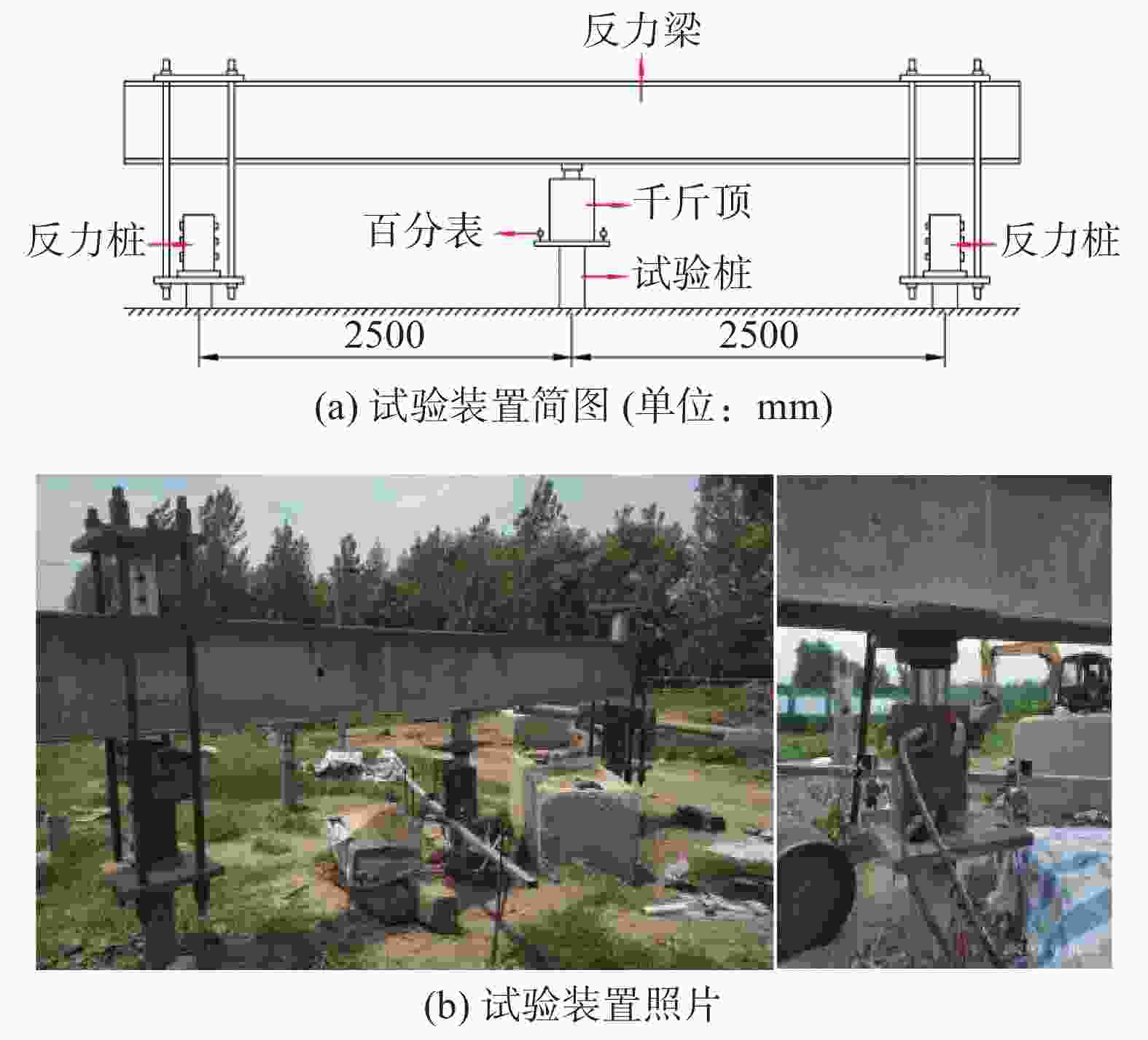
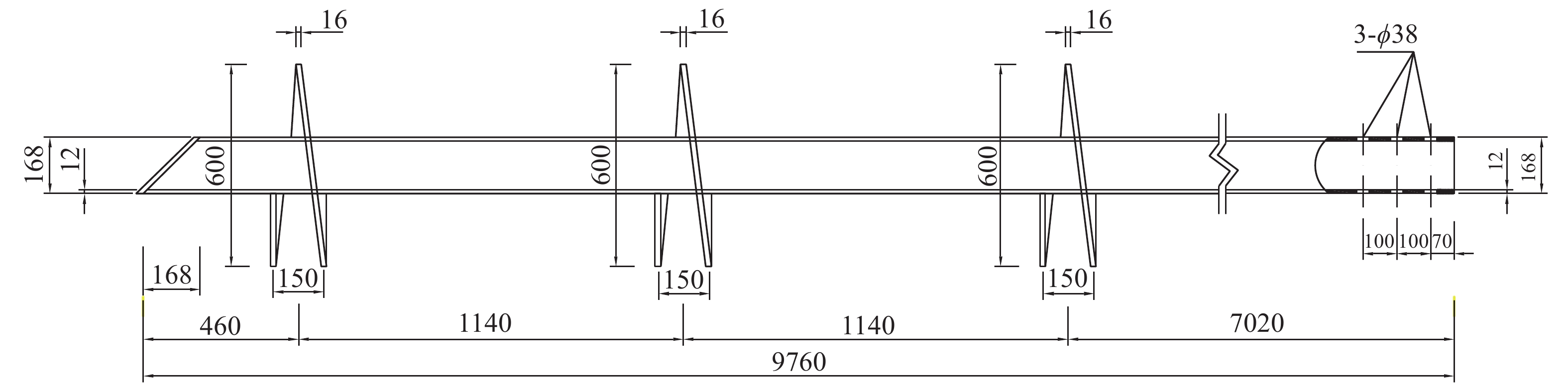
Compressive bearing performance of the helical pile embedded in silty clay
-
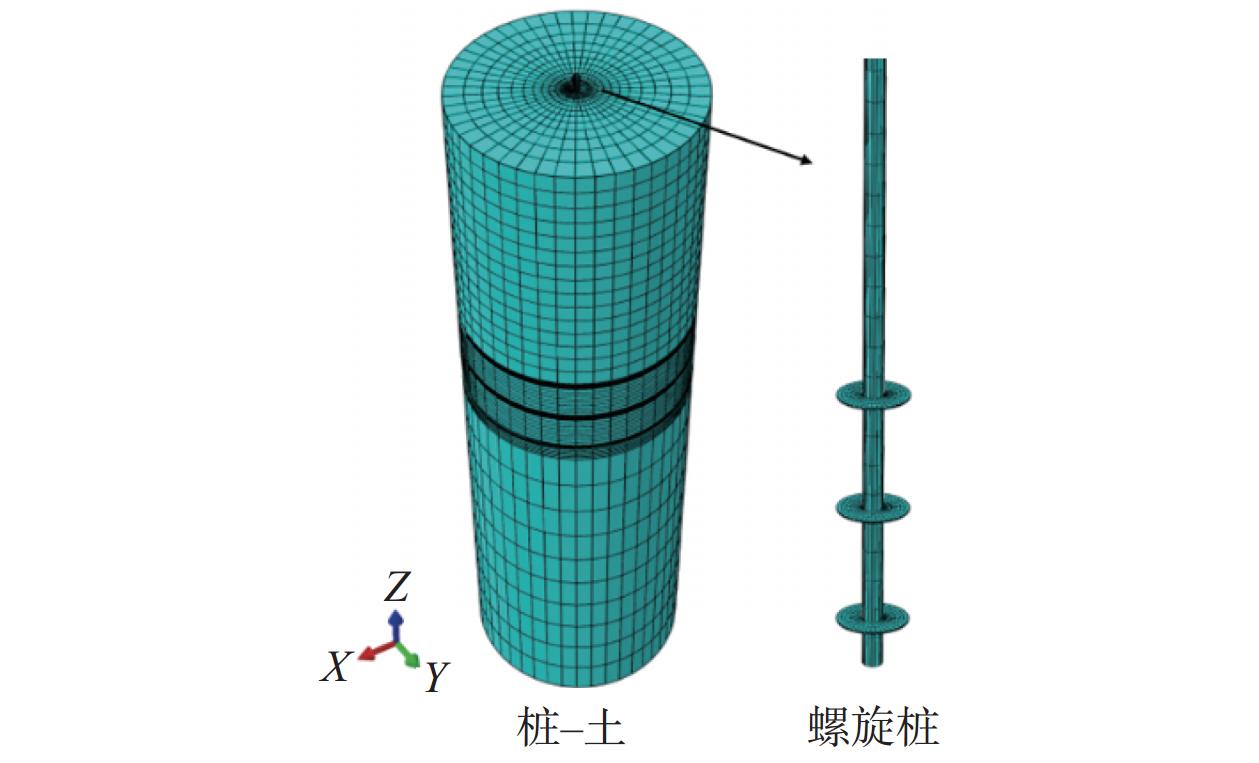
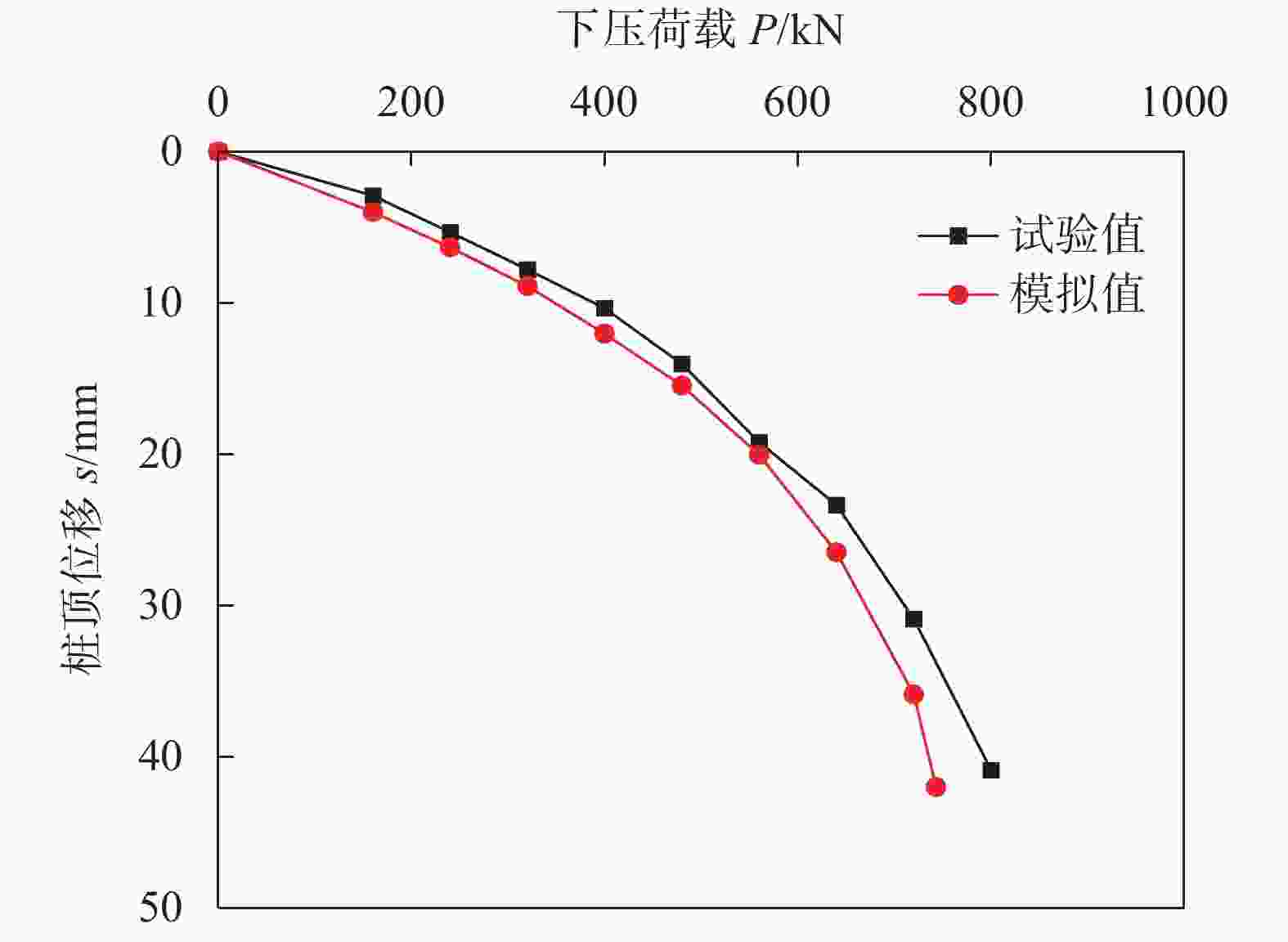
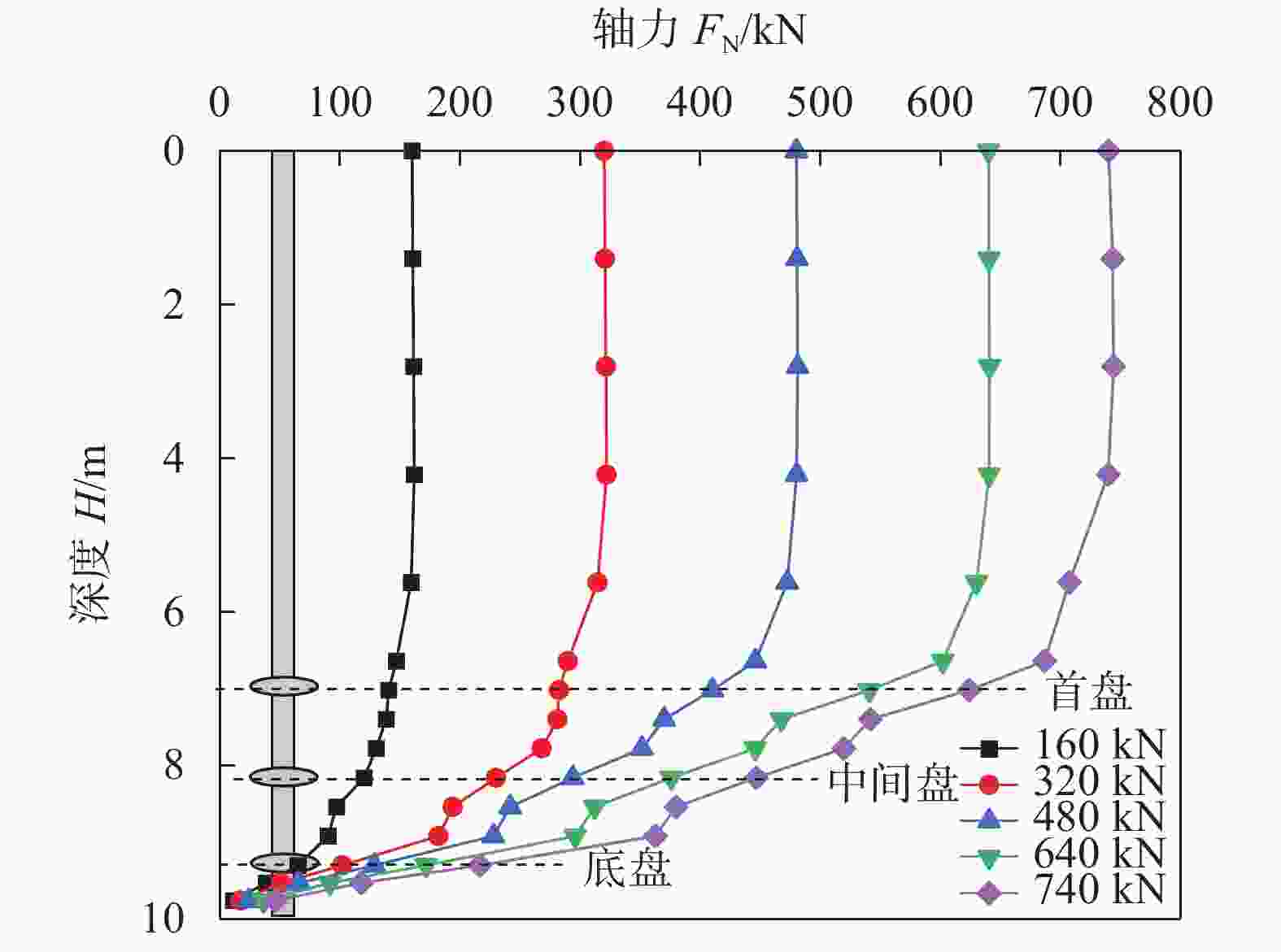
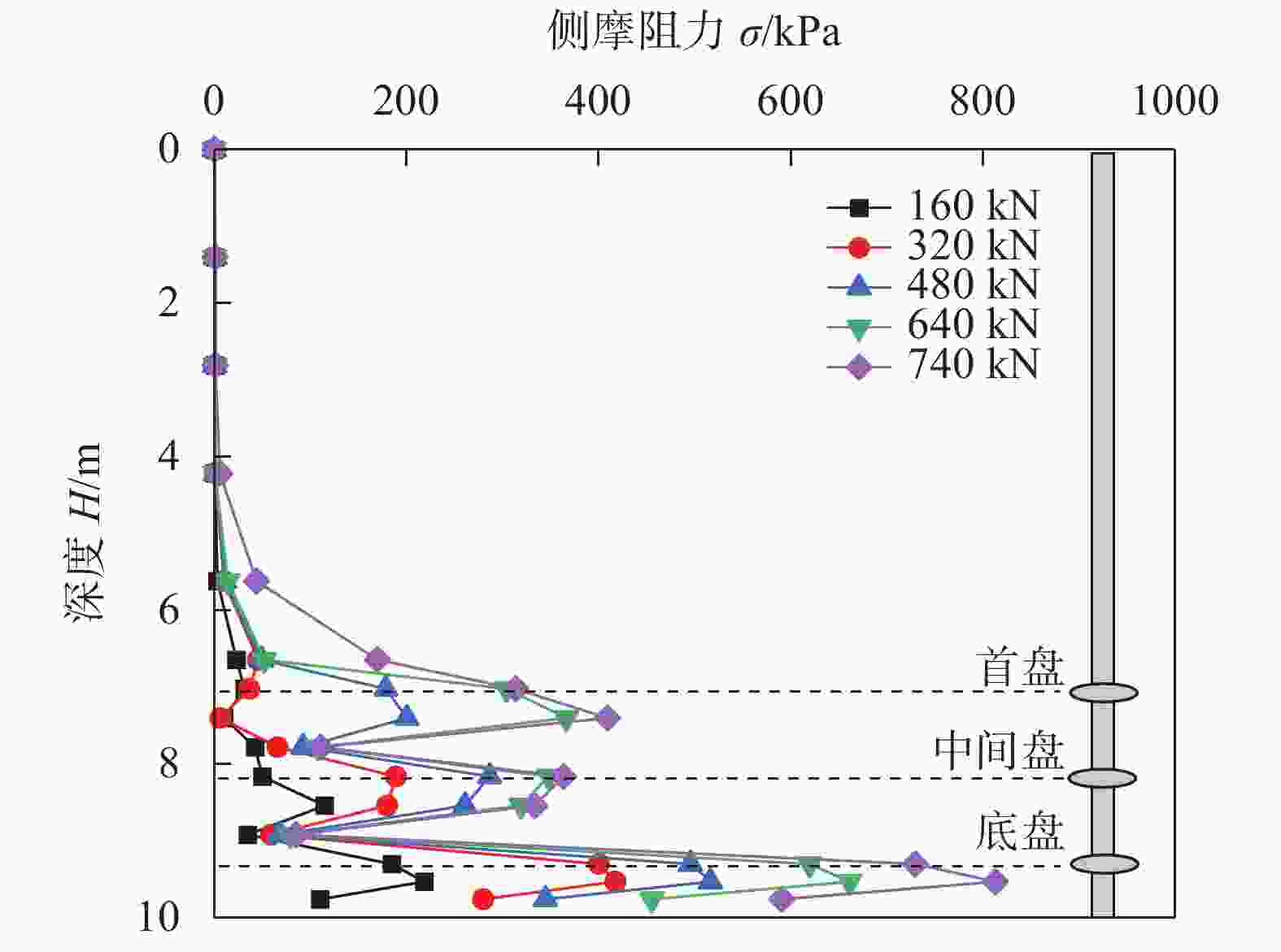
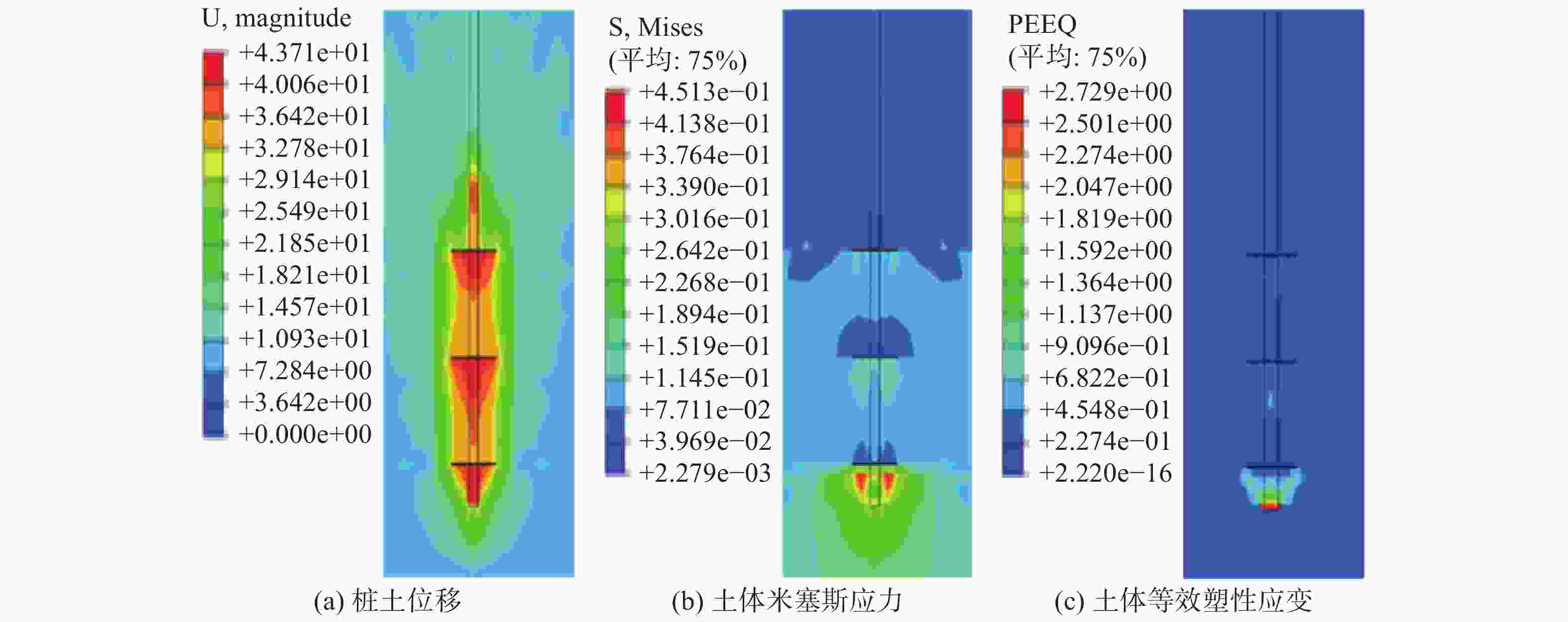
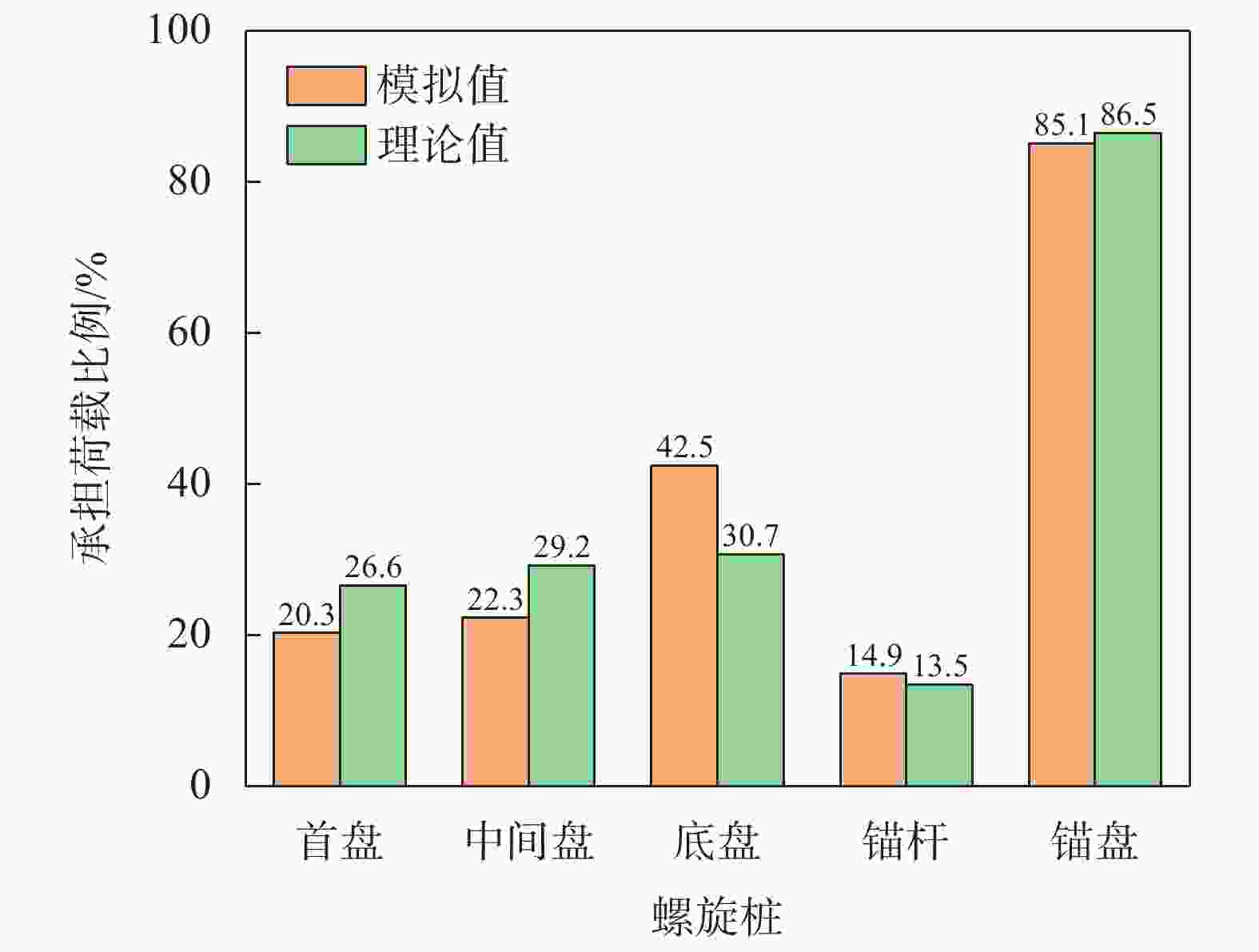
摘要: 螺旋桩结构简单、施工方便、绿色环保,正逐渐应用于输电线塔基础。开展粉质黏土地基中螺旋桩抗压承载力现场试验,探讨了不同极限承载力判定方法的适用性;基于有限元软件ABAQUS建立螺旋桩–土体现场试验三维模型,研究了下压荷载作用下螺旋桩的桩身轴力、侧摩阻力及土体破坏形式,通过规范计算和数值模拟对比分析了极限状态下锚杆和锚盘的荷载分担占比。结果表明:下压荷载作用下螺旋桩的荷载–桩顶位移曲线整体呈现出典型的线性–高度非线性–近似线性趋势,可使用lg P-s法与Reese & O’Neill方法辅助确定极限抗压承载力;螺旋桩锚盘上部区域锚杆发挥侧摩阻力较少,主要通过锚盘端阻力和锚盘之间锚杆的侧摩阻力抵抗下压荷载;极限荷载下3个锚盘之间的土体位移产生贯穿,形成较为完整的圆柱形滑裂面;底盘下部土体应力和塑性应变最大,率先发生剪切破坏;极限状态下螺旋桩各部位承担荷载比例大小依次为底盘>中间盘>首盘>锚杆,锚盘共可承担约85%的荷载。Abstract: The helical pile has advantages such as simple structure, convenient construction, and environmental friendliness, and is gradually being applied to the foundation of transmission line towers. Field tests on compressive bearing capacity of helical pile in silty clay foundation were carried out, and the applicability of different determination methods for ultimate bearing capacity was discussed. A three-dimensional model of the helical pile and soil was established using the finite element software ABAQUS. The axial force and lateral frictional resistance of the helical pile, and soil failure mode under vertical compression load were studied. The load sharing ratio of anchor rod and anchor plates under ultimate state was comparatively analyzed through code-based calculation and numerical simulation. The research results show that under vertical compression load, the load-displacement curve of the helical pile exhibits a typical linear-highly nonlinear-approximate linear trend. The lg P-s method and Reese & O’Neill method can be used to assist in determining the ultimate compressive bearing capacity. The upper region of anchor plate exhibits less lateral frictional resistance from the anchor rod, the vertical compression load is mainly resisted through the end resistance of the anchor plate and the lateral friction resistance of the anchor rod between anchor plates. Under ultimate load, soil displacement occurs through three anchor plates to form a relatively complete cylindrical slip surface. The maximum stress and plastic strain of soil under the bottom plate occur first, leading to shear failure. Under ultimate conditions, the load distribution among different parts of the helical pile is as follows: bottom plate > middle plate > top plate > anchor rod. The anchor plates collectively bear around 85% of the load.
-
Key words:
- helical pile /
- silty clay /
- compressive bearing performance /
- field test /
- numerical simulation
-
表 1 桩周土体物理性质和力学参数
土质 层厚/m 重度γ
/(kN·m−3)黏聚力
c/kPa内摩擦角
φ/(°)压缩模量
Es/MPa承载力
特征值fak/kPa粉质黏土 9.0 18.8 35 12 7.0 140 粉土 2.0 19.5 25 12 160 表 2 不同方法确定螺旋桩的抗压极限承载力
编号 方法名称 判定依据 对应极限承载力的
桩顶位移/mm极限承
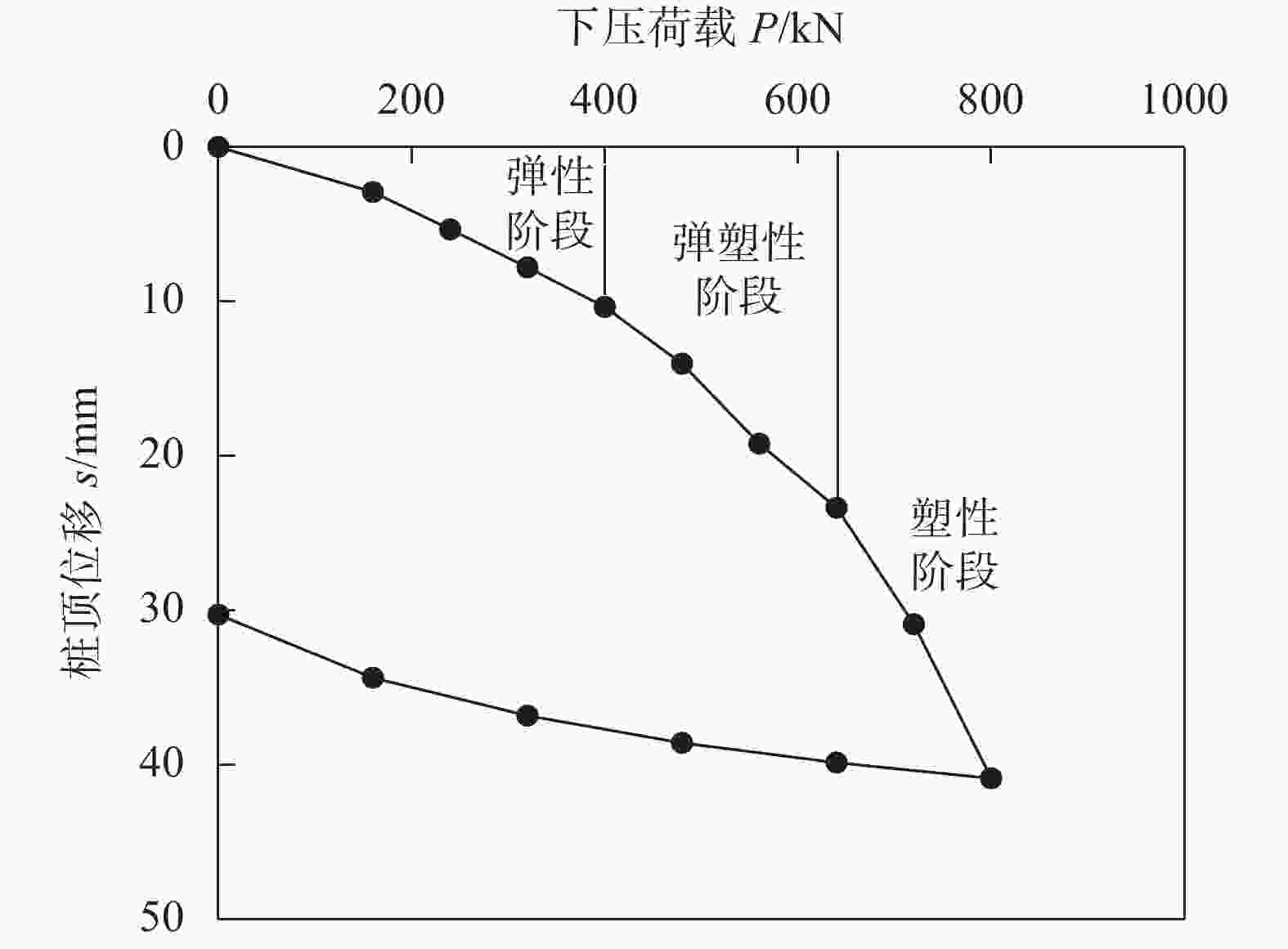
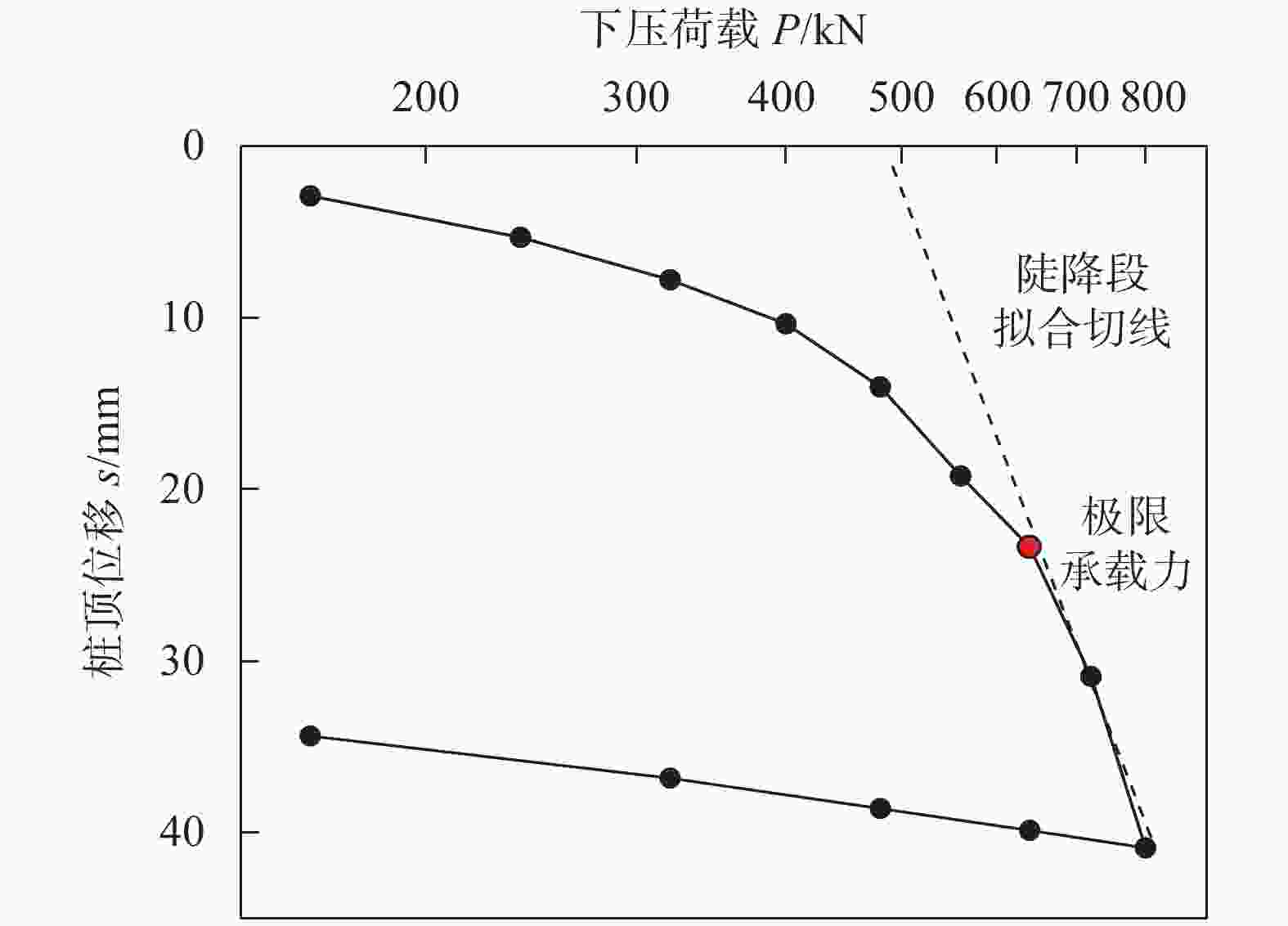
载力/kN1 B Livneh & M H El Naggar法[14] 对应极限承载力的桩顶位移:$ s = \dfrac{{PL}}{{AE}} + 0.08{D_{\max }} $ 54.3 2 修正Davisson方法[15] 对应极限承载力的桩顶位移:$ s = \dfrac{{PL}}{{AE}} + 0.1{D_{{\text{avg}}}} $ 66.3 3 Davisson方法[10] 对应极限承载力的桩顶位移:$ s = \dfrac{{PL}}{{AE}} + \dfrac{D}{{120}} + 4 $ 15.3 560 4 lg P-s法[11] 首先将桩P-s曲线处理为lg P-s曲线,找出相应的
陡降初始点为极限荷载23.4 640 5 Reese & O’Neill方法[12] 桩顶位移为5%D时对应的荷载 30 720 6 《建筑基桩检测技术规范》
(JGJ 106–2014)[13]对于缓变型Q-s曲线,宜根据桩顶总沉降量,
取s等于40 mm对应的荷载值40 800 注:L为锚杆的总长度;P为桩顶荷载;A为锚杆截面面积;E为钢材弹性模量;D为螺旋桩锚盘直径,其中Dmax和Davg分别为锚盘的最大直径和平均直径,本次试验中锚盘直径都相同,Dmax=Davg=D。 表 3 极限状态下螺旋桩各锚盘和锚杆承担荷载
获取方式 首盘承担
荷载/kN中间盘承
担荷载/kN底盘承担
荷载/kN锚杆承担
荷载/kN极限承
载力/kN模拟值 150 164 315 110 740 理论值 207.97 227.89 240.0 104.67 780.53 实测值 800 -
[1] 张 武, 姚晓旭, 张 波, 等. 沉降控制条件下的基桩设计实例[J]. 岩土工程技术,2023,37(5):553-558. (ZHANG W, YAO X X, ZHANG B, et al. An example of foundation pile design under settlement control[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique,2023,37(5):553-558. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2023.05.007ZHANG W, YAO X X, ZHANG B, et al. An example of foundation pile design under settlement control[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique, 2023, 37(5): 553-558. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2023.05.007 [2] MERIFIELD R S. Ultimate uplift capacity of multiplate helical type anchors in clay[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2011,137(7):704-716. [3] 刘志鹏, 孔纲强, 文 磊, 等. 砂土地基中倾斜螺旋桩群桩上拔与水平承载特性模型试验[J]. 岩土力学,2021,42(7):1944-1950. (LIU Z P, KONG G Q, WEN L, et al. Model tests on uplift and lateral bearing characteristics of inclined helical pile group embedded in sand[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2021,42(7):1944-1950. (in Chinese)LIU Z P, KONG G Q, WEN L, et al. Model tests on uplift and lateral bearing characteristics of inclined helical pile group embedded in sand[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(7): 1944-1950. (in Chinese) [4] KWON O, LEE J, KIM G, et al. Investigation of pullout load capacity for helical anchors subjected to inclined loading conditions using coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian analyses[J]. Computers and Geotechnics,2019,111:66-75. [5] SAKR M. Installation and performance characteristics of high capacity helical piles in cohesive soils[J]. DFI Journal-The Journal of the Deep Foundations Institute,2012,6(1):41-57. [6] 屈讼昭, 郭咏华, 王 仪, 等. 大锚片螺旋锚在粉质黏土中的下压承载性能[J]. 土木与环境工程学报(中英文),2021,43(5):34-44. (QU S Z, GUO Y H, WANG Y, et al. Bearing capacity of screw anchor with large anchor plate in silty clay[J]. Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering,2021,43(5):34-44. (in Chinese)QU S Z, GUO Y H, WANG Y, et al. Bearing capacity of screw anchor with large anchor plate in silty clay[J]. Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering, 2021, 43(5): 34-44. (in Chinese) [7] 董天文, 梁 力. 竖向受压螺旋桩荷载沉降函数解[J]. 岩土工程学报,2007,29(10):1483-1487. (DONG T W, LIANG L. Solution of load-settlement function of single screw pile under axial pressure[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2007,29(10):1483-1487. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2007.10.009DONG T W, LIANG L. Solution of load-settlement function of single screw pile under axial pressure[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2007, 29(10): 1483-1487. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2007.10.009 [8] 张亚军, 梁 力, 董天文, 等. 竖向承压螺旋桩基础极限承载力判定[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版),2009,28(4):570-573. (ZHANG Y J, LIANG L, DONG T W, et al. Estimation of ultimate load for a screw pile under the vertical pressure[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University (Natural Science),2009,28(4):570-573. (in Chinese)ZHANG Y J, LIANG L, DONG T W, et al. Estimation of ultimate load for a screw pile under the vertical pressure[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University (Natural Science), 2009, 28(4): 570-573. (in Chinese) [9] 宗钟凌, 曹 博, 黄蕴晗, 等. 注浆螺旋钢管桩抗压承载性能试验研究[J]. 工业建筑,2022,52(6):127-132. (ZONG Z L, CAO B, HUANG Y H, et al. Experimental study on compressive bearing capacity of helical steel grounting pipe piles[J]. Industrial Construction,2022,52(6):127-132. (in Chinese)ZONG Z L, CAO B, HUANG Y H, et al. Experimental study on compressive bearing capacity of helical steel grounting pipe piles[J]. Industrial Construction, 2022, 52(6): 127-132. (in Chinese) [10] DAVISSON M T. High capacity piles[C]//Proceedings of Lecture Series on Innovations in Foundation Construction. Chicago: American Society of Civil Engineers, Illinois Section, 1972: 81-112. [11] 沈保汉. 评价桩工作特性的新方法-P/PU-S/SU曲线法[J]. 建筑技术开发, 1994(2): 11-21. (SHEN B H. A new method for evaluating the working characteristics of piles-P/PU-S/SU curve method[J]. Building Technology Development, 1994(2): 11-21. (in Chinese)SHEN B H. A new method for evaluating the working characteristics of piles-P/PU-S/SU curve method[J]. Building Technology Development, 1994(2): 11-21. (in Chinese) [12] REESE L C, O’NEILL M W. Drilled shafts: construction and aw design[R]. Federal Highway Administration, McLean, Virginia, 1988. [13] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑桩基检测技术规范: JGJ 106−2014[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2014. (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Technical code for testing of building foundation piles: JGJ 106−2014[S]. Beijing: China Building Industry Press, 2014. (in Chinese)Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Technical code for testing of building foundation piles: JGJ 106−2014[S]. Beijing: China Building Industry Press, 2014. (in Chinese) [14] LIVNEH B, EL NAGGAR M H. Axial testing and numerical modeling of square shaft helical piles under compressive and tensile loading[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2008,45(8):1142-1155. [15] PERKO H A. Helical piles: a practical guide to design and installation[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2009: 205-207. [16] 李绪勇, 杨忠平, 刘 纲, 等. 隔离式螺旋桩抗压承载与抗地基冻融特性[J]. 岩土工程学报,2024,46(6):1187-1196. (LI X Y, YANG Z P, LIU G, et al. Characteristics of compressive bearing capacity and resistance to foundation freeze-thaw of the isolation helical pile[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2024,46(6):1187-1196. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE20230209LI X Y, YANG Z P, LIU G, et al. Characteristics of compressive bearing capacity and resistance to foundation freeze-thaw of the isolation helical pile[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2024, 46(6): 1187-1196. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE20230209 [17] ALWALAN M F, EL NAGGAR M H. Finite element analysis of helical piles subjected to axial impact loading[J]. Computers and Geotechnics,2020,123:103597. [18] 孙玉辉, 张 辉, 陈昌彦, 等. 桩基竖向承载力测试及桩土作用数值模拟分析[J]. 岩土工程技术,2020,34(6):311-315. (SUN Y H, ZHANG H, CHEN C Y, et al. Vertical bearing capacity test of bridge pile foundation and numerical simulation analysis of pile-soil interaction[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique,2020,34(6):311-315. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2020.06.001SUN Y H, ZHANG H, CHEN C Y, et al. Vertical bearing capacity test of bridge pile foundation and numerical simulation analysis of pile-soil interaction[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique, 2020, 34(6): 311-315. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2020.06.001 [19] NOWKANDEH M J, CHOOBBASTI A J. Numerical study of single helical piles and helical pile groups under compressive loading in cohesive and cohesionless soils[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2021,80(5):4001-4023. [20] 国家电网有限公司. 架空输电线路螺旋锚基础设计规范: Q/GDW 10584−2022[S]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2022. (State Grid Corporation of China. Code for design of helical anchor foundation of overhead transmission line: Q/GDW 10584−2022[S]. Beijing: China Electric Power Press, 2022. (in Chinese)State Grid Corporation of China. Code for design of helical anchor foundation of overhead transmission line: Q/GDW 10584−2022[S]. Beijing: China Electric Power Press, 2022. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: