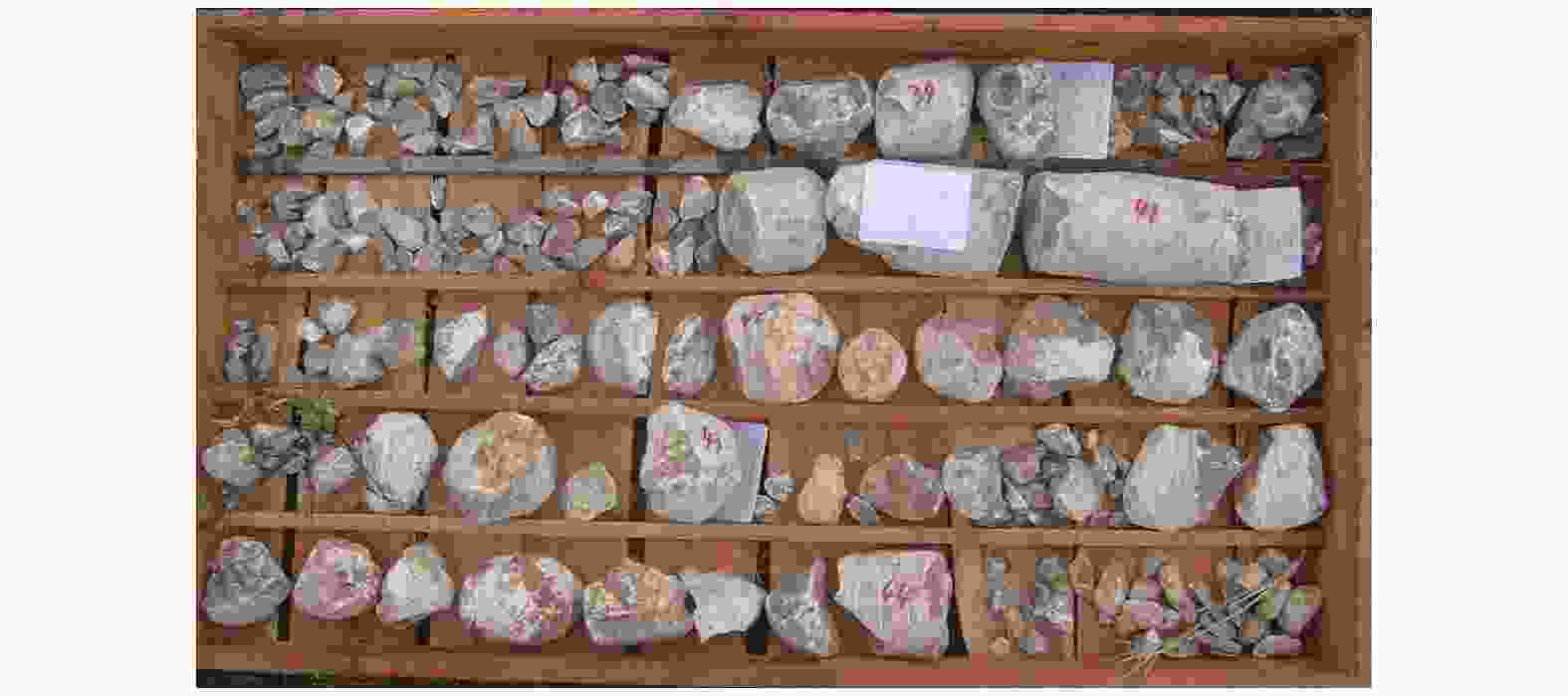
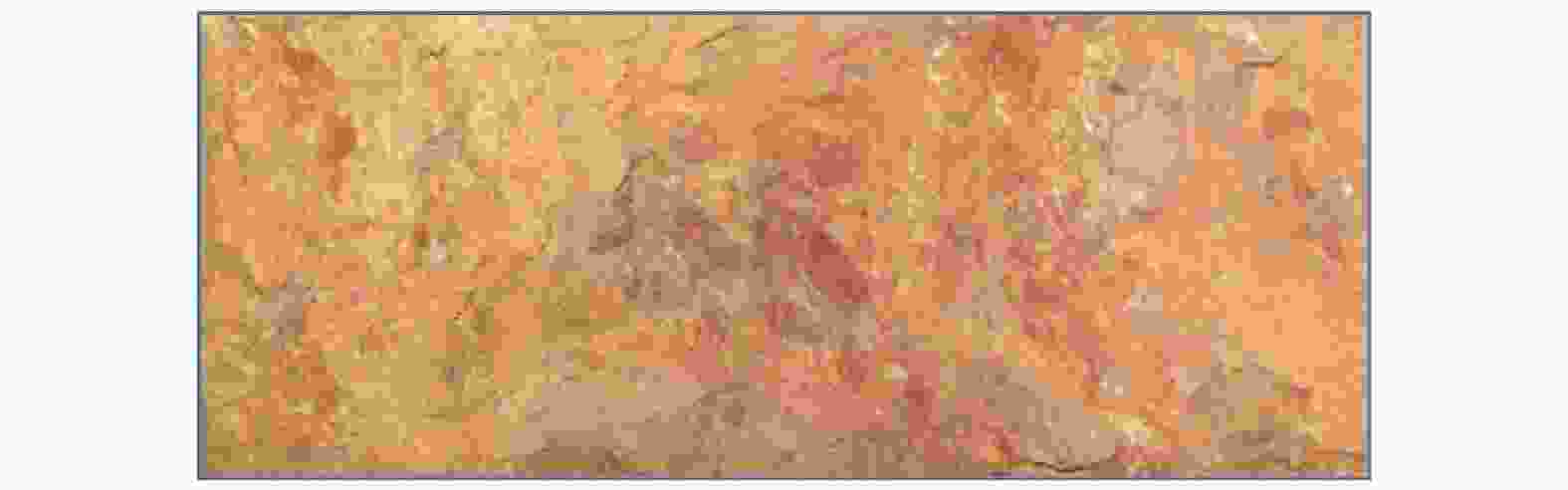
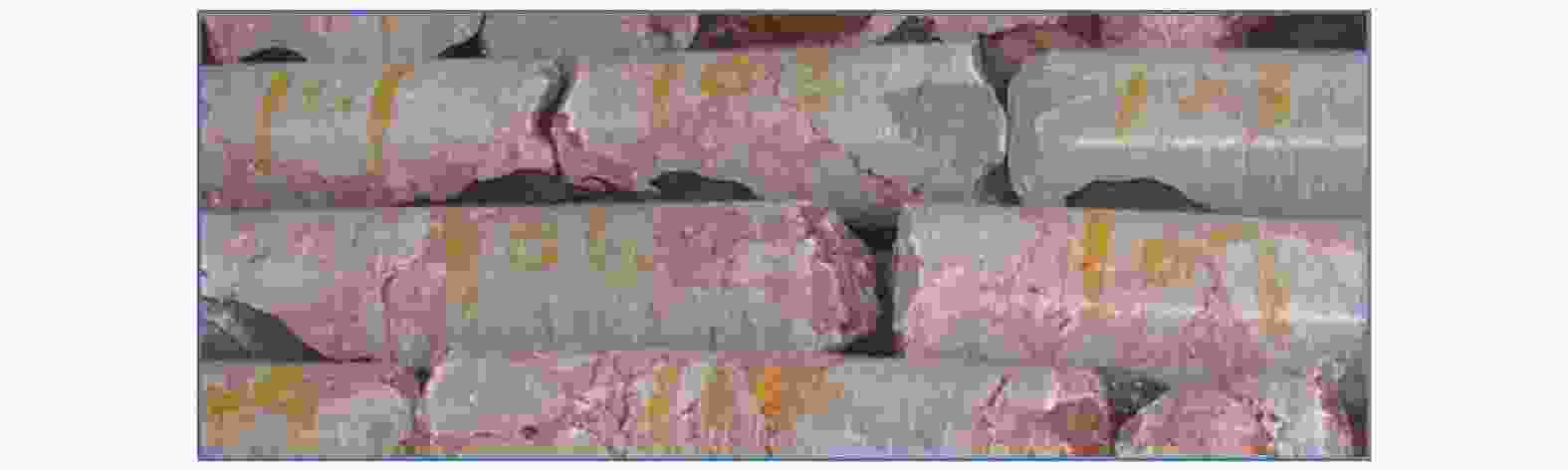
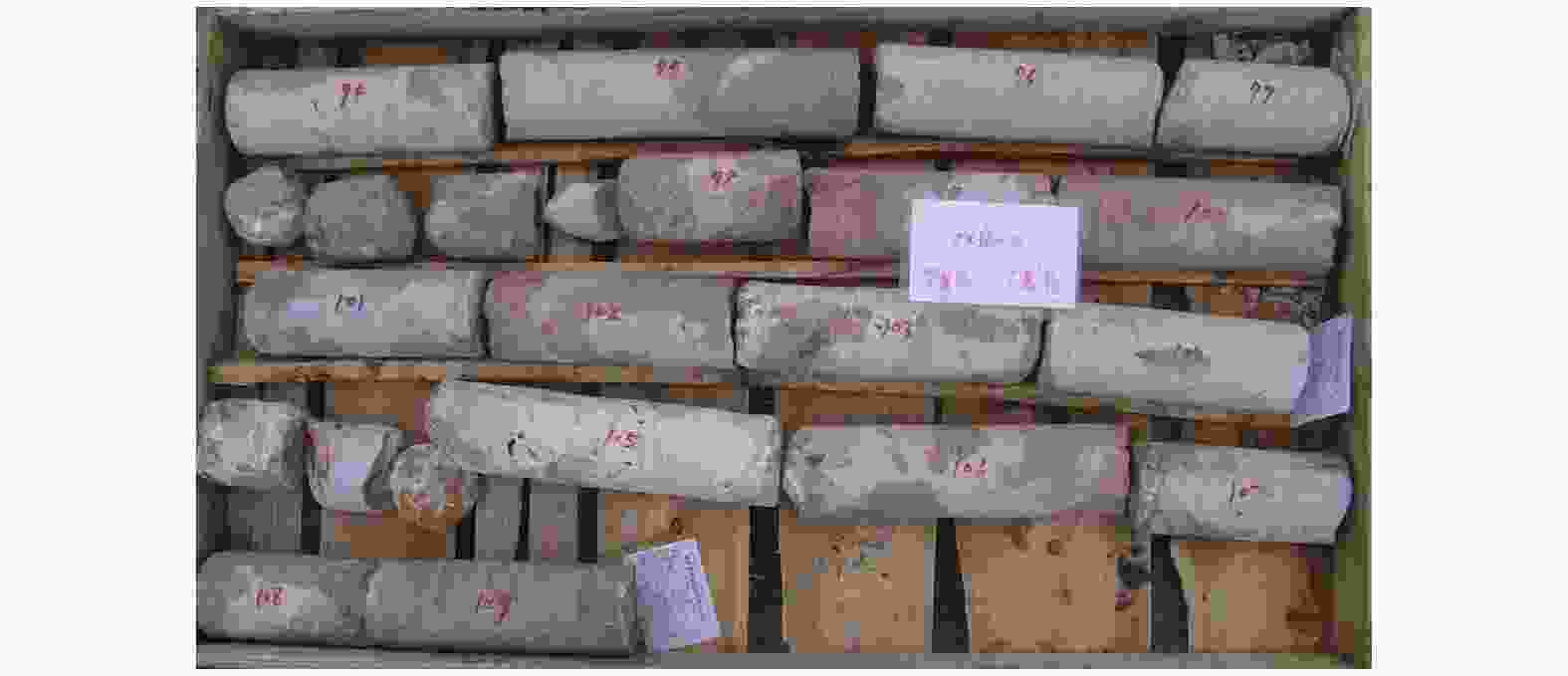
Suitability of highway bridge foundation in karst breccia canyon slope
-
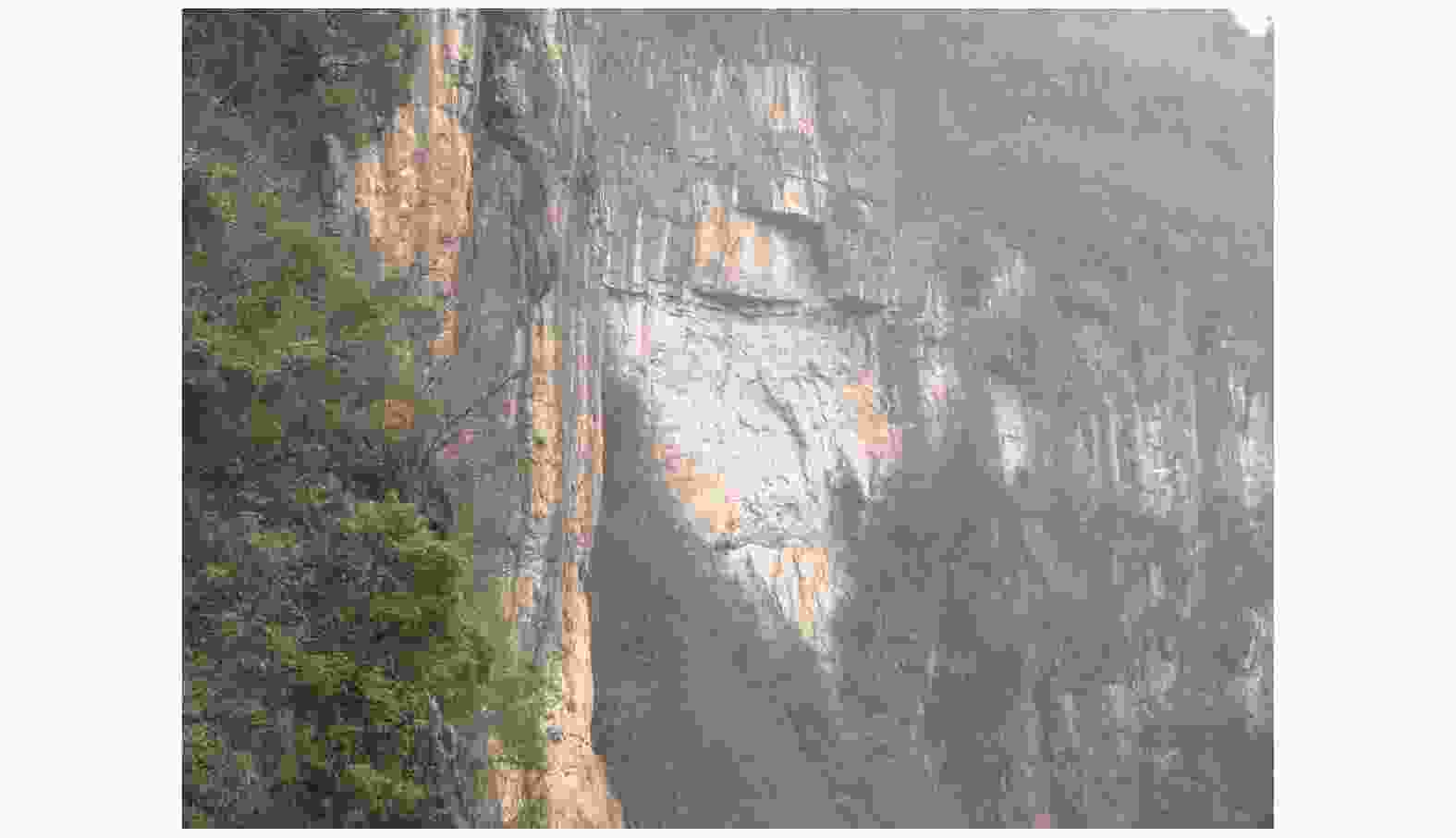
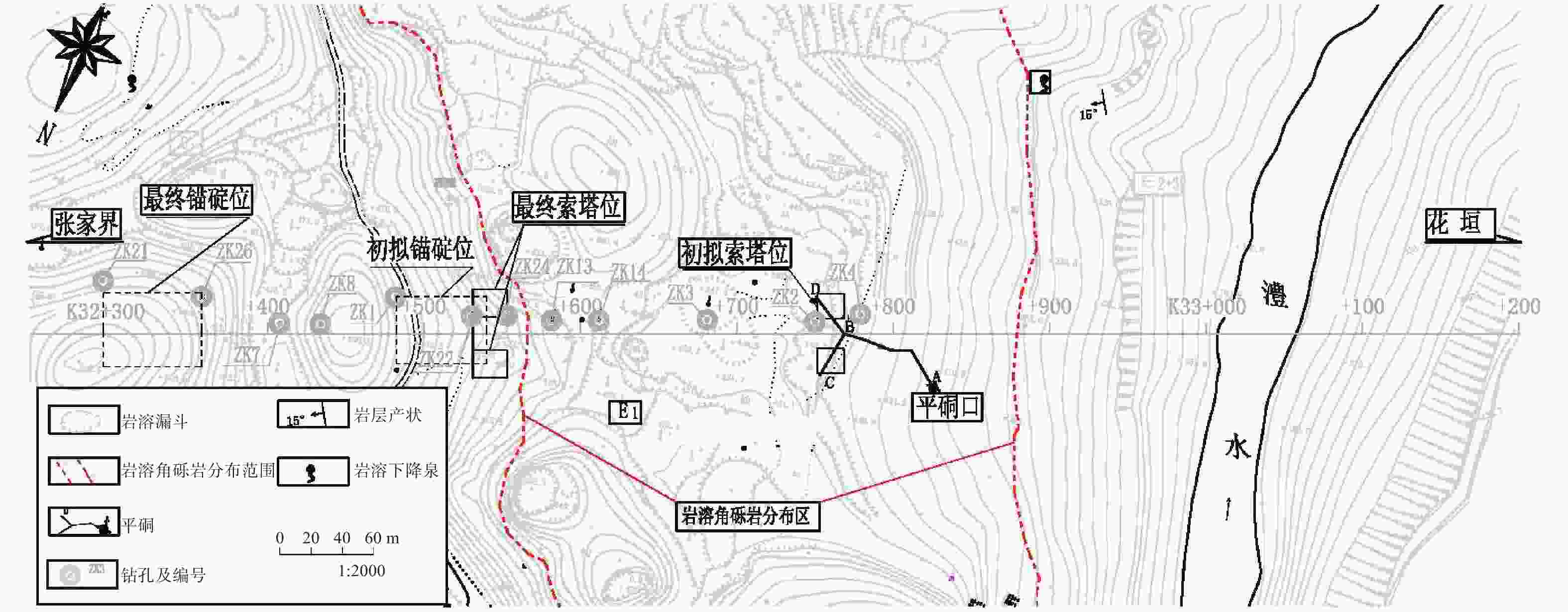
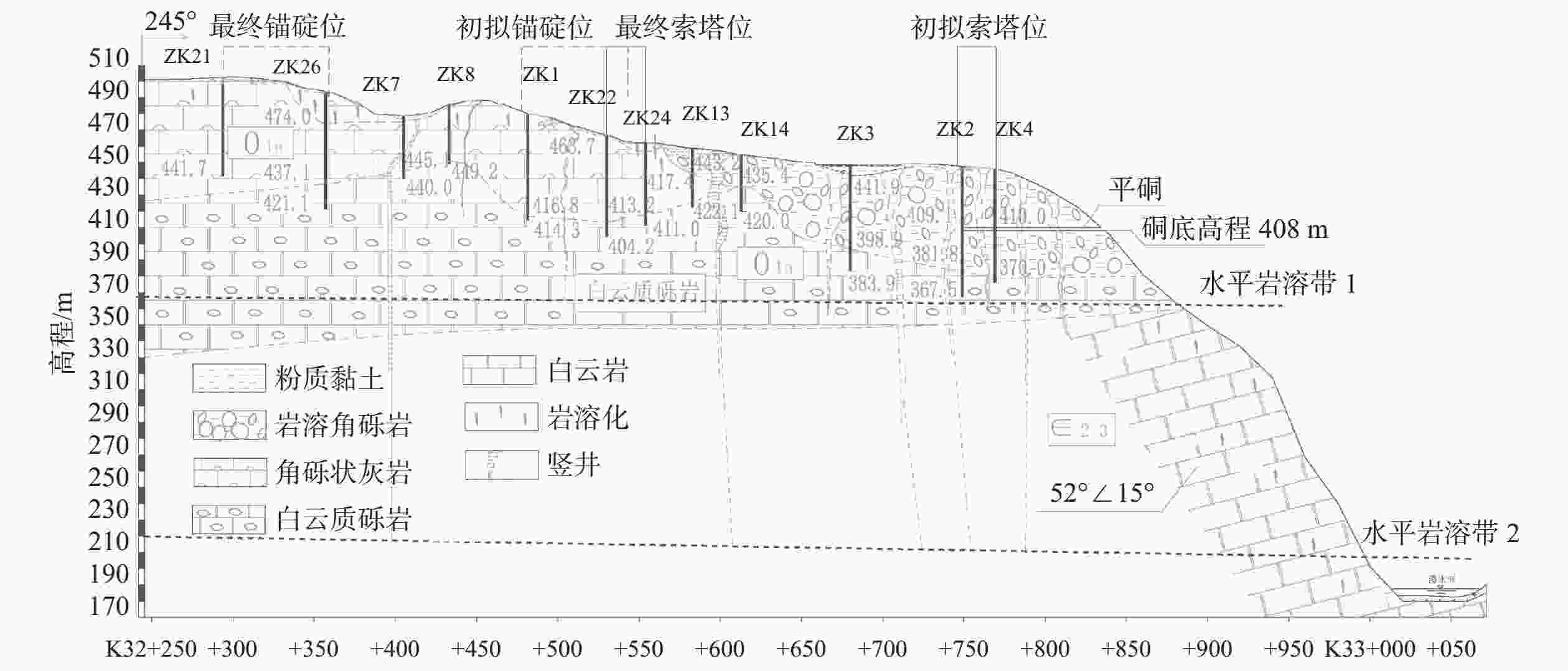
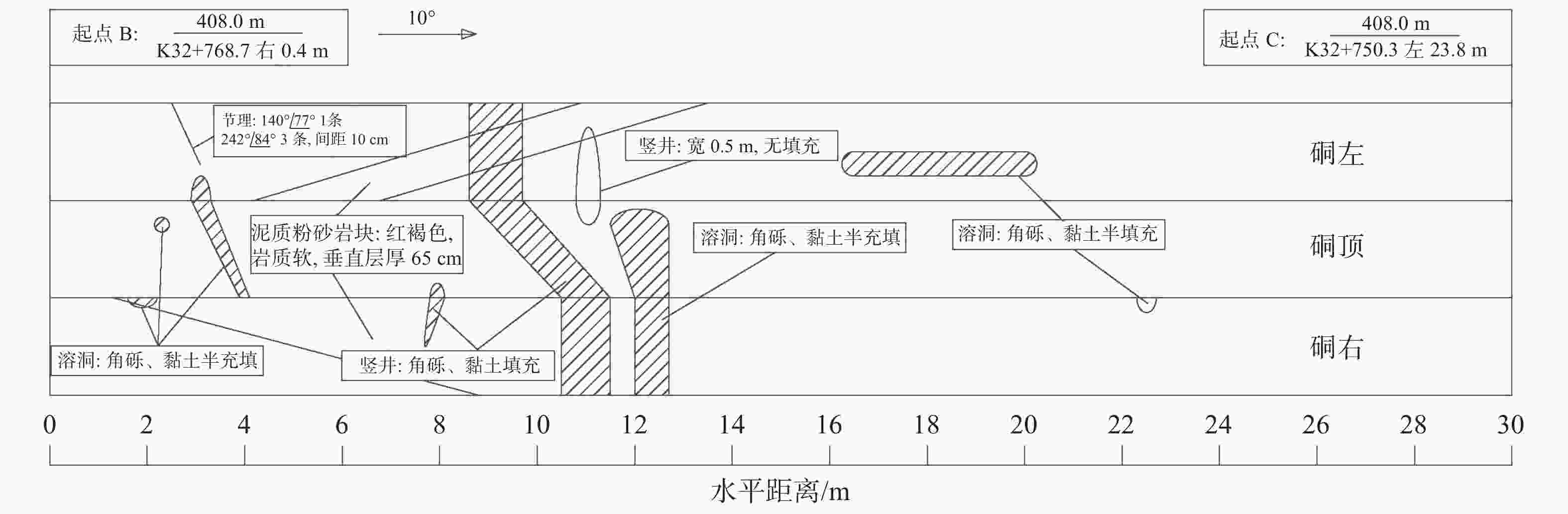
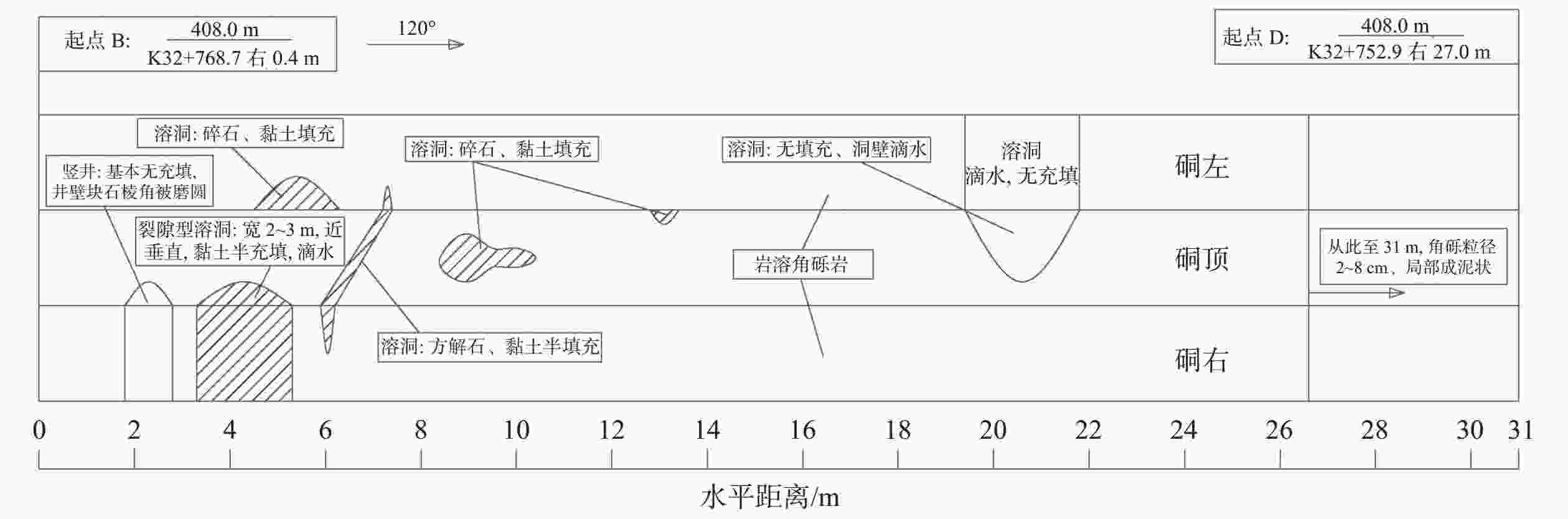
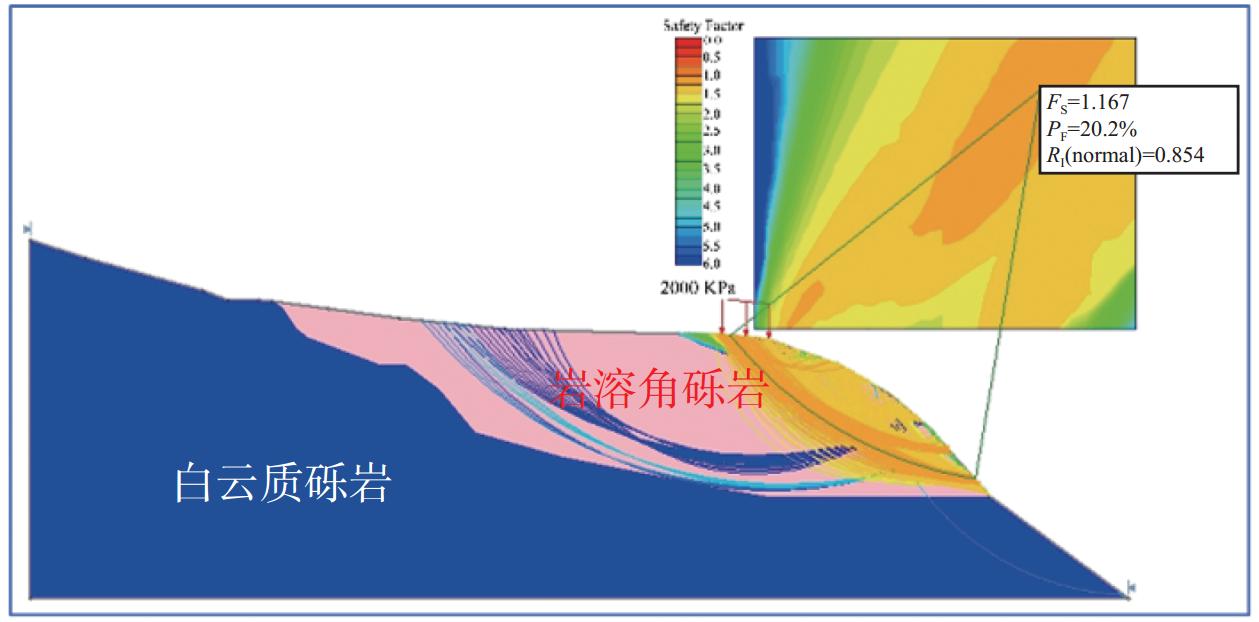
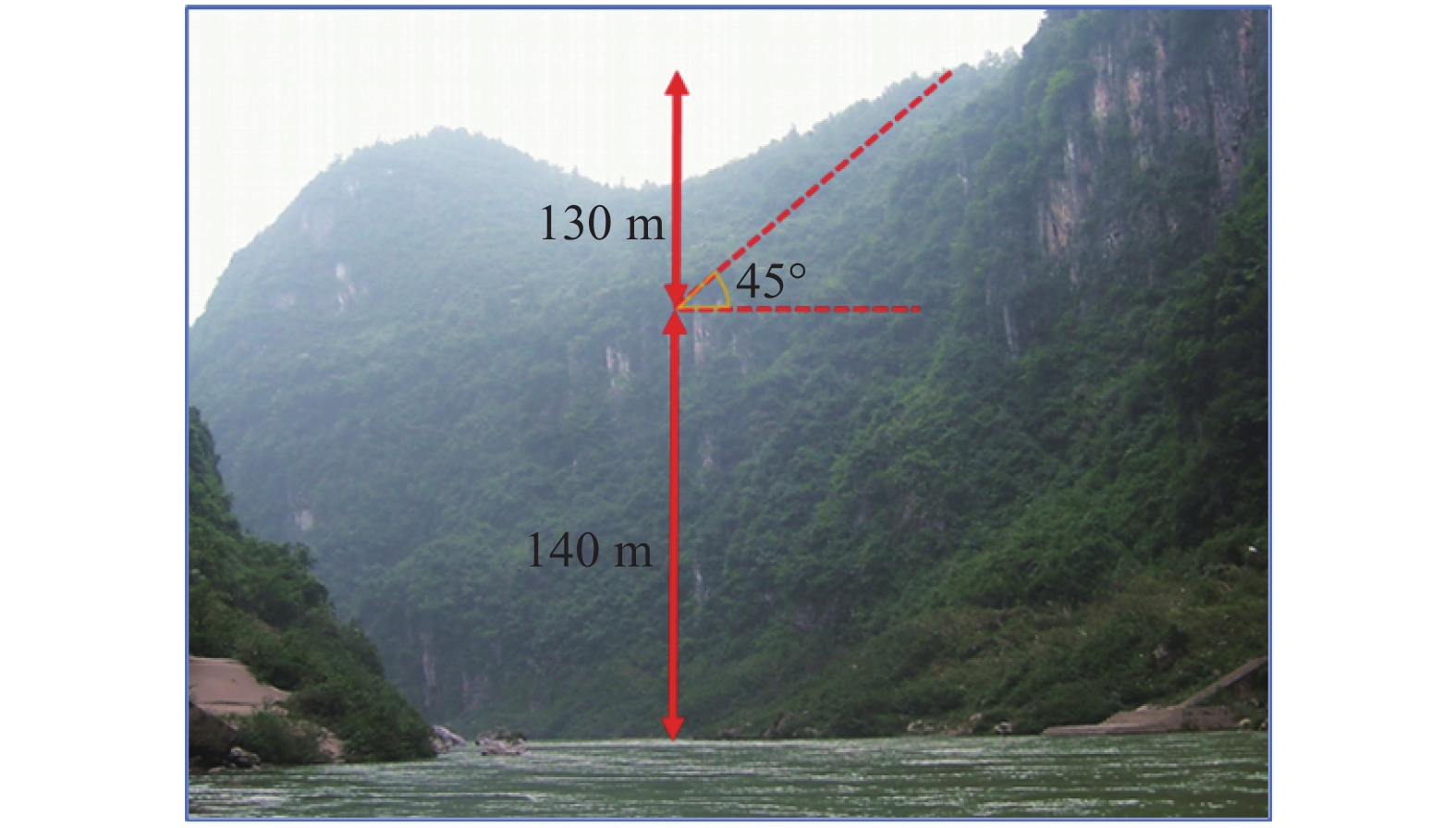
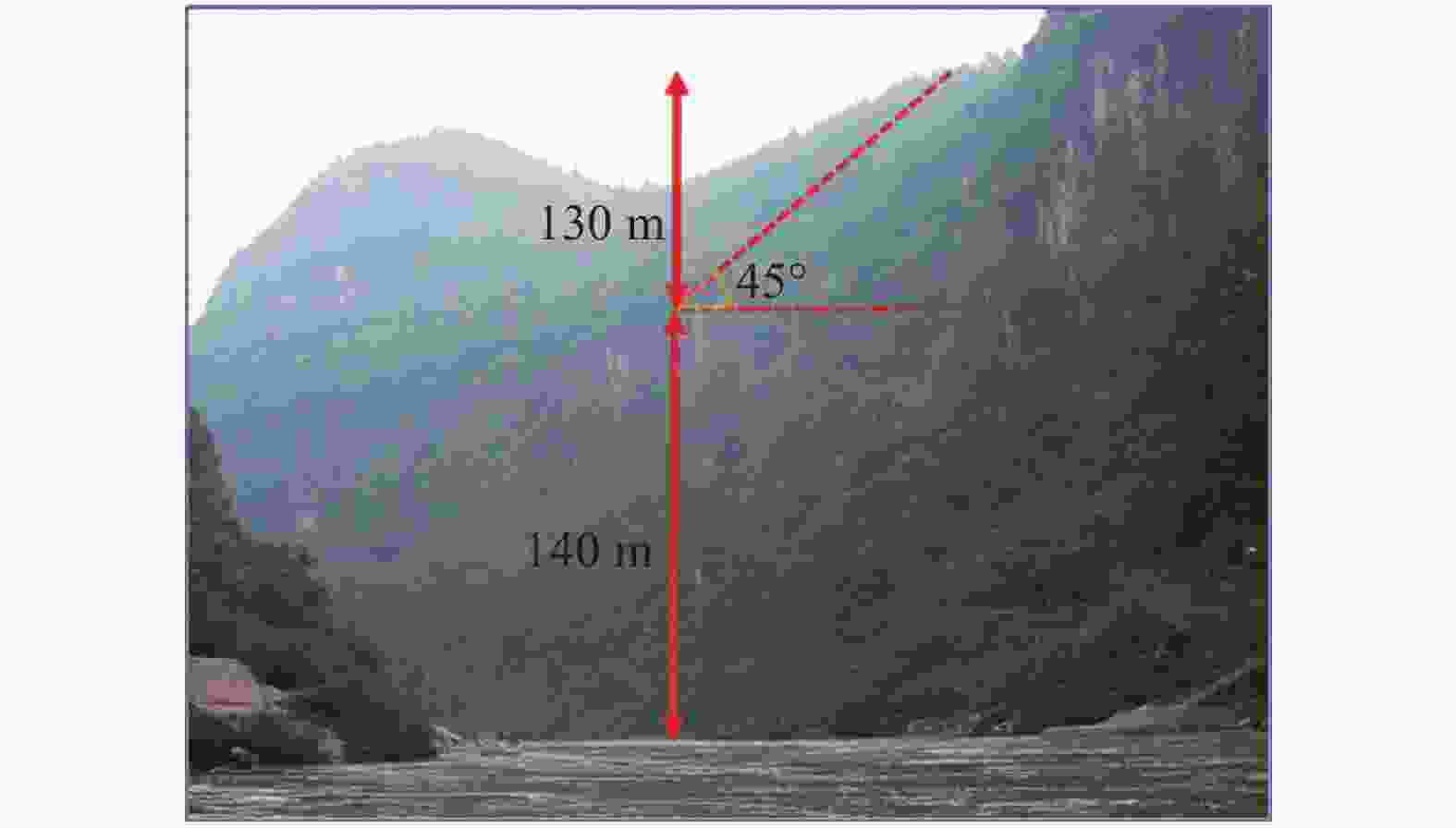
摘要: 岩溶角砾岩是一种特殊的沉积岩,具有独特的成岩环境和成生特征,特别是位于峡谷岸坡的岩溶角砾岩,在有利的地下水排泄条件下,后期的岩溶作用会进一步劣化岩体的力学性质,从而影响地基稳定性和岸坡的整体稳定性。因此,工程建设中对岩溶角砾岩组成的峡谷岸坡作为特大型桥梁地基的适宜性进行评价尤为关键和重要。以张家界至花垣高速公路澧水特大桥工程为背景,通过开挖平硐和钻探相结合的手段对大桥所处的峡谷岸坡进行勘察,揭示了岩溶角砾岩的结构特征和岩溶发育特征;整体边坡可靠度分析表明,初拟索塔位在设计荷载作用下岸坡发生滑移变形破坏概率超过20%,不满足悬索桥结构对地基变形的严格要求;综合工程地质分析,认为张家界岸岩溶角砾岩不适宜作为悬索桥索塔地基,将索塔基础位置调整至力学性质较好的白云质砾岩,保证了澧水特大桥的建成通车。研究成果可为跨越峡谷的特大型桥梁的勘察设计提供参考。Abstract: Karst breccia is a special type of sedimentary rock with a unique diagenetic environment and characteristics. Especially the karst breccia located on the slope of the canyon bank, under favorable groundwater discharge conditions, the later karst process will further deteriorate the mechanical properties of the rock mass and affect the stability of the foundation and the overall stability of the bank slope. Therefore, the suitability evaluation of the foundation of canyon bank slope composed of karst breccia for super large bridges is particularly crucial and important, which determines the type and scale of bridge structure based on this in engineering construction. This article takes the bank slope of the Lishui Grand Bridge Canyon on the Zhangjiajie Huayuan Expressway as the engineering background, and the structural characteristics and karst development characteristics of karst breccia have been revealed through adits and drilling surveys. Through overall slope reliability analysis, it has been demonstrated that the probability of deformation and failure of the bank slope under design loads exceeds 20%. According to a comprehensive engineering geological analysis, the karst breccia on the Zhangjiajie shore is not suitable as the foundation for the suspension bridge tower. Thus, a geological decision was made to adjust the cable bent tower to a dolomite conglomerate with better mechanical properties. This research has ensured the completion and opening of the Lishui Extra Large Bridge and provided new important references for the survey and design of super large bridges crossing canyons.
-
表 1 岩溶角砾岩胶结物物理力学参数
指标 含水率w/% 湿密度
/(g·cm−3)干密度
/(g·cm−3)比重Gs 液限wL 塑限
wp塑性指数Ip 自由膨胀率/% 抗剪强度参数 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 样本数 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 6 6 最大值 41.4 1.9 1.5 2.8 69.3 39.6 35.6 65.0 73 13.3 最小值 25.8 1.7 1.2 2.7 42.5 23.0 19.5 30.0 12 5.0 平均值 36.6 1.8 1.3 2.7 56.0 30.1 25.9 49.5 39 7.3 标准差 4.26 0.08 0.098 0.02 7.91 5.34 4.93 10.36 22.68 3.10 变异系数 0.12 0.05 0.08 0.01 0.14 0.18 0.19 0.21 0.59 0.42 标准值 39.0 1.7 1.3 2.7 51.6 27.1 23.2 55.3 20 4.8 表 2 反算法得出的岩溶角砾岩强度参数
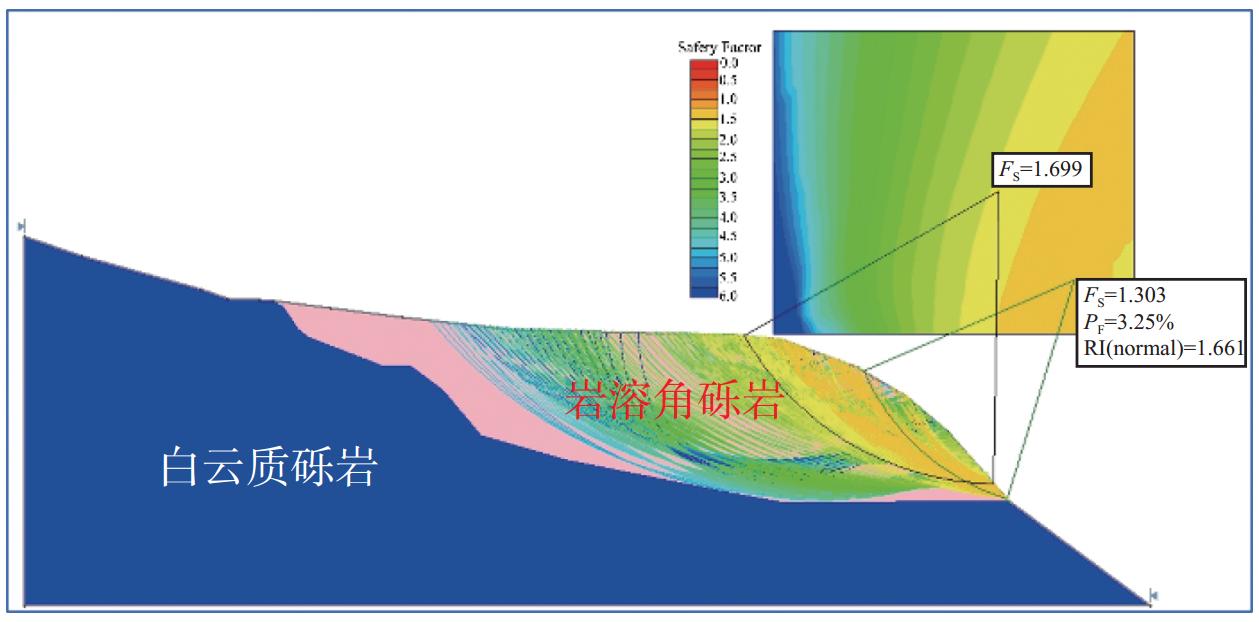
重度/(kN·m−3) 黏聚力c/kPa 内摩擦角φ/(°) 稳定系数Fs 破坏概率PF/% 可靠性指数RI 平均值 最小值 最大值 平均值 最小值 最大值 22 41 36 46 36 31 41 1.303 3.25 1.66 -
[1] YIN X S, XIE L M, XIAO D Y, et al. Engineering properties and slope failure mode of Karst Breccia[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2018, 189: 022046. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/189/2/022046 [2] 谢礼明, 张少锋, 殷先松, 等. 乌江某电站岩溶角砾岩发育特征及对工程的影响[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2008, 22(S1): 43-46. (XIE L M, ZHANG S F, YIN X S, et al. Development characteristics of karst breccia in a power station of Wujiang River and its engineering influence[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2008, 22(S1): 43-46. (in Chinese)XIE L M, ZHANG S F, YIN X S, et al. Development characteristics of karst breccia in a power station of Wujiang River and its engineering influence[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2008, 22(S1): 43-46. (in Chinese) [3] 张文勇, 李 阳. 岩溶角砾岩成因及工程影响研究[J]. 北方交通, 2023(12): 8-12. (ZHANG W Y, LI Y. Research on reasons for karst breccia and engineering impact[J]. Northern Communications, 2023(12): 8-12. (in Chinese)ZHANG W Y, LI Y. Research on reasons for karst breccia and engineering impact[J]. Northern Communications, 2023(12): 8-12. (in Chinese) [4] 高 健, 陈 浩, 邱志刚, 等. 三峡库区某滑坡岩溶角砾岩特征及成因分析[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2022, 36(1): 43-48. (GAO J, CHEN H, QIU Z G, et al. Characteristics and genesis of karst breccia in a landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2022, 36(1): 43-48. (in Chinese)GAO J, CHEN H, QIU Z G, et al. Characteristics and genesis of karst breccia in a landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2022, 36(1): 43-48. (in Chinese) [5] 郭喜峰, 吴相超, 熊诗湖. 岩溶角砾岩物理力学特性现场试验研究[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2022, 43(10): 1447-1453. (GUO X F, WU X C, XIONG S H. Field test study on the physical and mechanical characteristics of karst breccia[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2022, 43(10): 1447-1453. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11990/jheu.202108041GUO X F, WU X C, XIONG S H. Field test study on the physical and mechanical characteristics of karst breccia[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2022, 43(10): 1447-1453. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11990/jheu.202108041 [6] 王增银, 沈继方, 万军伟. 清江高坝洲地区古岩溶角砾岩特征及形成条件[J]. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 1998, 23(5): 524-528,536. (WANG Z Y, SHEN J F, WAN J W. An analysis of the formation of paleokarst breccia and the karst evolution in Gaobazhou area of Qingjiang River[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1998, 23(5): 524-528,536 (in Chinese)WANG Z Y, SHEN J F, WAN J W. An analysis of the formation of paleokarst breccia and the karst evolution in Gaobazhou area of Qingjiang River[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1998, 23(5): 524-528,536 (in Chinese) [7] 袁 斌. 溶塌角砾岩浅埋地段施工技术[J]. 智能城市, 2021(10): 161-162. (YUAN B. Construction technology for shallow buried karst collapse breccia sections[J]. Intelligent City, 2021(10): 161-162. (in Chinese)YUAN B. Construction technology for shallow buried karst collapse breccia sections[J]. Intelligent City, 2021(10): 161-162. (in Chinese) [8] 谭志希, 郭 毅, 夏云东. 夹岩水利枢纽工程溶塌角砾岩隧洞涌水塌方处置浅析[J]. 水利水电快报, 2019, 40(6): 63-64,70. (TAN Z X, GUO Y, XIA Y D. Analysis on treatment of water gushing and collapse in karst collapse breccia tunnel of Jiayan Water Control Project[J]. Express Water Resources & Hydropower Information, 2019, 40(6): 63-64,70. (in Chinese)TAN Z X, GUO Y, XIA Y D. Analysis on treatment of water gushing and collapse in karst collapse breccia tunnel of Jiayan Water Control Project[J]. Express Water Resources & Hydropower Information, 2019, 40(6): 63-64,70. [9] 邓万平. 凉水湾大桥岩溶角砾岩地层的钻孔桩施工[J]. 路基工程, 2006(1): 108-110. (DENG W P. Board pile construction in karst breccia stratum for Liangshuiwan major bridge[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2006(1): 108-110. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8825.2006.01.041DENG W P. Board pile construction in karst breccia stratum for Liangshuiwan major bridge[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2006(1): 108-110. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8825.2006.01.041 [10] 王青松, 任少强, 冯军武, 等. 岗乌隧道岩溶角砾岩段大变形控制技术[J]. 中国铁路, 2023(8): 24-32. (WANG Q S, REN S Q, FENG J W, et al. Large deformation control technology of karst breccia section in Gangwu tunnel[J]. China Railway, 2023(8): 24-32. (in Chinese)WANG Q S, REN S Q, FENG J W, et al. Large deformation control technology of karst breccia section in Gangwu tunnel[J]. China Railway, 2023(8): 24-32. (in Chinese) [11] 袁道先, 蒋勇军, 沈立成, 等. 现代岩溶学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016: 3. (YUAN D X, JIANG Y J, SHEN L C, et al. Modern karstology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016: 3. (in Chinese)YUAN D X, JIANG Y J, SHEN L C, et al. Modern karstology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016: 3. (in Chinese) [12] 王光进, 袁利伟, 孔祥云, 等. 边坡工程稳定与不确定性分析Slide程序的应用[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2015: 3. (WANG G J, YUAN L W, KONG X Y, et al. Application of Slide program for stability and uncertainty analysis of slope engineering[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2015: 3. (in Chinese)WANG G J, YUAN L W, KONG X Y, et al. Application of Slide program for stability and uncertainty analysis of slope engineering[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2015: 3. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: