Meso structure analysis of fluid-solidified soil with different materials under freeze-thaw cycles
-
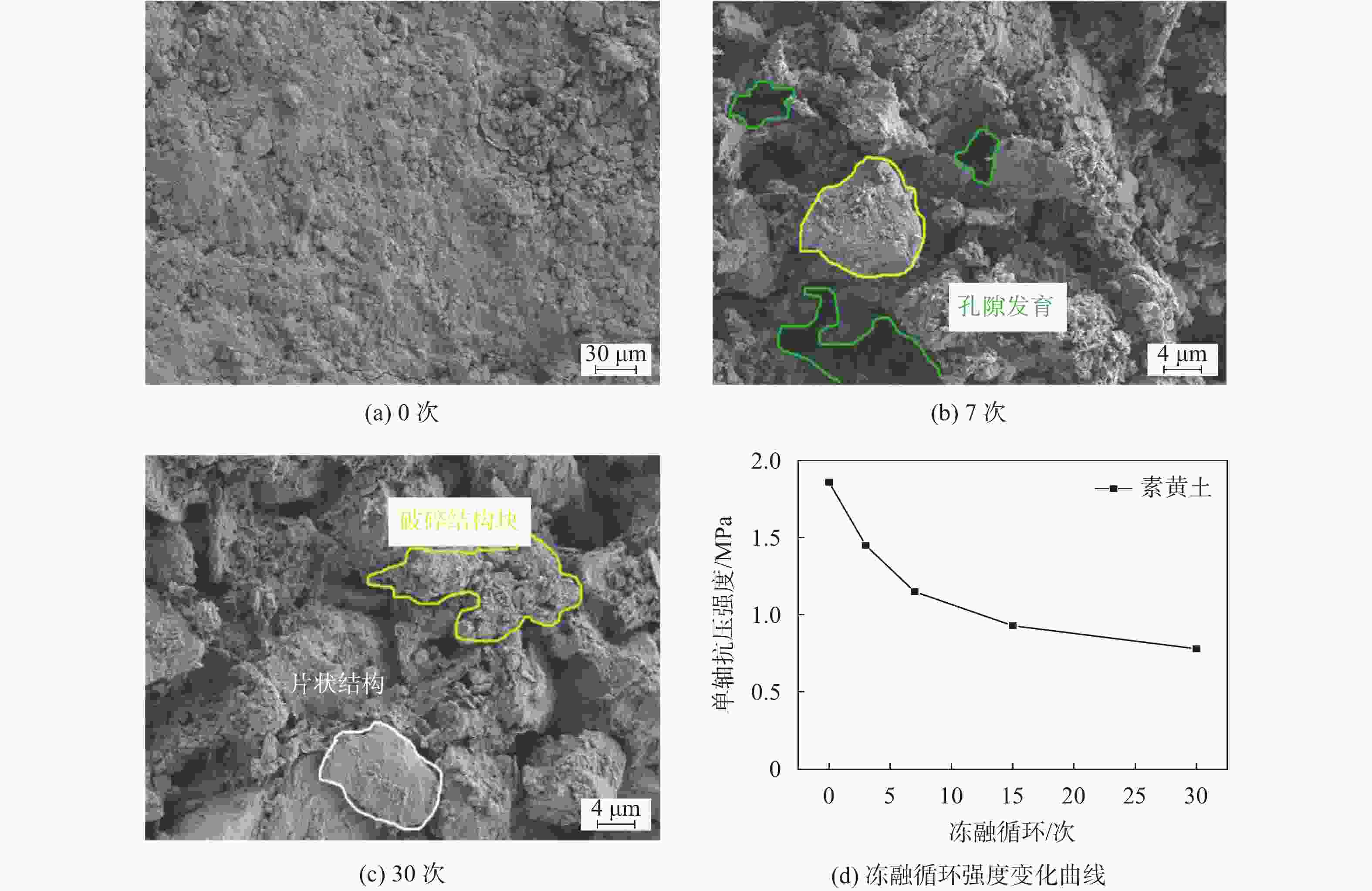
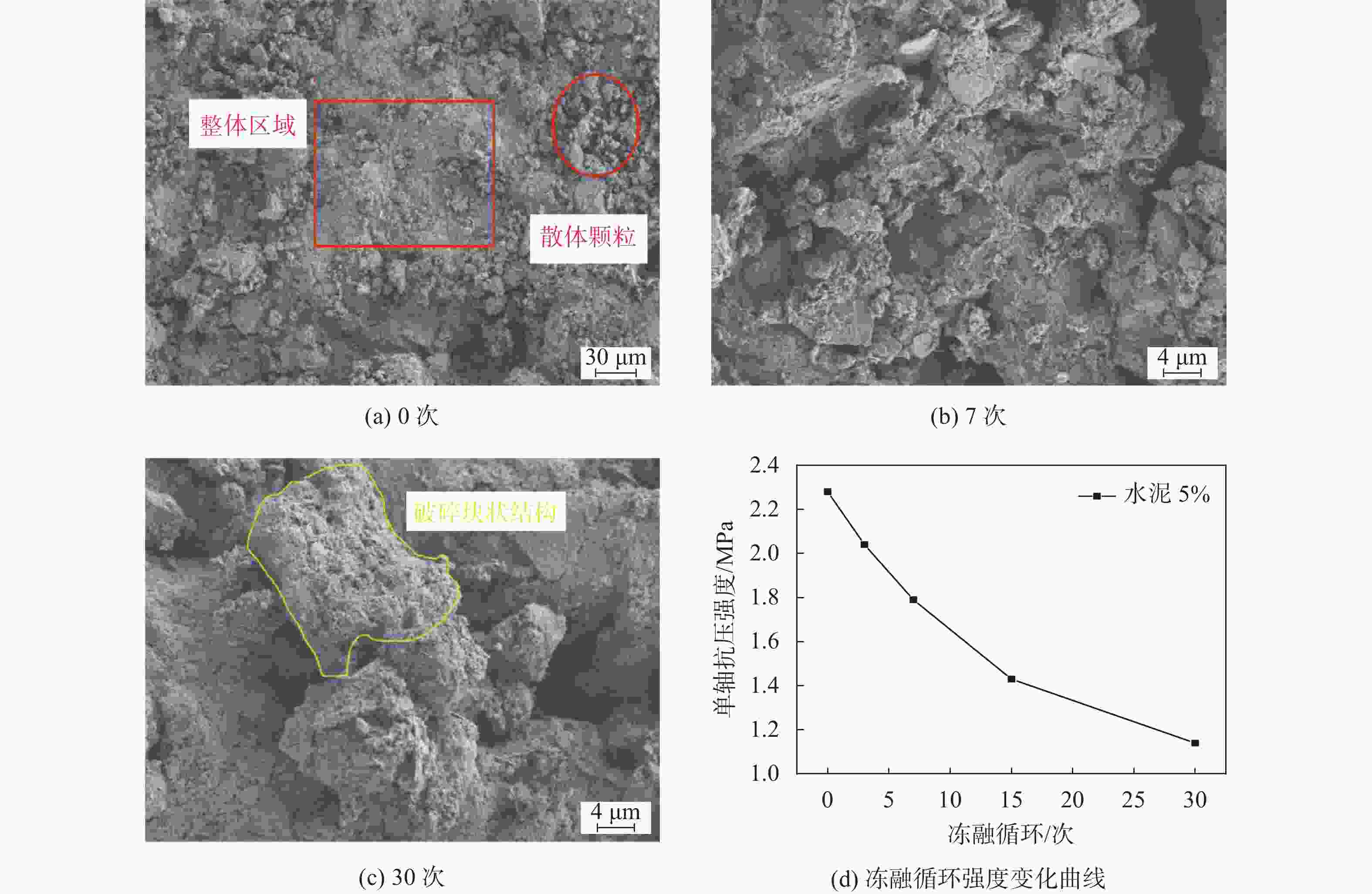
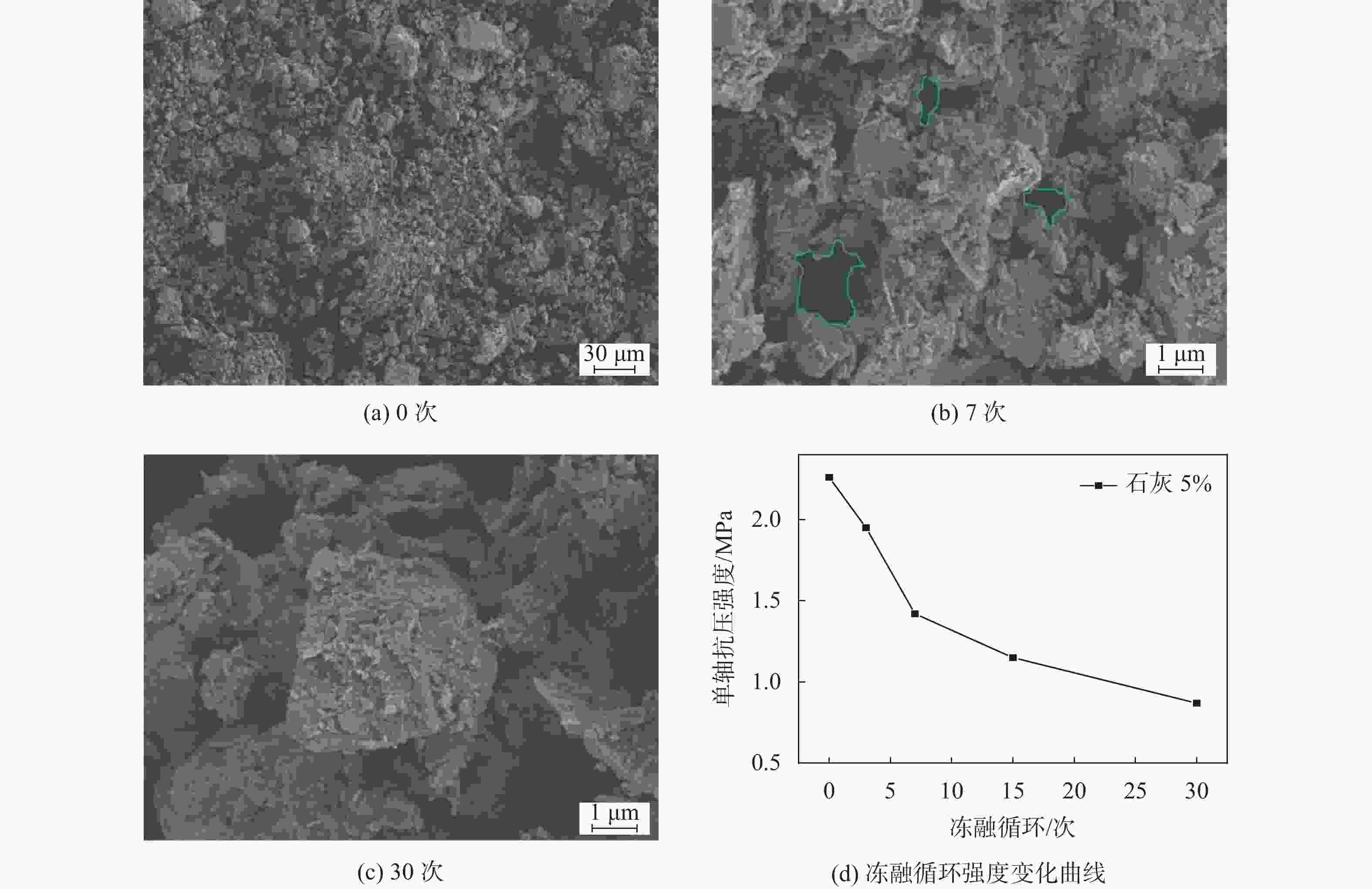
摘要: 流态固化土常应用于回填工程。为探究流态土受材料、季节性气候影响而导致的力学性能劣化机理,开展冻融循环下预拌流态复合土的细观损伤变化规律研究,通过电镜扫描(SEM)及核磁共振(NMR)试验探究其细观结构变化规律,并对复合材料内部机制进行分析。研究结果表明:冻融循环作用会改变土体的孔隙形态,随冻融循环次数的增加微小孔隙逐渐演化为中、大孔隙;不同材料损伤程度不一,以水泥复合材料的破损程度最小,其次为石灰材料,在水化作用下会形成具有强度的胶结块,是抵抗变形的主要结构部分。该研究成果可为流态固化土材料研发和应用提供借鉴。Abstract: Fluid-solidified soil is often used in backfill engineering. To explore the deterioration mechanism of the mechanical properties of fluid-solidified soil caused by the influence of materials and seasonal climate, the change law of meso damage of ready mixed fluid composite soil under freeze-thaw cycle was studied. The change law of meso structure was explored by scanning electron microscope (SEM) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) tests, and the internal mechanism of the composite material was analyzed. The results show that the freeze-thaw cycle will damage the pore size and morphology of soil, and with the increase in times, the micro pores gradually evolve into medium and large pores. The damage degree is different under different materials. The damage degree of the cement composite is the smallest, followed by the lime material. Under the hydration effect, it will form a strong adhesive block, which is the main structural part to resist deformation. The research results can provide a reference for the research and application of fluid-solidified soil materials.
-
表 1 土样基本物理指标
Table 1. Basic physical indicators of soil samples
土体类别 天然
含水率/%天然干密度
/(g·cm−3)孔隙比 液限
/%塑限
/%黄土 14.1 1.65 0.69 31.8 17.8 表 2 电镜扫描试样
Table 2. Scanning electron microscopy sample
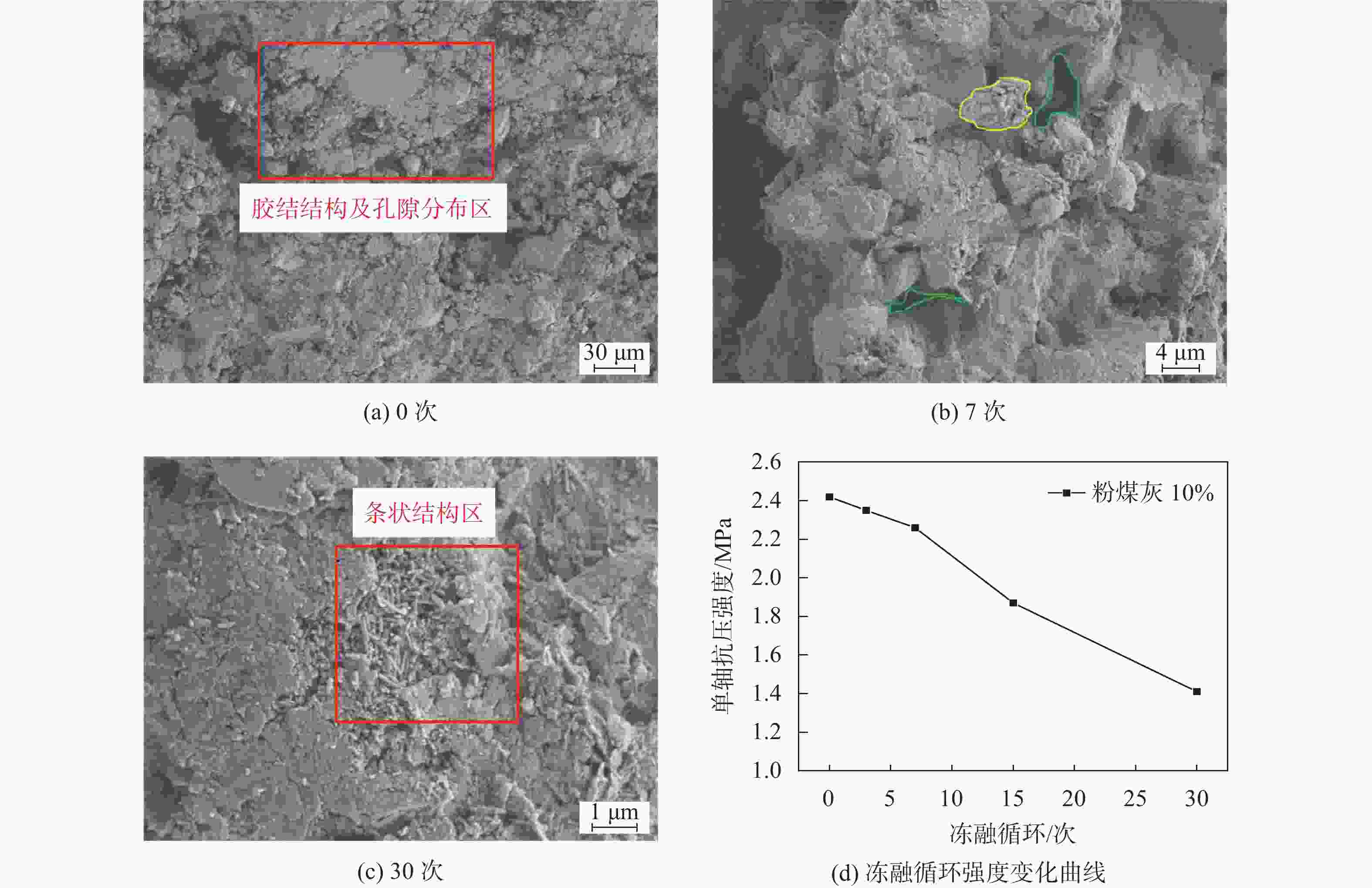
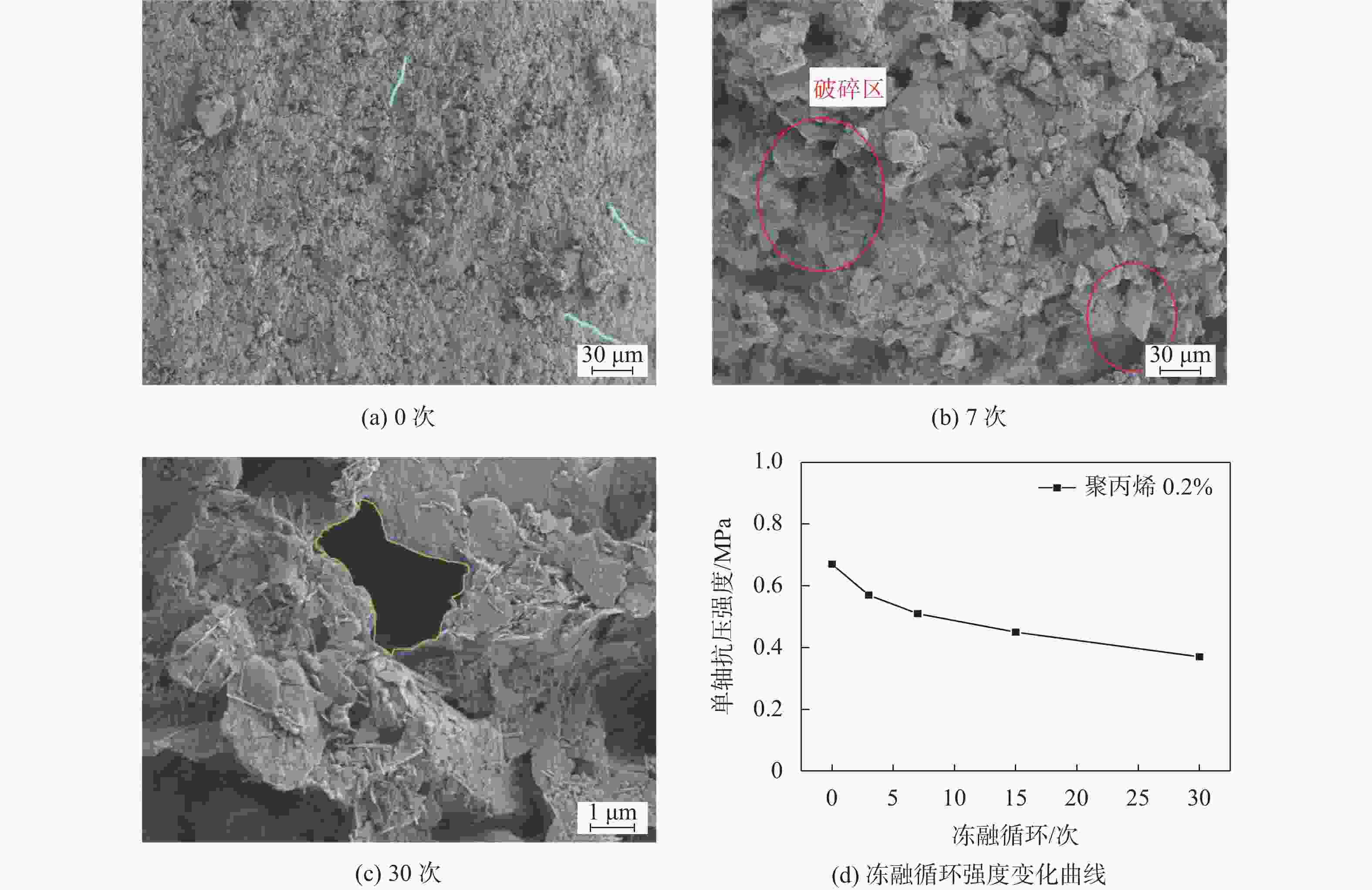
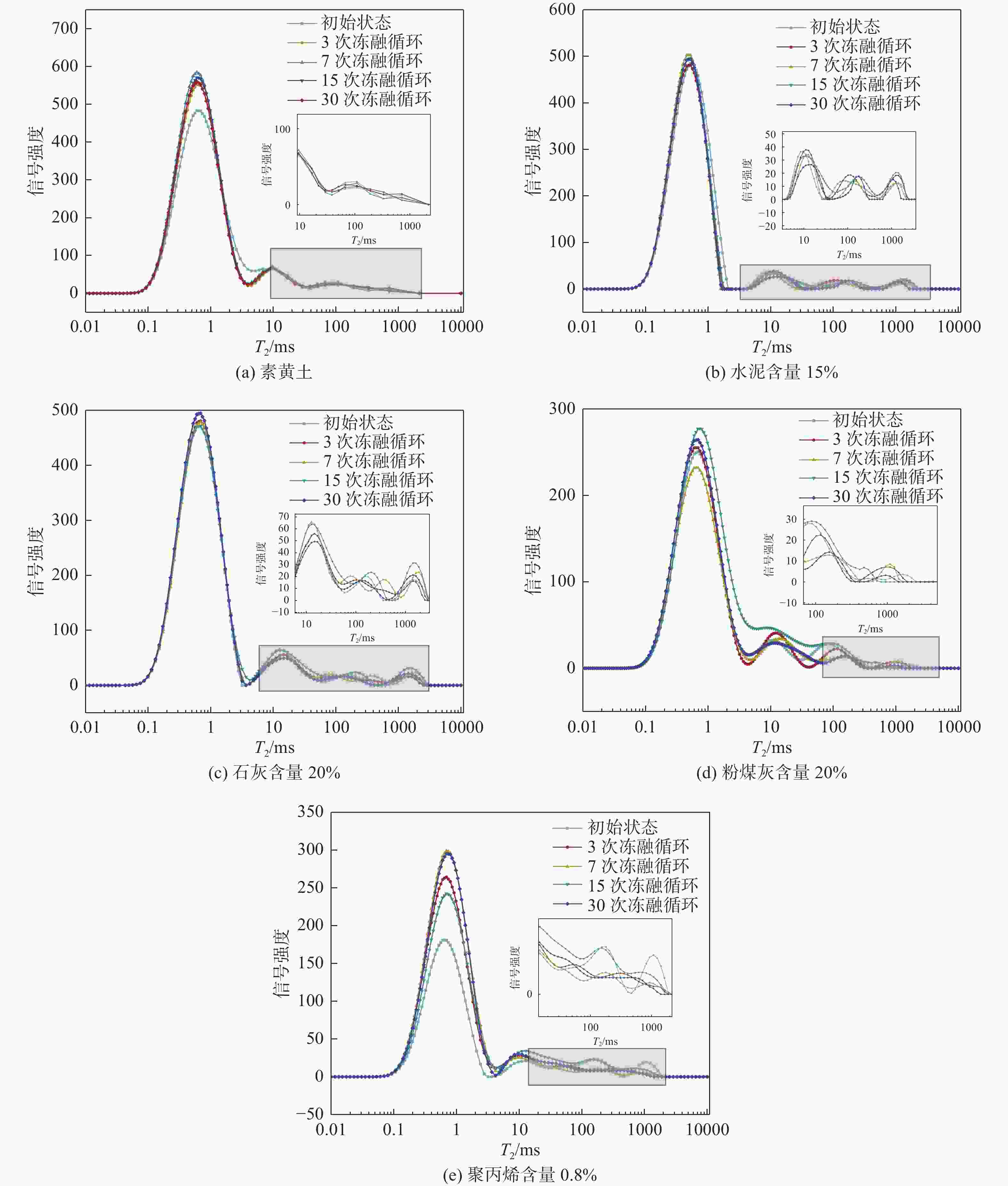
样品名称 冻融循环次数 素土 0 7 30 粉煤灰10% 0 7 30 聚丙烯0.2% 0 7 30 石灰5% 0 7 30 水泥15% 0 7 30 表 3 孔隙分布统计表
Table 3. Statistical table of pore distribution
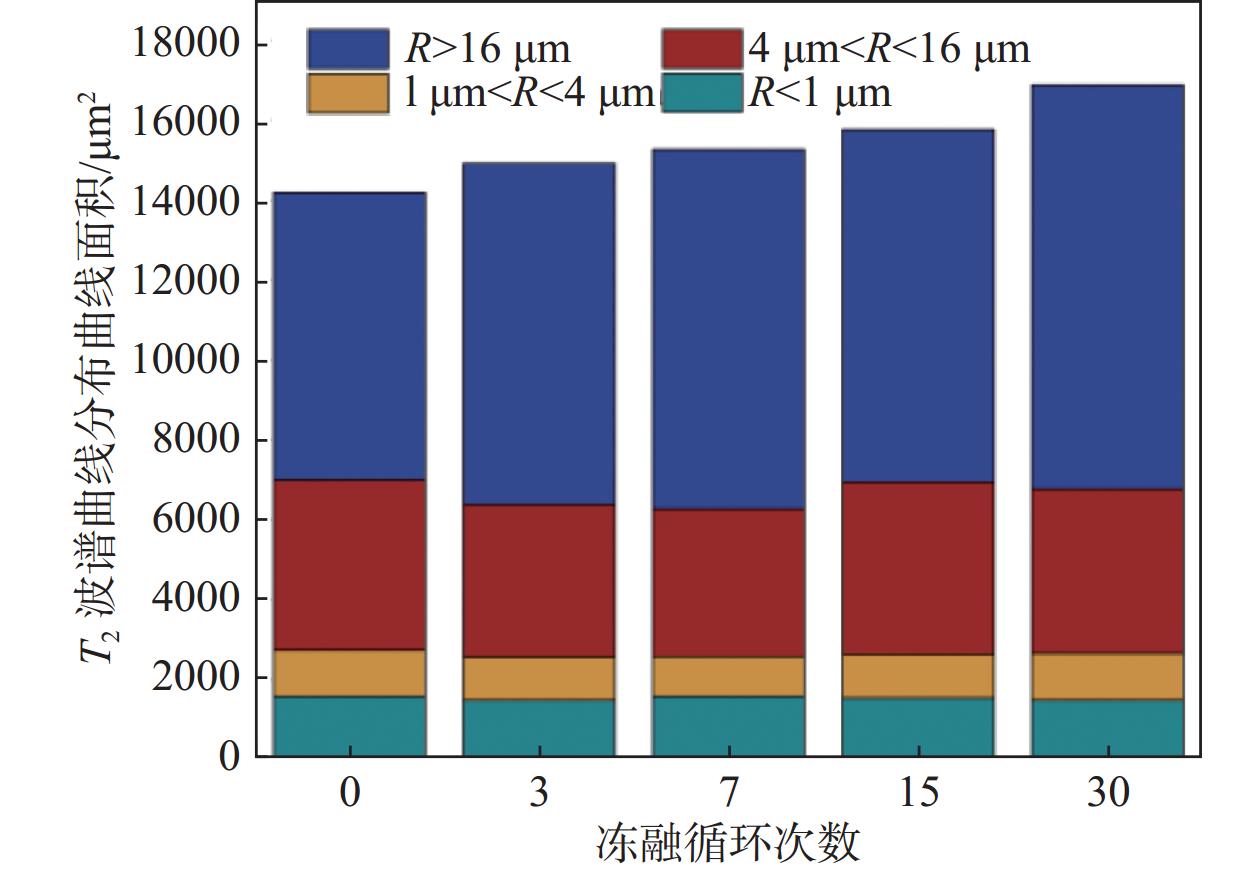
试样名称 孔隙分布/% 冻融循环0次 冻融循环7次 冻融循环30次 素黄土 1.64 12.31 13.31 粉煤灰10 7.74 12.77 15.54 粉煤灰20 14.04 15.76 23.62 聚丙烯0.2 3.67 16.67 17.14 聚丙烯0.8 13.64 6.05 21.35 石灰5 18.31 24.65 27.13 石灰20 20.07 22.68 32.74 水泥5 2.24 9.88 12.24 水泥10 13.85 5.49 15.18 水泥15 14.24 10.36 24.74 -
[1] 李明月, 陈少军, 郑 巍, 等. 深基坑狭窄肥槽预拌流态固化土回填施工技术[J]. 建筑施工, 2024, 46(2): 169-172. (LI M Y, CHEN S J, ZHENG W, et al. Backfill construction technology of deep foundation excavation narrow trench premixed fluidized solidified soil[J]. Building Construction, 2024, 46(2): 169-172. (in Chinese)LI M Y, CHEN S J, ZHENG W, et al. Backfill construction technology of deep foundation excavation narrow trench premixed fluidized solidified soil[J]. Building Construction, 2024, 46(2): 169-172. (in Chinese) [2] 李 敏, 朱晏礼, 李 磊, 等. 基坑肥槽液态固化拌和土回填技术[J]. 安装, 2023(S2): 90-91. (LI M, ZHU Y L, LI L, et al. Technology of liquid curing mixing soil backfill for foundation pit extra-excavated area[J]. Installation, 2023(S2): 90-91. (in Chinese)LI M, ZHU Y L, LI L, et al. Technology of liquid curing mixing soil backfill for foundation pit extra-excavated area[J]. Installation, 2023(S2): 90-91. (in Chinese) [3] 刘佃勇, 马成刚, 唐 勇, 等. 预拌流态水泥土在沟槽回填中的应用技术研究[J]. 建筑技术开发, 2023, 50(2): 109-112. (LIU D Y, MA C G, TANG Y, et al. Study on the application technology of ready mixed fluid cement soil in trench backfilling[J]. Building Technology Development, 2023, 50(2): 109-112. (in Chinese)LIU D Y, MA C G, TANG Y, et al. Study on the application technology of ready mixed fluid cement soil in trench backfilling[J]. Building Technology Development, 2023, 50(2): 109-112. (in Chinese) [4] 马 强. 预拌流态固化土基坑肥槽回填技术应用[J]. 建筑技术开发, 2023, 50(1): 155-157. (MA Q. Application of backfilling technology of pre-mixed fluid solidified soil foundation pit fertilizer tank[J]. Building Technology Development, 2023, 50(1): 155-157. (in Chinese)MA Q. Application of backfilling technology of pre-mixed fluid solidified soil foundation pit fertilizer tank[J]. Building Technology Development, 2023, 50(1): 155-157. (in Chinese) [5] 陈 曦, 竺寅威, 沙玉琪, 等. 淤泥质土改良流态固化土强度及流动度试验研究[J]. 低碳世界, 2024, 14(1): 109-111. (CHEN X, ZHU Y W, SHA Y Q, et al. Experimental study on strength and fluidity of improved fluid-solidified soil of silty soil[J]. Low Carbon World, 2024, 14(1): 109-111. (in Chinese)CHEN X, ZHU Y W, SHA Y Q, et al. Experimental study on strength and fluidity of improved fluid-solidified soil of silty soil[J]. Low Carbon World, 2024, 14(1): 109-111. (in Chinese) [6] 王聪聪, 刘茂青, 宋红旗, 等. 赤泥−钢渣粉−水泥固化流态土性能试验研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2023, 42(7): 2488-2496. (WANG C C, LIU M Q, SONG H Q, et al. Experimental study on properties of red mud, steel slag powder and cement solidified fluidized soil[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2023, 42(7): 2488-2496. (in Chinese)WANG C C, LIU M Q, SONG H Q, et al. Experimental study on properties of red mud, steel slag powder and cement solidified fluidized soil[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2023, 42(7): 2488-2496. (in Chinese) [7] 李泽暄. 流态固化土的改良性状及其工程应用[D]. 石家庄: 石家庄铁道大学, 2023. (LI Z X. Improvement properties of fluid solidified soil and its engineering application[D]. Shijiazhuang: Shijiazhuang Tiedao University, 2023. (in Chinese)LI Z X. Improvement properties of fluid solidified soil and its engineering application[D]. Shijiazhuang: Shijiazhuang Tiedao University, 2023. (in Chinese) [8] 苏文轩. 水泥−AASF复合铁尾矿砂流态固化盐渍土试验研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳工业大学, 2023. (SU W X. Experimental study on fluid solidified saline soil of cement-AASF composite iron tailings sand[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University of Technology, 2023. (in Chinese)SU W X. Experimental study on fluid solidified saline soil of cement-AASF composite iron tailings sand[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University of Technology, 2023. (in Chinese) [9] 苏 悦, 闫 楠, 白晓宇, 等. 预拌流态固化土的工程特性研究进展及应用[J]. 材料导报, 2024, 38(9): 23070212. (SU Y, YAN N, BAI X Y, et al. Research progress and application on engineering characteristics of ready-mixed fluid solidified soil[J]. Materials Reports, 2024, 38(9): 23070212. (in Chinese)SU Y, YAN N, BAI X Y, et al. Research progress and application on engineering characteristics of ready-mixed fluid solidified soil[J]. Materials Reports, 2024, 38(9): 23070212. (in Chinese) [10] 胡海涛, 招 松, 朱泰康, 等. 自密实固化土的无侧限抗压强度试验研究[J]. 江苏建筑, 2023(3): 123-127. (HU H T, ZHAO S, ZHU T K, et al. Experimental study on unconfined compressive strength of self compacting solidified soil[J]. Jiangsu Construction, 2023(3): 123-127. (in Chinese)HU H T, ZHAO S, ZHU T K, et al. Experimental study on unconfined compressive strength of self compacting solidified soil[J]. Jiangsu Construction, 2023(3): 123-127. (in Chinese) [11] 李晓亮, 李 鹏, 吴东阳, 等. 预拌流态固化土填筑施工技术的实践与应用[J]. 四川建筑, 2023, 43(3): 234-236. (LI X L, LI P, WU D Y, et al. Practice and application of filling construction technology of ready-mixed fluidized solidified soil[J]. Sichuan Architecture, 2023, 43(3): 234-236. (in Chinese)LI X L, LI P, WU D Y, et al. Practice and application of filling construction technology of ready-mixed fluidized solidified soil[J]. Sichuan Architecture, 2023, 43(3): 234-236. (in Chinese) [12] 高子琛. 预拌流态固化土的路用性能研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2023. (GAO Z C. Study on road performance of premixed fluid solidified soil[D]. Xi’an: Chang'an University, 2023. (in Chinese)GAO Z C. Study on road performance of premixed fluid solidified soil[D]. Xi’an: Chang'an University, 2023. (in Chinese) [13] 王艺程. 流态固化土在路基工程中的应用研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2021. (WANG Y C. Research on application of fluid-solidified soil in subgrade engineering[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2021. (in Chinese)WANG Y C. Research on application of fluid-solidified soil in subgrade engineering[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2021. (in Chinese) [14] 邵应峰, 周云东, 黄安国, 等. 自密实固化土的冻融循环力学特性试验研究[J]. 河南科学, 2022, 40(9): 1398-1403. (SHAO Y F, ZHOU Y D, HUANG A G, et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties of self compacting solidified soil under the function of freeze-thaw cycle[J]. Henan Science, 2022, 40(9): 1398-1403. (in Chinese)SHAO Y F, ZHOU Y D, HUANG A G, et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties of self compacting solidified soil under the function of freeze-thaw cycle[J]. Henan Science, 2022, 40(9): 1398-1403. (in Chinese) [15] 陈四利, 赵百超, 侯 芮. 冻融循环作用下水泥土疲劳特性[J]. 沈阳工业大学学报, 2021, 43(6): 692-697. (CHEN S L, ZHAO B C, HOU R. Fatigue properties of cement soil under action of freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Journal of Shenyang University of Technology, 2021, 43(6): 692-697. (in Chinese)CHEN S L, ZHAO B C, HOU R. Fatigue properties of cement soil under action of freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Journal of Shenyang University of Technology, 2021, 43(6): 692-697. (in Chinese) [16] 陈四利, 史建军, 于 涛, 等. 冻融循环对水泥土力学特性的影响[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2014, 22(2): 343-349. (CHEN S L, SHI J J, YU T, et al. Effect of freezing-thawing cycle on the mechanical behaviors of cemented soil[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2014, 22(2): 343-349. (in Chinese)CHEN S L, SHI J J, YU T, et al. Effect of freezing-thawing cycle on the mechanical behaviors of cemented soil[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2014, 22(2): 343-349. (in Chinese) [17] 谈云志, 吴 翩, 付 伟, 等. 改良粉土强度的冻融循环效应与微观机制[J]. 岩土力学, 2013, 34(10): 2827-2834. (TAN Y Z, WU P, FU W, et al. Strength and micromechanism of improved silt under freeze-thaw cycle effect[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(10): 2827-2834. (in Chinese)TAN Y Z, WU P, FU W, et al. Strength and micromechanism of improved silt under freeze-thaw cycle effect[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(10): 2827-2834. (in Chinese) [18] 王天亮, 刘建坤, 田亚护. 冻融作用下水泥及石灰改良土静力特性研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2011, 32(1): 193-198. (WANG T L, LIU J K, TIAN Y H. Static properties of cement-and lime-modified soil subjected to freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(1): 193-198. (in Chinese)WANG T L, LIU J K, TIAN Y H. Static properties of cement-and lime-modified soil subjected to freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(1): 193-198. (in Chinese) [19] 宁宝宽, 陈四利, 刘 斌. 冻融循环对水泥土力学性质影响的研究[J]. 低温建筑技术, 2004(5): 10-12. (NING B K, CHEN S L, LIU B. Influence of freezing and thawing cycles on mechanical properties of cemented soil[J]. Low Temperature Architecture Technology, 2004(5): 10-12. (in Chinese)NING B K, CHEN S L, LIU B. Influence of freezing and thawing cycles on mechanical properties of cemented soil[J]. Low Temperature Architecture Technology, 2004(5): 10-12. (in Chinese) [20] 申约拿, 王新泉, 王康宇, 等. 流态固化土特性影响因素及应用进展[J]. 重庆建筑, 2024, 23(12): 89-93. (SHEN Y N, WANG X Q, WANG K Y, et al. Factors influencing the characteristics of flowable stabilized soil and advances in its applications[J]. Chongqing Architecture, 2024, 23(12): 89-93. (in Chinese)SHEN Y N, WANG X Q, WANG K Y, et al. Factors influencing the characteristics of flowable stabilized soil and advances in its applications[J]. Chongqing Architecture, 2024, 23(12): 89-93. (in Chinese) [21] 郅 彬, 王尚杰. 干湿−冻融循环下黄土力学特性及损伤机制研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2024, 45(4): 1092-1102. (ZHI B, WANG S J. Mechanical properties and damage mechanism of loess under dry-wet freeze-thaw cycle[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2024, 45(4): 1092-1102, (in Chinese) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2023.0627ZHI B, WANG S J. Mechanical properties and damage mechanism of loess under dry-wet freeze-thaw cycle[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2024, 45(4): 1092-1102, doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2023.0627 [22] 卢 鑫, 杨更社, 叶万军, 等. 冻融循环作用下不同粒径砂岩强度劣化规律与机制研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2024, 32(6): 2198-2209. (LU X, YANG G S, YE W J, et al. Study on the strength deterioration law and mechanism of sandstone with different grain sizes under freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2024, 32(6): 2198-2209, (in Chinese) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2023-0380LU X, YANG G S, YE W J, et al. Study on the strength deterioration law and mechanism of sandstone with different grain sizes under freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2024, 32(6): 2198-2209, doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2023-0380 [23] 叶万军, 强艳红, 景宏君, 等. 基于核磁共振的不同含水率黄土古土壤冻融循环试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2022, 30(1): 144-153. (YE W J, QIANG Y H, JING H J, et al. Freeze-thaw cycle experiment of loess paleosol with different water content based on nuclear magnetic resonance[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2022, 30(1): 144-153. (in Chinese)YE W J, QIANG Y H, JING H J, et al. Freeze-thaw cycle experiment of loess paleosol with different water content based on nuclear magnetic resonance[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2022, 30(1): 144-153. (in Chinese) [24] 范荣全, 李敬雄, 冯 川, 等. 冻融循环作用下泥炭土强度劣化研究[J]. 工业建筑, 2024, 54(10): 168-174. (FAN R Q, LI J X, FENG C, et al. Study on strength deterioration of peat soil in freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Industrial Construction, 2024, 54(10): 168-174. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3724/j.gyjzG22101822FAN R Q, LI J X, FENG C, et al. Study on strength deterioration of peat soil in freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Industrial Construction, 2024, 54(10): 168-174. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3724/j.gyjzG22101822 -






 下载:
下载: