Intelligent identification of landslide region based on MobileNet network
-
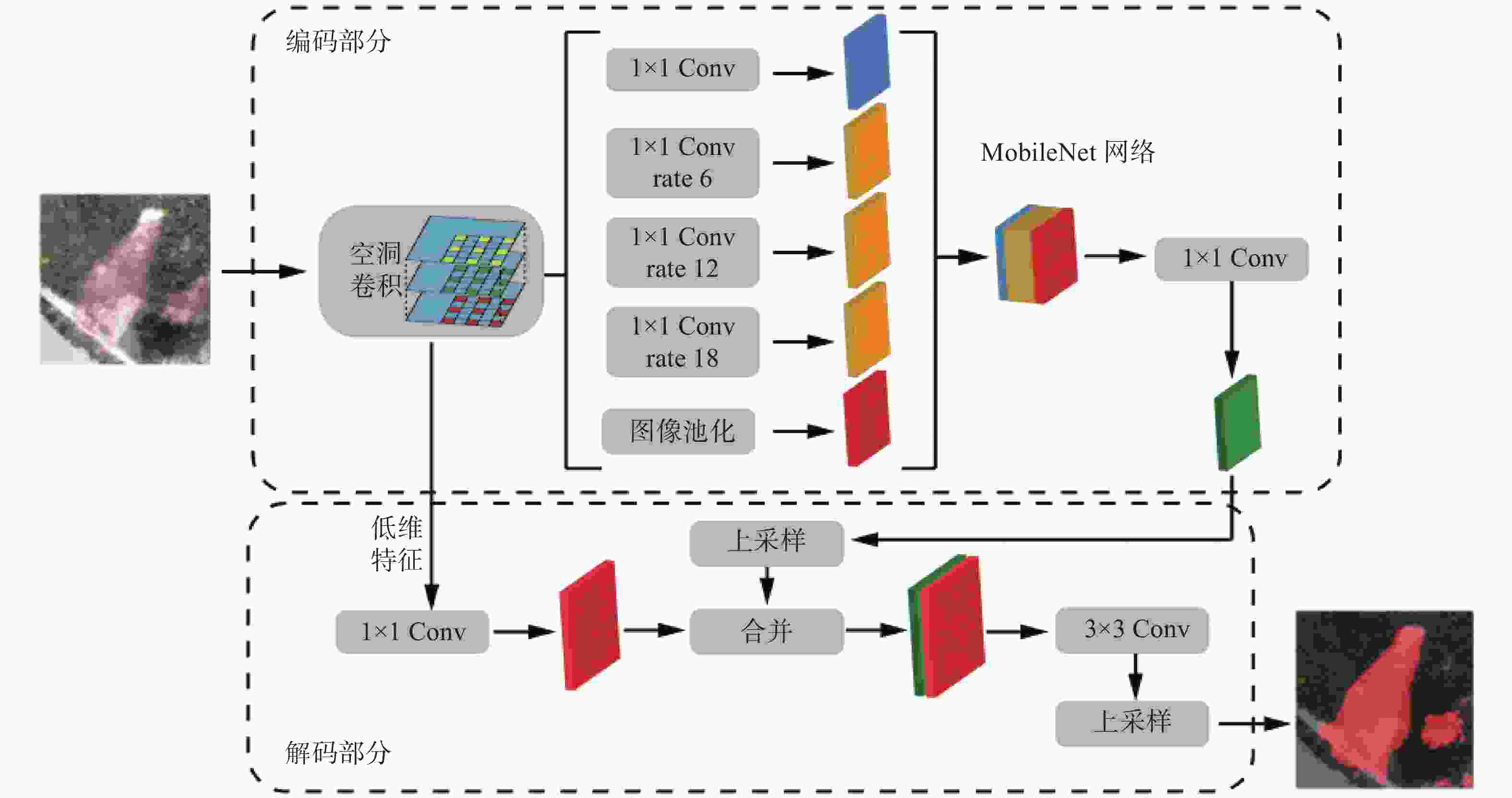
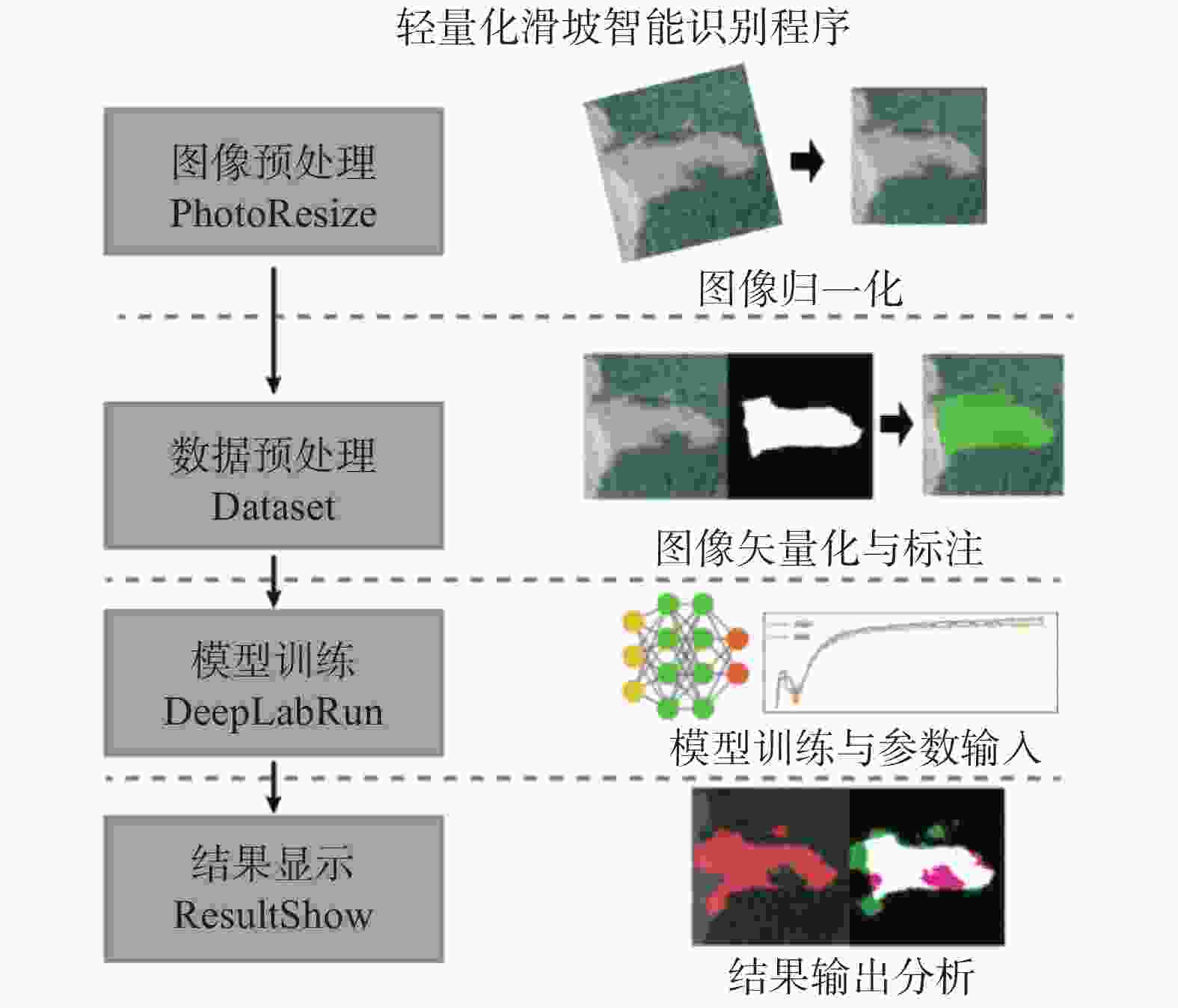
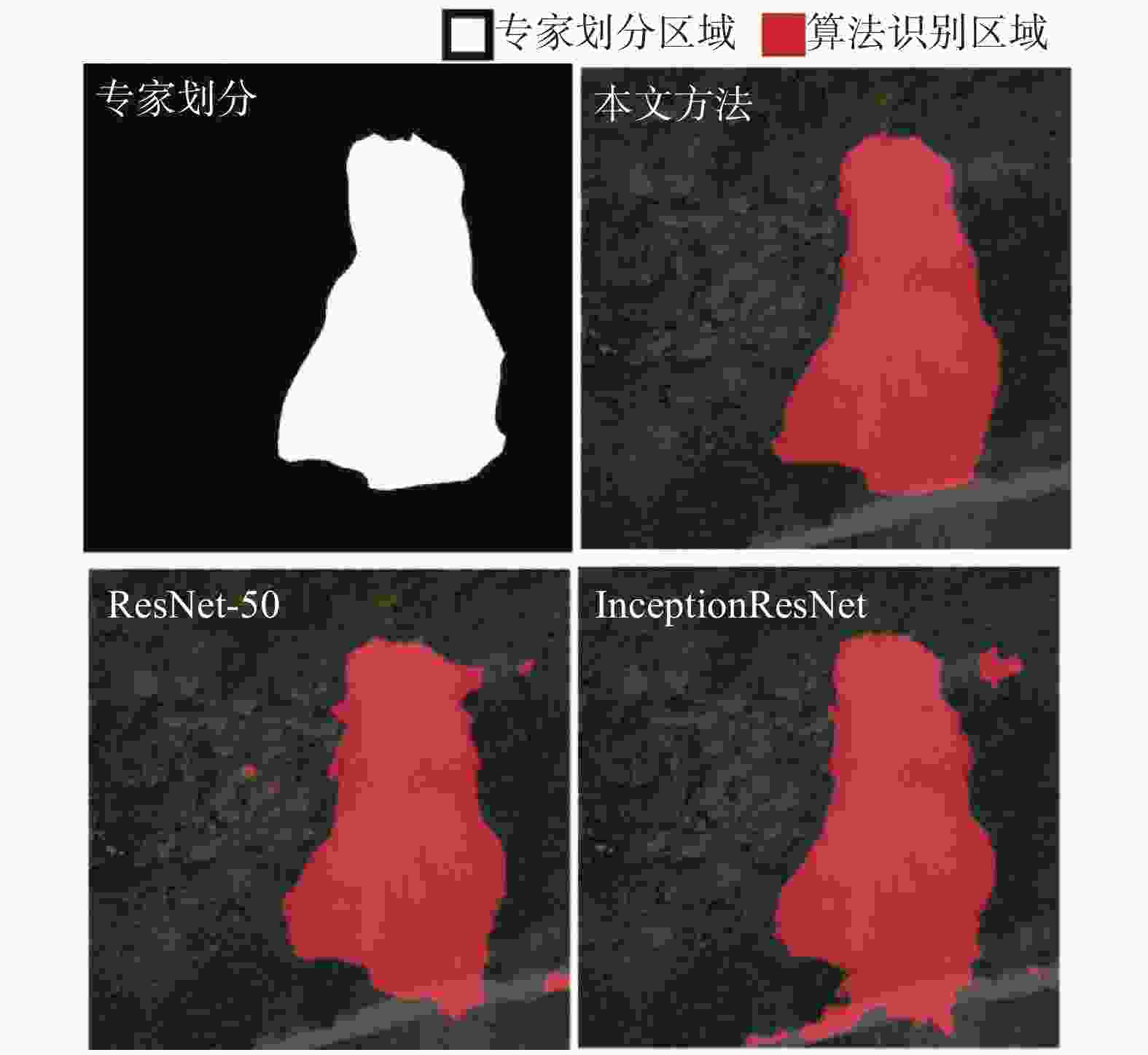
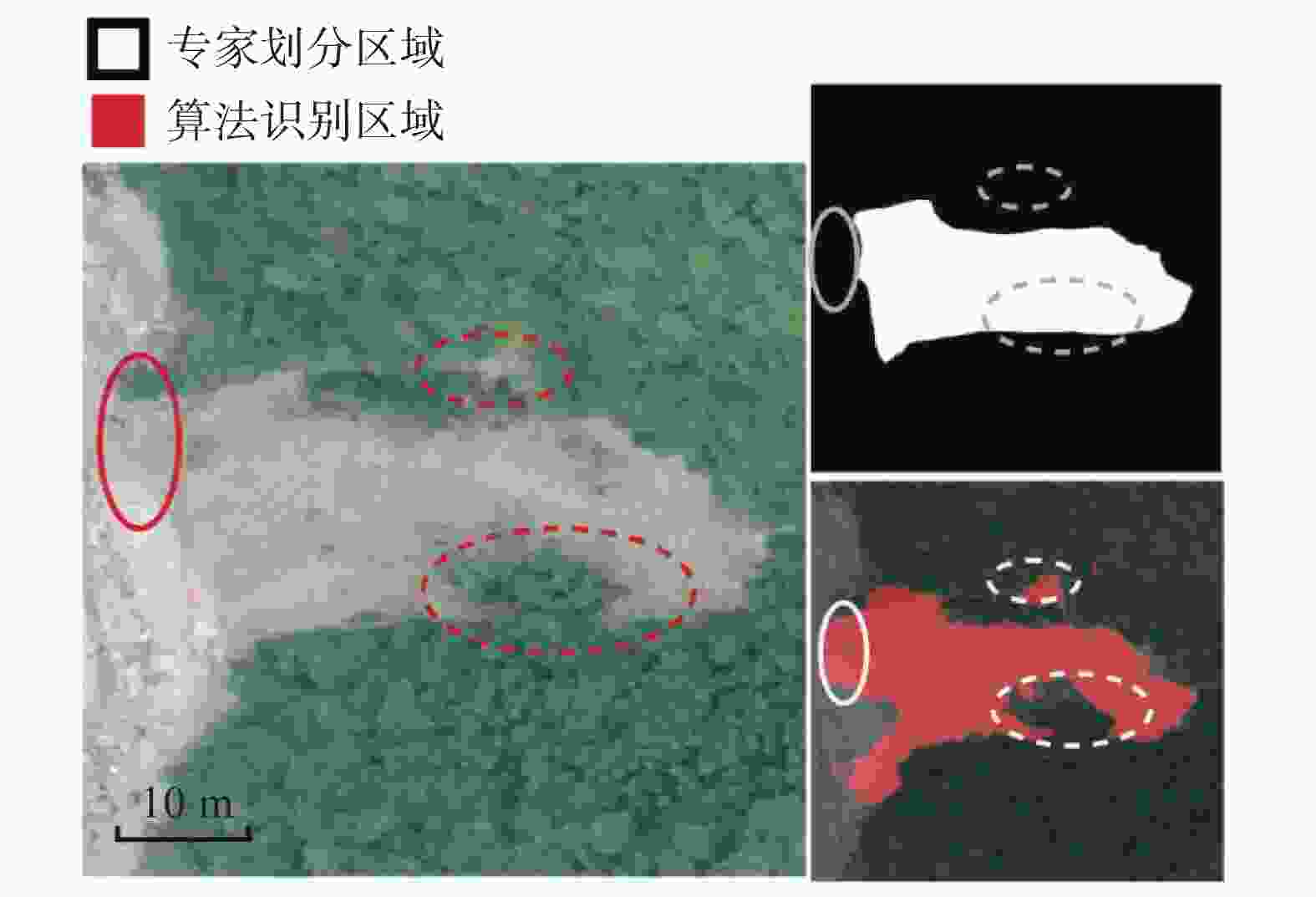
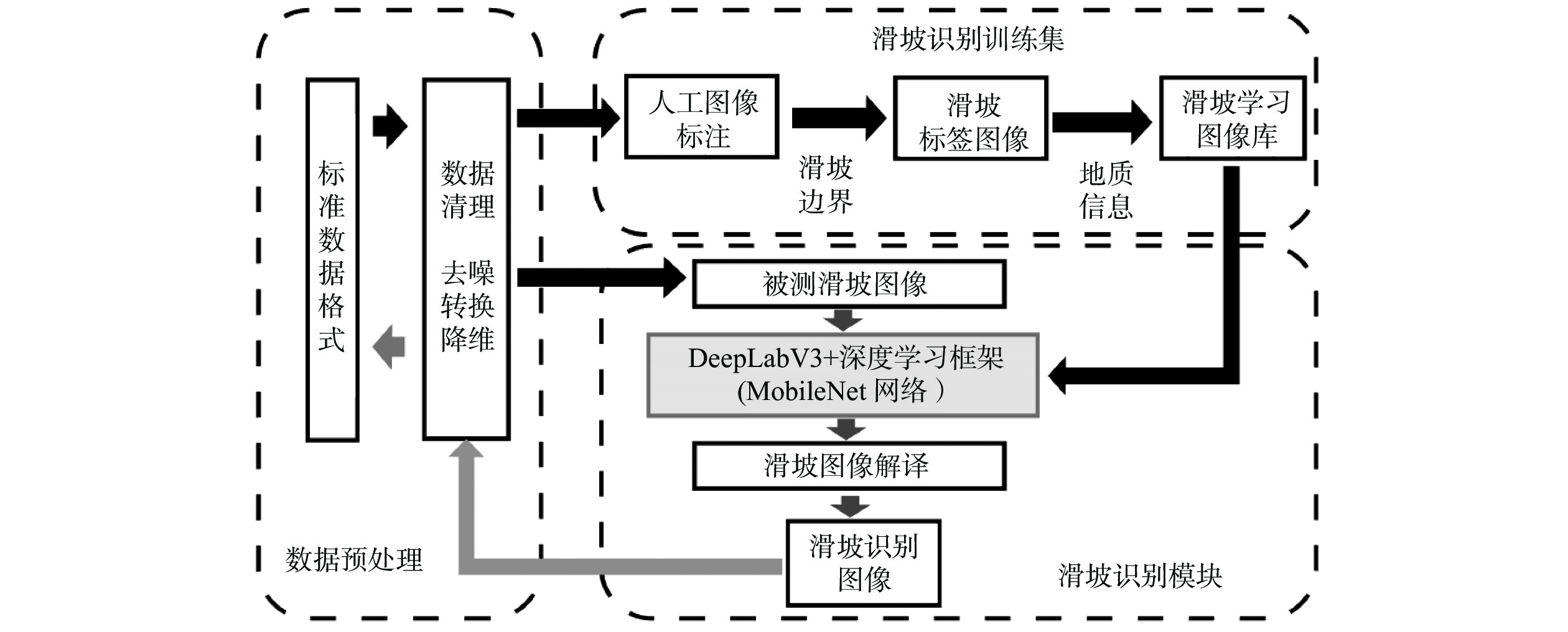
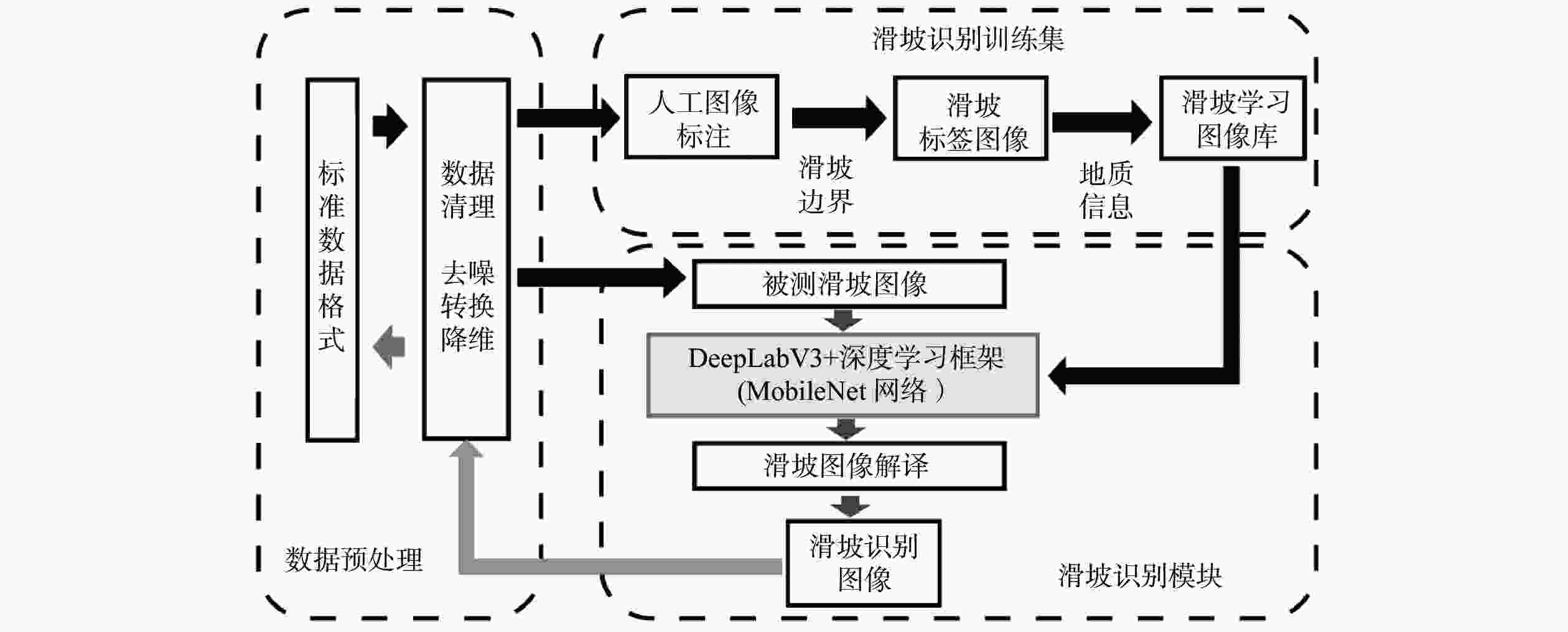
摘要: 传统的滑坡编录统计通常采用人工现场踏勘形式,效率低下且可能遗漏部分区域。目前,主流的基于图像识别的滑坡编录技术通常需要高性能设备,并需要较高的模型训练成本,因而不适合在滑坡现场快速筛查中应用。本研究引入MoblieNet轻量化模型,使用DeepLabV3架构对航空摄影图像中的滑坡进行快速智能识别和边界定位。与传统的卷积神经网络(CNN)图像分割方法相比,该方法可以在传统方案10%的训练时间内,实现超过90%的准确度,可以更好地契合工程上对于显性滑坡快速智能识别需求,适用于大面积区域滑坡点的快速筛查与编录。
-
关键词:
- 滑坡 /
- 智能识别 /
- 深度学习 /
- MobileNet网络
Abstract: Conventional landslide cataloging and statistical analysis predominantly rely on manual field surveys, which are characterized by inefficiency and the potential for omitting certain areas. Currently, mainstream slope cataloging techniques based on image recognition typically necessitate high-performance equipment and incur substantial model training costs, thereby hindering their efficient application in on-site rapid screening scenarios. This study incorporates the MobileNet lightweight model and leverages the DeepLabV3 architecture to realize rapid intelligent identification and boundary localization of landslides in aerial photographic imagery. In comparison with traditional convolutional neural network (CNN) image segmentation approaches, the proposed method can achieve an accuracy exceeding 90% within 10% of the training duration required by conventional schemes. This renders it more adept at satisfying engineering demands for the rapid intelligent recognition of landslides and makes it suitable for the rapid screening and cataloging of landslide points across large-scale regions.-
Key words:
- landslides /
- intelligent recognition /
- deep learning /
- MobileNet network
-
表 1 训练设备与训练参数
Table 1. Training equipment and training parameters
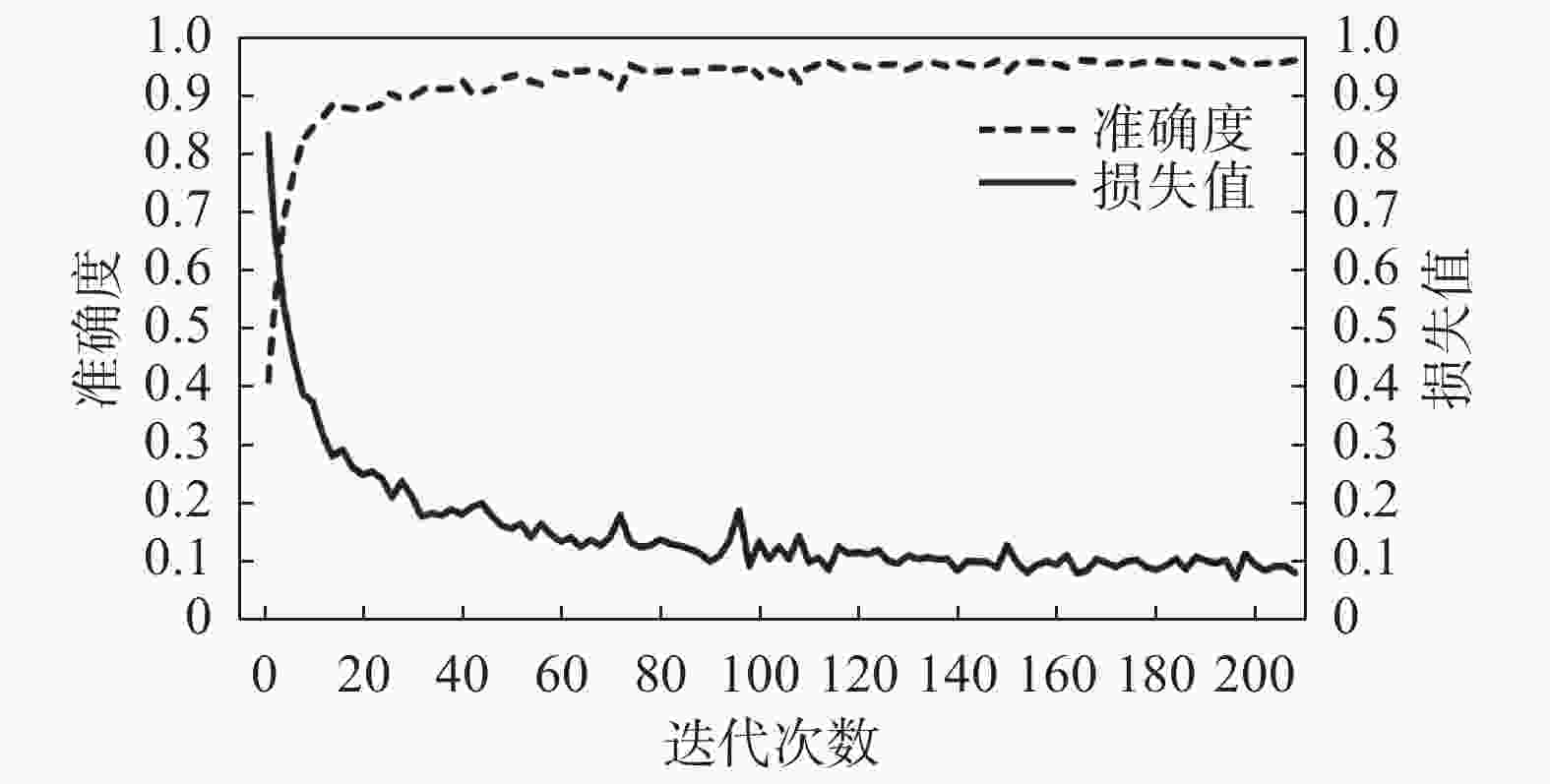
训练设备 训练参数 CPU Intel Xeon Gold 5218 @2.3GHZ 优化器 Adam GPU Nvidia RTX A4000 16G 学习率方案 Piecewise RAM DDR4 2666MHZ 128G 最大步长 20 初始学习率 1×10−4 L2正则化率 0.005 最小批大小 8 表 2 本文算法与经典分割算法时间准确度对比
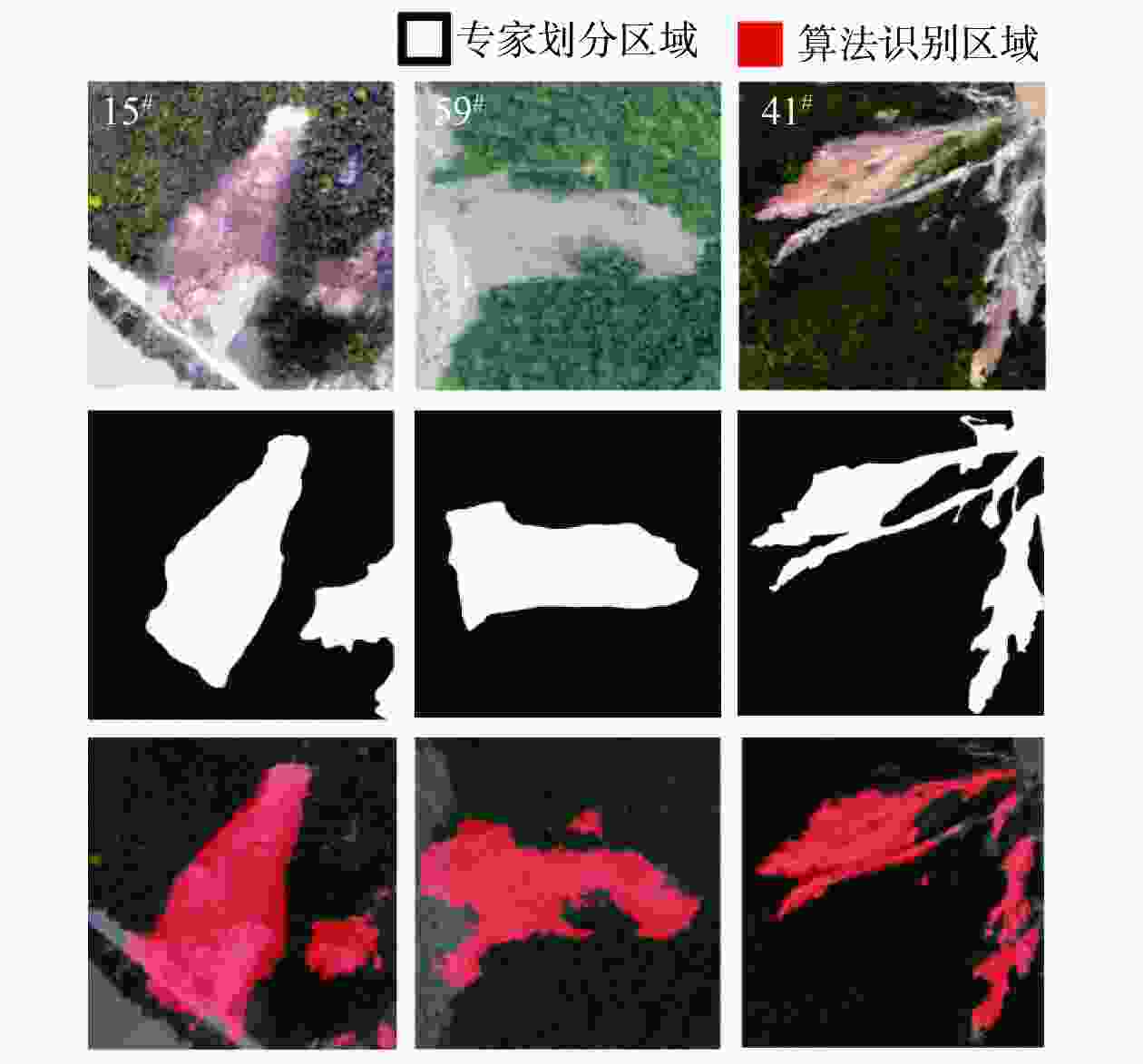
Table 2. Comparison of time and accuracy between the proposed algorithm and classic segmentation algorithms
测试模型 训练用时 最大准确度/% 本文 1 min 51 s 95.91 ResNet-50 3 min 53 s 97.50 InceptionResNet 6 min 8 s 94.93 -
[1] WANG H J, ZHANG L M, YIN K S, et al. Landslide identification using machine learning[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2021, 12(1): 351-364. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2020.02.012 [2] 巨袁臻, 许 强, 金时超, 等. 使用深度学习方法实现黄土滑坡自动识别[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2020, 45(11): 1747-1755. (JU Y Z, XU Q, JIN S C, et al. Automatic object detection of loess landslide based on deep learning[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2020, 45(11): 1747-1755. (in Chinese)JU Y Z, XU Q, JIN S C, et al. Automatic object detection of loess landslide based on deep learning[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2020, 45(11): 1747-1755. (in Chinese) [3] 王 涛. 遥感目标识别的轻量化深度学习方法研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2022. (WANG T. Research on lightweight deep learning method for remote sensing object[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2022. (in Chinese)WANG T. Research on lightweight deep learning method for remote sensing object[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2022. (in Chinese) [4] 毛佳琪. 基于对抗性DeepLabV3+算法的滑坡识别[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2023. (MAO J Q. Landslide identification based on the adversarial DeepLabV3+ algorithm[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2023. (in Chinese)MAO J Q. Landslide identification based on the adversarial DeepLabV3+ algorithm[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2023. (in Chinese) [5] DONG A N, DOU J, LI C D, et al. Accelerating cross-scene co-seismic landslide detection through progressive transfer learning and lightweight deep learning strategies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 4410213. [6] JIANG Z Y, WANG M, LIU K. Comparisons of convolutional neural network and other machine learning methods in landslide susceptibility assessment: a case study in Pingwu[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(3): 798. doi: 10.3390/rs15030798 [7] 蔡浩杰, 韩海辉, 张雨莲, 等. 基于地形特征融合的卷积神经网络滑坡识别[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2022, 44(3): 568-579. (CAI H J, HAN H H, ZHANG Y L, et al. Convolutional neural network landslide recognition based on terrain feature fusion[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2022, 44(3): 568-579. (in Chinese)CAI H J, HAN H H, ZHANG Y L, et al. Convolutional neural network landslide recognition based on terrain feature fusion[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2022, 44(3): 568-579. (in Chinese) [8] 高秉海, 何 毅, 张立峰, 等. 顾及InSAR形变的CNN滑坡易发性动态评估——以刘家峡水库区域为例[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2023, 42(2): 450-465. (GAO B H, HE Y, ZHANG L F, et al. Dynamic evaluation of landslide susceptibility by CNN considering InSAR deformation: a case study of Liujiaxia reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(2): 450-465. (in Chinese)GAO B H, HE Y, ZHANG L F, et al. Dynamic evaluation of landslide susceptibility by CNN considering InSAR deformation: a case study of Liujiaxia reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(2): 450-465. (in Chinese) [9] 赵占骜, 王继周, 毛 曦, 等. 多维CNN耦合的滑坡易发性评价方法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2024, 49(8): 1466-1481. (ZHAO Z A, WANG J Z, MAO X, et al. A multi-dimensional CNN coupled landslide susceptibility assessment method[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2024, 49(8): 1466-1481. (in Chinese)ZHAO Z A, WANG J Z, MAO X, et al. A multi-dimensional CNN coupled landslide susceptibility assessment method[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2024, 49(8): 1466-1481. (in Chinese) [10] SANDLER M, HOWARD A, ZHU M L, et al. MobileNetV2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018: 4510-4520. [11] CHEN L C, ZHU Y K, PAPANDREOU G, et al. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich: Springer, 2018: 833-851. [12] 曾 超, 曹振宇, 苏凤环, 等. 四川及周边滑坡泥石流灾害高精度航空影像及解译数据集(2008-2020年)[J]. 中国科学数据: 中英文网络版, 2022, 7(2): 195-205. (Zeng C, Cao Z Y, Su F H, et al. High-precision aerial image and interpretation dataset of landslide and debris flow disasters in Sichuan and its surrounding areas (2008–2020)[J]. China Scientific Data (Online in Chinese and English), 2022, 7(2): 195-205. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11922/noda.2021.0005.zhZeng C, Cao Z Y, Su F H, et al. High-precision aerial image and interpretation dataset of landslide and debris flow disasters in Sichuan and its surrounding areas (2008–2020)[J]. China Scientific Data (Online in Chinese and English), 2022, 7(2): 195-205. doi: 10.11922/noda.2021.0005.zh [13] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas: IEEE, 2016: 770-778. [14] SZEGEDY C, IOFFE S, VANHOUCKE V, et al. Inception-v4, inception-ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning[C]//Proceedings of the 31st AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco: AAAI Press, 2017: 4278-4284. -





 下载:
下载: