MJS reinforcement of foundation pits adjacent to existing stations and settlement analysis of surrounding buildings
-
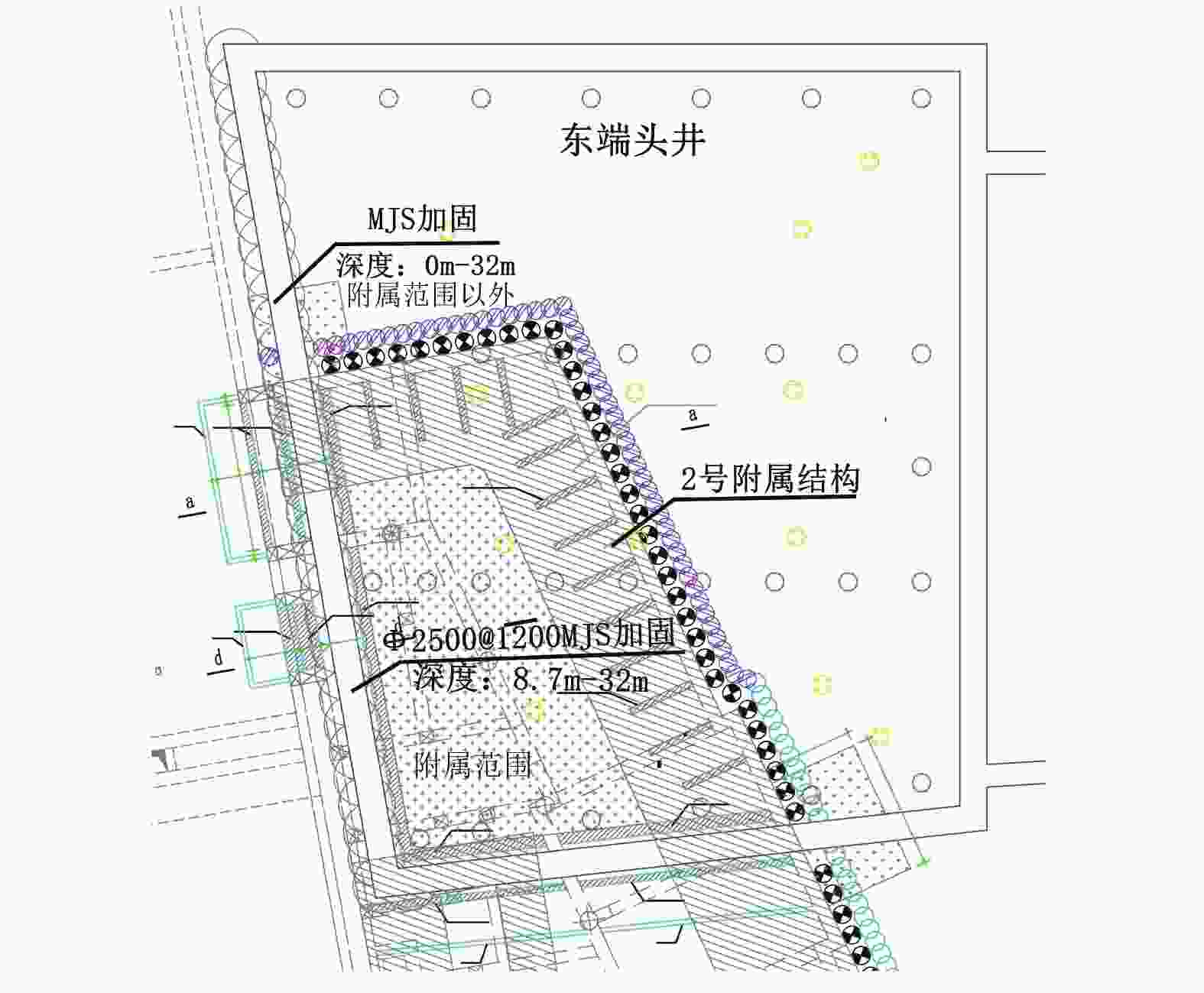
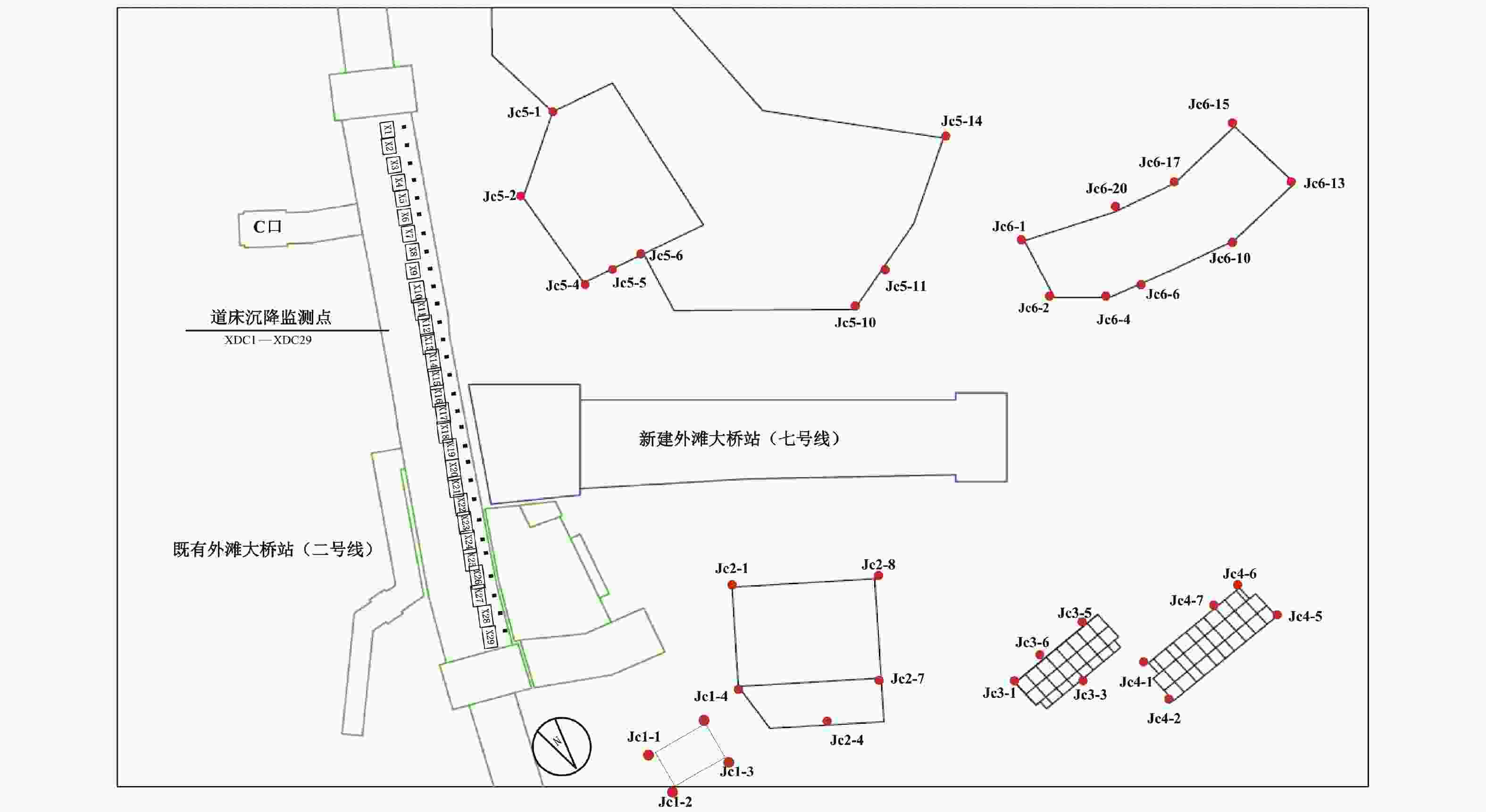
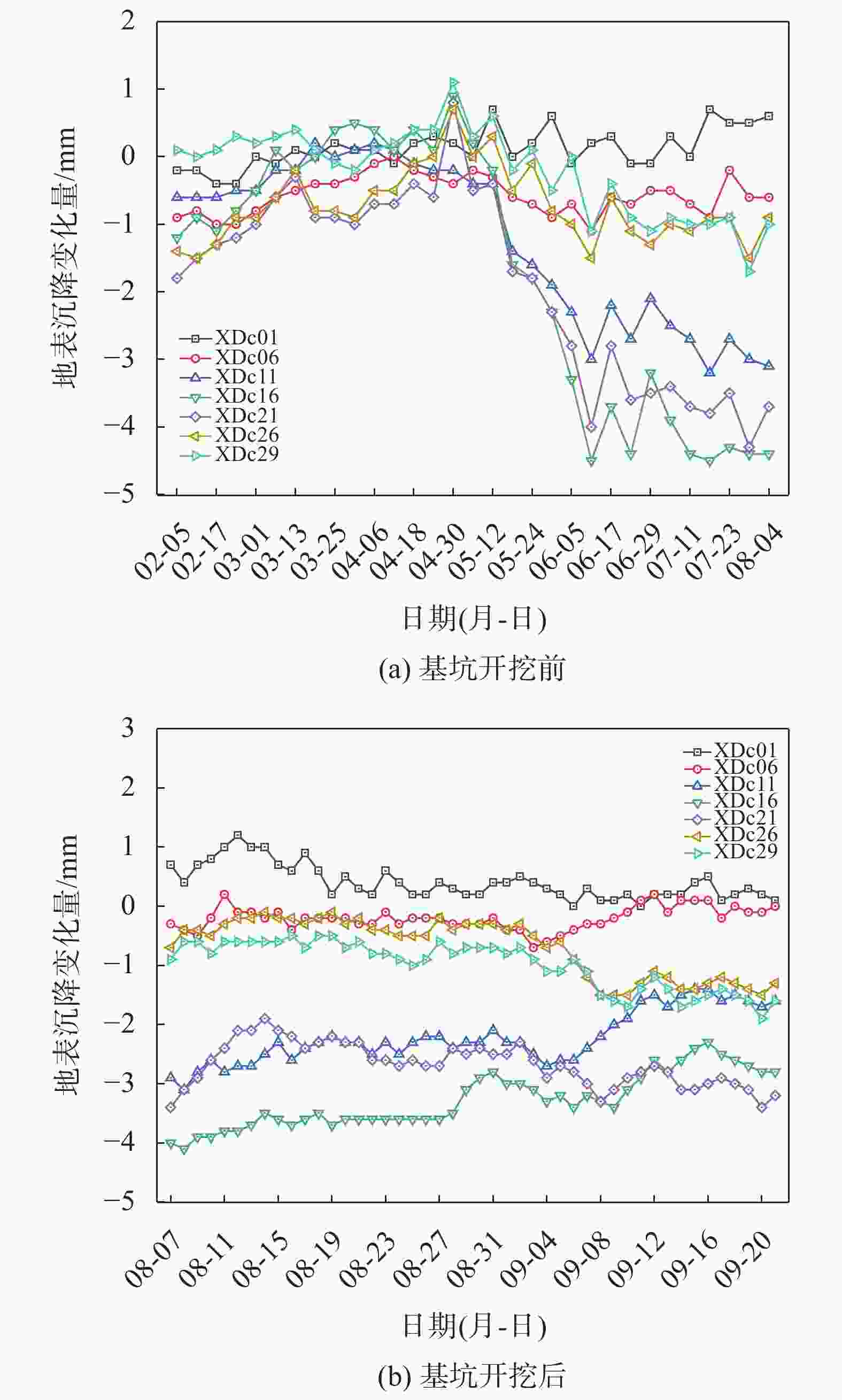
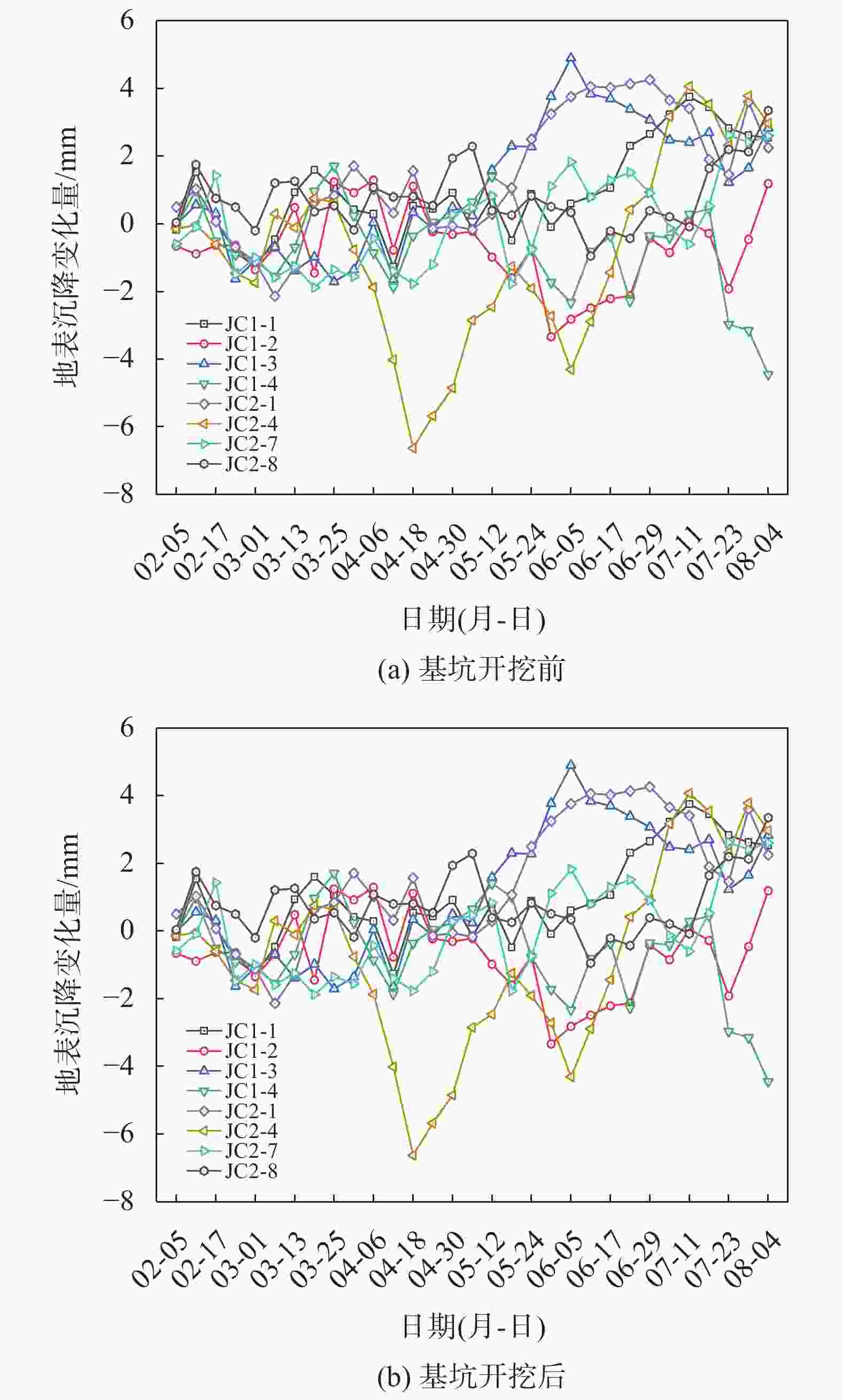
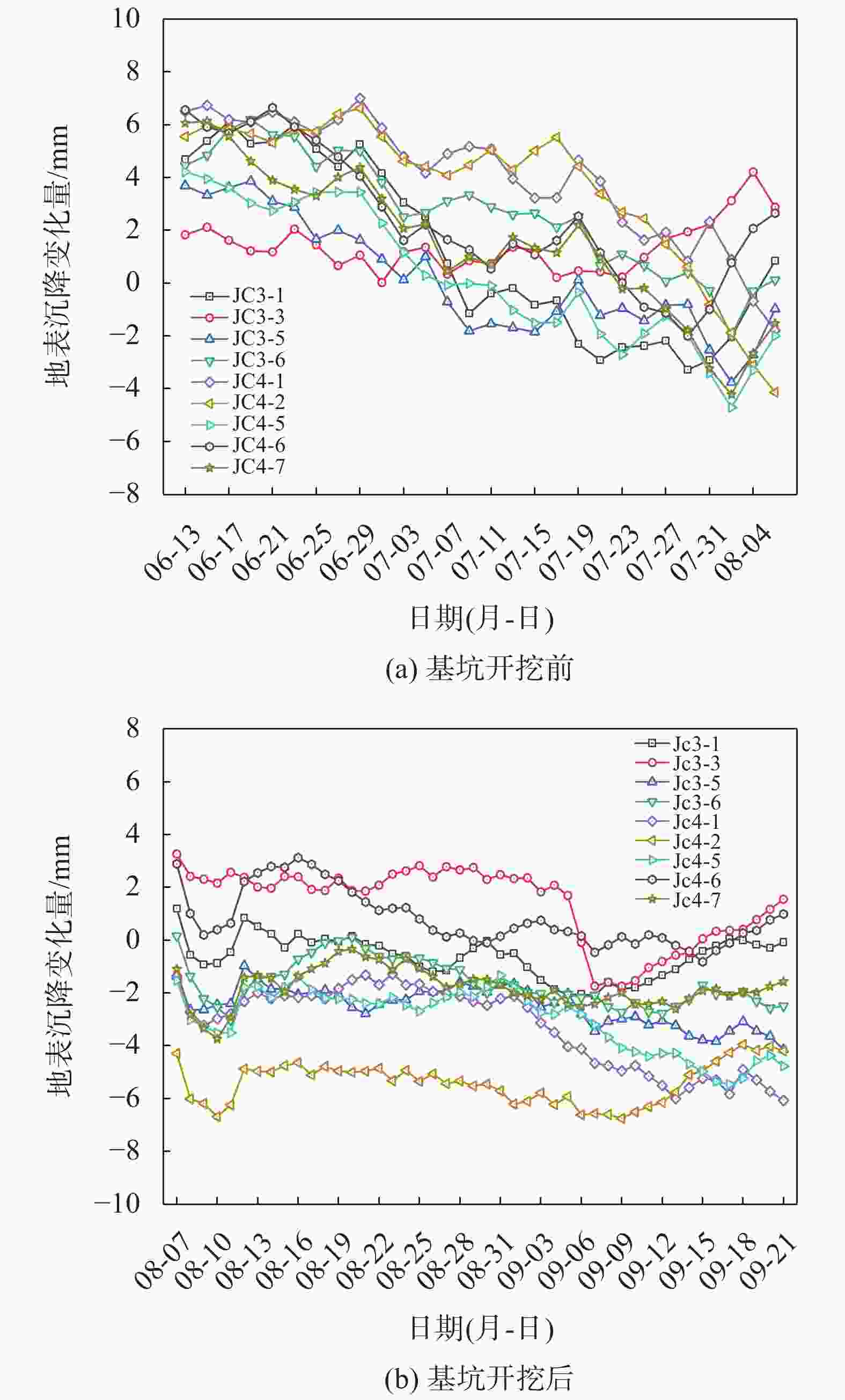
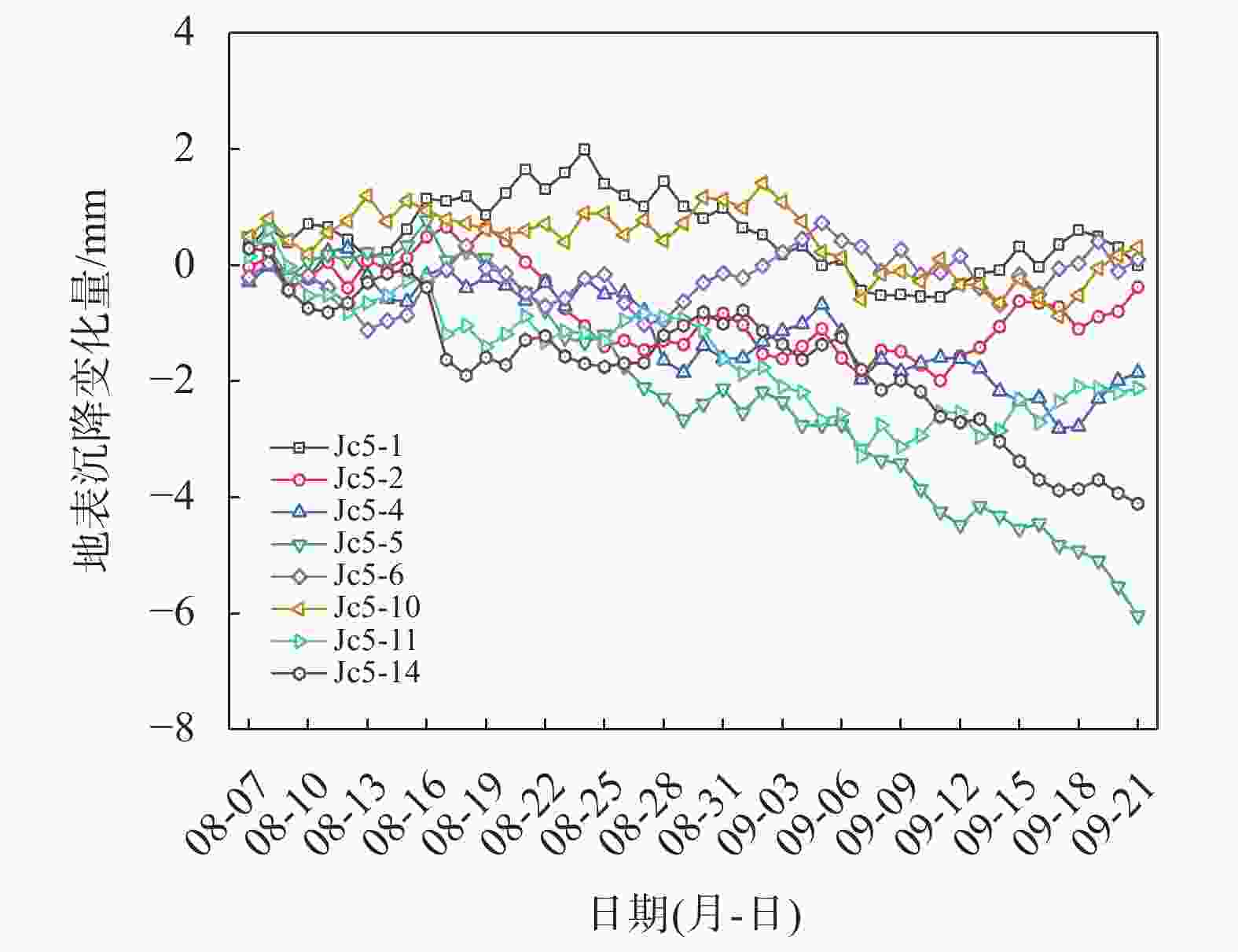
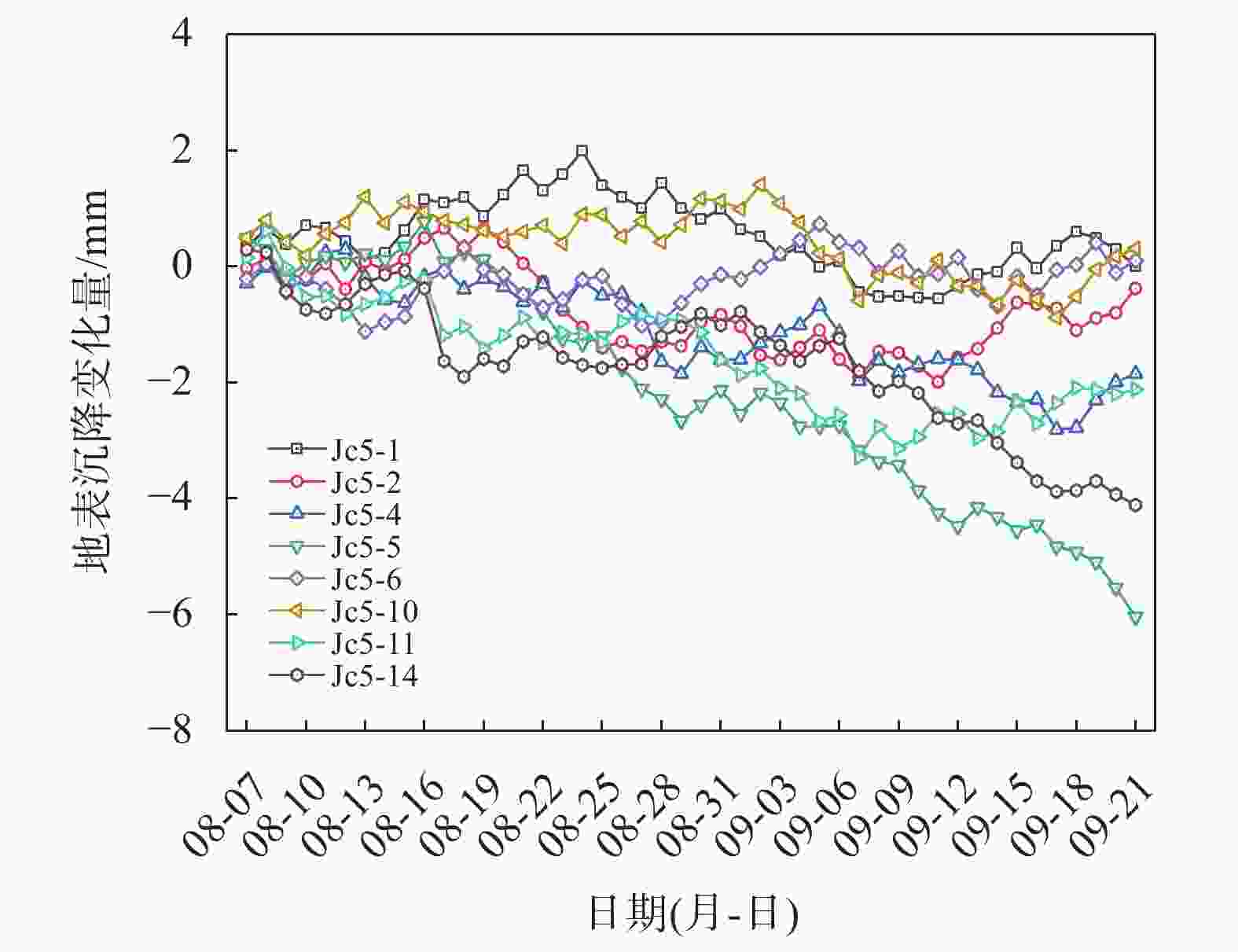
摘要: 宁波市轨道交通7号线外滩大桥站为7号线与既有2号线换乘站,该车站基坑位于软土地层,基坑东侧紧邻既有2号线车站且周边环境复杂,基坑施工易引起围护结构及周边建(构)筑物过大变形,为此采用MJS工法对既有车站西侧土体进行加固,并对基坑及周边建筑进行监测。基坑监测结果表明:基坑施工期间周边建筑沉降量整体呈增大趋势,沉降的最大值更多出现在基坑影响范围内的建筑转角区域;在基坑开挖前,经MJS加固的基坑东侧变形基本控制在−2~4 mm,基坑西侧变形则在−5~7 mm;基坑开挖后,东西两侧的变形量则均控制在−6~4 mm,相比开挖前基坑变形增量较小,且总体变形远低于监测控制值25 mm。本研究表明MJS工法加固可有效控制基坑周边建(构)筑物变形,增加基坑开挖的安全性,可以为后续类似工程施工提供借鉴。Abstract: During the construction of the transfer node at Waitan Bridge Station on Line 7 of Ningbo Rail Transit, it was recognized that the proximity of the new building to the existing Line 2 station, within a complex environment characterized by soft soil layers, posed a risk of excessive deformation to both the project structure and surrounding buildings. To address this concern, the MJS construction method was employed to reinforce the soil on the west side of the existing station, while closely monitoring nearby buildings. The monitoring results revealed an overall increase in settlement of surrounding buildings, with maximum settlement occurring primarily in corner areas within the influence range of foundation pit. Prior to excavation, deformation on the east side of the foundation pit—strengthened by MJS—was effectively controlled within −2 ~ 4 mm; meanwhile, deformation on its west side ranged from −5 ~ 7 mm. Post-excavation, deformations on both sides were managed within −6 ~ 4 mm. In comparison with pre-excavation increments in deformation levels around foundation pit—which remained significantly lower than a monitored control value set at 25 mm—it is evident that implementation of MJS construction method has effectively mitigated structural deformations in surrounding buildings and enhanced safety during foundation pit excavation. These findings can offer valuable insights for similar projects moving forward.
-
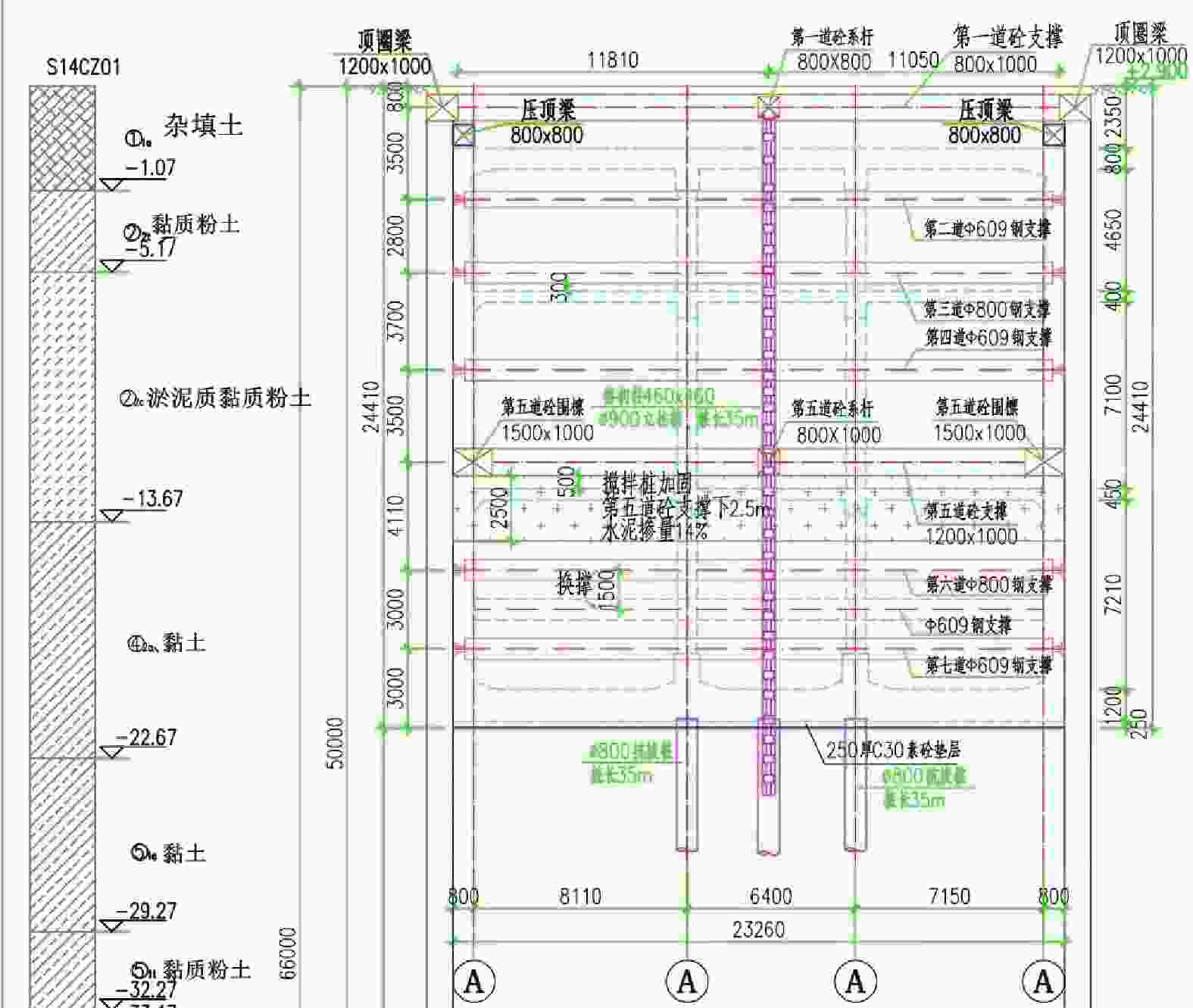
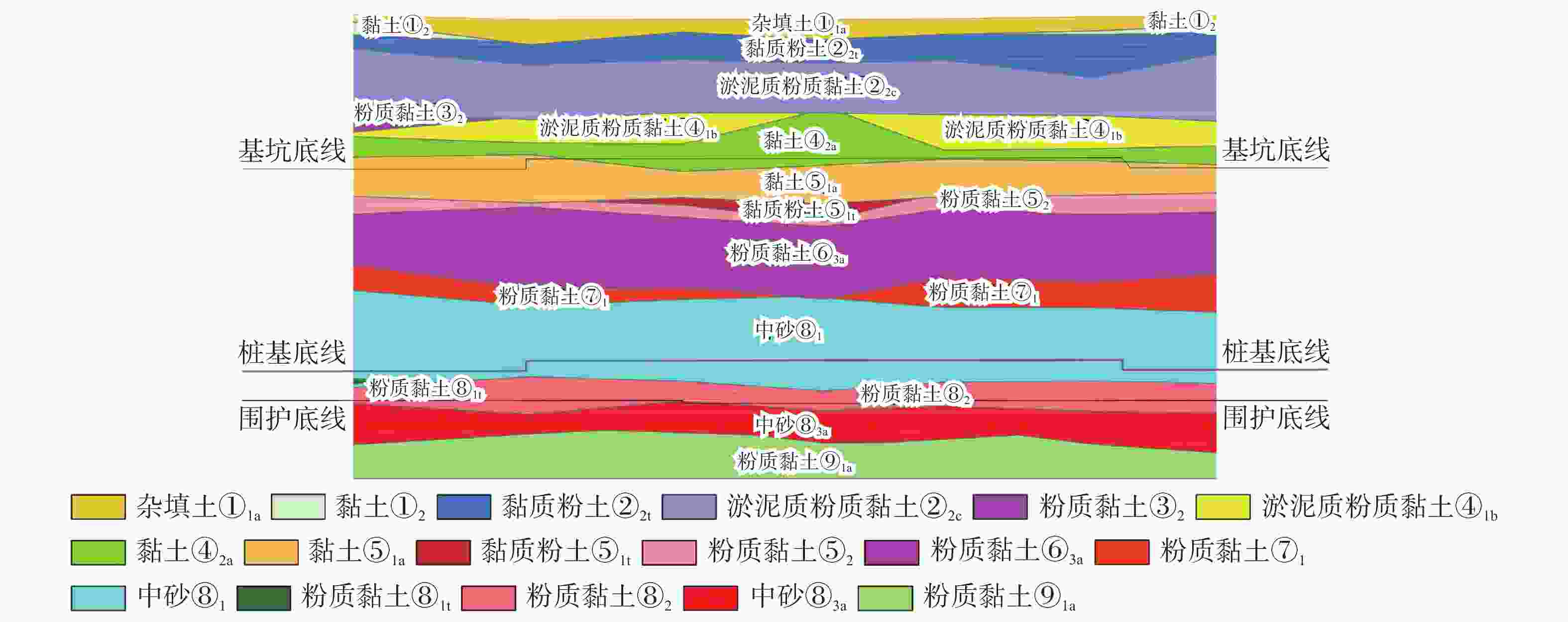
表 1 换乘节点位置主要地层物理力学参数
层号 土层 天然含水率
w/%天然重度
γ/(kN·m−3)孔隙比
e压缩模量
Es /MPa土体静止侧压力
系数K0渗透系数
k/(×10−6cm·s−1)黏聚力
c/kPa内摩擦角
φ/(°)层底
标高/m①1a 杂填土 20.0 2.5 0.55 2500 1.67 ①2 黏土 28.9 19.3 0.825 3.5 0.52 0.15 18 13 −0.33 ②2t 黏土 31.6 18.8 0.895 5.0 0.46 150 −2.83 ②2c 淤泥质粉质黏土 44.4 17.3 1.250 2.6 0.58 3.5 13.9 16.1 −13.83 ③2 粉质黏土 32.8 18.6 0.950 3.0 0.49 0.15 13 14 −16.83 ④1b 淤泥质粉质黏土 37.9 18.3 1.067 2.8 0.58 0.35 19.9 18.9 −17.83 ④2a 黏土 39.6 18.1 1.118 3.0 0.56 0.8 13.9 16.3 −21.33 ⑤1a 黏土 29.2 19.4 0.824 6.0 0.38 0.28 39.4 16.1 −28.03 ⑤2 粉质黏土 30.7 19.2 0.856 5.5 0.43 0.08 14.3 18.7 −30.93 ⑥3a 粉质黏土 33.0 18.8 0.929 4.2 0.47 0.65 24.7 18.6 −39.93 ⑦1 粉质黏土 23.2 19.4 0.656 6.5 0.40 0.4 −44.23 ⑧1 中砂 19.7 0.700 10 0.42 3500 −59.33 ⑧2 粉质黏土 27.4 19.3 0.775 6.5 0.40 0.65 −63.63 表 2 周边主要建筑基本信息
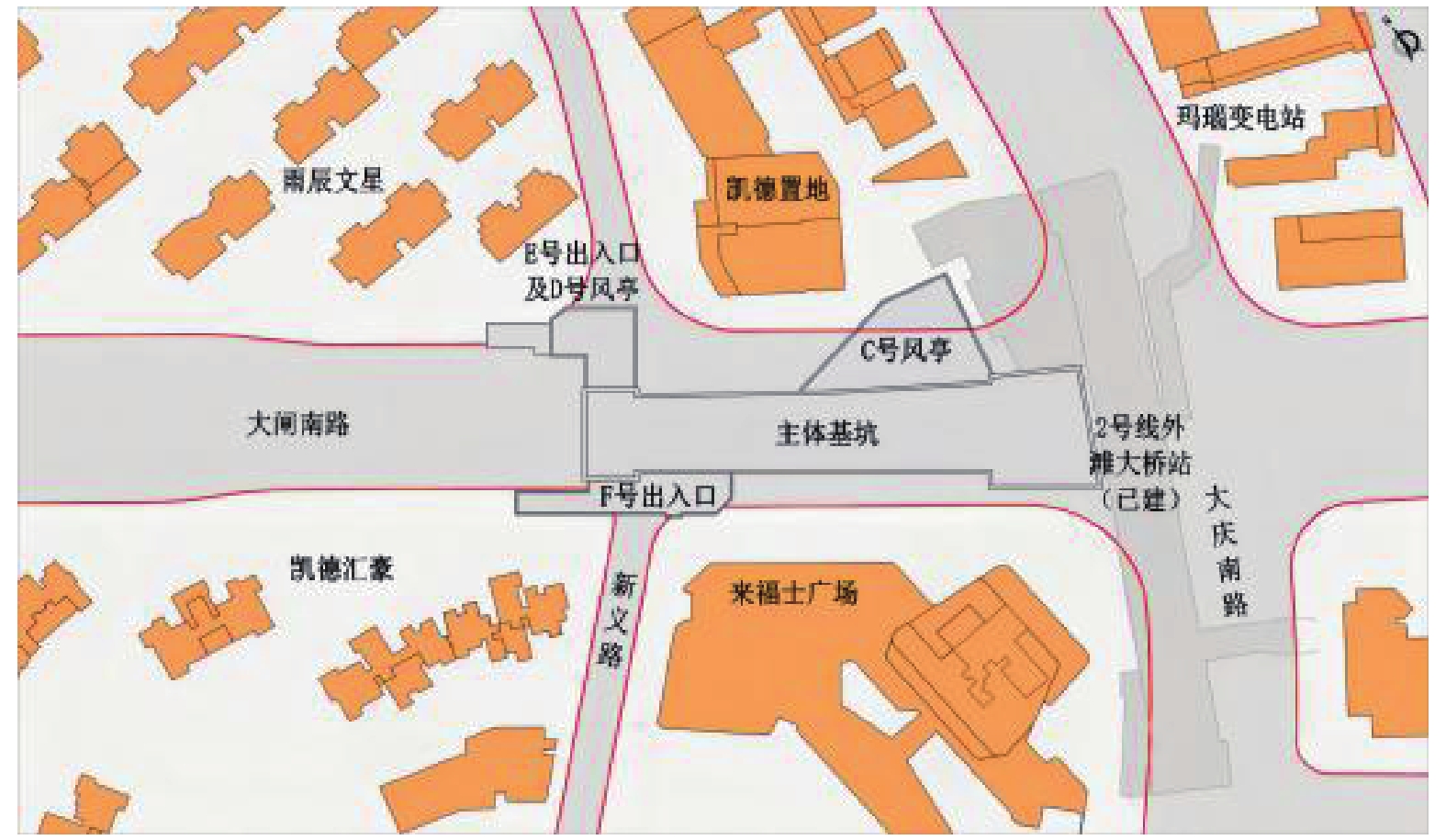
序号 建构筑物 与车站基坑相对位置 结构形式及层数 基础形式 基础埋深情况 1 2号线外滩大桥站主体 位于车站东侧,距离基坑0.8 m 单柱双跨钢筋混凝土
箱型结构,地下2层叠合墙形式,无桩基 基坑底埋深15.77 m 2 2号线1号出入口及风亭 位于车站北侧,紧邻基坑 钢筋混凝土结构,地下1层 ϕ800钻孔灌注桩基础 基坑底埋深8.76 m,
桩底埋深约57 m3 凯德置地 位于车站北侧,距离基坑23.6 m 框剪结构,13层 ϕ800钻孔灌注桩基础 桩底埋深约53 m 4 雨辰文星 位于车站西北侧,距离基坑44.3 m 框架结构,7层 ϕ400预应力混凝土管桩基础 桩底埋深约33 m 5 来福士广场 位于车站南侧,距高基坑17.2 m 框架及框剪结构,4~19层 ϕ700(800)钻孔灌注桩基础 桩底埋深约56 m 6 凯德汇豪 位于车站西南侧,距离基坑18.2 m 框剪结构,23~25层 ϕ700钻孔灌注桩基础 柱底埋深约56 m 表 3 MJS工法施工参数
参数 数值 参数 数值 桩径/mm 2500 削孔水压力/MPa 10~30 水灰质量比 1.0 成桩角度误差控制 ≦1/300 水泥浆压力/MPa 40 提升速度/(min·m–1) 20~40 水泥浆液流量/ (L·min–1) 90 步距行程/mm 25 主空气压力/MPa 0.70~1.05 步距提升时间/s 60 主空气流量/(m3·min–1) 1.0~2.0 转速/(r·min–1) 3 倒吸水压力/MPa 5~20 地内压力系数 1.3~1.6 倒吸水流量/(L·min–1) 5~60 水泥掺量/% 40 -
[1] 邵先奎, 马 骏, 刘甲军. 浅谈城市地下空间大数据平台构建与应用研究背景[J]. 中国科技期刊数据库 工业A, 2024(1): 99-102. (SHAO X K, MA J, LIU J J. A brief discussion on the construction and application research background of urban underground space big data platform[J]. China Science and Technology Journal Database Industry A, 2024(1): 99-102. (in Chinese)SHAO X K, MA J, LIU J J. A brief discussion on the construction and application research background of urban underground space big data platform[J]. China Science and Technology Journal Database Industry A, 2024(1): 99-102. [2] 韦宗科, 陈 健, 陈 斌, 等. 软土基坑开挖对临近既有隧道变形影响研究[J]. 人民长江, 2022, 53(6): 198-206. (WEI Z K, CHEN J, CHEN B, et al. Influence of excavation in soft soil foundation pit on deformation of adjacent existing tunnel[J]. Yangtze River, 2022, 53(6): 198-206. (in Chinese)WEI Z K, CHEN J, CHEN B, et al. Influence of excavation in soft soil foundation pit on deformation of adjacent existing tunnel[J]. Yangtze River, 2022, 53(6): 198-206. (in Chinese) [3] HU Z F, YUE Z Q, ZHOU J, et al. Design and construction of a deep excavation in soft soils adjacent to the Shanghai Metro Tunnels[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2003, 40(5): 933-948. doi: 10.1139/t03-041 [4] 洪成泼. 上海软土地层MJS工法施工及应用研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017. (HONG C P. Study on construction and application of MJS (metro jet system) construction method for soft soil layer in Shanghai[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017. (in Chinese)HONG C P. Study on construction and application of MJS (metro jet system) construction method for soft soil layer in Shanghai[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017. (in Chinese) [5] TONON F. ADECO full-face tunnel excavation of two 260 m2 tubes in clays with sub-horizontal jet-grouting under minimal urban cover[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2011, 26(2): 253-266. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2010.09.006 [6] 张文博, 张 康, 陈卫军. MJS工法在富水砂层隧道密贴下穿既有车站工程中的应用[J]. 现代城市轨道交通, 2018(10): 35-38. (ZHANG W B, ZHANG K, CHEN W J. Application of MJS method in construction of rich water sand layer tunnel under existing station[J] Modern Urban Transit, 2018(10): 35-38. (in Chinese)ZHANG W B, ZHANG K, CHEN W J. Application of MJS method in construction of rich water sand layer tunnel under existing station[J] Modern Urban Transit, 2018(10): 35-38. (in Chinese) [7] 翟志国, 花 楠, 刘 柳. MJS水平旋喷桩在京沈高铁盾构隧道联络通道中的应用[J]. 隧道建设(中英文), 2021, 41(S2): 512-519. (ZHAI Z G, HUA N, LIU L. Application of metro jet system horizontal jet grouting pile in connection gallery of beijing-shenyang high-speed railway shield tunnel[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2021, 41(S2): 512-519. (in Chinese)ZHAI Z G, HUA N, LIU L. Application of metro jet system horizontal jet grouting pile in connection gallery of beijing-shenyang high-speed railway shield tunnel[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2021, 41(S2): 512-519. (in Chinese) [8] 朱劲锋. 近距离下穿既有地铁线MJS水平加固技术应用[J]. 建筑机械化, 2018, 39(8): 52-53. (ZHU J F. Application of MJS horizontal reinforcement technology to close the existing subway line at close distance[J]. Construction Mechanization, 2018, 39(8): 52-53. (in Chinese)ZHU J F. Application of MJS horizontal reinforcement technology to close the existing subway line at close distance[J]. Construction Mechanization, 2018, 39(8): 52-53. (in Chinese) [9] 周 朋. MJS工法在砂卵石地层盾构近距离下穿运营地铁隧道的应用[J]. 都市快轨交通, 2018, 31(6): 122-128. (ZHOU P. Application of MJS method in traversing under the operating metro line near the sand gravel layer[J]. Urban Rapid Rail Transit, 2018, 31(6): 122-128. (in Chinese)ZHOU P. Application of MJS method in traversing under the operating metro line near the sand gravel layer[J]. Urban Rapid Rail Transit, 2018, 31(6): 122-128. (in Chinese) [10] 路 平, 蒋 辉, 郑 刚. 盾构隧道的近接施工对已建隧道产生的影响[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2014, 40(8): 1121-1127. (LU P, JIANG H, ZHENG G. Impact on existing tunnel due to construction of new shield tunnel in close proxomity[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2014, 40(8): 1121-1127. (in Chinese)LU P, JIANG H, ZHENG G. Impact on existing tunnel due to construction of new shield tunnel in close proxomity[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2014, 40(8): 1121-1127. (in Chinese) [11] 李恒一. 深圳地铁9号线盾构区间近接既有隧道施工力学行为研究[J]. 湖南城市学院学报(自然科学版), 2015, 24(1): 30-33. (LI H Y. Research on mechanics behavior of approaching construction to existing tunnels for shield tunnels of Shenzhen subway NO. 9 line[J] Journal of Hunan City University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 24(1): 30-33. (in Chinese)LI H Y. Research on mechanics behavior of approaching construction to existing tunnels for shield tunnels of Shenzhen subway NO. 9 line[J] Journal of Hunan City University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 24(1): 30-33. (in Chinese) [12] 陈树杰, 易路行. MJS工法在城市轨道交通车站施工中的应用[J]. 铁道勘察, 2023, 49(5): 143-148. (CHEN S J, YI L X. The application of MJS method in transfer node engineering of urban rail transit station in water-rich sand layer[J]. Railway Investigation and Surveying, 2023, 49(5): 143-148. (in Chinese)CHEN S J, YI L X. The application of MJS method in transfer node engineering of urban rail transit station in water-rich sand layer[J]. Railway Investigation and Surveying, 2023, 49(5): 143-148. (in Chinese) [13] 住房和城乡建设部. 工程测量通用规范: GB 55018—2021[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2021. (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. General code for engineering survey: GB 55018—2021[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2021. (in Chinese)Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. General code for engineering survey: GB 55018—2021[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2021. (in Chinese) [14] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 国家市场监督管理总局. 地下铁道工程施工质量验收标准: GB/T 50299—2018[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2018. (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. Standard for construction quality acceptance of metro engineering: GB/T 50299—2018[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2018. (in Chinese)Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. Standard for construction quality acceptance of metro engineering: GB/T 50299—2018[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2018. (in Chinese) [15] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 建筑地基基础工程施工质量验收标准: GB 50202—2018[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2018. (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for acceptance of construction quality of building foundation: GB 50202—2018[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2018. (in Chinese)Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for acceptance of construction quality of building foundation: GB 50202—2018[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2018. (in Chinese) [16] 白海卫. 基于脆弱性的穿越工程中既有地铁线风险评估与控制[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2020. (BAI H W. Research on risk assessment and control of existing metro lines ina new crossing construction based on vulnerability[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2020. (in Chinese)BAI H W. Research on risk assessment and control of existing metro lines ina new crossing construction based on vulnerability[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2020. (in Chinese) [17] 夏华灿. MJS工法在福州滨海涉铁软基加固工程中的应用研究[D]. 福州: 福建工程学院, 2023. (XIA H C. Study on the application of MJS method in the softfoundation reinforcement project involving railwayin Fuzhou Binhai[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian University of Technology, 2023. (in Chinese)XIA H C. Study on the application of MJS method in the softfoundation reinforcement project involving railwayin Fuzhou Binhai[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian University of Technology, 2023. (in Chinese) [18] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑基坑工程监测技术标准: GB 50497—2019[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2019. (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Technicai standard for monitoring of building excavation engineering: GB 50497—2019[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2019. (in Chinese)Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Technicai standard for monitoring of building excavation engineering: GB 50497—2019[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2019. (in Chinese) [19] 宋 飞. 车站深基坑长距离近接施工对既有运营线影响研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2022. (SONG F. Reserch on the influence of longdistance parallel deep station-pitexcavation on the adjacent existingmetro[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022. (in Chinese)SONG F. Reserch on the influence of longdistance parallel deep station-pitexcavation on the adjacent existingmetro[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: