Large area construction squeezing effect of PST piles in deep soft soil sites based on CPTU testing
-
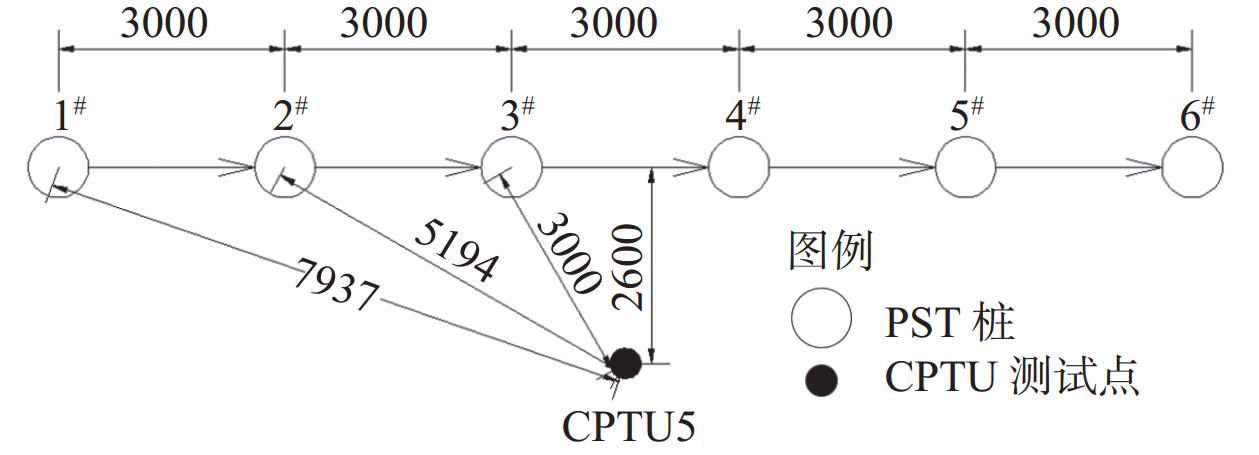
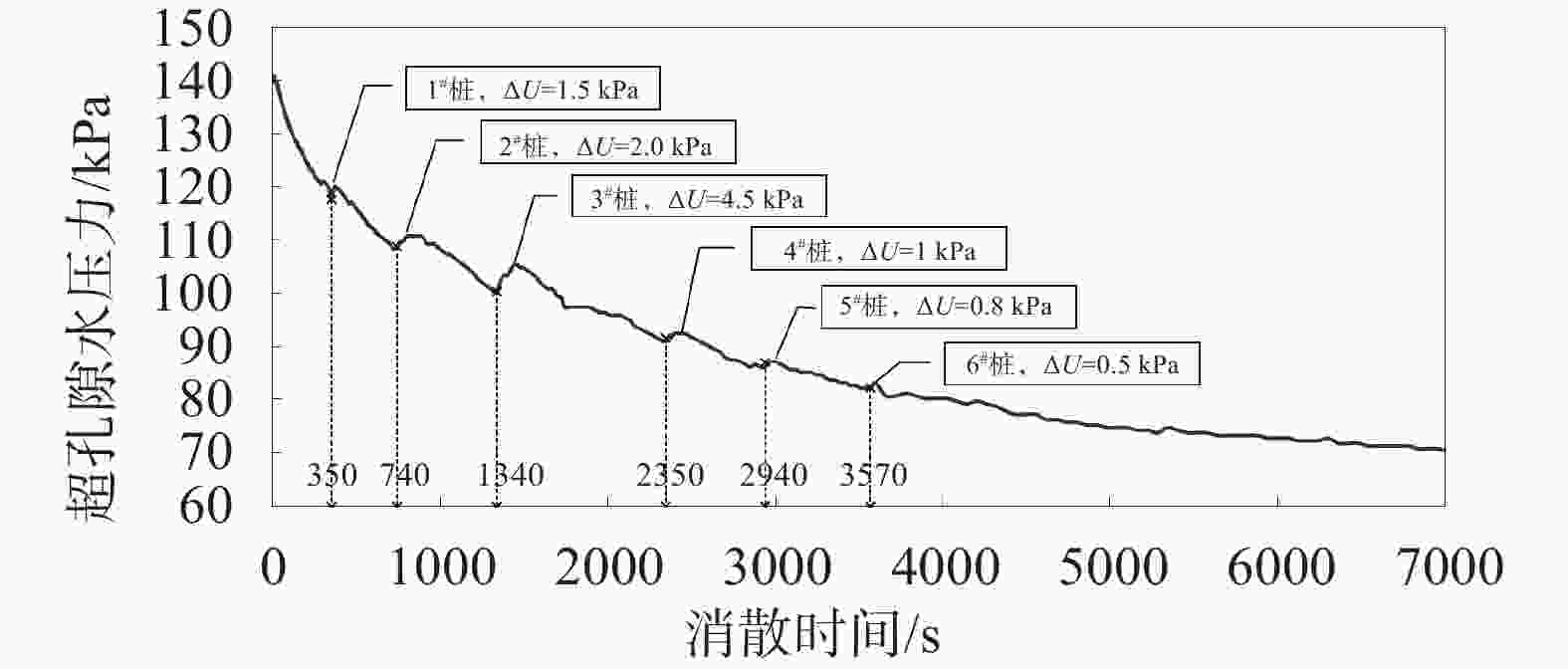
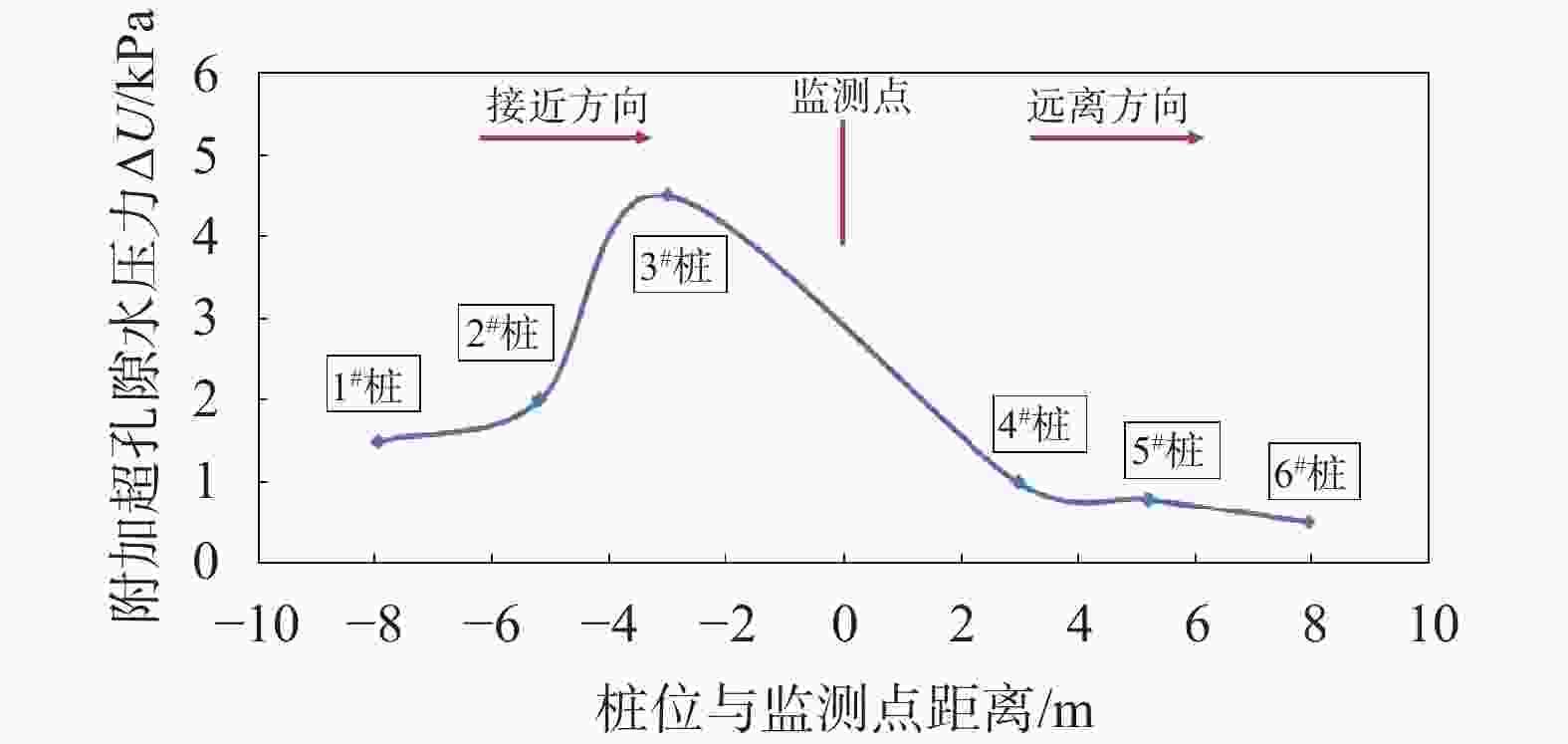
摘要: 为了分析 PST管桩在深厚软土场地大面积施工过程中的挤土效应,采用多功能高精度孔压静力触探(CPTU)测试技术对PST桩施工前后软土层的侧壁摩阻力、超孔隙水压力及其消散过程进行了测试。测试结果表明:同层淤泥中,水平固结系数随深度的加深不断减小,同时挤土效应本身也会加剧软土固结系数的降低,管桩越长,挤土效应缓解所需要的时间越久;群桩施工组织顺序对挤土效应影响显著,远离测点施工引起的孔隙水压力增量仅为朝向测点施工时的29%;在PST 桩施工后一段时间内,场地软土强度受扰动降低,降低幅度可达40%,约120 d后软土层的土体强度可基本恢复至施工前水平;对于近接上部透水层的浅层软土,在打桩后软土发生了动力固结,长期强度较施工前有所提升。Abstract: To analyze the soil squeezing effect during the large-scale construction process of PST pipe piles, the multifunctional high-precision pore pressure static penetration test (CPTU) technology was used to test the side wall friction resistance, excess pore water pressure, and dissipation process of the soft soil layer before, during, and after the construction of PST piles. The test results show that in the same layer of silt, the horizontal consolidation coefficient decreases continuously with depth, and the squeezing effect itself also intensifies the decrease in the consolidation coefficient of soft soil. When the pipe piles are longer, the time required to alleviate the squeezing effect is longer; The influence of pile group construction organization on the control of the soil compaction effect is significant, and the pore water pressure increment caused by construction away from the measuring point is only 29% of that caused by construction towards the measuring point; After the construction of PST piles, the strength of the soft soil on the site was reduced by disturbance, with a reduction of up to 40%. After about 120 days, the soil strength of the soft soil layer can recover to the level before construction. For shallow soft soil adjacent to the upper permeable layer, dynamic consolidation occurs after pile driving, and the long-term strength has improved compared to before construction.
-
Key words:
- PST pipe pile /
- squeezing effect /
- CPTU /
- excess pore water pressure
-
表 1 土层物理力学性质指标
土层名称 厚度/m 状态 重度/(kN·m−3) 含水量/% 天然孔隙比e 灵敏度 超固结比OCR 压缩模量/MPa 黏聚力 c/kPa 内摩擦角φ/(°) 素填土 0.60~3.80 松散 18.5 4 1 20 淤泥 2.00~18.40 流塑 15.7 67.67 1.831 4.27 0.81 1.74 5.93 6.15 粉质黏土 0.60~9.80 可塑 18.6 32.45 0.903 6.24 20.65 15.90 卵石 0.90~12.20 稍密—中密 20.5 26 3 35 角砾 0.50~13.00 稍密 20.1 22 2 30 表 2 各工况淤泥层的t50及水平固结系数
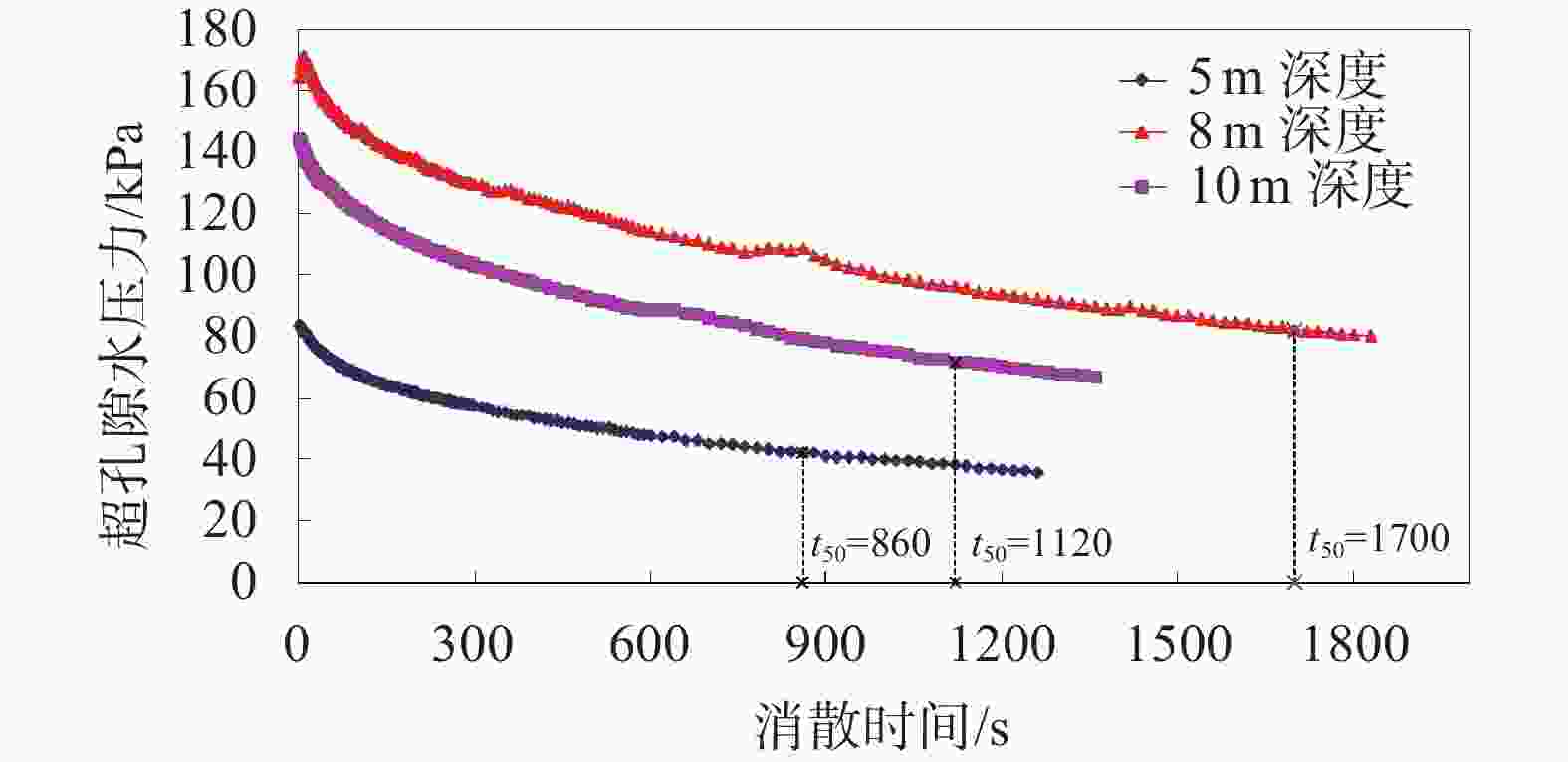
序号 测试点编号 对应桩径/mm 测试深度/m 对应土层 t50/s 对应时间段 计算水平固结系数Ch /(10−3 cm2·s−1) 1 CPTU1 400 5 淤泥 860 管桩施工前 0.250 8 淤泥 1120 管桩施工前 0.192 10 淤泥 1700 管桩施工前 0.126 2 CPTU2 400 5 淤泥 2640 管桩施工中 0.080 3 CPTU3 400 5 淤泥 9020 管桩施工中 0.024 4 CPTU4 400 5 淤泥 11880 管桩施工中 0.018 -
[1] 林 巧. 滨海软土地基超大面积浅基坑支护技术工程实践研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2014,36(S1):109-117. (LIN Q. Practices of supporting technology for shallow super-large excavations in coastal area under soft foundation conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2014,36(S1):109-117. (in Chinese)LIN Q. Practices of supporting technology for shallow super-large excavations in coastal area under soft foundation conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(S1): 109-117. (in Chinese) [2] 张玉成, 杨光华, 胡海英, 等. 珠三角深厚软土地区浅基坑支护若干问题探讨[J]. 岩土工程学报,2014,36(S1):1-11. (ZHANG Y C, YANG G H, HU H Y, et al. Some problems about retaining structures for shallow pits in deep and soft soil areas of Pearl River Delta[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2014,36(S1):1-11. (in Chinese)ZHANG Y C, YANG G H, HU H Y, et al. Some problems about retaining structures for shallow pits in deep and soft soil areas of Pearl River Delta[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(S1): 1-11. (in Chinese) [3] 王 虎, 李 栋, 唐昌意, 等. 深基坑开挖影响下深厚软土路基变形规律研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2023,19(6):2011-2019. (WANG H, LI D, TANG C Y, et al. Study on the deformation law of deep soft soil subgrade under the influence of deep foundation pit excavation[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering,2023,19(6):2011-2019. (in Chinese)WANG H, LI D, TANG C Y, et al. Study on the deformation law of deep soft soil subgrade under the influence of deep foundation pit excavation[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2023, 19(6): 2011-2019. (in Chinese) [4] 王绍平. PST桩在高等级公路软土地基中的应用[J]. 福建地质,2023,42(2):155-160. (WANG S P. Application of PST pile in the soft soil foundation of high-class highway[J]. Geology of Fujian,2023,42(2):155-160. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3970.2023.02.010WANG S P. Application of PST pile in the soft soil foundation of high-class highway[J]. Geology of Fujian, 2023, 42(2): 155-160. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3970.2023.02.010 [5] 李丽华, 陈 轮, 高盛焱. 翠湖湿地软土触变性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2010,31(3):765-768. (LI L H, CHEN L, GAO S Y, et al. Experimental research on thixotropy of wetland soft soil in Cuihu[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2010,31(3):765-768. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2010.03.041LI L H, CHEN L, GAO S Y, et al. Experimental research on thixotropy of wetland soft soil in Cuihu[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010, 31(3): 765-768. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2010.03.041 [6] 杨生彬, 李友东. PHC管桩挤土效应试验研究[J]. 岩土工程技术,2006,20(3):117-120. (YANG S B, LI Y D. Experimental research on compacting effect of PHC piles[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique,2006,20(3):117-120. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2006.03.003YANG S B, LI Y D. Experimental research on compacting effect of PHC piles[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique, 2006, 20(3): 117-120. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2006.03.003 [7] 李国维, 边圣川, 陆晓岑, 等. 软基路堤拓宽静压PHC管桩挤土效应现场试验[J]. 岩土力学,2013,34(4):1089-1096. (LI G W, BIAN S C, LU X C, et al. Field test on extruding soil caused of PHC pipe pile driving by static pressure for improving soft foundation of widened embankment[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2013,34(4):1089-1096. (in Chinese)LI G W, BIAN S C, LU X C, et al. Field test on extruding soil caused of PHC pipe pile driving by static pressure for improving soft foundation of widened embankment[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(4): 1089-1096. (in Chinese) [8] 李双龙, 魏丽敏, 杜 猛, 等. 大面积静压群桩对邻近场地挤土变形影响试验研究[J]. 中国铁道科学,2020,41(3):31-40. (LI S L, WEI L M, DU M, et al. Experimental study on squeezing deformation in adjacent site caused by the construction of large-area jacked pile group[J]. China Railway Science,2020,41(3):31-40. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2020.03.04LI S L, WEI L M, DU M, et al. Experimental study on squeezing deformation in adjacent site caused by the construction of large-area jacked pile group[J]. China Railway Science, 2020, 41(3): 31-40. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2020.03.04 [9] 张金磊. 深厚淤泥场地桩基施工的挤土效应分析[D]. 保定: 河北大学, 2021. (ZHANG J L. Analysis of soil squeezing effect of pipe pile construction in deep silt site[D]. Baoding: Hebei University, 2021.(in Chinese)ZHANG J L. Analysis of soil squeezing effect of pipe pile construction in deep silt site[D]. Baoding: Hebei University, 2021.(in Chinese) [10] 朱 锐, 周 峰, 陈廷柱, 等. 劲性复合桩挤土效应及承载力作用机制研究[J]. 岩土力学,2023,44(12):3577-3586. (ZHU R, ZHOU F, CHEN T Z, et al. Soil squeezing effect and bearing mechanism of strength composite pile[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2023,44(12):3577-3586. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2023.0347ZHU R, ZHOU F, CHEN T Z, et al. Soil squeezing effect and bearing mechanism of strength composite pile[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2023, 44(12): 3577-3586. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2023.0347 [11] 桑松魁, 白晓宇, 孔 亮, 等. 层状黏性土中静压桩沉贯特性现场试验[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2022,41(10):2135-2148. (SANG S K, BAI X Y, KONG L, et al. Field test of penetration characteristics of jacked piles in layered clay[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2022,41(10):2135-2148. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2021.1246SANG S K, BAI X Y, KONG L, et al. Field test of penetration characteristics of jacked piles in layered clay[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(10): 2135-2148. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2021.1246 [12] 赵春风, 杜兴华, 赵 程, 等. 中掘预应力管桩挤土效应试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2013,35(3):415-421. (ZHAO C F, DU X H, ZHAO C, et al. Squeezing effect of inner-digging prestressed piles[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2013,35(3):415-421. (in Chinese)ZHAO C F, DU X H, ZHAO C, et al. Squeezing effect of inner-digging prestressed piles[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(3): 415-421. (in Chinese) [13] 朱向荣, 何耀辉, 徐崇峰, 等. 饱和软土单桩沉桩超孔隙水压力分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2005,24(S2):5740-5744. (ZHU X R, HE Y H, XU C F, et al. Excess pore water pressure caused by single pile driving in saturated soft soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2005,24(S2):5740-5744. (in Chinese)ZHU X R, HE Y H, XU C F, et al. Excess pore water pressure caused by single pile driving in saturated soft soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(S2): 5740-5744. (in Chinese) [14] 雷华阳, 李 肖, 陆培毅, 等. 管桩挤土效应的现场试验和数值模拟[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(4):1006-1012. (LEI H Y, LI X, LU P Y, et al. Field test and numerical simulation of squeezing effect of pipe pile[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2012,33(4):1006-1012. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2012.04.039LEI H Y, LI X, LU P Y, et al. Field test and numerical simulation of squeezing effect of pipe pile[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(4): 1006-1012. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2012.04.039 [15] 黄院雄, 许清侠, 胡中雄. 饱和土中打桩引起桩周围土体的位移[J]. 工业建筑,2000,30(7):15-19,32. (HUANG Y X, XU Q X, HU Z X. Soil's displacemnet due to driving pile in saturated clay[J]. Industrial Construction,2000,30(7):15-19,32. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13204/j.gyjz2000.07.004HUANG Y X, XU Q X, HU Z X. Soil's displacemnet due to driving pile in saturated clay[J]. Industrial Construction, 2000, 30(7): 15-19,32. doi: 10.13204/j.gyjz2000.07.004 [16] 罗战友. 静压桩挤土效应及施工措施研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2004. (LUO Z Y. Study on compacting effects and construction measures of jacked pile[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2004. (in Chinese)LUO Z Y. Study on compacting effects and construction measures of jacked pile[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2004. (in Chinese) [17] 陆培毅, 杨志锋, 付海峰, 等. 饱和软土中沉桩引起的超孔隙水压力分析[J]. 工业建筑,2012,42(S1):416-419. (LU P Y, YANG Z F, FU H F, et al. The analysis of excess pore water pressure caused by pile driving in saturated soft soil[J]. Industrial Construction,2012,42(S1):416-419. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13204/j.gyjz2012.s1.094LU P Y, YANG Z F, FU H F, et al. The analysis of excess pore water pressure caused by pile driving in saturated soft soil[J]. Industrial Construction, 2012, 42(S1): 416-419. doi: 10.13204/j.gyjz2012.s1.094 [18] 邢皓枫, 赵红崴, 徐 超, 等. PHC管桩锤击施工效应分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2009,31(8):1208-1212. (XING H F, ZHAO H W, XU C, et al. Driving effect of PHC pipe piles[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2009,31(8):1208-1212. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2009.08.009XING H F, ZHAO H W, XU C, et al. Driving effect of PHC pipe piles[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2009, 31(8): 1208-1212. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2009.08.009 [19] 朱小军. 大面积预制桩静压施工对周边环境的影响控制研究[J]. 建筑施工, 2015, 37(4): 516, 521. (ZHU X J. Study on impact control of large area precast pile static pressure construction on surrounding environment[J]. Building Construction, 2015, 37(4): 516, 521.(in Chinese)ZHU X J. Study on impact control of large area precast pile static pressure construction on surrounding environment[J]. Building Construction, 2015, 37(4): 516, 521.(in Chinese) [20] 蔡国军, 刘晓燕, 刘路路, 等. 基于孔压消散改进模型的土体孔隙水压力预测[J]. 南京工业大学学报(自然科学版),2021,43(4):492-496. (CAI G J, LIU X Y, LIU L L, et al. Prediction of pore water pressure based on improved pore pressure dissipation model in soil[J]. Journal of Nanjing Tech University (Natural Science Edition),2021,43(4):492-496. (in Chinese)CAI G J, LIU X Y, LIU L L, et al. Prediction of pore water pressure based on improved pore pressure dissipation model in soil[J]. Journal of Nanjing Tech University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 43(4): 492-496. (in Chinese) [21] RANDOLPH M F, LEONG E C, HOULSBY G T. One-dimensional analysis of soil plugs in pipe piles[J]. Géotechnique,1991,41(4):587-598. [22] 王树成. 用双桥静力触探计算粘性土承载力的经验公式[J]. 吉林建筑工程学院学报,1995(1):25-28. (WANG S C. Empirical formulae for calculating clay bearing capacity with double-bridge tactile impression exploration[J]. Journal of Jilin Architectural and Civil Engineering Institute,1995(1):25-28. (in Chinese)WANG S C. Empirical formulae for calculating clay bearing capacity with double-bridge tactile impression exploration[J]. Journal of Jilin Architectural and Civil Engineering Institute, 1995(1): 25-28. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: