Interface bearing characteristics of reinforced fine soil of scrap tire grille under drawing load
-
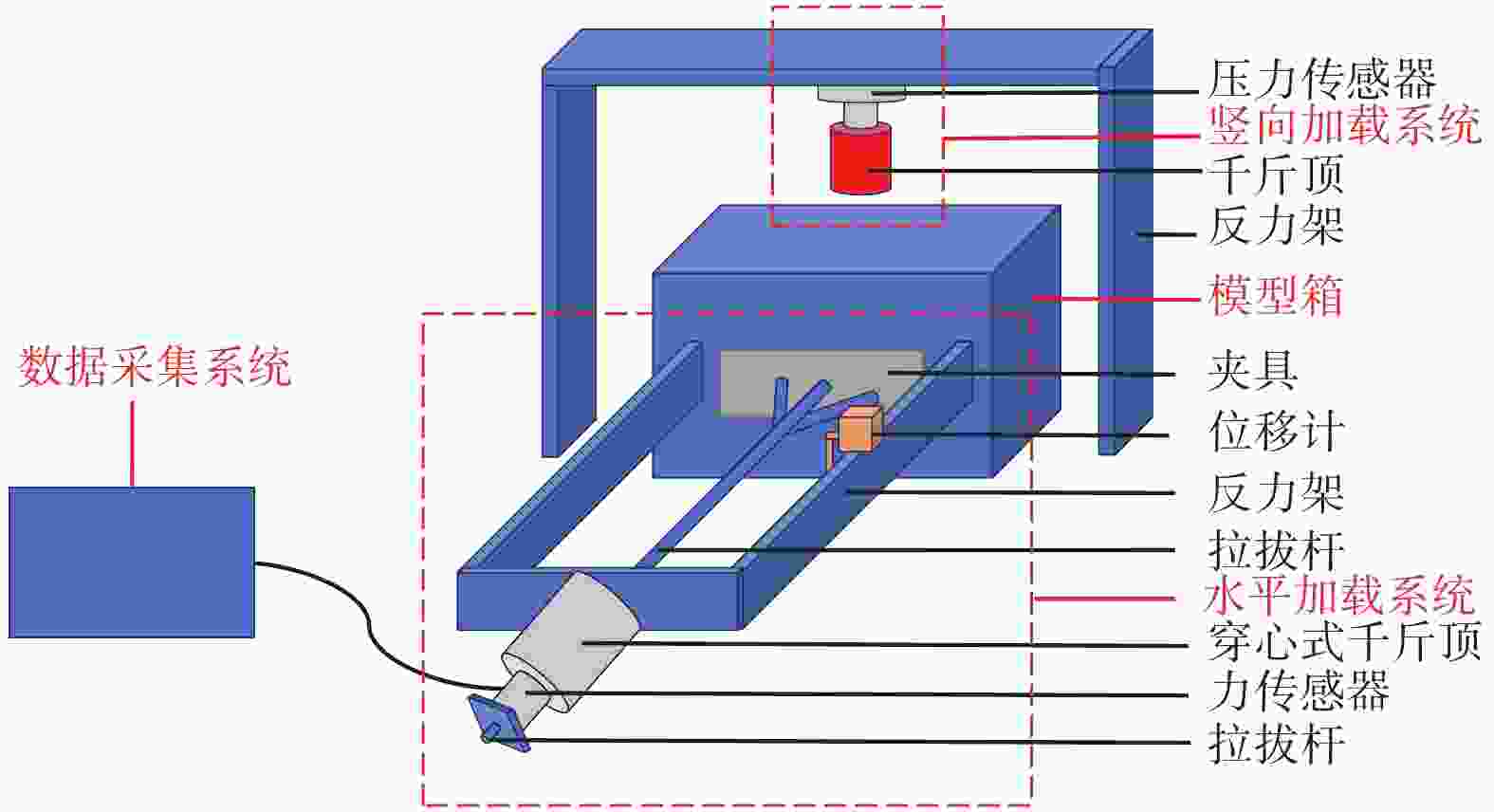
摘要: 为保证地基结构稳定性,提升土体抗拉强度,通常在地基中放置加筋材料。基于废旧轮胎良好的抗拉伸性与界面粗糙性,提出将废旧轮胎格栅作为地基加筋新材料。通过拉拔试验研究了不同上覆荷载、填料压实度、轮胎条带宽度、网孔尺寸等因素对废旧轮胎格栅加筋细粒土承载性能的影响。结果表明:轮胎条带加筋粉土的承载能力随上覆荷载的增大而提高,细粒土填料越密实轮胎条带峰值拉拔力越大,条带宽度对粉土地基加筋效果影响最明显,条带宽度增加2 cm,峰值拉拔力提高接近50%;轮胎格栅承载力随网孔尺寸的增大而逐渐减弱。研究结果证实废旧轮胎格栅可以有效提高细粒土地基的承载能力,增强土体的抗拉强度,并为进一步的理论研究和技术应用提供了参考。Abstract: Reinforcement materials were usually used in the structure to ensure the foundation's stability and improve the tensile strength of the soil. The scrap tire grille was proposed as a new material for foundation reinforcement based on tensile resistance and interface roughness. The influence of different overburden loads, packing compaction degree, tire strip width, and mesh size on the bearing capacity of reinforced tire silt was studied by drawing test. The results show that the bearing capacity of reinforced tire silt increases with the overlying load. The denser the fine-grained soil filler is, the greater the peak pulling force of the tire strip is. Strip width has the most obvious effect on the reinforcement effect of silt soil foundation. When strip width increases by 2 cm, the peak pulling force increases by nearly 50%. The bearing capacity decreases with the mesh size increases. The results show that the scrap tire grille can improve the bearing capacity of silt soil foundation effectively and enhance the tensile strength of soil. The research provides a reference for further theoretical research and technical application.
-
Key words:
- tire grille /
- horizontal drawing load /
- fine-grained soil /
- bearing characteristics /
- drawing formula
-
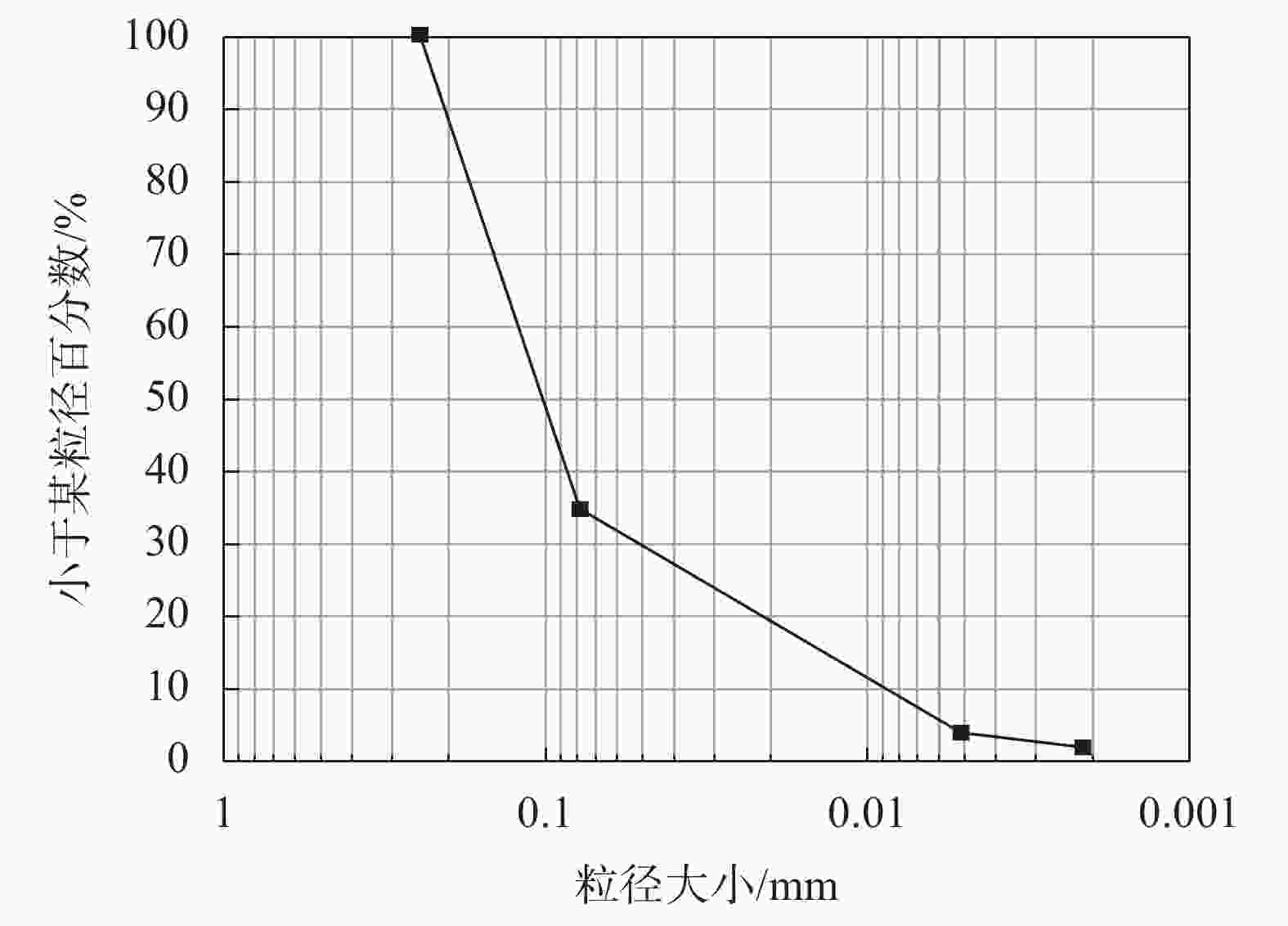
表 1 粉土的颗粒组成特征
配料
含水量/%实际
含水量/%湿密度ρ
/(g·cm−3)干密度ρd
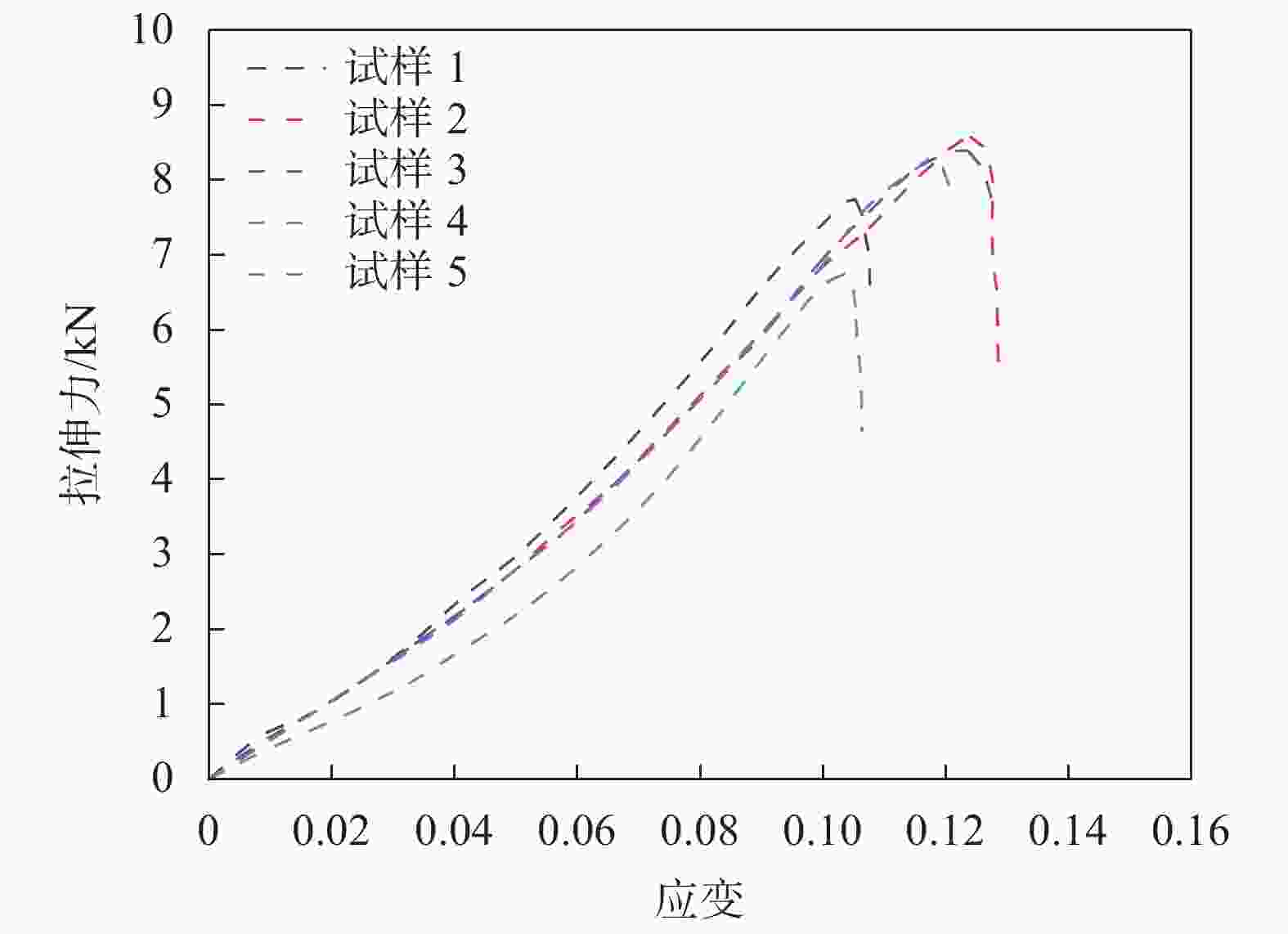
/(g·cm−3)粉土 10.0 8.9 1.66 1.53 12.0 12.0 1.72 1.54 14.0 13.9 1.76 1.55 16.0 16.2 1.83 1.58 18.0 17.0 1.83 1.57 20.0 20.0 1.80 1.55 均值 15.00 14.67 1.77 1.55 表 2 旋切下轮胎条带拉伸试验均值
试样编号 2%应变 5%应变 10%应变 峰值应变 拉伸力
F2%/kN拉伸强度
/(kN·m−1)拉伸力
F5%/kN拉伸强度
/(kN·m−1)拉伸力
F10%/kN拉伸强度
/(kN·m−1)拉伸力
Fmax/kN拉伸强度
/(kN·m−1)峰值应变
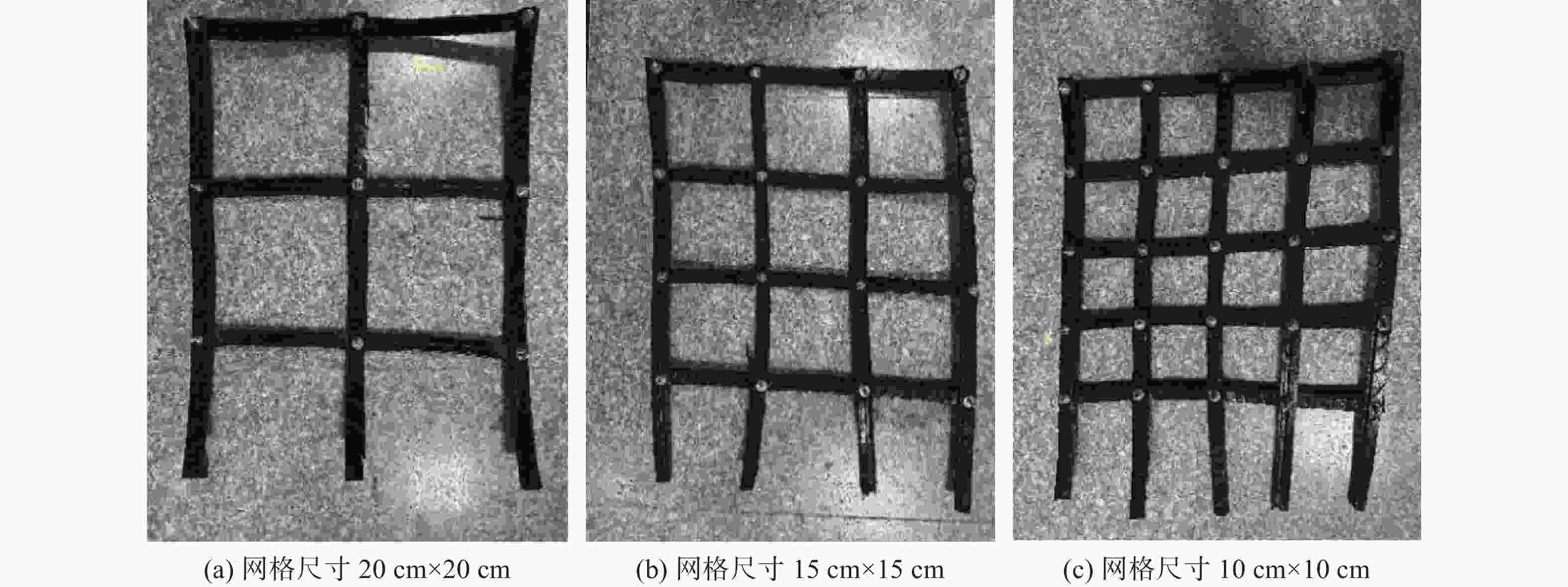
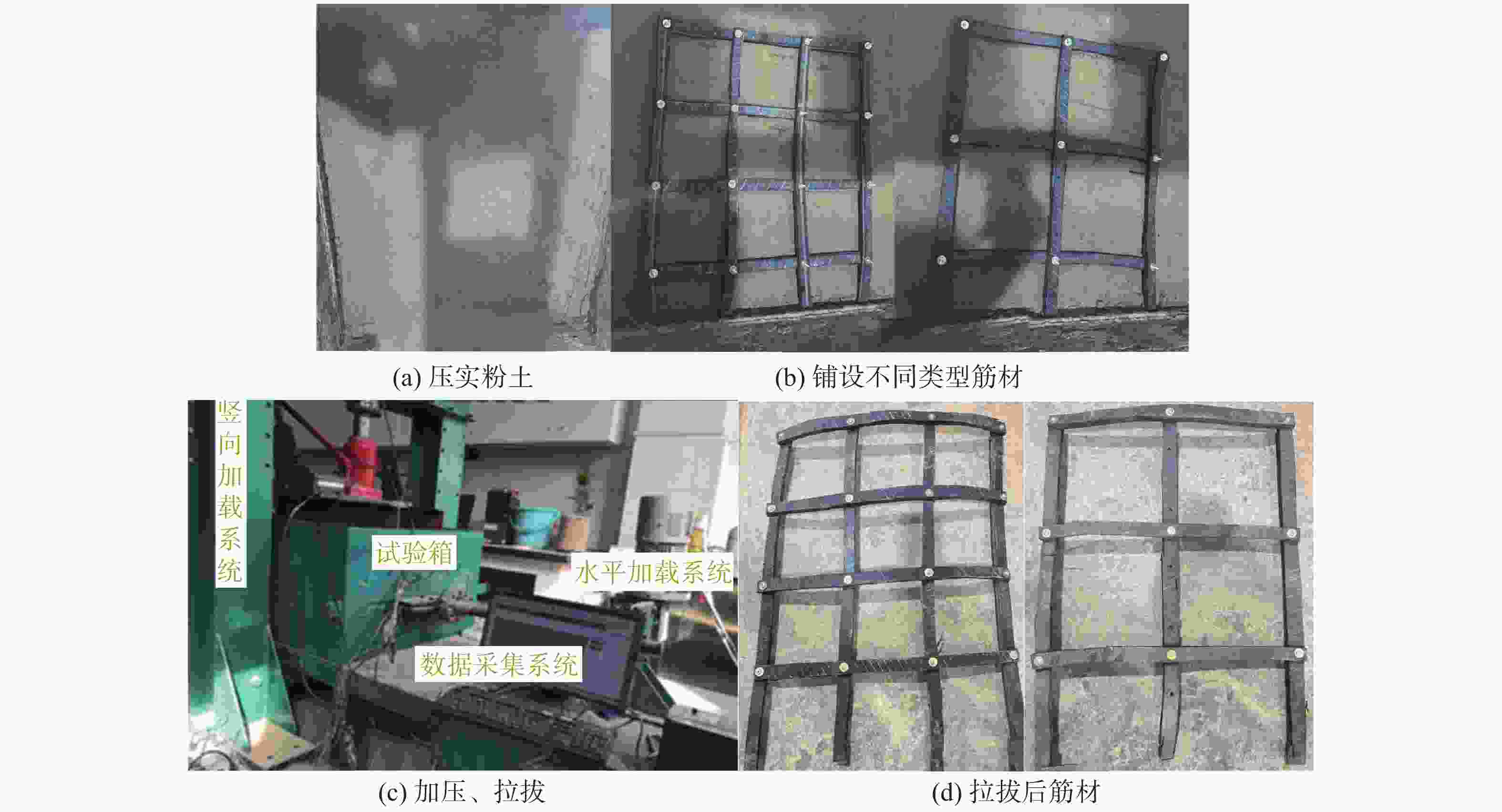
/%1 1.036 51.800 2.917 58.340 7.382 73.820 7.685 73.190 10.500 2 1.020 50.989 2.759 55.184 6.709 67.090 8.526 67.670 12.600 3 1.047 52.350 2.759 55.180 6.867 68.670 8.370 66.960 12.500 4 0.764 38.200 2.202 44.040 6.499 64.990 6.689 64.320 10.400 5 1.016 50.800 2.716 54.320 6.794 67.940 8.254 69.360 11.900 均值 0.976 48.820 2.671 53.410 6.850 68.500 7.905 68.300 11.580 表 3 不同筋材类型的对比试验工况
筋材类型 填料类型 条带宽度
/cm填料压实度
/%上覆荷载
/kPa网孔尺寸
/cm轮胎条带 粉土 2 90 80 4 6 2 80 80 85 2 90 60 100 轮胎格栅 粉土 2 90 80 10×10 15×15 20×20 表 4 不同上覆荷载下轮胎条带的峰值拉拔力
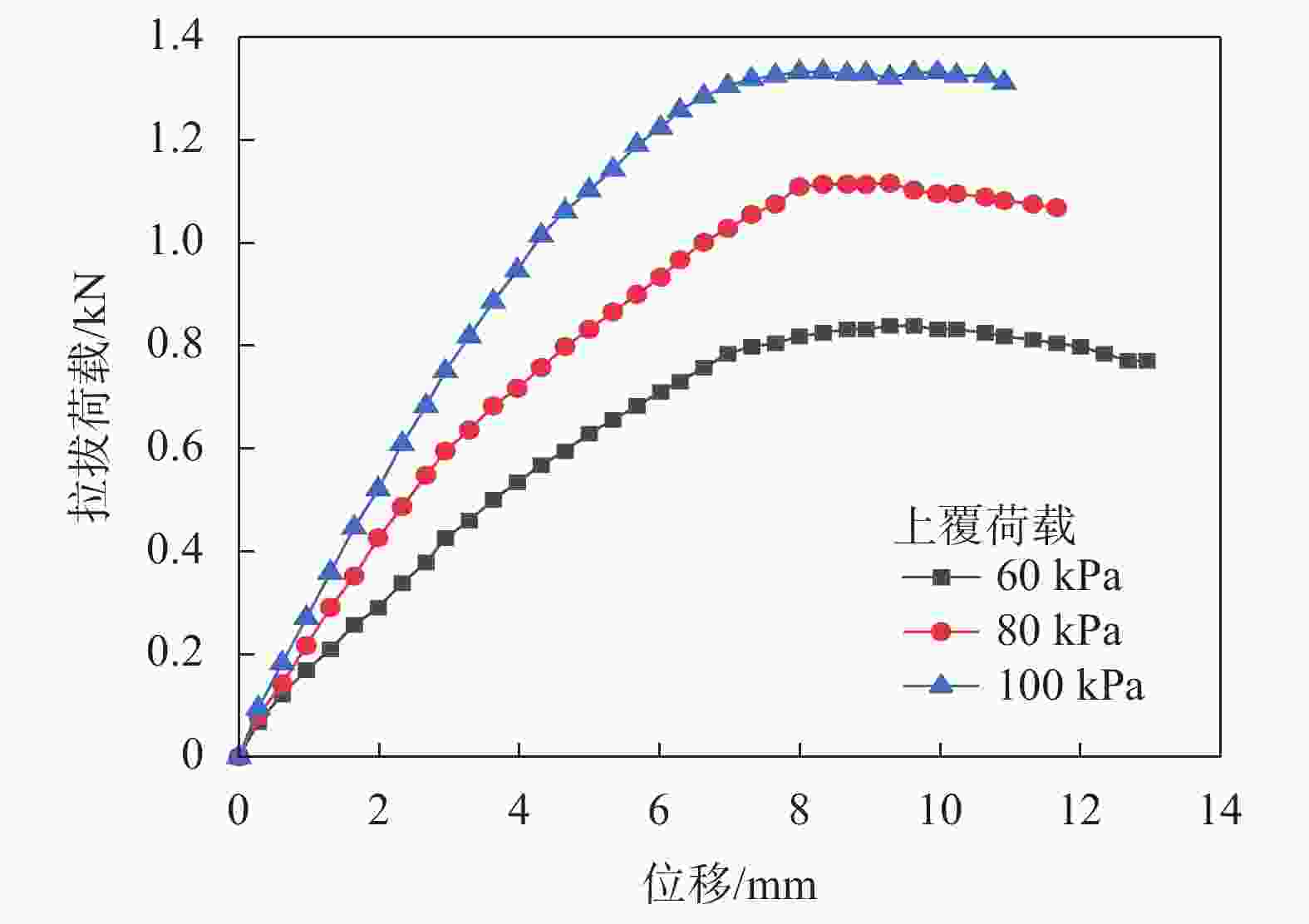
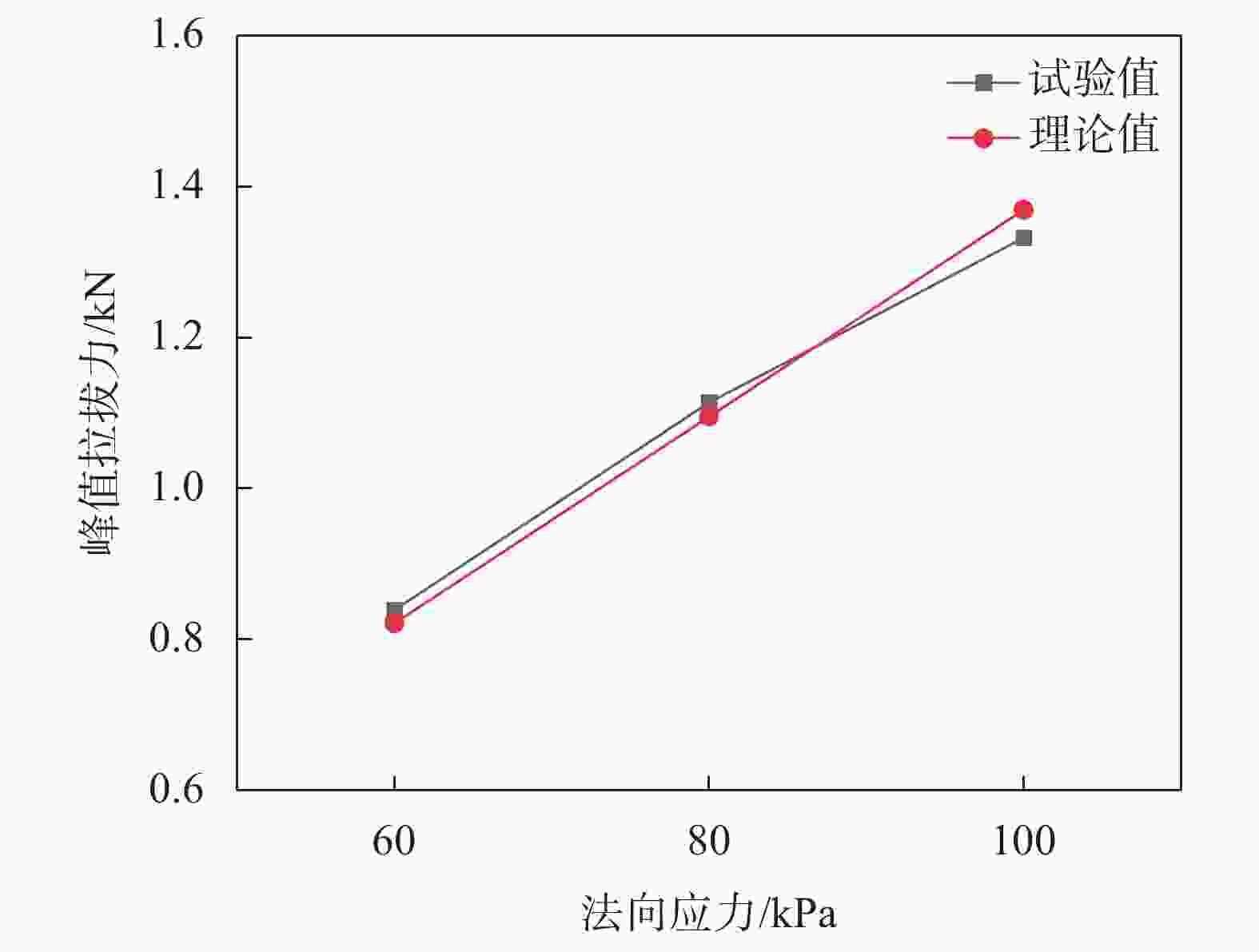
上覆荷载/kPa 峰值拉拔力/kN 对应位移量/mm 初始模量/MPa 60 0.839 9.283 3.828 80 1.114 8.331 5.948 100 1.332 7.991 8.025 表 5 不同压实度下轮胎条带的峰值拉拔力
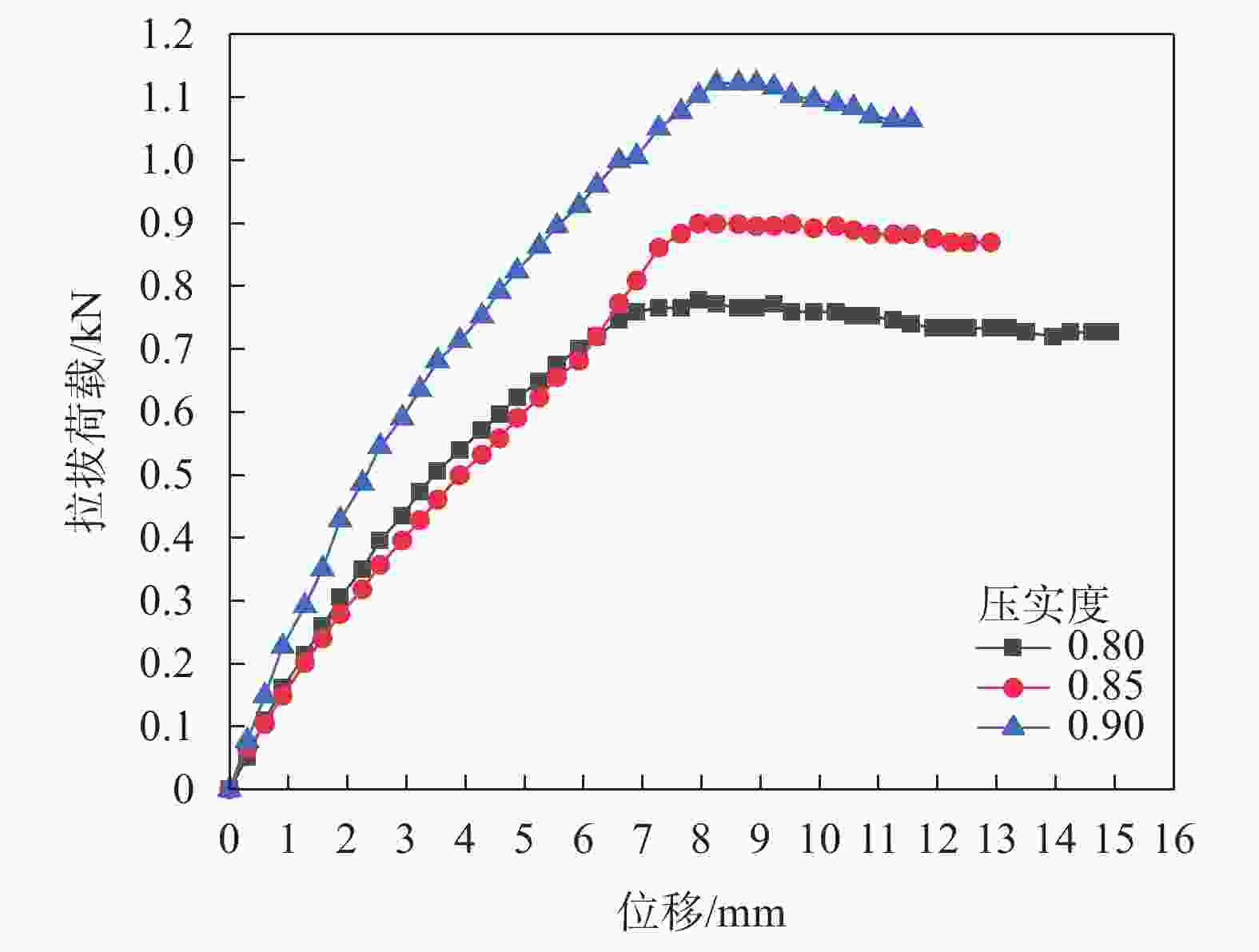
压实度/% 峰值拉拔力/kN 对应位移量/mm 初始模量/MPa 80 0.759 6.900 4.213 85 0.899 7.950 5.044 90 1.120 8.250 5.765 表 6 不同条带宽度下轮胎条带的峰值拉拔力
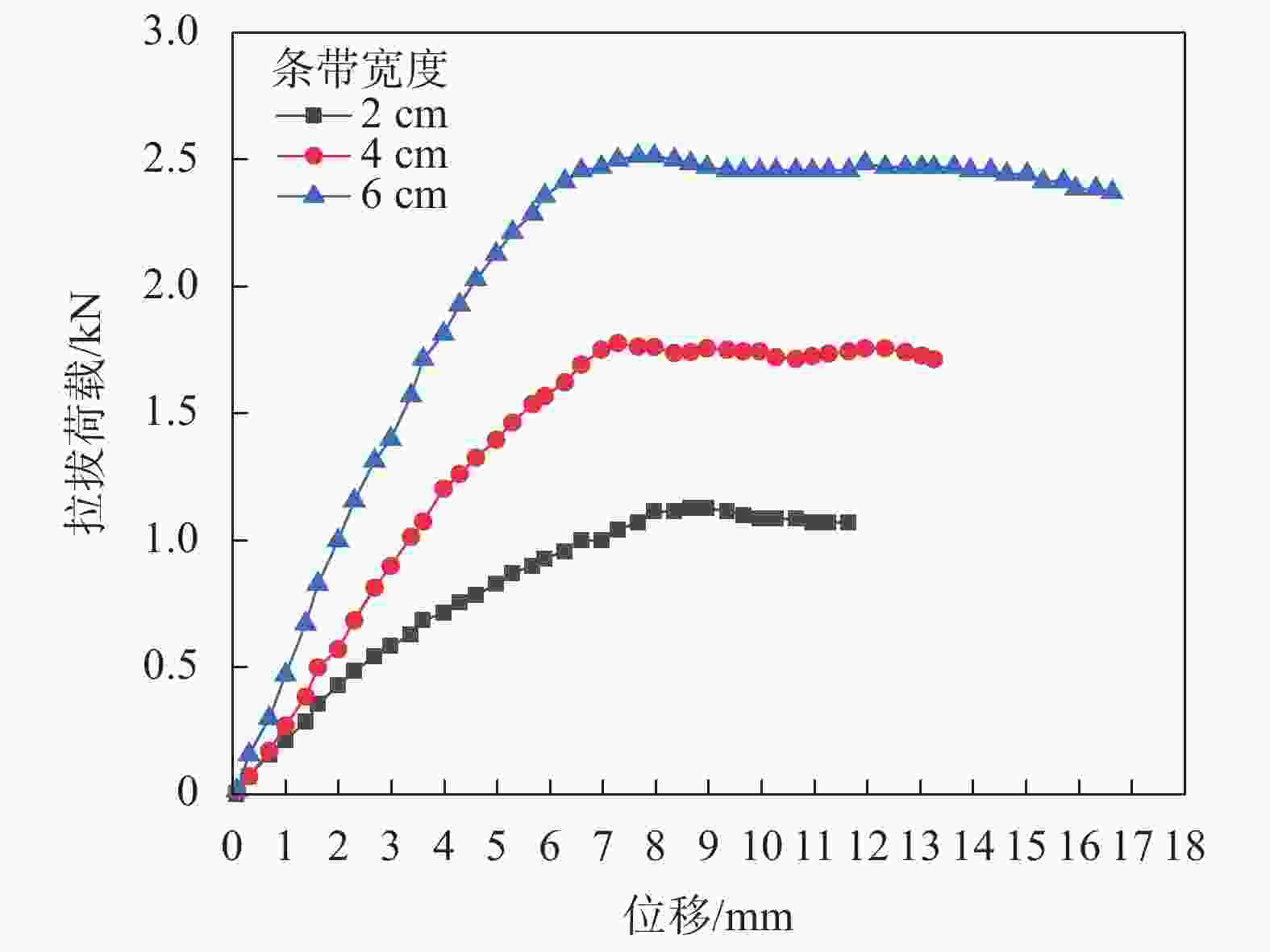
宽度
/cm峰值拉
拔力/kN对应位
移量/mm单位宽度下的极限
拉拔力/(kN·cm−1)横截
面积/m2初始
模量/MPa2 1.114 7.966 0.557 0.0003 9.326 4 1.778 7.277 0.444 0.0006 12.676 6 2.511 6.970 0.419 0.0009 21.084 表 7 不同格栅孔径下轮胎条带的峰值拉拔力
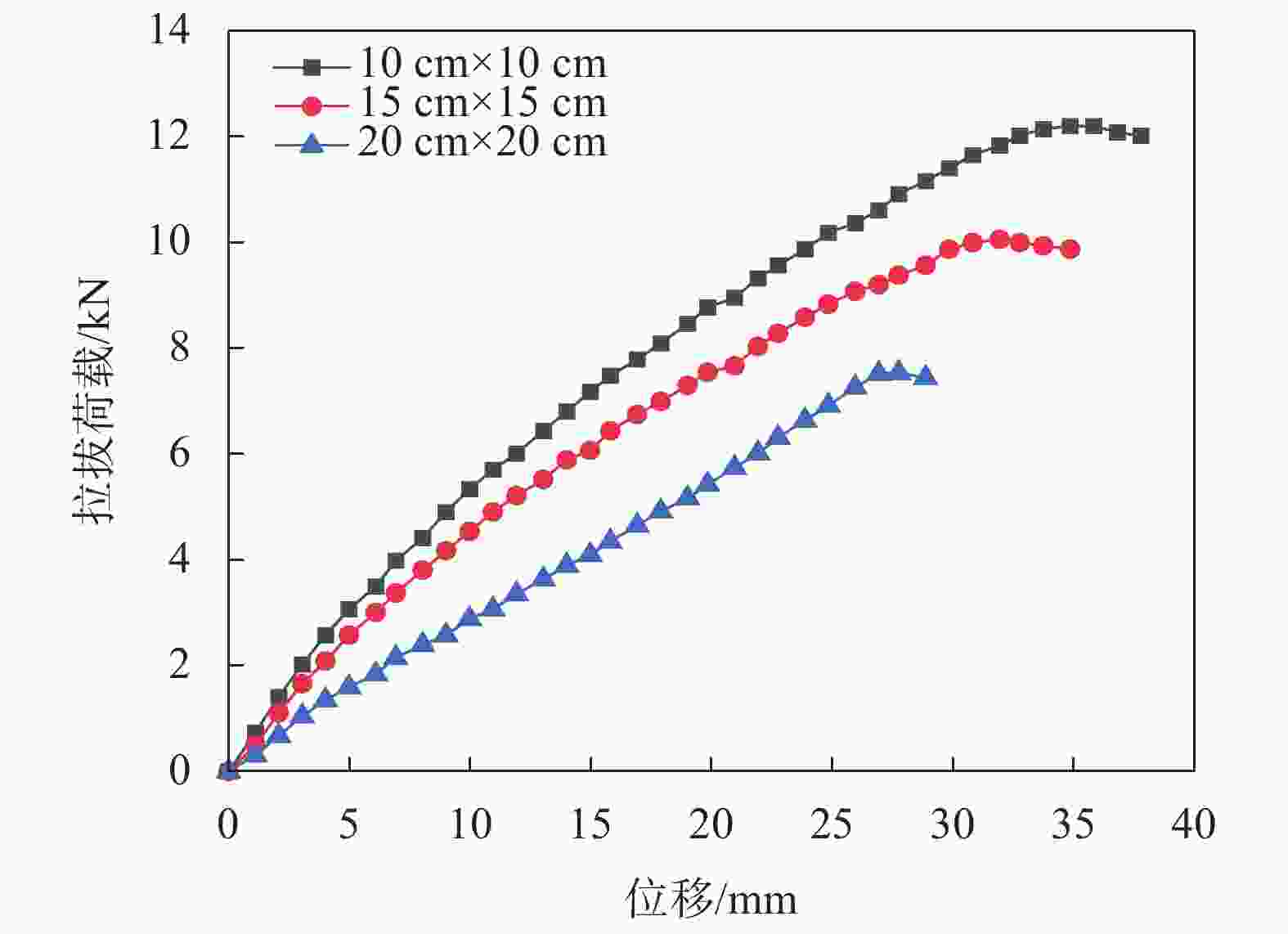
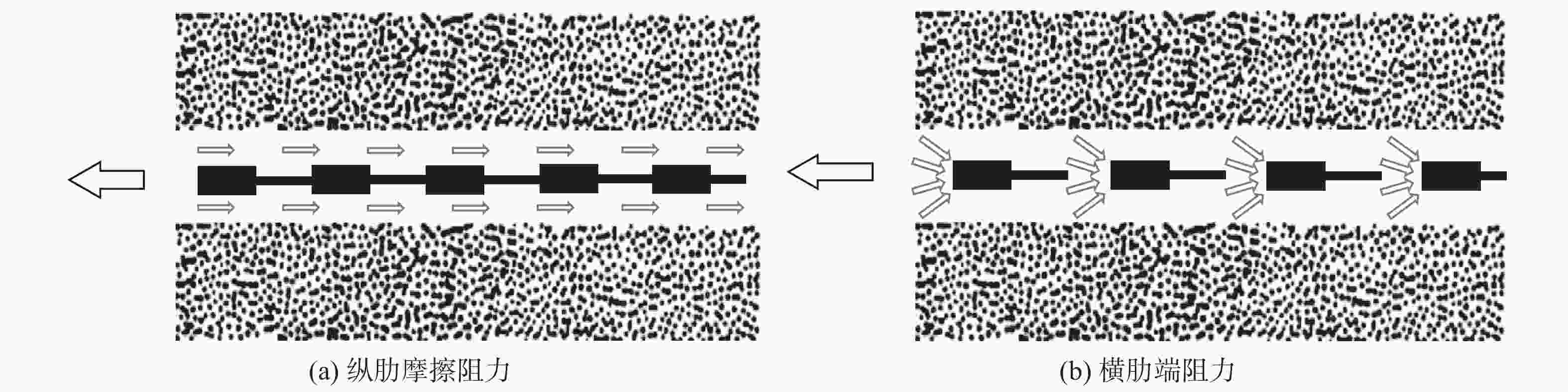
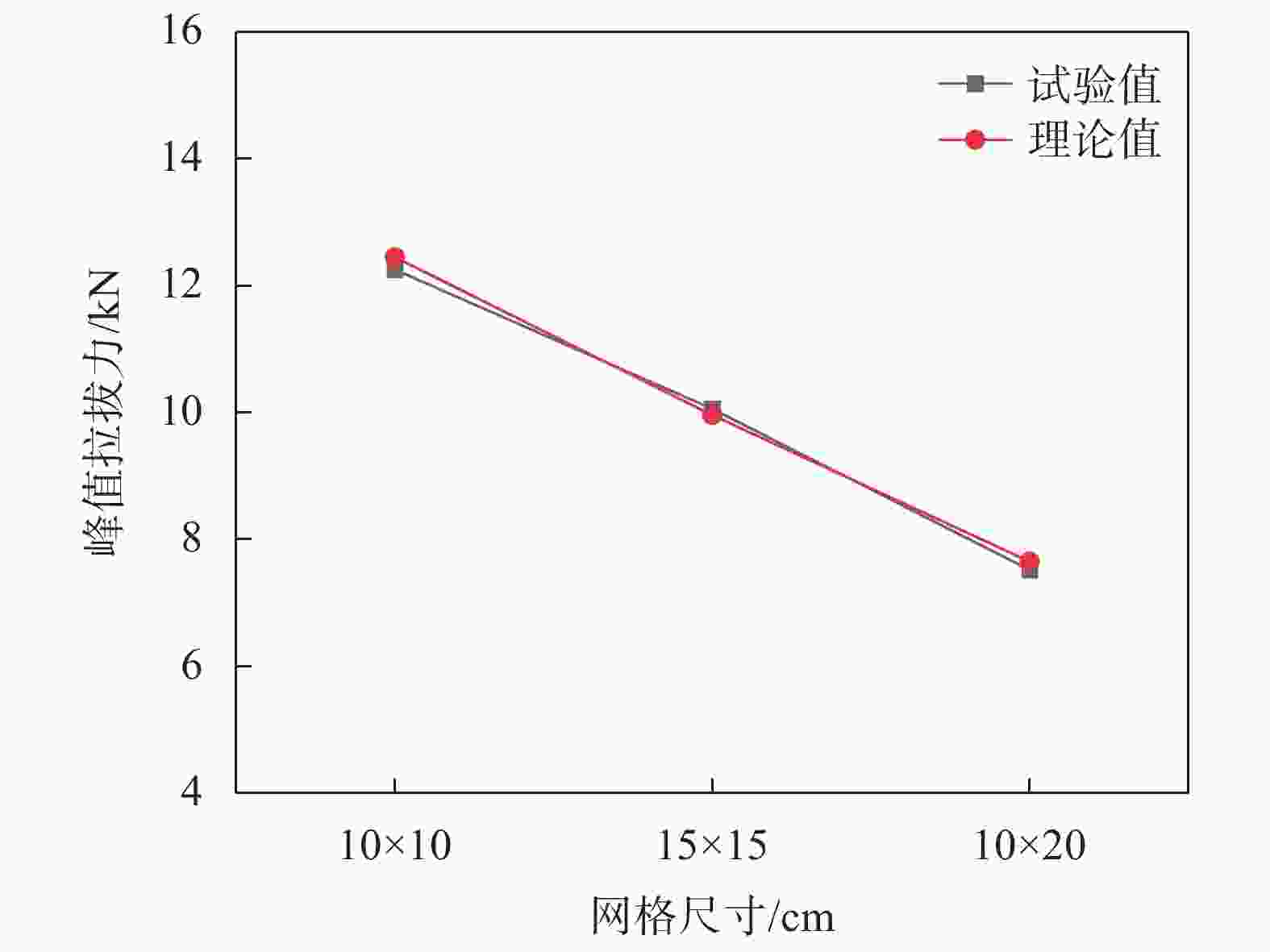
网孔尺寸/cm 峰值拉拔力/kN 对应位移量/mm 初始模量/MPa 10×10 12.250 34.850 26.670 15×15 10.057 31.928 53.332 20×20 7.519 25.950 66.667 表 8 不同法向应力下摩阻参数
法向应力
/kPa条带宽度
/cm加筋面积
/m2内摩擦角
/(°)有效接触
面系数摩擦
阻力/kN60 2 0.012 28.8 1.038 0.822 80 1.095 100 1.369 表 9 不同网格尺寸下端阻计算参数
网格尺
寸/cm峰值拉
拔力/kN摩擦
阻力/kN条带总
个数/个横肋单元
个数/个横肋单元
有效系数/kPa横肋单元
承载力/kN10×10 12.250 1.095 10 5 122.125 0.164 15×15 10.057 8 4 20×20 7.519 6 3 表 10 轮胎格栅峰值拉拔力计算结果
网格尺寸/cm 摩擦阻力/kN 端阻力PRB
/kN峰值拉拔力/kN 10×10 10$ \mathrm{\mathit{P}}_{\mathrm{R}\mathrm{S}} $=10.950 1.499 12.449 15×15 8$ \mathrm{\mathit{P}}_{\mathrm{R}\mathrm{S}} $=8.760 1.199 9.959 20×20 $ 6\mathrm{\mathit{P}}_{\mathrm{R}\mathrm{S}} $=6.750 $ 0.900 $ 7.650 -
[1] 余文章, 李向清, 庞金波. 软弱土地基不均匀沉降的桩基加固应用及研究[J]. 工程质量, 2018, 36(8): 48-51. (YU W Z, LI X Q, PANG J B. The application and research of pile foundation reinforcement for differential settlement of soft soil foundation[J]. Construction Quality, 2018, 36(8): 48-51. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3702.2018.08.011YU W Z, LI X Q, PANG J B. The application and research of pile foundation reinforcement for differential settlement of soft soil foundation[J]. Construction Quality, 2018, 36(8): 48-51. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3702.2018.08.011 [2] 王家全, 张亮亮, 刘政权, 等. 土工格栅加筋砂土地基大模型动载试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(10): 3539-3547. (WANG J Q, ZHANG L L, LIU Z Q, et al. Large model test on geogrid reinforced sand soil foundation under dynamic loading[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(10): 3539-3547. (in Chinese)WANG J Q, ZHANG L L, LIU Z Q, et al. Large model test on geogrid reinforced sand soil foundation under dynamic loading[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(10): 3539-3547. (in Chinese) [3] 郭力群, 马时冬. 土工格栅加筋垫层用于处理特殊地基[J]. 岩土工程技术, 2005, 19(3): 109-112. (GUO L Q, MA S D. Geogrid reinforcement cushion for special ground treatment[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique, 2005, 19(3): 109-112. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2005.03.001GUO L Q, MA S D. Geogrid reinforcement cushion for special ground treatment[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique, 2005, 19(3): 109-112. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2005.03.001 [4] WU J T H, PHAM T Q. Load-carrying capacity and required reinforcement strength of closely spaced soil-geosynthetic composites[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2013, 139(9): 1468-1476. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000885 [5] AMBRIZ B, MUN W, MCCARTNEY J S. Impact of temperature on the pullout of reinforcing geotextiles from unsaturated silt[J]. Geosynthetics International, 2020, 27(1): 1-15. doi: 10.1680/jgein.19.00040 [6] 王 昊. TDA-粉土复合填料中废旧轮胎条带拉拔特性及承载机理研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2022. (WANG H. Research on the pullout behavior and bearing mechanism of waste tire strips embedded in TDA-silt composite[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2022. (in Chinese)WANG H. Research on the pullout behavior and bearing mechanism of waste tire strips embedded in TDA-silt composite[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2022. (in Chinese) [7] 李丽华, 余长道. 废旧轮胎加筋土性能试验研究[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2019, 36(11): 1-6. (LI L H, YU C D. Properties of soil reinforced by waste tire[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2019, 36(11): 1-6. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20190233LI L H, YU C D. Properties of soil reinforced by waste tire[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2019, 36(11): 1-6. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20190233 [8] 李晓亮, 刘 源, 李玉鑫, 等. 砂土介质中废旧轮胎加筋条带拉拔特性[J]. 山东大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 54-60,70. (LI X L, LIU Y, LI Y X, et al. The pullout features of reinforced strips of waste tires in sandy media[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Engineering Science), 2021, 51(4): 54-60,70. (in Chinese)LI X L, LIU Y, LI Y X, et al. The pullout features of reinforced strips of waste tires in sandy media[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Engineering Science), 2021, 51(4): 54-60,70. (in Chinese) [9] 孙 杰, 张宏博, 程 钰, 等. 基于TDA填料的废旧轮胎条带加筋砂土边坡承载特性[J]. 山东大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 49-59,67. (SUN J, ZHANG H B, CHENG Y, et al. Bearing characteristics of reinforced sand slope with scrap tire strips and TDA backfills[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Engineering Science), 2023, 53(1): 49-59,67. (in Chinese)SUN J, ZHANG H B, CHENG Y, et al. Bearing characteristics of reinforced sand slope with scrap tire strips and TDA backfills[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Engineering Science), 2023, 53(1): 49-59,67. (in Chinese) [10] 程 阳. 废旧轮胎颗粒改良砂土路基动力特性研究[D]. 北京: 北京建筑大学, 2020. (CHENG Y. Study on dynamic characteristics of sand subgrade improved by waste tire particles[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 2020. (in Chinese)CHENG Y. Study on dynamic characteristics of sand subgrade improved by waste tire particles[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 2020. (in Chinese) [11] MA Q, DENG Q, MOU J, et al. Large-scale direct shear test on scrap tire strip reinforced brick powder[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2019, 2019(1): 6046037. doi: 10.1155/2019/6046037 [12] 章清涛, 刘晓威, 高 健, 等. 坡顶荷载作用下废旧轮胎条带加筋边坡承载特性[J]. 山东大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 70-79. (ZHANG Q T, LIU X W, GAO J, et al. Bearing capacities of reinforced slope with scrap tire strips under vertical loading[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Engineering Science), 2022, 52(3): 70-79. (in Chinese)ZHANG Q T, LIU X W, GAO J, et al. Bearing capacities of reinforced slope with scrap tire strips under vertical loading[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Engineering Science), 2022, 52(3): 70-79. (in Chinese) [13] 谢红梅. 格栅(条带式/返包式)加筋塞土轮胎的界面力学特性研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏科技大学, 2022. (XIE H M. Study on interface mechanical properties of geogrid (striped reinforcement/wrapped reinforcement) reinforced plug-soil tire[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, 2022. (in Chinese)XIE H M. Study on interface mechanical properties of geogrid (striped reinforcement/wrapped reinforcement) reinforced plug-soil tire[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, 2022. (in Chinese) [14] 程 钢, 赵国群, 管延锦, 等. 轮胎橡胶材料力学性能试验研究[J]. 弹性体, 2003, 13(4): 6-9. (CHENG G, ZHAO G Q, GUAN Y J, et al. Experimental study on mechanical properities of tyre rubber materials[J]. China Elastomerics, 2003, 13(4): 6-9. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3174.2003.04.002CHENG G, ZHAO G Q, GUAN Y J, et al. Experimental study on mechanical properities of tyre rubber materials[J]. China Elastomerics, 2003, 13(4): 6-9. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3174.2003.04.002 [15] 陈艳君. 废旧轮胎加筋土界面力学性能研究[D]. 武汉: 湖北工业大学, 2017. (CHEN Y J. Research on the interface mechanical properties of waste tyre-reinforced soil[D]. Wuhan: Hubei University of Technology, 2017. (in Chinese)CHEN Y J. Research on the interface mechanical properties of waste tyre-reinforced soil[D]. Wuhan: Hubei University of Technology, 2017. (in Chinese) [16] JEWELL R A, MILLIGAN G W E, DUBOIS D, et al. Interaction between soil and geogrids[M]//Science and Engineering Research Council. Polymer Grid Reinforcement. London: T. Telford, 1984: 18-30. -





 下载:
下载: