Characteristics and practice of marine new energy geotechnical engineering under the carbon peaking and carbon neutrality goals
-
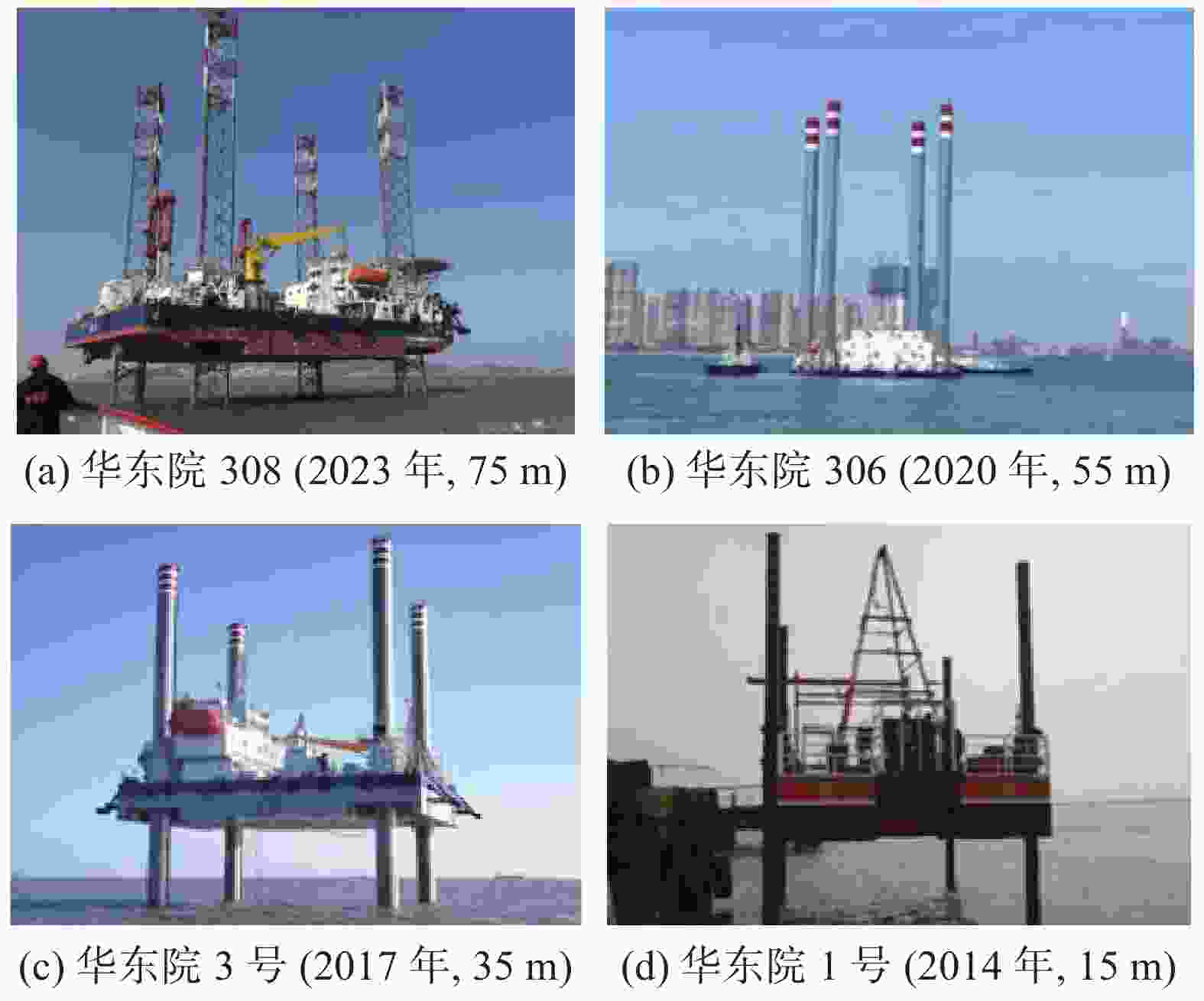
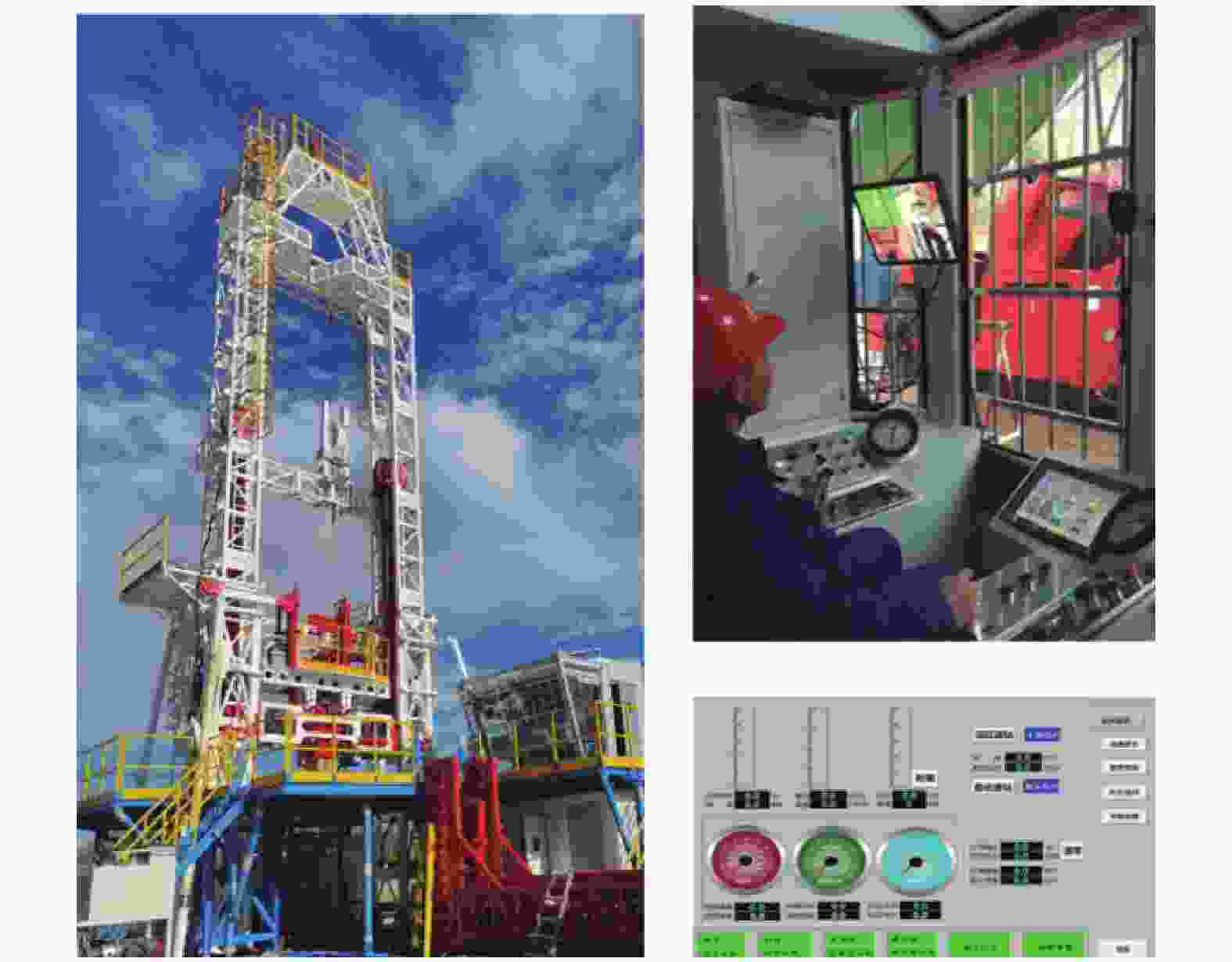
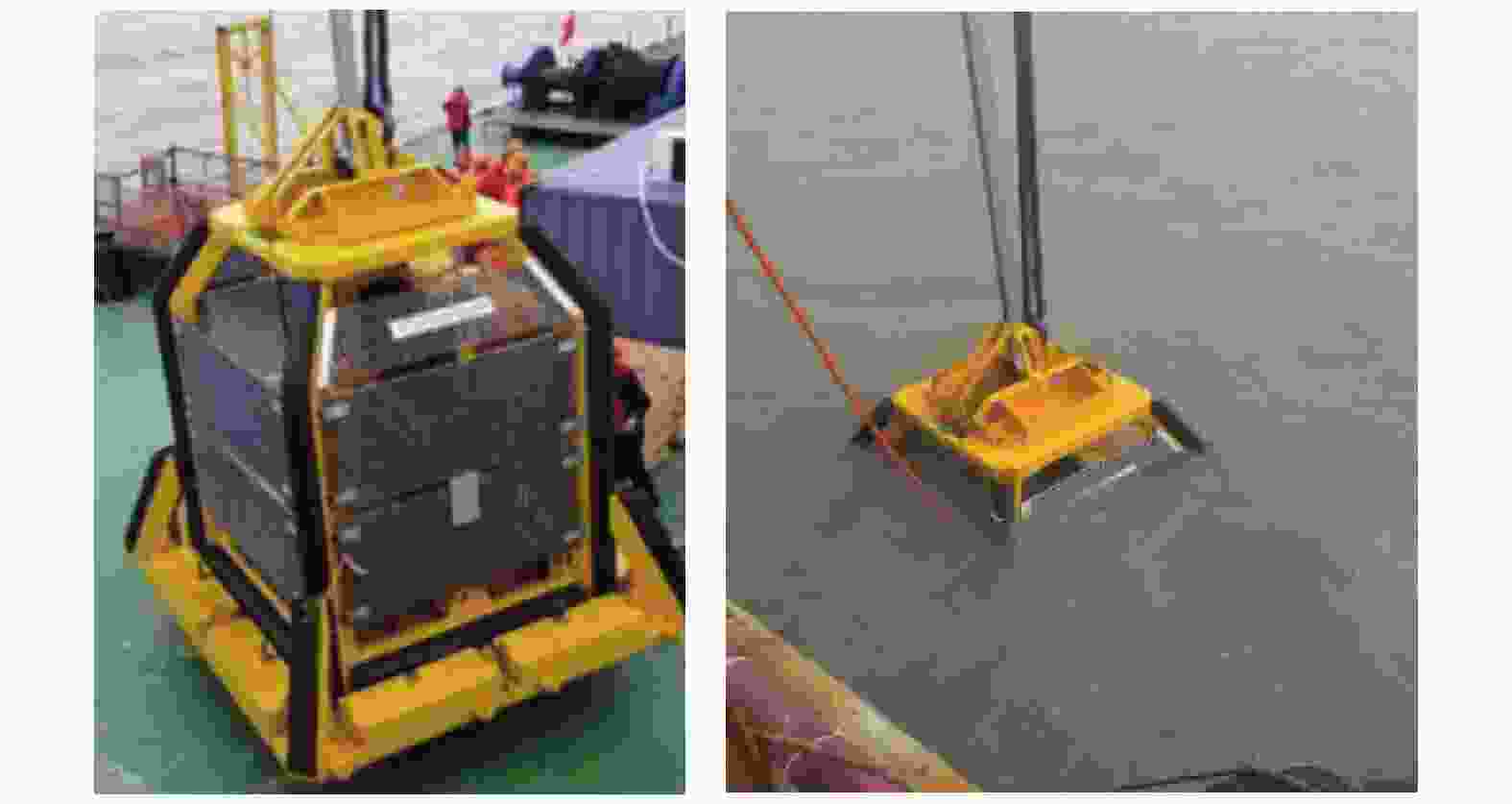
摘要: 复杂的海洋环境和地质条件使海上风电岩土工程勘探试验实施困难,评价难度大。针对目前海上风电勘察存在的主要问题,依托大量海上风电岩土工程勘察实践,从海上岩土工程勘探装备、海上精准探测和原位测试技术、海上岩土工程勘察评价体系构建三个方面,对系统对策的研究成果进行了详细梳理,形成了海洋岩土工程勘察装备与技术体系。勘探装备方面,涵盖不同水深自升式平台(如75 m级“华东院308”,极限水深80 m)、综合勘察船、波浪补偿套管系统(补偿量1.5~2.0 m,最大钻孔1500 m)及系列取样装置。技术上,形成精准定位(平面中误差≤5 cm,高程中误差≤10 cm)、综合物探组合方法及改进的原位测试技术。评价体系含不良地质评价、4类抗震地段划分,提出基于CPTU的参数取值技术。成果应用于近百个风电场,覆盖全国70%并网容量,支撑4000余座海洋基础等建设,形成多项国家标准,为海上风电工程提供技术支撑。Abstract: The complex marine environment and geological conditions make it difficult to implement and evaluate geotechnical engineering exploration and testing for offshore wind power. This study aims to address the main problems existing in current offshore wind power investigation, based on a large number of practices in offshore wind power geotechnical engineering investigation, systematically sorts out the countermeasures from three aspects: offshore geotechnical engineering exploration equipment, offshore precise detection and in-situ testing technologies, and the construction of offshore geotechnical engineering investigation and evaluation system. In terms of exploration equipment, it covers jack-up platforms for different water depths (e.g., the 75 m-class "Huadong Institute 308" with a maximum water depth of 80 m), comprehensive investigation vessels, wave-compensated casing systems (with a compensation range of 1.5~2.0 m and a maximum drilling depth of 1500 m), and a series of sampling devices. In terms of technologies, precision positioning (with a mean error of plane and elevation of ≤5 cm and 10 cm, respectively), comprehensive geophysical prospecting combination methods, and improved in-situ testing technologies have been developed. The evaluation system includes the evaluation of unfavorable geology and the division of 4 types of seismic zones, and proposes a parameter selection technology based on CPTU. These achievements have been applied to nearly 100 wind farms, covering 70% of the national grid-connected capacity, supporting the construction of over 4,000 marine foundations and other structures, and formulating multiple national standards, thus providing technical support for offshore wind power projects.
-
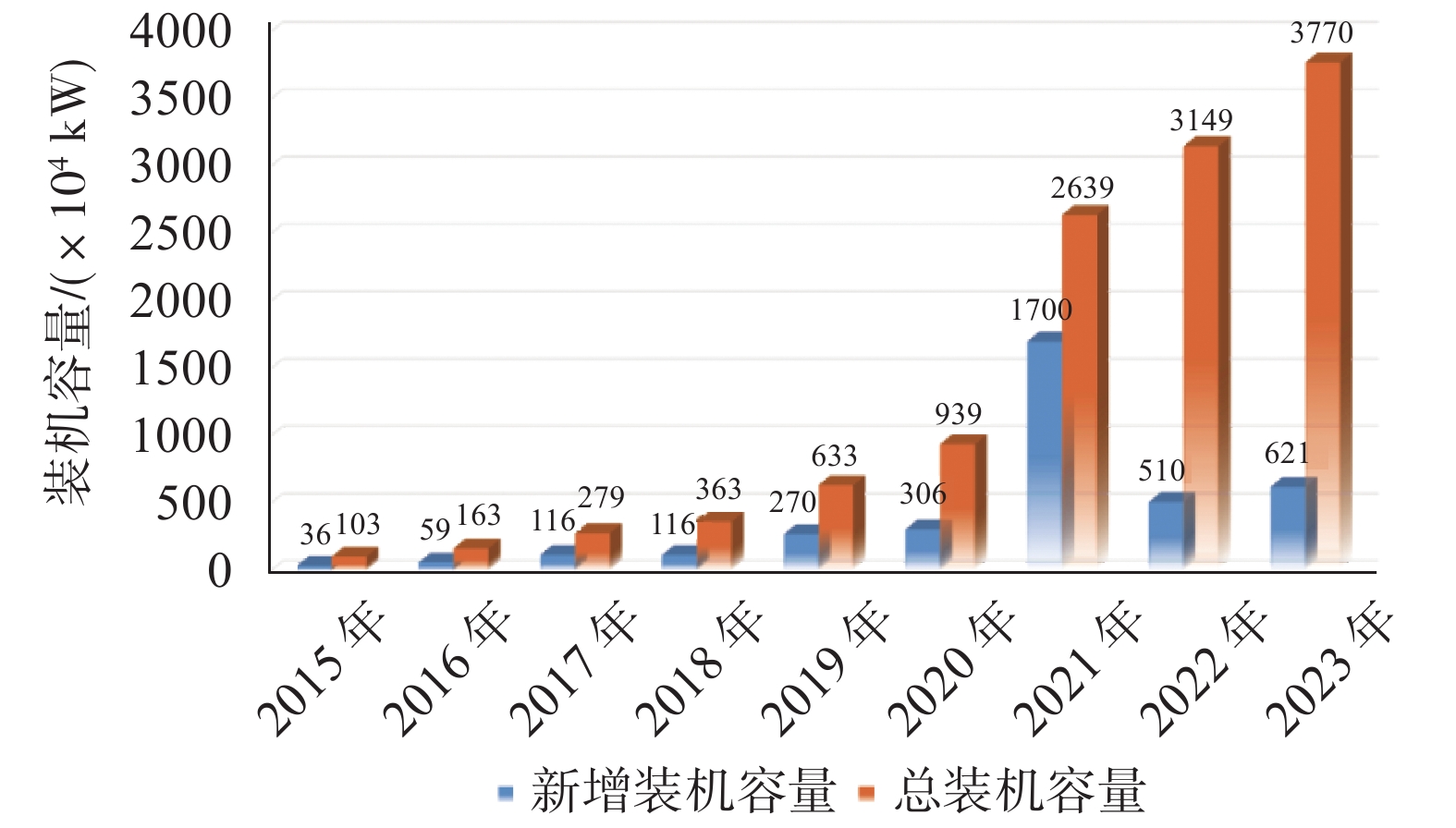
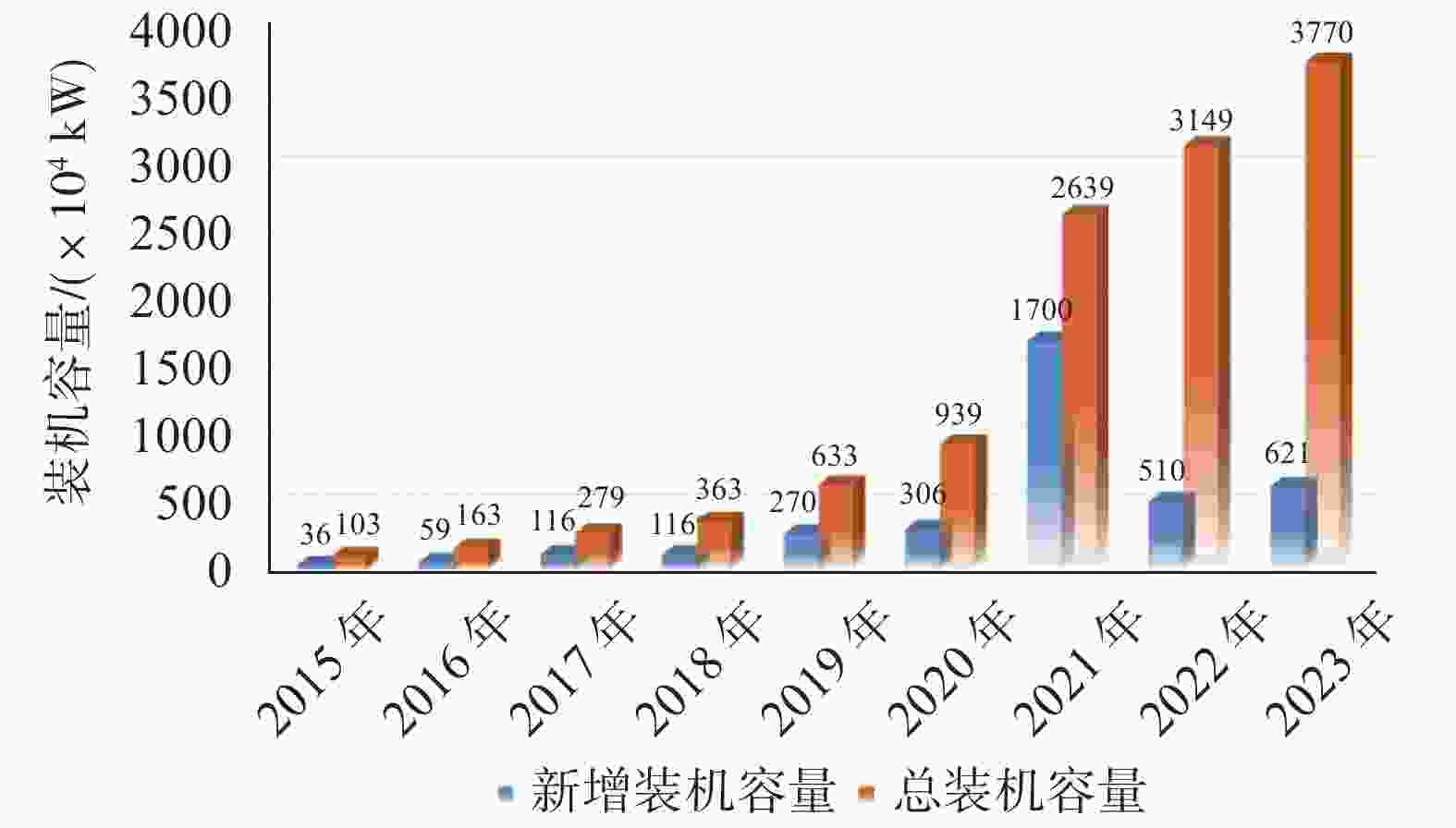
图 1 海上风电装机我国容量(截至2023年)[1]
表 1 海底浅层气分类[4]
类型 特征 按赋存
形态分层状浅层气 沉积环境比较稳定,沉积物中有机质丰富,分解生成的气体与沉积物伴生,埋藏深度不一、大面积层状分布 团块状、囊状浅层气 分布受沉积层中有机质含量、孔隙率大小控制,呈团块状、囊状相对富集于某一区块或某几个区块 柱状或羽状、烟囱状浅层气 较深部位生成的气体沿断层带、孔隙或裂隙等通道向海底浅部土层运移,形成柱状、羽状、烟囱状分布。常与底辟、泥火山和断层伴生 按气体
压力分高压浅层气 气体压力大于或等于0.4 MPa 中压浅层气 气体压力在0.2~0.4 MPa 低压浅层气 气体压力小于0.2 MPa 表 2 海底沙丘沙波的活动性分类[22]
分类 依据 形态特征 砂粒组成 运移速率 强活动性 脊线弯曲,两坡交切尖锐,沙波指数和沙波不对称指数均大,坡表面光滑,或叠置顺流小沙丘 细、中砂分选好,松散、轻、重矿物比高,
有孔虫壳有磨损,破碎整体运移速率大于或
等于1 m/a中等活动性 脊线直,两坡交切尖锐,沙波指数和沙波不对称指数较大,坡面叠置异向小沙波 松散的中、细砂,分选较好,
有孔虫壳有磨损,破碎整体运移速率小于1 m/a 弱活动性 两坡交切浑圆,脊线模糊,沙波指数和沙波不对称指数均较小,表面有植物碎屑和生物痕迹 细、中砂为主,含5%~10%以上的粉砂黏土,
硬度较大,有孔虫壳有锈染整体轻微移动 不活动 丘状起伏可见,脊线模糊不清,表面见植物碎屑和生物活动痕迹 沙丘表面粉砂黏土层覆盖砂层,致密或胶结 整体长期不移动 表 3 建筑物抗震地段划分[4]
地段类别 分级要素 区域构造稳定性 地基条件和边坡稳定性 有利地段 稳定性好 海域地形开阔、平坦,较完整的岩体或中密、密实土层。边坡稳定性好 一般地段 稳定性较好 不属于有利、不利和危险的地段。边坡稳定性较好 不利地段 稳定性较差 海域海底沟槽、起伏较大的凹凸地、陡坎、沙丘沙波、含浅层气地层。有可液化土层或软土层分布。边坡稳定性较差 危险地段 稳定性差 地震时,海域可能产生滑坡、崩塌、地裂缝、浊流、泥火山、活动沙丘沙波。边坡稳定性差 -
[1] 司俊龙, 艾 琳, 邱 辰. 2023年中国风电发展现状与展望[J]. 水力发电, 2024, 50(12): 1-4,17. (SI J L, AI L, QIU C. Status and prospect of China’s wind power development in 2023[J]. Water Power, 2024, 50(12): 1-4,17. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0559-9342.2024.12.001SI J L, AI L, QIU C. Status and prospect of China’s wind power development in 2023[J]. Water Power, 2024, 50(12): 1-4,17. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0559-9342.2024.12.001 [2] 王卫东, 高文生, 龚维明, 等. 基础工程技术的发展与创新[J]. 土木工程学报, 2025, 58(2): 97-117. (WANG W D, GAO W S, GONG W M, et al. Development and innovation of technologies in foundation engineering[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2025, 58(2): 97-117. (in Chinese)WANG W D, GAO W S, GONG W M, et al. Development and innovation of technologies in foundation engineering[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2025, 58(2): 97-117. (in Chinese) [3] 唐辉明. 工程地质学基础[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008. (TANG H M. Fundamentals of engineering geology[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2008. (in Chinese)TANG H M. Fundamentals of engineering geology[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2008. (in Chinese) [4] 单治钢, 周光辉, 张明林. 复杂条件地质钻探与取样技术[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2022. (SHAN Z G, ZHOU G H, ZHANG M L. Geological drilling and sampling technology of complex conditions[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2022. (in Chinese)SHAN Z G, ZHOU G H, ZHANG M L. Geological drilling and sampling technology of complex conditions[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2022. (in Chinese) [5] 陆忠民, 李健英, 林毅峰. 海上风电场全生命周期降本增效途径与实践[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2021. (LU Z M, LI J Y, LIN Y F. Ways and practices of cost decreasing and benefits increasing in full lifecycle of offshore wind farms[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2021. (in Chinese)LU Z M, LI J Y, LIN Y F. Ways and practices of cost decreasing and benefits increasing in full lifecycle of offshore wind farms[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2021. (in Chinese) [6] 毕亚雄, 赵生校, 孙 强, 等. 海上风电发展研究[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2017. (BI Y X, ZHAO S X, SUN Q, et al. Research on the development of offshore wind power[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2017. (in Chinese)BI Y X, ZHAO S X, SUN Q, et al. Research on the development of offshore wind power[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2017. (in Chinese) [7] 龚晓南, 王立忠. 海洋岩土工程[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2022. (GONG X N, WANG L Z. Marine geotechnical engineering[M]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2022. (in Chinese)GONG X N, WANG L Z. Marine geotechnical engineering[M]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2022. (in Chinese) [8] 杨晓东, 赵明华. 2023水利水电地基与基础工程技术创新与发展[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2023. (YANG X D, ZHAO M H. 2023 innovation and development of hydraulic and hydroelectric foundation engineering technology[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2023. (in Chinese)YANG X D, ZHAO M H. 2023 innovation and development of hydraulic and hydroelectric foundation engineering technology[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2023. (in Chinese) [9] 汪华安, 周 川, 王占华. 海上风电场工程勘测技术[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2021. (WANG H A, ZHOU C, WANG Z H. Engineering survey technology of offshore wind farm[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2021. (in Chinese)WANG H A, ZHOU C, WANG Z H. Engineering survey technology of offshore wind farm[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2021. (in Chinese) [10] 潘永坚, 姚燕明, 李高山, 等. 滨海软土城市工程勘察关键技术[M]. 杭州: 浙江工商大学出版社, 2021. (PAN Y J, YAO Y M, LI G S, et al. Key technologies for engineering investigation in coastal soft soil cities[M]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Gongshang University Press, 2021. (in Chinese)PAN Y J, YAO Y M, LI G S, et al. Key technologies for engineering investigation in coastal soft soil cities[M]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Gongshang University Press, 2021. (in Chinese) [11] 曹 辉. 关于浅层气灾害的预防与控制研究[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量, 2017, 37(18): 102-103. (CAO H. Study on prevention and control of shallow gas disasters[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standard and Quality, 2017, 37(18): 102-103. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4076.2017.18.050CAO H. Study on prevention and control of shallow gas disasters[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standard and Quality, 2017, 37(18): 102-103. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4076.2017.18.050 [12] 陈岱新, 丁宗国, 郝高建, 等. 南黄海西部某风电场区浅层气特征与分析[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2018, 34(4): 56-62. (CHEN D X, DING Z G, HAO G J, et al. Characteristics and analysis of submarine shallow gas at the South Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2018, 34(4): 56-62. (in Chinese)CHEN D X, DING Z G, HAO G J, et al. Characteristics and analysis of submarine shallow gas at the South Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2018, 34(4): 56-62. (in Chinese) [13] 凌 通. 深水浅层气地层钻孔放喷作业气体释放特性研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2023. (LING T. Study on gas release characteristics of release operation by drilling borehole in deepwater shallow gas formations[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2023. (in Chinese)LING T. Study on gas release characteristics of release operation by drilling borehole in deepwater shallow gas formations[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2023. (in Chinese) [14] 刘乐军, 修宗祥, 周庆杰, 等. 能源安全的海洋地质灾害研究发展与展望[J]. 海岸工程, 2022, 41(4): 451-466. (LIU L J, XIU Z X, ZHOU Q J, et al. Prospect of marine geological hazards research on energy security status[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2022, 41(4): 451-466. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12362/j.issn.1002-3682.20221010001LIU L J, XIU Z X, ZHOU Q J, et al. Prospect of marine geological hazards research on energy security status[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2022, 41(4): 451-466. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12362/j.issn.1002-3682.20221010001 [15] 陈雨沣. 长江水下三角洲浅层气发育特征与环境效应[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2023. (CHEN Y F. Development and environmental effects of shallow gas in the Yangtze Subaqueous Delta[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2023. (in Chinese)CHEN Y F. Development and environmental effects of shallow gas in the Yangtze Subaqueous Delta[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2023. (in Chinese) [16] 段晓勇, 印 萍, 谢永清, 等. 中国近海浅层气调查研究进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2024, 44(3): 183-196. (DUAN X Y, YIN P, XIE Y Q, et al. Advancements in the study of shallow gas in the coastal waters of China[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2024, 44(3): 183-196. (in Chinese)DUAN X Y, YIN P, XIE Y Q, et al. Advancements in the study of shallow gas in the coastal waters of China[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2024, 44(3): 183-196. (in Chinese) [17] 杨肖迪, 淳明浩, 徐 爽. 海底浅层气探测识别技术研究[J]. 石油工程建设, 2020, 46(S1): 255-261. (YANG X D, CHUN M H, XU S. Research of detecting and identifying method for seabed shallow gas[J]. Petroleum Engineering Construction, 2020, 46(S1): 255-261. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2206.2020.S.049YANG X D, CHUN M H, XU S. Research of detecting and identifying method for seabed shallow gas[J]. Petroleum Engineering Construction, 2020, 46(S1): 255-261. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2206.2020.S.049 [18] 单治钢, 孙淼军, 王振红, 等. 海上风电重大工程地质问题与对策研究[C]//2021年全国工程地质学术年会论文集. 青岛: 中国地质学会, 2021: 210-219. (SHAN Z G, SUN M J, WANG Z H, et al. Research on major engineering geological problems and corresponding countermeasures in offshore wind power[C]//Qingdao: Geological Society of China, 2021: 210-219. (in Chinese)SHAN Z G, SUN M J, WANG Z H, et al. Research on major engineering geological problems and corresponding countermeasures in offshore wind power[C]//Qingdao: Geological Society of China, 2021: 210-219. (in Chinese) [19] 高 敏, 马小川, 何艺玮, 等. 单向流作用下活动沙丘对过境管道附近底床冲刷影响研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2025, 49(1): 21-31. (GAO M, MA X C, HE Y W, et al. Study on the effect of active sand dune on seabed scouring near transit pipeline under unidirectional flow[J]. Marine Sciences, 2025, 49(1): 21-31. (in Chinese)GAO M, MA X C, HE Y W, et al. Study on the effect of active sand dune on seabed scouring near transit pipeline under unidirectional flow[J]. Marine Sciences, 2025, 49(1): 21-31. (in Chinese) [20] 李勇航, 牟泽霖, 倪玉根, 等. 海南东方近岸海底活动沙波的地球物理特征及其迁移机制[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(4): 27-35. (LI Y H, MOU Z L, NI Y G, et al. Geophysical characteristics and migration mechanism of active submarime sand waves off the coast of Dongfang, Hainan[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(4): 27-35. (in Chinese)LI Y H, MOU Z L, NI Y G, et al. Geophysical characteristics and migration mechanism of active submarime sand waves off the coast of Dongfang, Hainan[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(4): 27-35. (in Chinese) [21] 赵德光. 海底双管道局部冲刷数值模拟研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2022. (ZHAO D G. Numerical simulation of local scour of submarine double pipelines[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2022. (in Chinese)ZHAO D G. Numerical simulation of local scour of submarine double pipelines[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2022. (in Chinese) [22] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 海上风力发电场勘测标准: GB 51395—2019[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2019: 170. (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for engineering investigation of offshore wind farm: GB 51395—2019[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2019: 170. (in Chinese)Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for engineering investigation of offshore wind farm: GB 51395—2019[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2019: 170. (in Chinese) [23] 丁 智, 郑海洋, 冯丛烈, 等. 含气土工程特性研究现状综述及展望[J]. 隧道建设(中英文), 2021, 41(4): 537-553. (DING Z, ZHENG H Y, FENG C L, et al. Overview on research of engineering characteristics of gassy soil and prospects[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2021, 41(4): 537-553. (in Chinese)DING Z, ZHENG H Y, FENG C L, et al. Overview on research of engineering characteristics of gassy soil and prospects[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2021, 41(4): 537-553. (in Chinese) [24] 宋 杰, 刘乐乐, 刘 涛, 等. 海洋含气土高应力加卸载变形特征与渗流规律[J]. 力学学报, 2025, 57(2): 545-558. (SONG J, LIU L L, LIU T, et al. Deformation and seepage characteristics of marine gassy soil during high-stress loading and unloading[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2025, 57(2): 545-558. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-24-463SONG J, LIU L L, LIU T, et al. Deformation and seepage characteristics of marine gassy soil during high-stress loading and unloading[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2025, 57(2): 545-558. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-24-463 [25] 赵阳阳, 刘 润. 海洋含气土工程特性研究现状[J]. 石油工程建设, 2013, 39(1): 1-5,87. (ZHAO Y Y, LIU R. Current research situation of seabed gas-bearing soil engineering characteristics[J]. Petroleum Engineering Construction, 2013, 39(1): 1-5,87. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2206.2013.01.001ZHAO Y Y, LIU R. Current research situation of seabed gas-bearing soil engineering characteristics[J]. Petroleum Engineering Construction, 2013, 39(1): 1-5,87. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2206.2013.01.001 [26] 孙淼军, 施周桓, 周波翰, 等. 含气砂不排水单调及循环剪切特性研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2023, 45(S2): 165-170. (SUN M J, SHI Z H, ZHOU B H, et al. Undrained monotonic and cyclic shear behaviors of gas-bearing sand[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2023, 45(S2): 165-170. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE2023S20023SUN M J, SHI Z H, ZHOU B H, et al. Undrained monotonic and cyclic shear behaviors of gas-bearing sand[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2023, 45(S2): 165-170. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE2023S20023 -





 下载:
下载: