Modified model of moisture content distribution of loess profile for loess paleosoil interlayer
-
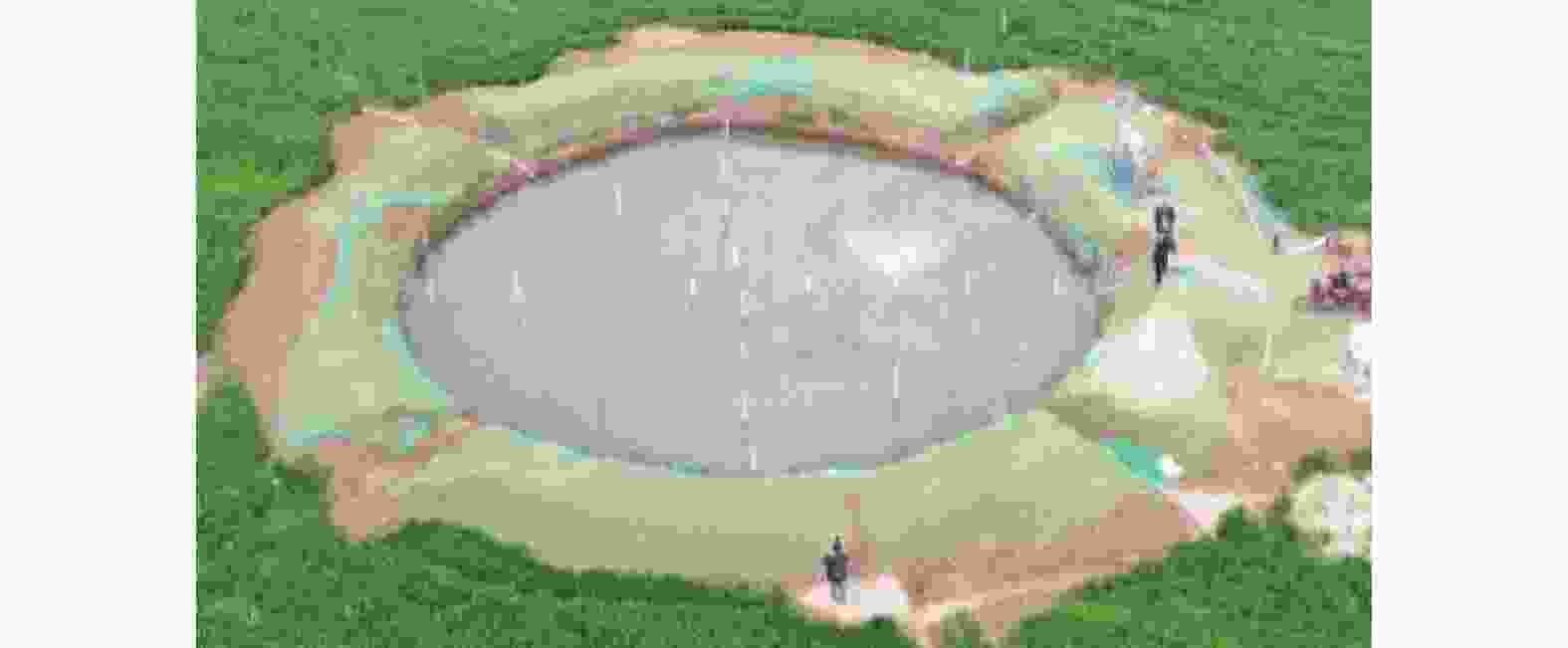
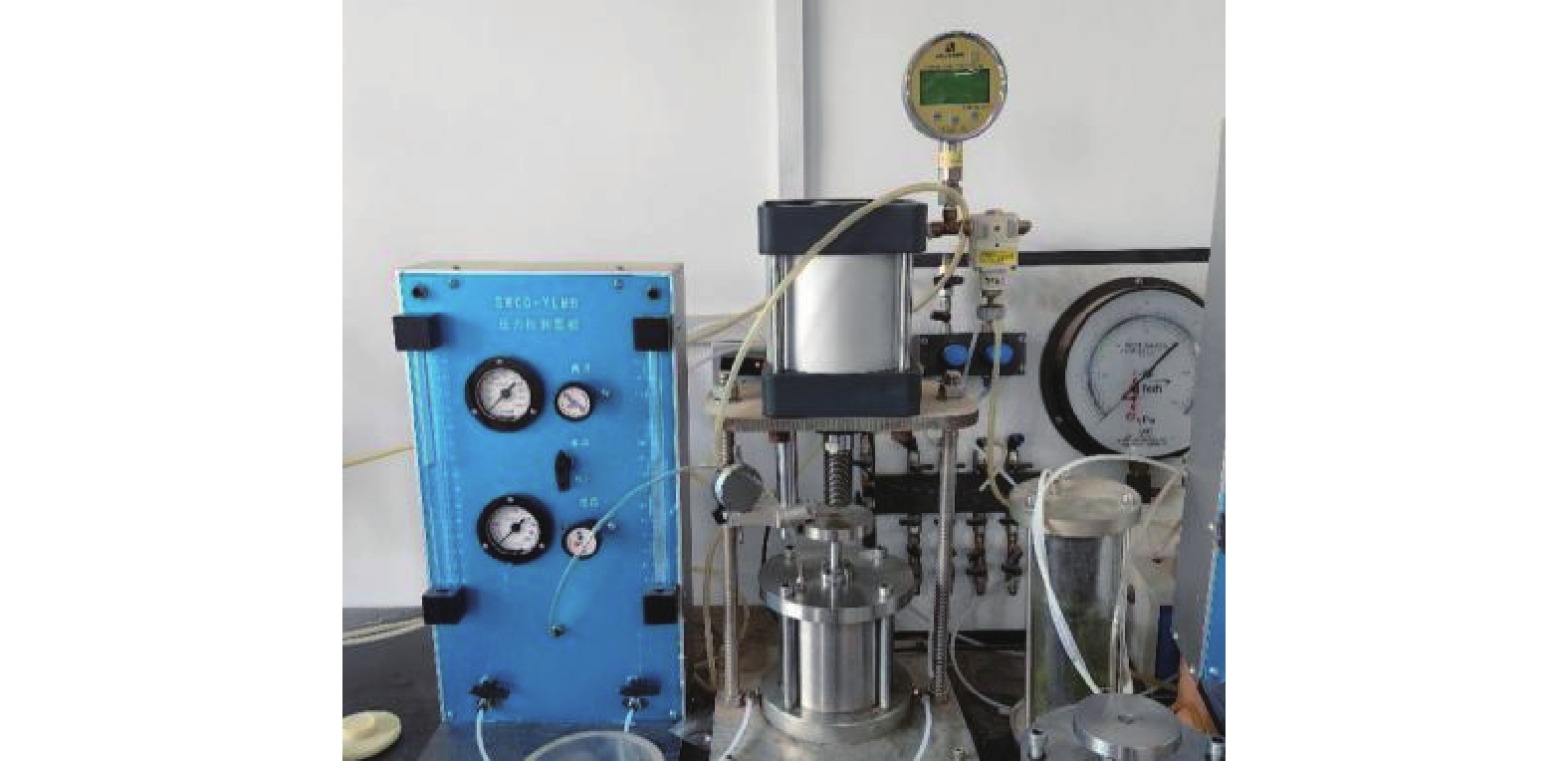
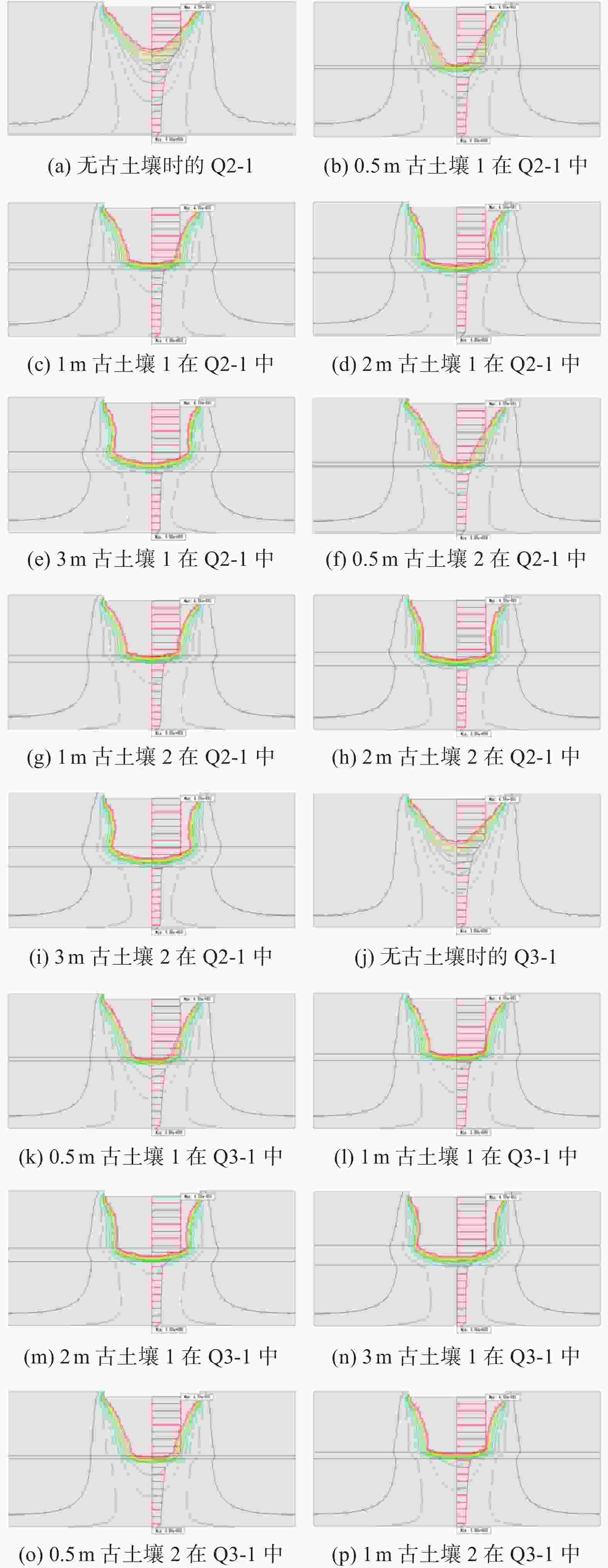
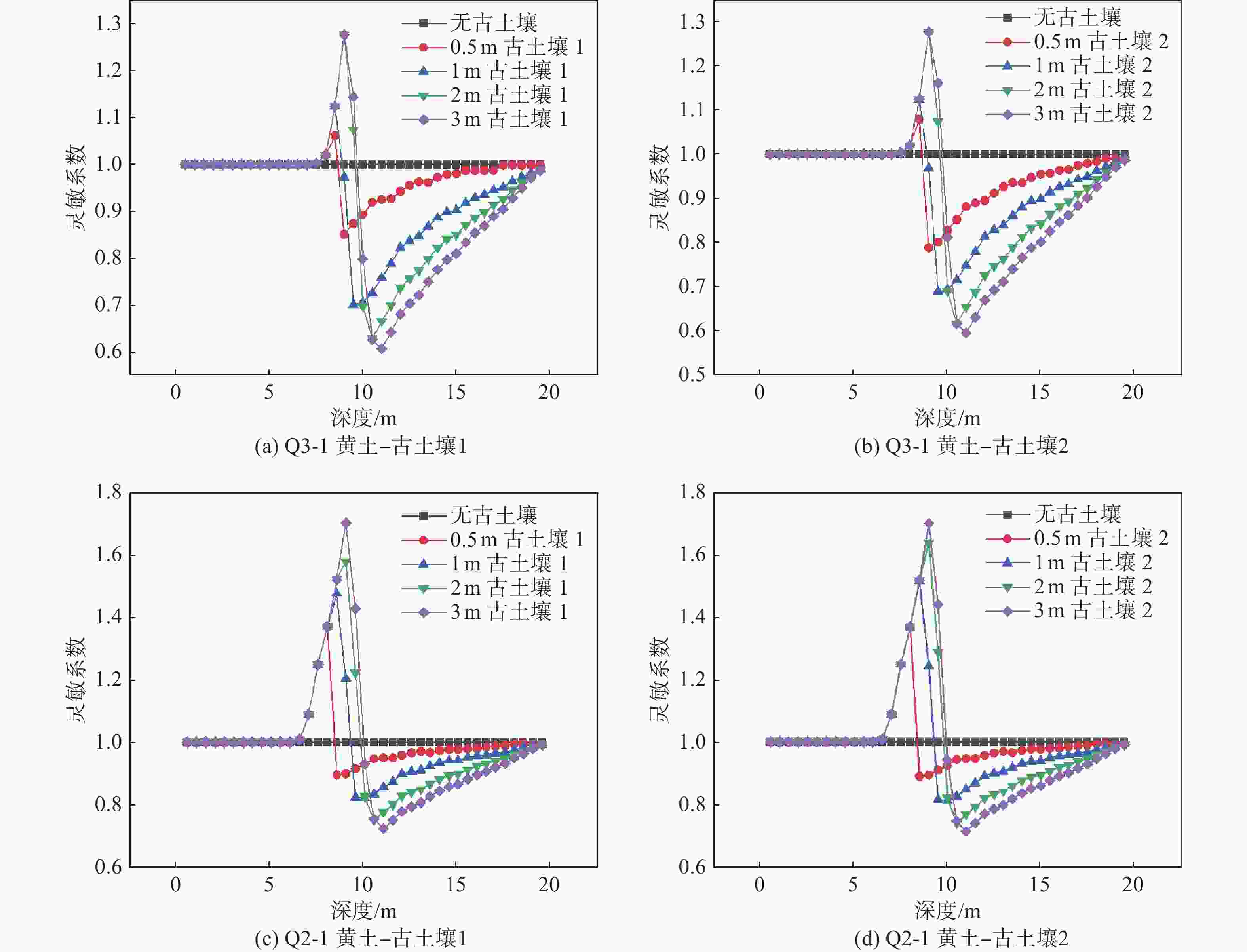
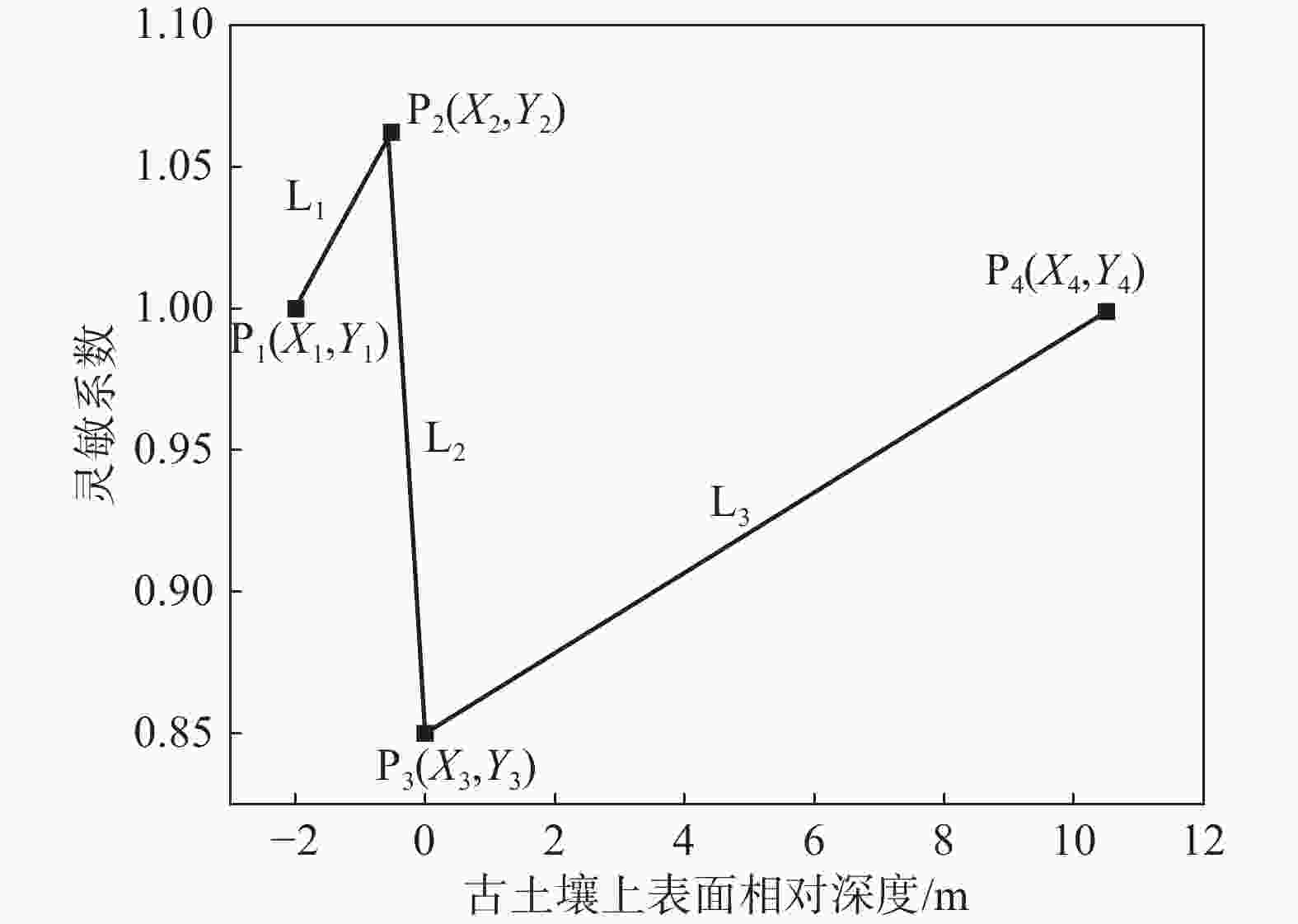
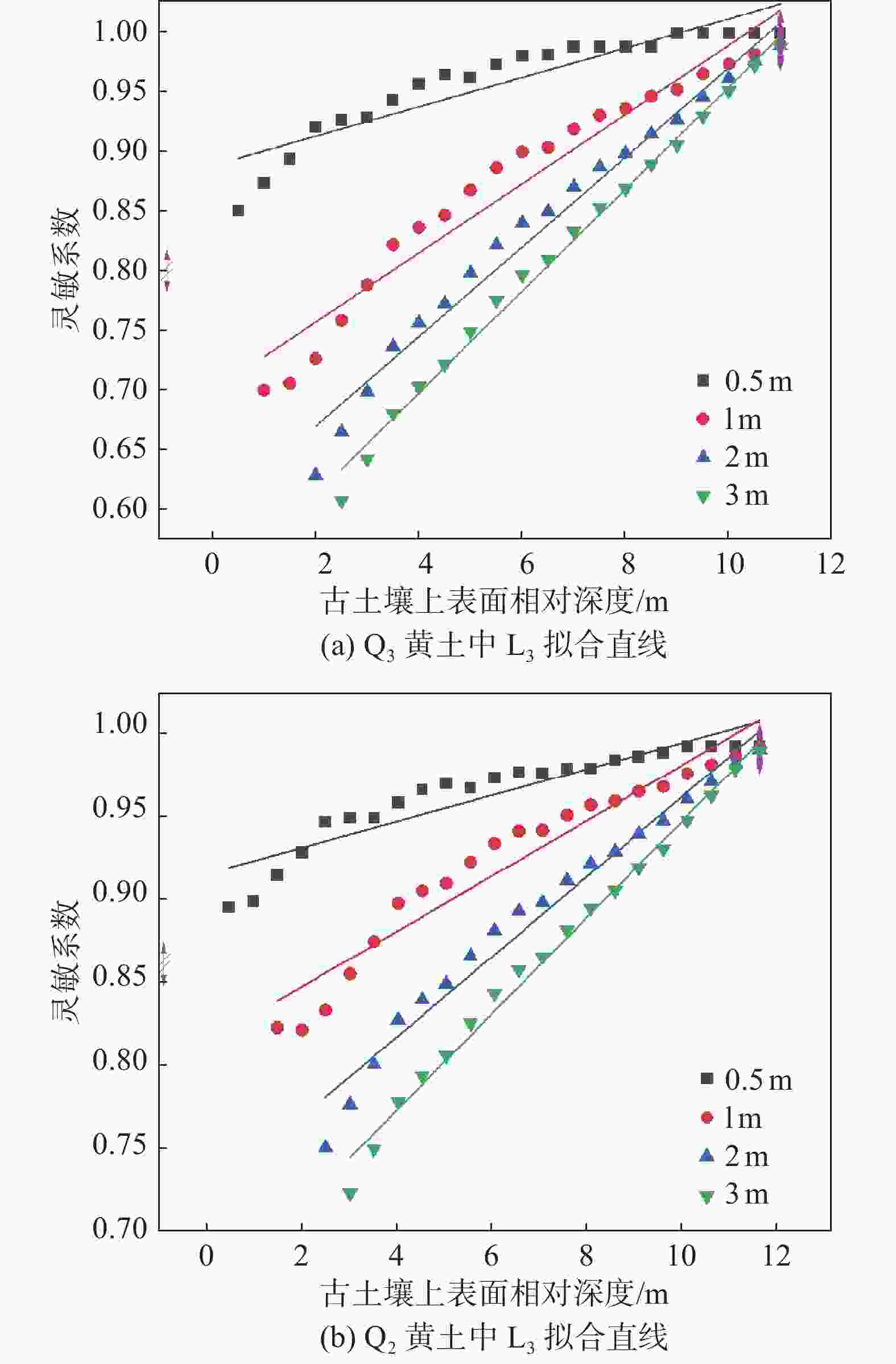
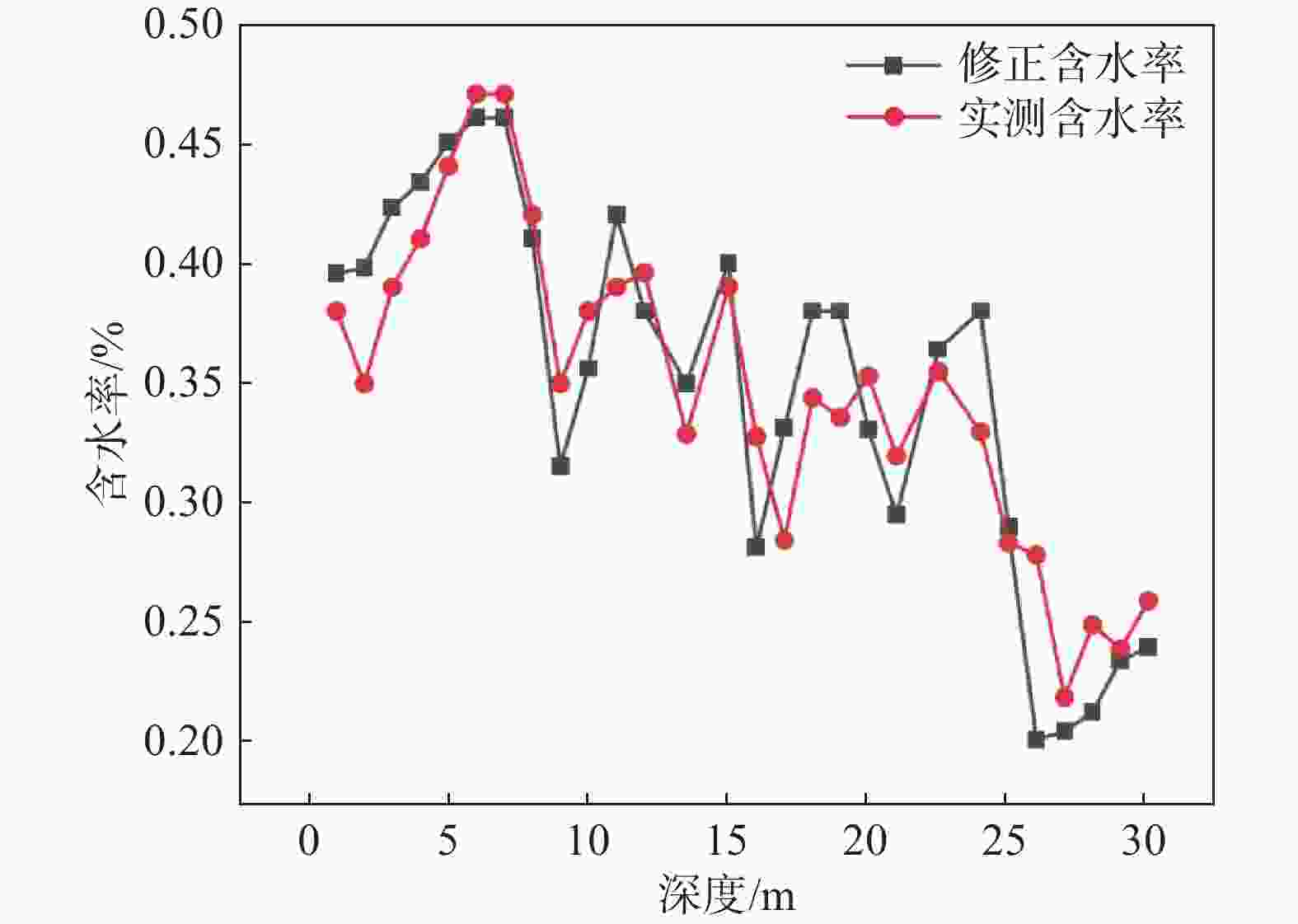
摘要: 为准确测量黄土古土壤互层下各土层的饱和程度,对黄土古土壤互层下黄土剖面含水率分布修正,用压力板法测得铜川地区黄土和古土壤的土壤水分特征曲线,进而用midas GTS NX软件进行非饱和渗流数值模拟,根据模拟数据建立含水率修正模型,并与现场浸水试验实测数据进行对比。研究表明:相同地质年代,不同古土壤受水分下渗的影响相对一致,但是不同地质时期,受影响的差异性变得明显;构建的含水率修正模型的计算值和实测值在黄土古土壤交接处等关键节点处的上下趋势基本一致,可以证明多层古土壤含水率模型计算的准确性和科学性。研究成果可为具有古土壤层的黄土地区含水率修正,进而提高黄土–古土壤互层地区湿陷性评价的精度提供参考。Abstract: To accurately measure the saturation levels of individual soil layers in loess-paleosol interbedded strata and revise the moisture content distribution in loess profiles, the pressure plate method were employed to obtain soil-water characteristic curves for both loess and paleosol in Tongchuan area. Unsaturated seepage numerical simulations were conducted using Midas GTS NX software. Based on simulation data, a moisture content correction model was established and validated against field immersion test measurements. The results of this model were then compared with the measurements from the in-situ immersion test. The study shows that in the same geological age, the influence of different ancient soil on water infiltration is relatively consistent, but in different geological periods, the difference of this influence becomes obvious. The calculated value and measured value of the constructed moisture content correction model are basically consistent with the upward and downward trend in the key nodes such as the junction of loess ancient soil, which can prove the accuracy and scientificity of the moisture content model calculation of multi-layer ancient soil. This study provides a reference for the moisture content correction in the loess areas with the ancient soil layer, which can improve the accuracy of the collapsibility evaluation in the loess-ancient soil reciprocal layer.
-
表 1 不同取土场地黄土古土壤的基本物性指标
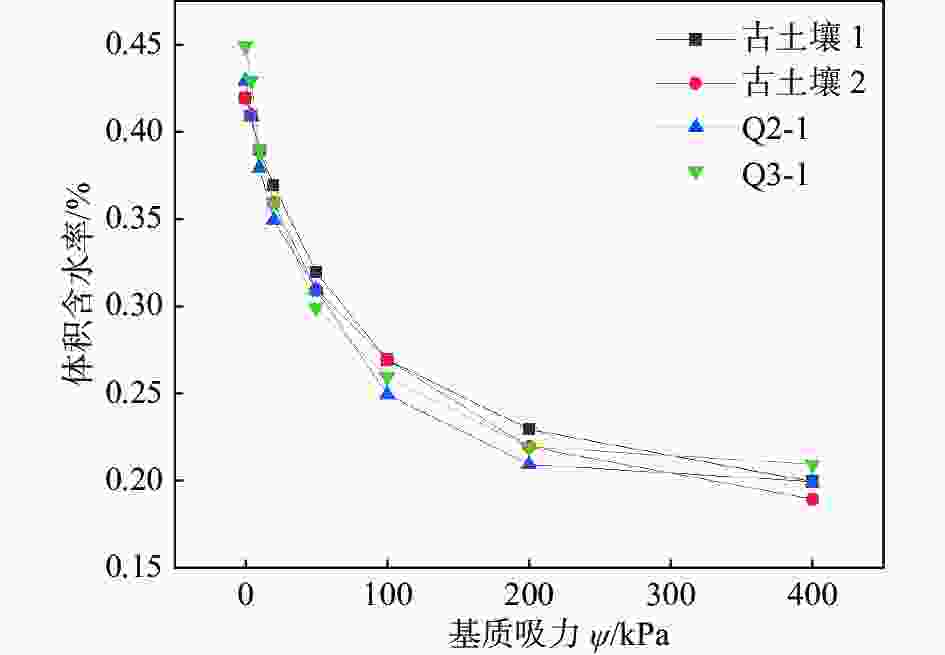
土样名称 取土深度/m 初始含水率w0/ % 土粒比重Gs 干密度ρd/(g·cm−3) 初始孔隙比e0 液限wL/ % 塑限 wp/ % 塑性指数 Ip Q2-1 11 18.9 2.71 1.37 0.95 28.8 19.2 9.6 Q3-1 5 17.2 2.71 1.28 1.133 28.4 19.4 9 古土壤1 8 18.5 2.71 1.43 0.788 27.6 17.2 10.4 古土壤2 11 10 2.7 1.56 0.734 27 19 8 表 2 VG模型中各参数拟合结果
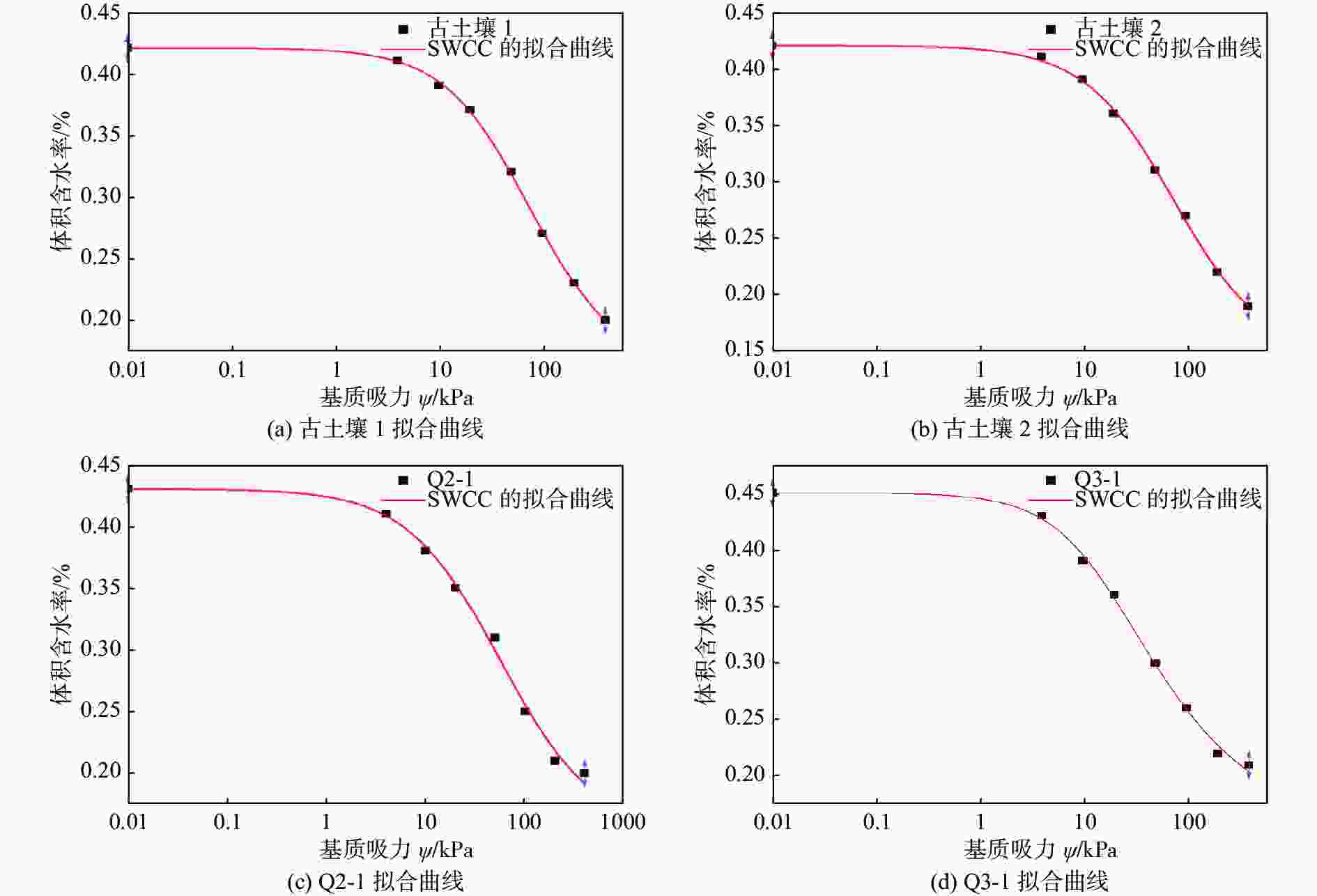
土样 a n m R2 古土壤1 0.012 1.084 0.774 0.99 古土壤2 0.012 0.992 1.093 0.99 Q2-1 0.025 0.935 0.920 0.99 Q3-1 0.037 1.173 0.452 0.99 表 3 L3线性拟合k3值
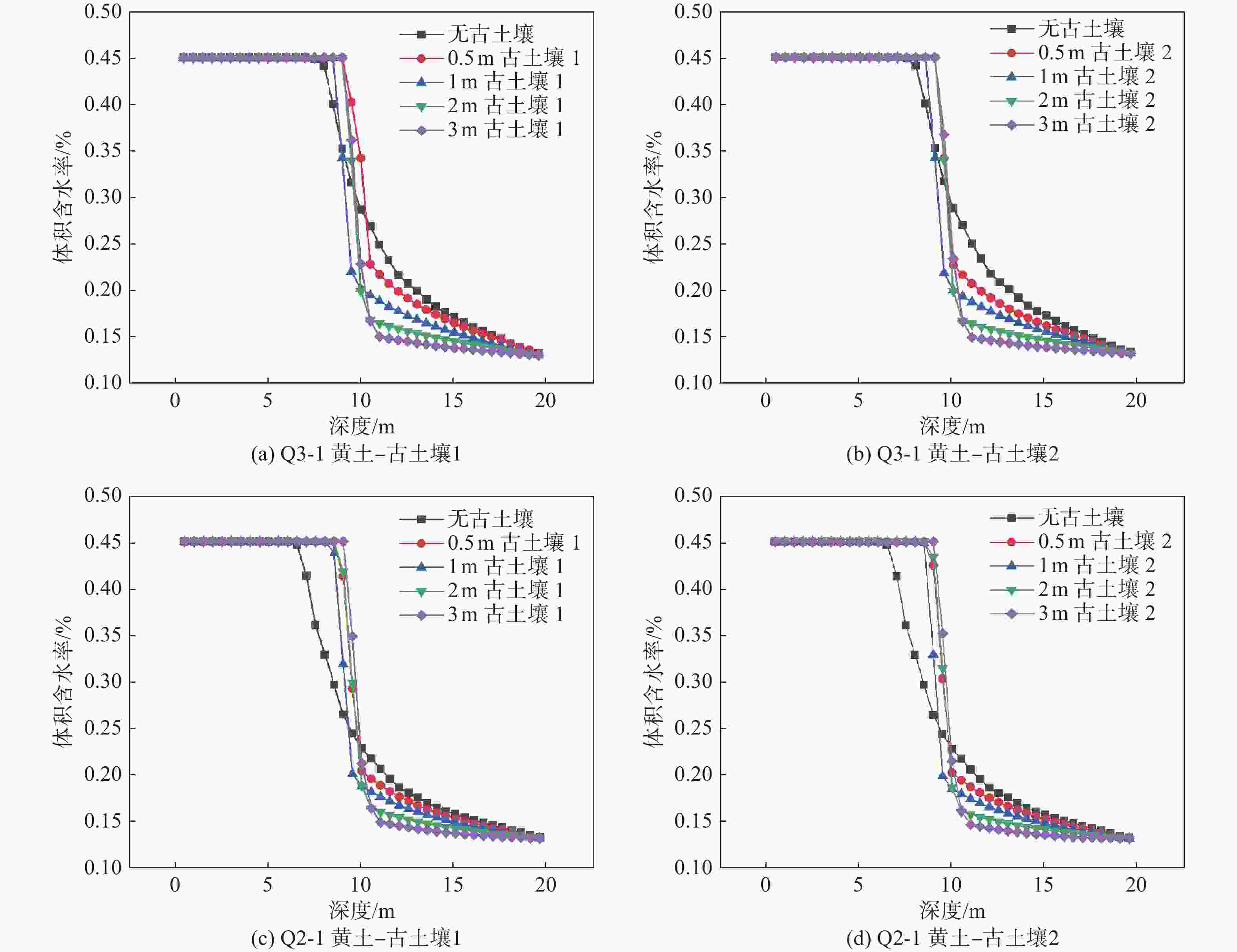
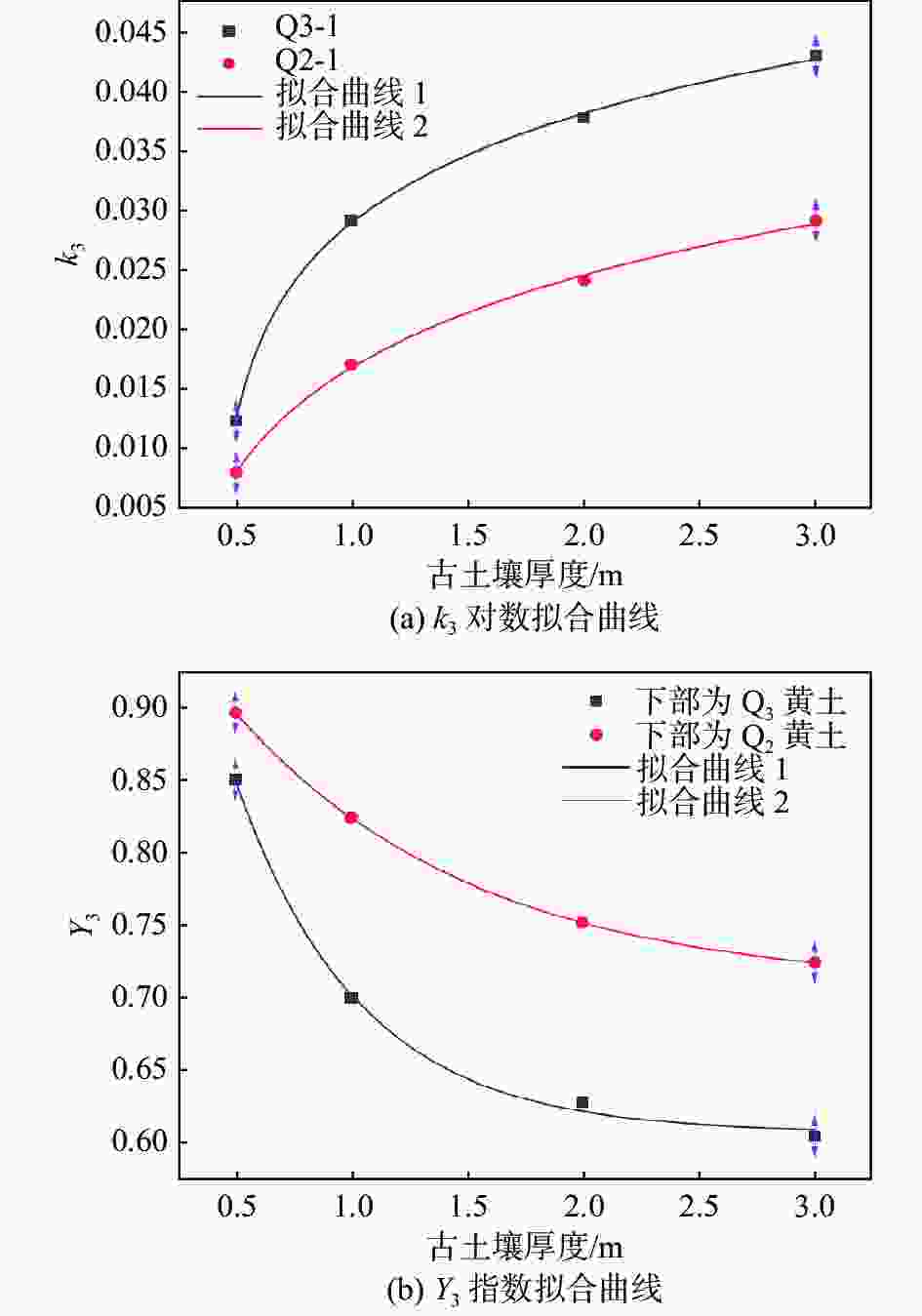
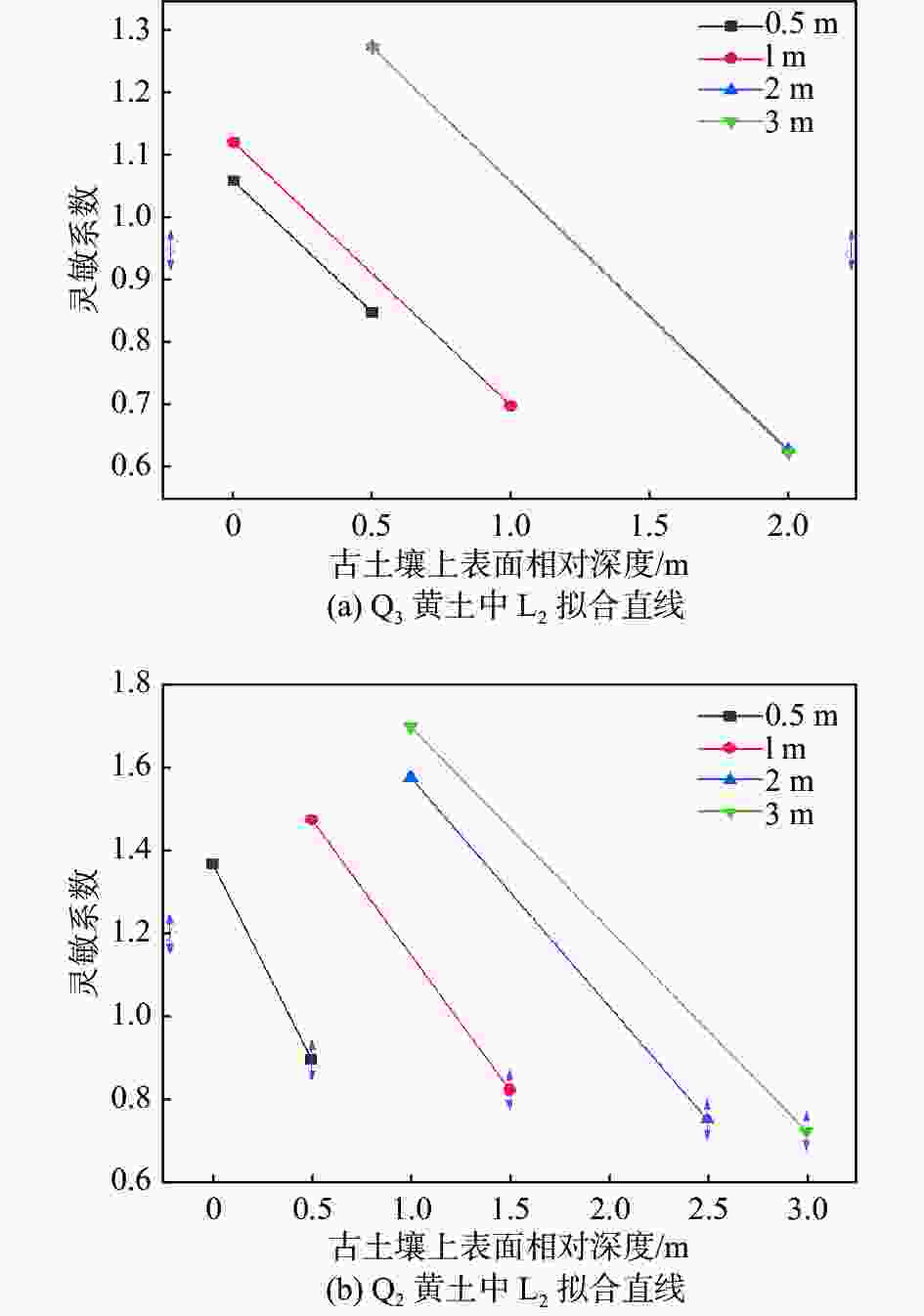
古土壤厚度/m 下伏Q3黄土时k3 下伏Q2黄土时k3 0.5 0.0123 0.008 1 0.0290 0.017 2 0.0375 0.024 3 0.0427 0.029 表 4 多层古土壤剖面含水率修正模型
深度/m 土层类型 基础含水率/% 含水率修正 古1层 古2层 古3层 … 1 Q3黄土 ws 2 ws 3 ws St(1, −1) 4 古土壤 ws St(2, 0) 5 Q3黄土 ws St(3, 1) 6 ws St(3, 2) 7 ws St(3, 2) St(1, −1) 8 古土壤 ws St(3, 2) St(2, 0) 9 Q3黄土 ws St(3, 2) St(3, 1) 10 ws St(3, 2) St(3, 2) 11 ws St(3, 2) St(3, 2) St(1, −2) 12 ws St(3, 2) St(3, 2) St(1, −1) 13 古土壤 ws St(3, 2) St(3, 2) St(2, 0) 14 Q2黄土 ws St(3, 2) St(3, 2) St(3, 1) 15 ws St(3, 2) St(3, 2) St(3, 2) … 注:将每行各数相乘得到每米深度内的修正含水率。ws为饱和含水率,表达式为e0/(1+e0 );St(i,j)为该层土的灵敏系数;i为使用单层古土壤修正模型中的第i段表达式;j为古土壤上表面相对深度, m。 表 5 铜川某园区地层含水率修正结果
土壤类型 代表深度/m 饱和含水率 第1层古土壤修正 第2层古土壤修正 第3层古土壤修正 第4层古土壤修正 计算修正含水率 Q3黄土L1 0~1.0 0.40 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.40 1.0~2.0 0.40 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.40 2.0~3.0 0.42 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.42 3.0~4.0 0.43 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.43 4.0~5.0 0.45 1.16 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.45 5.0~6.0 0.46 1.32 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.46 古土壤P1 6.0~7.0 0.46 1.25 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.46 Q2黄土L2 7.0~8.0 0.41 1.18 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.41 7.9~9.0 0.38 0.83 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.32 9.0~10.0 0.40 0.89 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.36 10.0~11.0 0.42 0.91 1.19 1.00 1.00 0.42 11.0~12.7 0.38 0.91 1.37 1.00 1.00 0.38 古土壤P2 12.7~14.0 0.35 0.91 1.51 1.00 1.00 0.35 14.0~15.1 0.40 0.91 1.20 1.00 1.00 0.40 Q2黄土L3 15.1~16.0 0.38 0.91 0.81 1.00 1.00 0.28 16.0~17.0 0.37 0.91 0.85 1.15 1.00 0.33 17.0~18.0 0.38 0.91 0.85 1.31 1.00 0.38 古土壤P3 18.0~19.0 0.38 0.91 0.85 1.45 1.00 0.38 19.0~20.0 0.38 0.91 0.85 1.14 1.00 0.33 20.0~21.2 0.38 0.91 0.85 0.85 1.19 0.30 Q2黄土L4 21.2~22.5 0.39 0.91 0.85 0.88 1.37 0.36 古土壤P4 22.5~24.0 0.38 0.91 0.85 0.88 1.51 0.38 24.0~24.8 0.36 0.91 0.85 0.88 1.20 0.29 Q2黄土L5 24.8~26.0 0.37 0.91 0.85 0.88 0.81 0.20 26.0~27.0 0.36 0.91 0.85 0.88 0.83 0.21 27.0~28.0 0.37 0.91 0.85 0.88 0.85 0.21 28.0~29.0 0.39 0.91 0.85 0.88 0.89 0.24 29.0~30.0 0.38 0.91 0.85 0.88 0.93 0.24 -
[1] HOU K, QIAN H, ZHANG Y T, et al. Seepage mechanisms and permeability differences between loess and paleosols in the critical zone of the Loess Plateau[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2021,46(10):2044-2059. doi: 10.1002/esp.5143 [2] 李 琳, 王家鼎, 谷 琪, 等. 古土壤层间富水对黄土场地湿陷性的影响[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版),2024,54(1):72-83. (LI L, WANG J D, GU Q, et al. The influence of moisture-rich interlayers in palesol strata on the collapsibility of loess terrain[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition),2024,54(1):72-83. (in Chinese)LI L, WANG J D, GU Q, et al. The influence of moisture-rich interlayers in palesol strata on the collapsibility of loess terrain[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 54(1): 72-83. (in Chinese) [3] 赵金刚, 吕远强, 晁 军, 等. 典型黄土–古土壤系列浸水渗透及湿陷变形规律[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2020,48(3):152-159,168. (ZHAO J G, LYU Y Q, CHAO J, et al. The law of soaking infiltration and collapse deformation in typical loess-paleosol series[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2020,48(3):152-159,168. (in Chinese)ZHAO J G, LYU Y Q, CHAO J, et al. The law of soaking infiltration and collapse deformation in typical loess-paleosol series[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2020, 48(3): 152-159,168. (in Chinese) [4] SHAO T J, WANG R J, XU Z P, et al. Permeability and groundwater enrichment characteristics of the loess-paleosol sequence in the southern Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Water,2020,12(3):870. doi: 10.3390/w12030870 [5] CHEN Y, QIAN H, HOU K, et al. Permeability and paleoenvironmental implications of loess-paleosol sequence from Jingyang Loess Plateau[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2021,80(1):18. doi: 10.1007/s12665-020-09282-y [6] 赵景波, 王长燕, 刘护军, 等. 陕西洛川黄土剖面上部土层水分入渗规律与含水条件研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2010,37(1):124-129,134. (ZHAO J B, WANG C Y, LIU H J, et al. A study of water infiltration and water-bearing condition of the L1–S4 layers in Luochuan, Shaanxi[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2010,37(1):124-129,134. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.01.025ZHAO J B, WANG C Y, LIU H J, et al. A study of water infiltration and water-bearing condition of the L1–S4 layers in Luochuan, Shaanxi[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2010, 37(1): 124-129,134. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.01.025 [7] 郁耀闯, 杨树瑶, 王长燕, 等. 宝鸡地区L1–S5黄土和古土壤水分入渗及影响因素[J]. 水土保持研究,2023,30(6):78-85. (YU Y C, YANG S Y, WANG C Y, et al. Water infiltration and influencing factors of L1–S5 loess-paleosol in Baoji region[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2023,30(6):78-85. (in Chinese)YU Y C, YANG S Y, WANG C Y, et al. Water infiltration and influencing factors of L1–S5 loess-paleosol in Baoji region[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2023, 30(6): 78-85. (in Chinese) [8] 李培月, 李佳慧, 吴健华, 等. 黄土–古土壤互层对土壤水分运移及土体微结构的影响[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2024,51(3):1-11. (LI P Y, LI J H, WU J H, et al. Effects of loess-paleosol interbedding on soil moisture transport and soil microstructure[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2024,51(3):1-11. (in Chinese)LI P Y, LI J H, WU J H, et al. Effects of loess-paleosol interbedding on soil moisture transport and soil microstructure[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2024, 51(3): 1-11. (in Chinese) [9] 赵志强, 戴福初, 闵 弘, 等. 原状黄土–古土壤中水分入渗过程研究[J]. 岩土力学,2021,42(9):2611-2621. (ZHAO Z Q, DAI F C, MIN H, et al. Research on infiltration process in undisturbed loess-paleosol sequence[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2021,42(9):2611-2621. (in Chinese)ZHAO Z Q, DAI F C, MIN H, et al. Research on infiltration process in undisturbed loess-paleosol sequence[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(9): 2611-2621. (in Chinese) [10] 刘建磊, 卫童瑶, 惠寒斌, 等. 大厚度非连续湿陷性黄土浸水变形特征分析[J]. 地质力学学报,2024,30(6):921-932. (LIU J L, WEI T Y, HUI H B, et al. Analysis of soaking deformation characteristics of large-thickness discontinuous collapsible loess[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2024,30(6):921-932. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2023174LIU J L, WEI T Y, HUI H B, et al. Analysis of soaking deformation characteristics of large-thickness discontinuous collapsible loess[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2024, 30(6): 921-932. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2023174 [11] 黄晓波, 高冰可. 土壤水分特征曲线研究综述[J]. 农技服务, 2016, 33(4): 22-23, 27. (HUANG X B, GAO B K. A review of soil moisture characteristic curves[J]. Agricultural Technology Service, 2016, 33(4): 22-23, 27. (in Chinese)HUANG X B, GAO B K. A review of soil moisture characteristic curves[J]. Agricultural Technology Service, 2016, 33(4): 22-23, 27. (in Chinese) [12] 王 俊, 黄岁樑. 土壤水分特征曲线模型对数值模拟非饱和渗流的影响[J]. 水动力学研究与进展,2010,25(1):16-22. (WANG J, HUANG S L. Effect of soil water characteristic models on numerical modeling of unsaturated flow[J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics,2010,25(1):16-22. (in Chinese)WANG J, HUANG S L. Effect of soil water characteristic models on numerical modeling of unsaturated flow[J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2010, 25(1): 16-22. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: