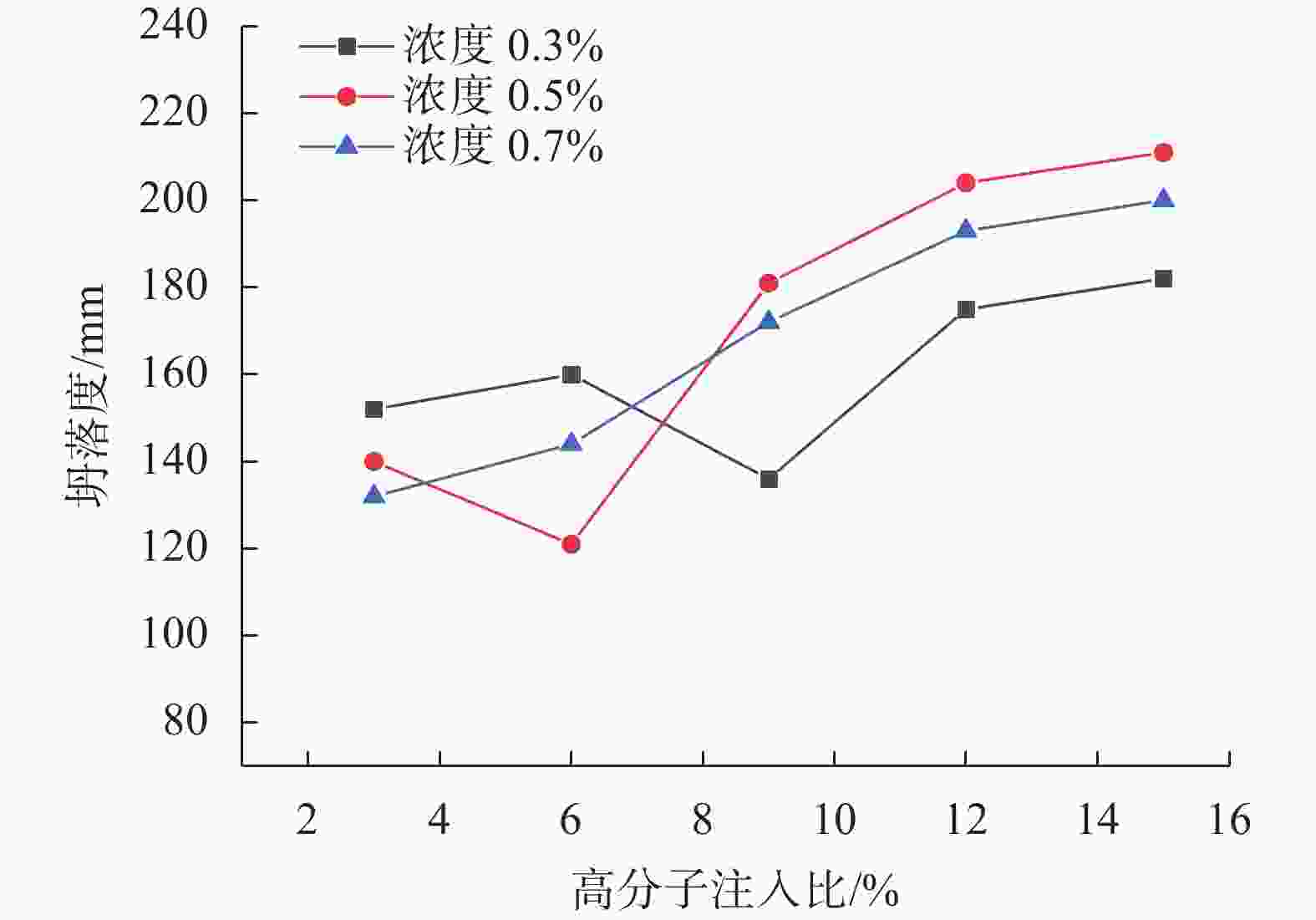
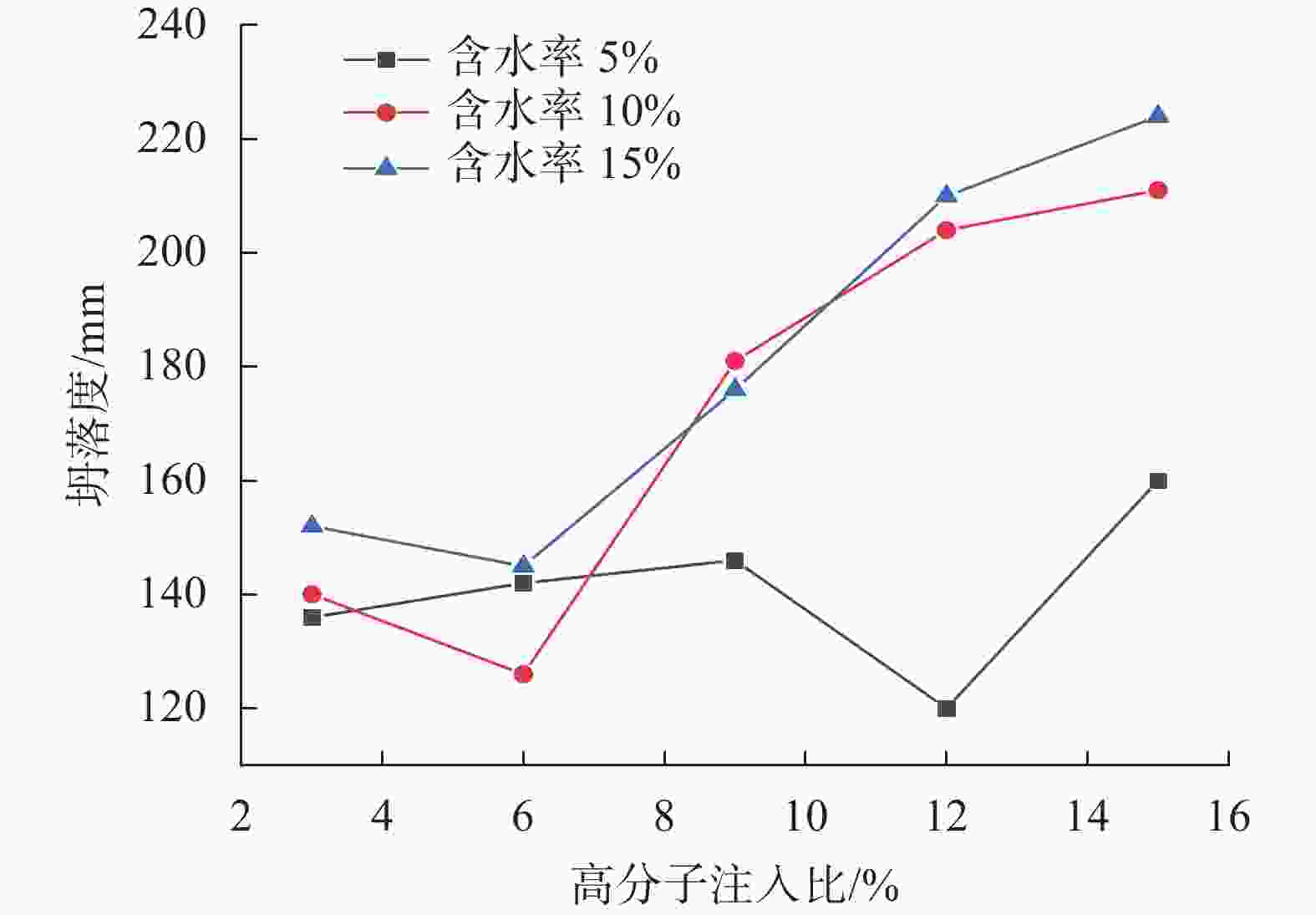
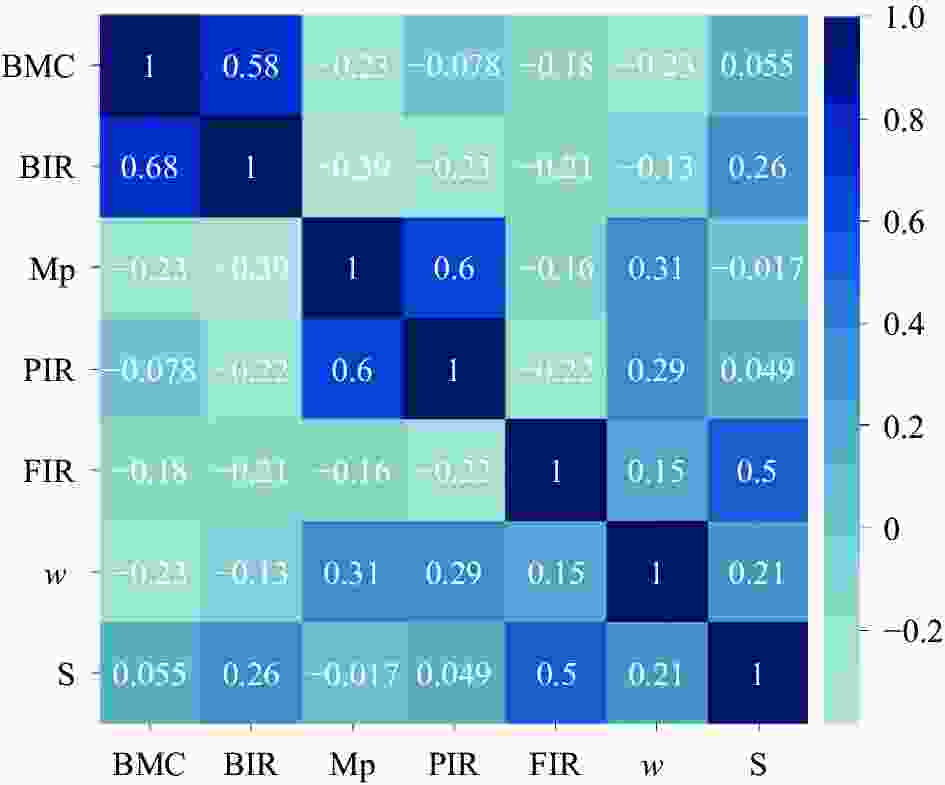
摘要: 在砾砂地层中掘进时,渣土改良效果是影响盾构掘进效率的关键因素。通过坍落度试验研究了泡沫、膨润土泥浆和高分子聚合物对改良土体流塑性的影响。以试验结果作为数据样本集,采用SVR,KNR,RFR和BPNN等常用机器学习方法构建了土体坍落度的预测模型,并将预测值与实际值进行了对比分析。研究结果表明:(1)泡沫对砾砂渣土流塑性的改良效果较好;(2)对于高含水率的砾砂地层,应使用高黏度的膨润土泥浆或PAM溶液进行改良,以起到保水增黏、防止喷涌的目的;(3)对比SVR,KNR和BPNN模型,RFR模型在预测时的性能表现最佳,能够更准确地预测改良渣土的坍落度,并且对模型进行了可解释性分析。Abstract: The impact of soil conditioning is a critical factor influencing shield tunneling efficiency in strata of gravelly sand. Through a slump test, the impacts of foam, bentonite slurry, and polymer on the enhanced soil’s flow plasticity were examined. A prediction model of soil slump was provided using machine learning techniques like SVR, KNR, RFR, and BPNN, utilizing the test results as the data sample set. The predicted and real values were then compared and examined. The study indicates that: (1) Foam has a greater impact on enhancing the gravelly sandy soil’s flow flexibility. (2) High-viscosity bentonite slurry or PAM solution should be applied over gravelly sandy stratum with high water content to retain water, improve viscosity, and prevent blowout. (3) The RFR model outperforms the SVR, KNR, and BPNN models regarding prediction accuracy. It can also forecast the slump of the improved waste soil with greater precision. The model’s interpretability was examined as well.
-
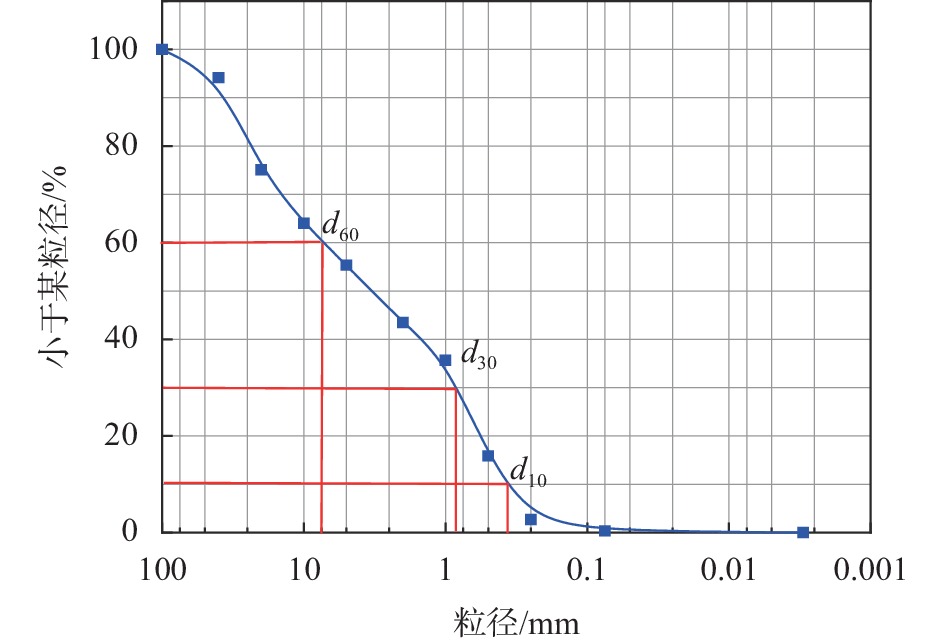
表 1 砾砂地层颗粒组成指标
有效粒径d10/mm 平均粒径d50/mm 限制粒径d60/mm 不均匀系数Cu 曲率系数
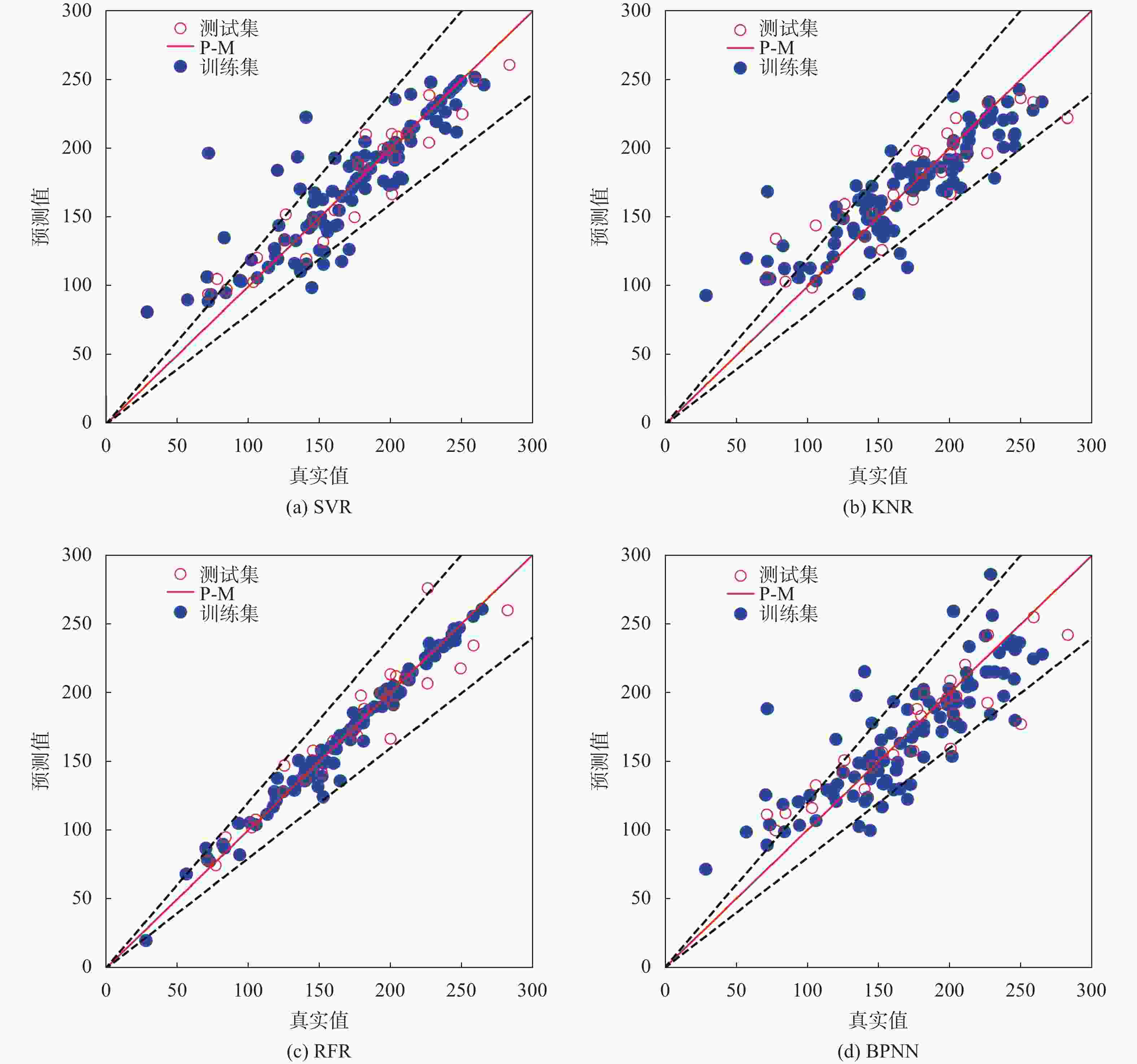
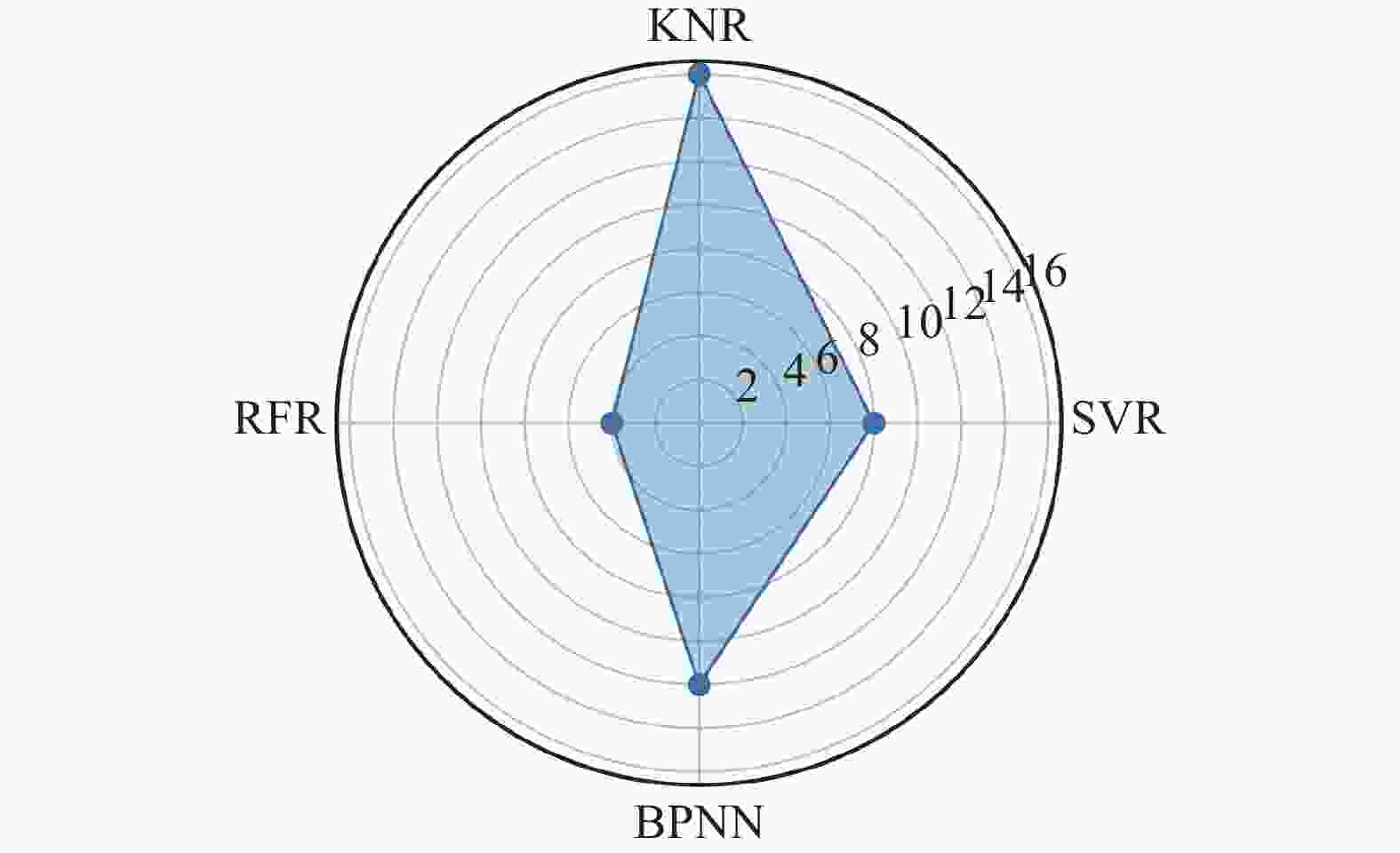
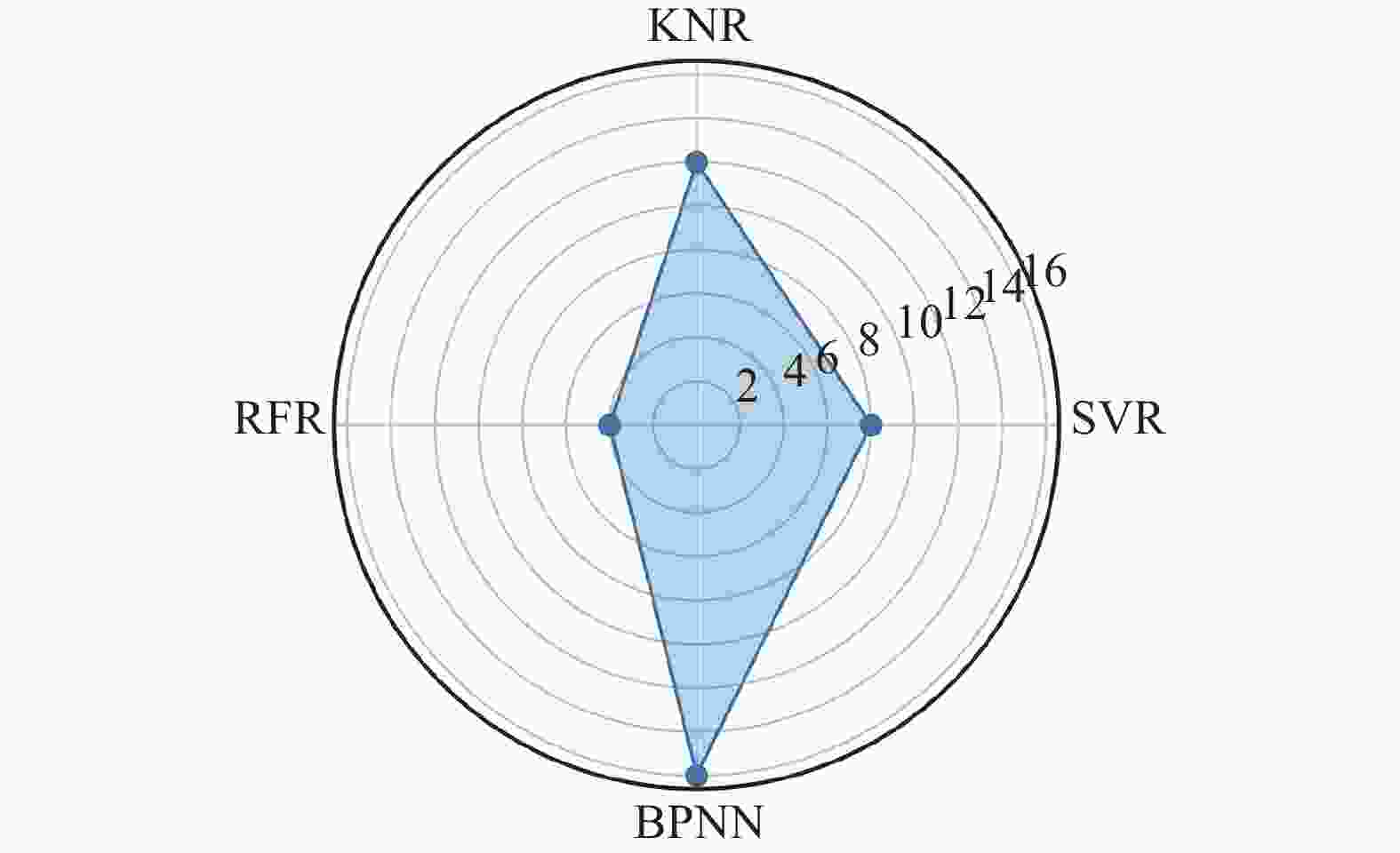
Cc0.37 3.42 7.37 19.92 0.27 表 2 四种模型的测试集评价指标及排名
测试集 R2 排名 MSE
/mm2排名 RMSE
/mm排名 MAE
/mm排名 汇总 SVR 0.75554 2 597.75 2 24.449 2 15.226 2 8 KNR 0.75402 3 601.45 3 24.524 3 18.041 3 12 RFR 0.90255 1 287.22 1 16.947 1 12.300 1 4 BPNN 0.68028 4 781.76 4 27.960 4 20.833 4 16 表 3 四种模型的训练集评价指标及排名
训练集 R2 排名 MSE
/mm2排名 RMSE
/mm排名 MAE
/mm排名 汇总 SVR 0.89994 2 294.92 2 17.173 2 14.192 2 8 KNR 0.78865 4 622.95 4 24.959 4 119.665 4 16 RFR 0.92914 1 50.991 1 7.1408 1 4.8726 1 4 BPNN 0.79995 3 589.64 3 24.282 3 18.257 3 12 -
[1] 胡长明, 张延杰, 谭 博, 等. 富水砂卵石地层土压平衡盾构隧道碴土改良试验研究[J]. 现代隧道技术,2017,54(6):45-55. (HU C M, ZHANG Y J, TAN B, et al. Soil conditioning experiments for EPB shield tunneling in water-rich sandy cobble strata[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology,2017,54(6):45-55. (in Chinese)HU C M, ZHANG Y J, TAN B, et al. Soil conditioning experiments for EPB shield tunneling in water-rich sandy cobble strata[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2017, 54(6): 45-55. (in Chinese) [2] 茅 华. 隧道施工盾构螺旋机喷涌应对措施[J]. 铁道建筑,2014(10):39-41. (MAO H. Countermeasures to stop muck-gushing from shield’s screw conveyer during tunnel construction[J]. Railway Engineering,2014(10):39-41. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2014.10.10MAO H. Countermeasures to stop muck-gushing from shield’s screw conveyer during tunnel construction[J]. Railway Engineering, 2014(10): 39-41. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2014.10.10 [3] 王洪新. 土压平衡盾构刀盘扭矩计算及其与盾构施工参数关系研究[J]. 土木工程学报,2009,42(9):109-113. (WANG H X. Calculation of cutterhead torque for EPB shield and the relationship between cutterhead torque and shield driving parameters[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal,2009,42(9):109-113. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2009.09.016WANG H X. Calculation of cutterhead torque for EPB shield and the relationship between cutterhead torque and shield driving parameters[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2009, 42(9): 109-113. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2009.09.016 [4] 肖 超, 阳军生, 王树英, 等. 土压平衡盾构改良渣土力学行为及其地层响应特征[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2016,47(7):2432-2440. (XIAO C, YANG J S, WANG S Y, et al. Conditioned soils mechanical behavior of earth pressure balance shield tunneling and its impact on formation response[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology),2016,47(7):2432-2440. (in Chinese)XIAO C, YANG J S, WANG S Y, et al. Conditioned soils mechanical behavior of earth pressure balance shield tunneling and its impact on formation response[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2016, 47(7): 2432-2440. (in Chinese) [5] MARTINELLI D, PEILA D, CAMPA E. Feasibility study of tar sands conditioning for earth pressure balance tunnelling[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering,2015,7(6):684-690. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2015.09.002 [6] BORIO L, PEILA D. Study of the permeability of foam conditioned soils with laboratory tests[J]. American Journal of Environmental Sciences,2010,6(4):365-370. doi: 10.3844/ajessp.2010.365.370 [7] 魏康林. 土压平衡盾构施工中泡沫和膨润土改良土体的微观机理分析[J]. 现代隧道技术,2007,44(1):73-77. (WEI K L. Micro-mechanism analysis for the soil improvement by foam and bentonite in EPB shield tunneling[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology,2007,44(1):73-77. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6582.2007.01.016WEI K L. Micro-mechanism analysis for the soil improvement by foam and bentonite in EPB shield tunneling[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2007, 44(1): 73-77. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6582.2007.01.016 [8] 汪国锋. 北京砂卵石地层土压平衡盾构土体改良技术试验研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2011. (WANG G F. Tset research on soil improvement technology for EPBS in Beijing sandy pebble stratum[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2011. (in Chinese)WANG G F. Tset research on soil improvement technology for EPBS in Beijing sandy pebble stratum[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2011. (in Chinese) [9] 徐琳琳, 余 金, 蒋亚龙, 等. 泡沫性能测试及其在富水砂层渣土改良中应用[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2021,17(S1):345-353. (XU L L, YU J, JIANG Y L, et al. Testing of foam properties and its application in soil conditioning for water bearing sandy grounds[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering,2021,17(S1):345-353. (in Chinese)XU L L, YU J, JIANG Y L, et al. Testing of foam properties and its application in soil conditioning for water bearing sandy grounds[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2021, 17(S1): 345-353. (in Chinese) [10] 乔国刚, 陶龙光, 刘 波, 等. 泡沫改良富水砂层工程性质的实验研究[J]. 现代隧道技术,2009,46(6):79-84. (QIAO G G, TAO L G, LIU B, et al. Study on engineering properties of foam-conditioned water-soaked sand strata[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology,2009,46(6):79-84. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6582.2009.06.013QIAO G G, TAO L G, LIU B, et al. Study on engineering properties of foam-conditioned water-soaked sand strata[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2009, 46(6): 79-84. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6582.2009.06.013 [11] 胡长明, 崔 耀, 王雪艳, 等. 土压平衡盾构施工穿越砂层渣土改良试验研究[J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报(自然科学版),2013,45(6):761-766. (HU C M, CUI Y, WANG X Y, et al. Soil improvement for earth pressure balance shields construction in full section sand layer[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology (Natural Science Edition),2013,45(6):761-766. (in Chinese)HU C M, CUI Y, WANG X Y, et al. Soil improvement for earth pressure balance shields construction in full section sand layer[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 45(6): 761-766. (in Chinese) [12] 郭付军, 赵振威, 张 杰, 等. 使用聚合物对纯砂层进行渣土改良的试验研究[J]. 隧道建设,2017,37(S1):53-58. (GUO F J, ZHAO Z W, ZHANG J, et al. Experimental study of ground conditioning of pure sand stratum by using polymer[J]. Tunnel Construction,2017,37(S1):53-58. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3973/j.issn.1672-741X.2017.S1.009GUO F J, ZHAO Z W, ZHANG J, et al. Experimental study of ground conditioning of pure sand stratum by using polymer[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2017, 37(S1): 53-58. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3973/j.issn.1672-741X.2017.S1.009 [13] VAPNIK V, GOLOWICH S E, SMOLA A. Support vector method for function approximation, regression estimation and signal processing[C]//Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge: MIT Press, 1996: 281-287. [14] FIX E, HODGES J L. Discriminatory analysis. Nonparametric discrimination: consistency properties[J]. International Statistical Review/Revue Internationale de Statistique,1989,57(3):238-247. [15] BREIMAN L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning,2001,45(1):5-32. doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324 [16] ESONYE C, ONUKWULI O D, OFOEFULE A U, et al. Multi-input multi-output (MIMO) ANN and Nelder-Mead’s simplex based modeling of engine performance and combustion emission characteristics of biodiesel-diesel blend in CI diesel engine[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering,2019,151:100-114. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.01.101 [17] LUNDBERG S M, LEE S I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook: Curran Associates, 2017: 4768-4777. [18] ZHANG A, LIPTON Z C, LI M, et al. Dive into deep learning[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2023. -





 下载:
下载: