Calculation method of urban embankment protection range based on stress diffusion method
-
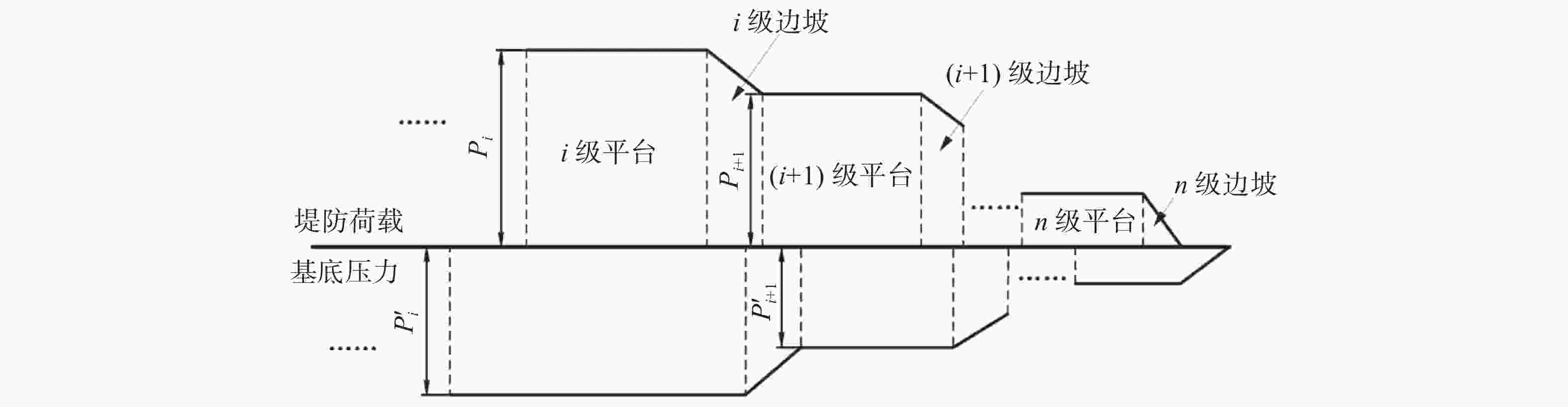
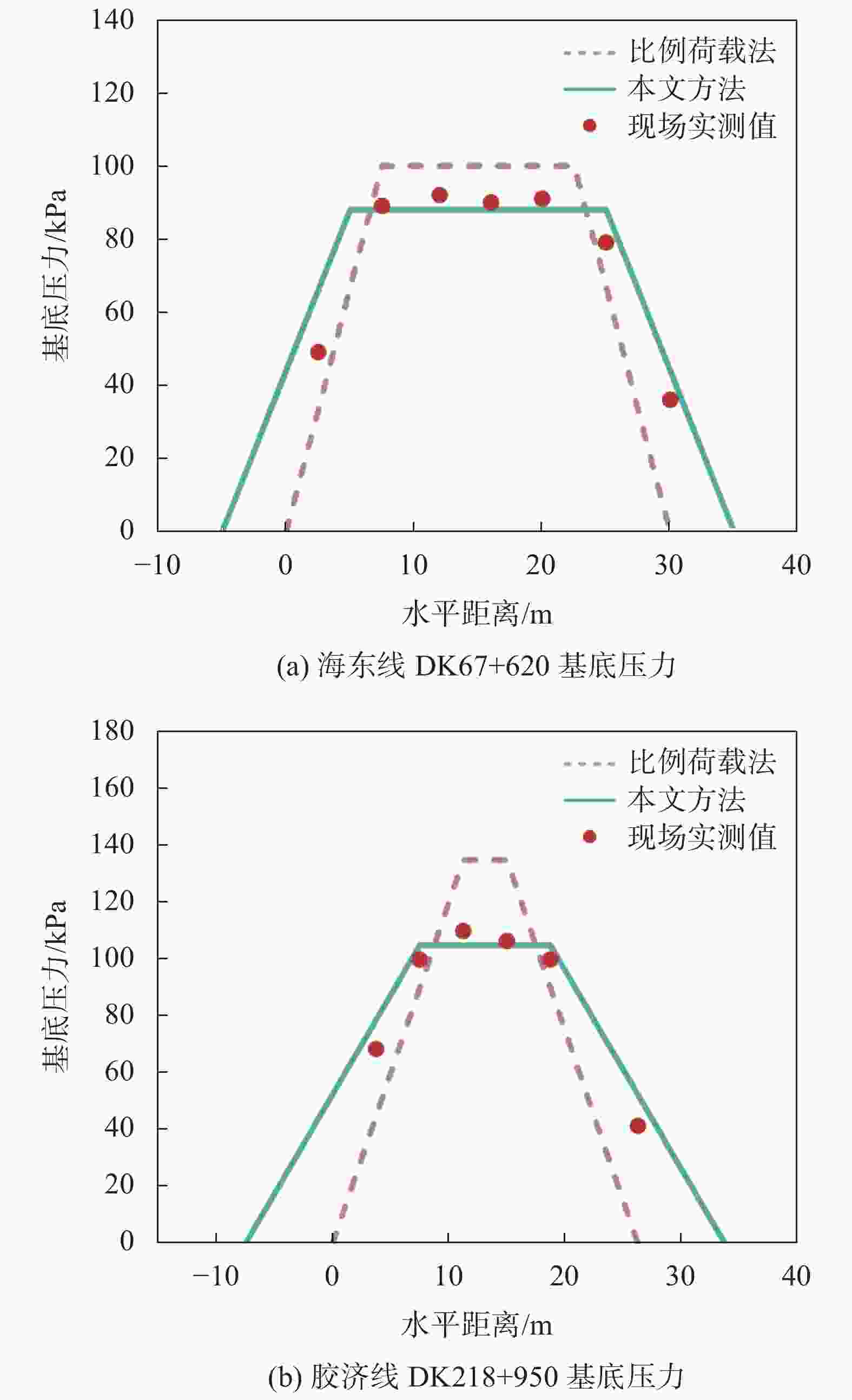
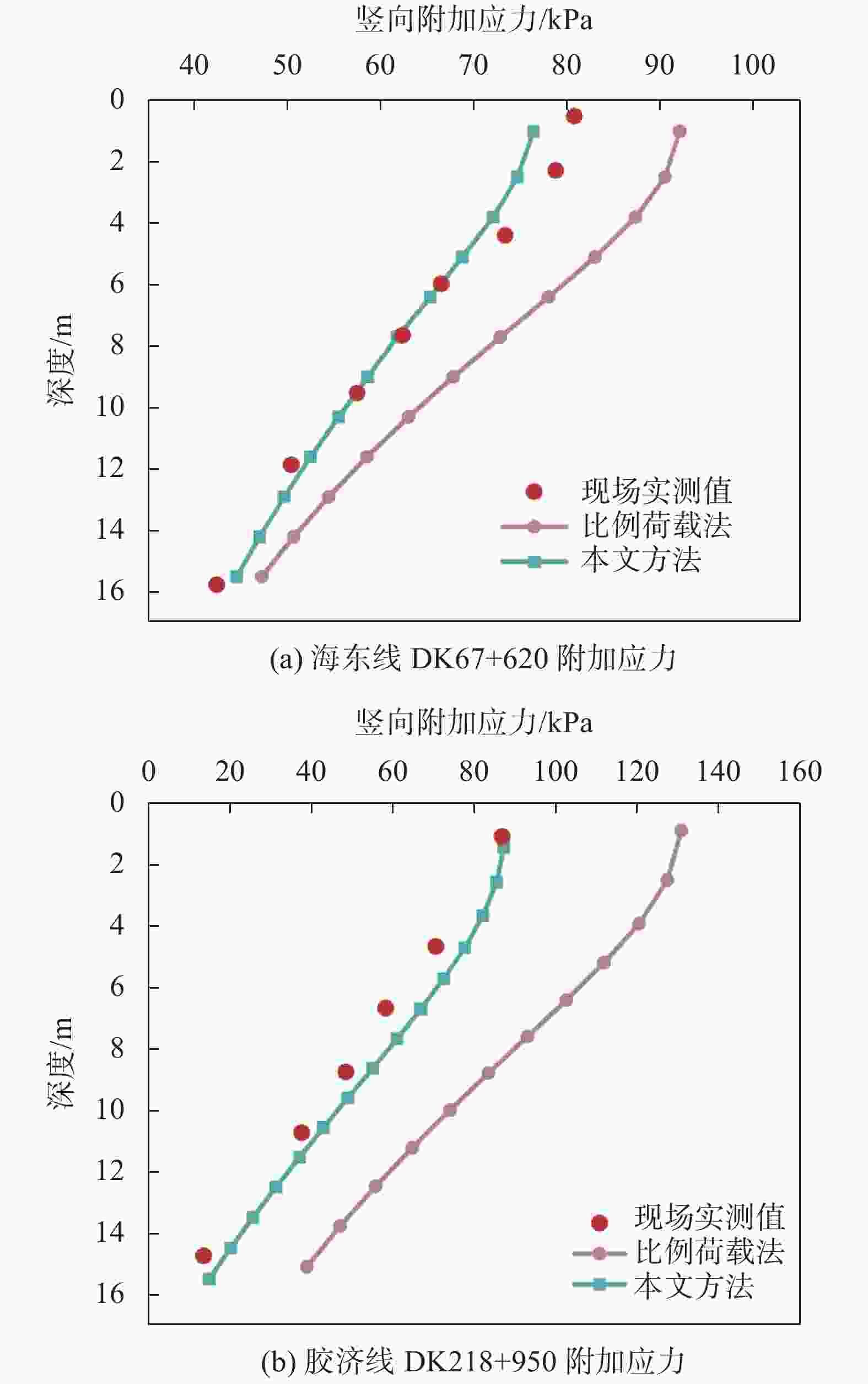
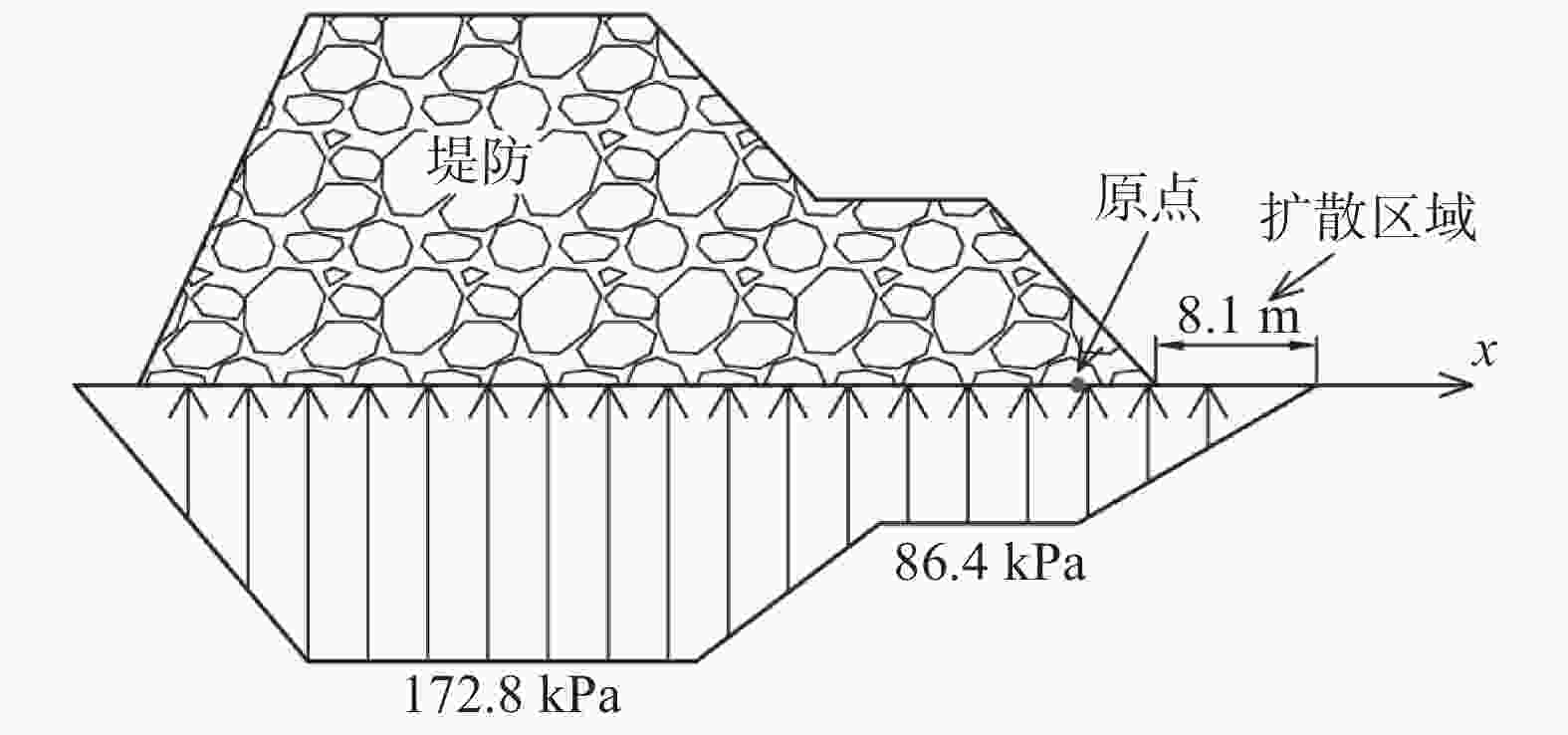
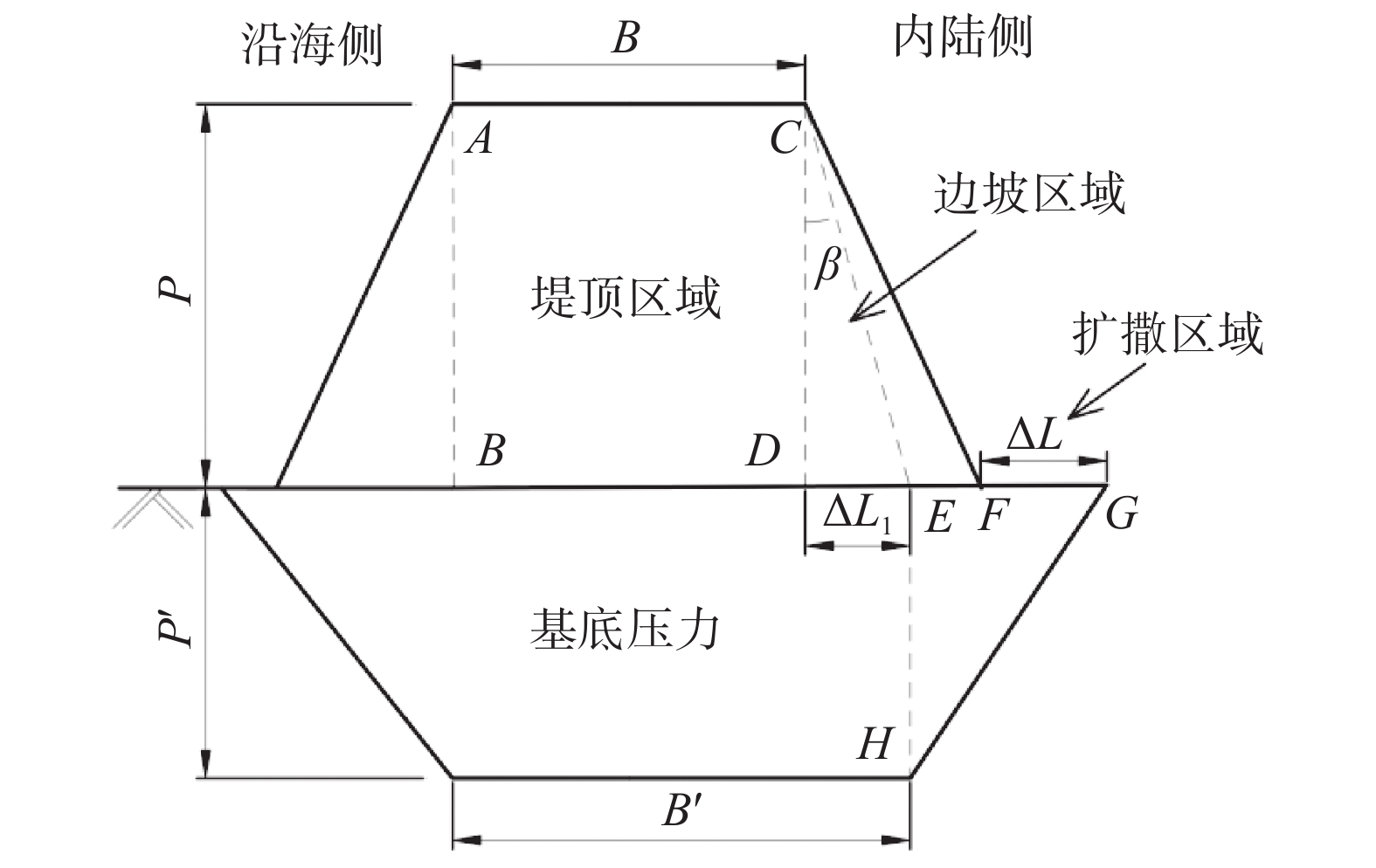
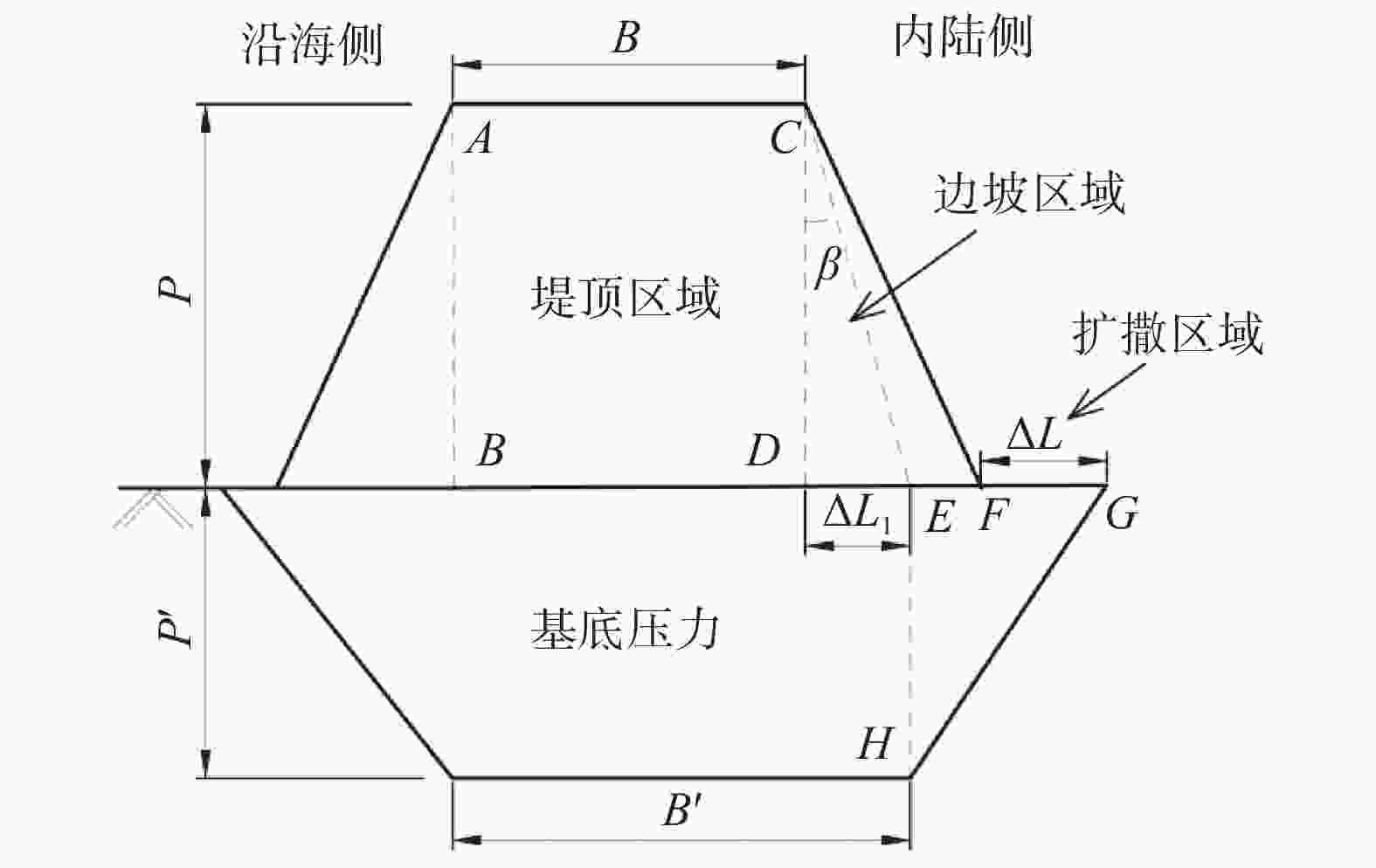
摘要: 高填方堤防、多级平台堤防以及堤防提标加固工程日益增多,堤防荷载的应力扩散效应对周边建筑可能构成严重威胁。传统设计方案中,未充分考虑堤防荷载的应力扩散效应,高估堤顶区域的附加应力,同时低估水平方向的扩散效应,导致设计中未能充分评估堤防荷载对周边建筑的潜在威胁。堤防荷载扩散中这一高一低的传统设计理念,给工程设计和分析判断带来了较大困难,也给设计方案的优化提供了新思路。基于应力扩散角法,将堤防荷载分为边坡区域荷载和堤顶区域荷载,量化了应力扩散效应对基底压力分布范围和大小的影响,为堤防设计提供了一个增强安全性的新工具。通过对比,该法相对于传统方法能更准确地反映基底压力的实际分布情况,经分析,其扩散程度与堤防截面几何尺寸相关。此外,依据工程实测数据量化了堤防之外的扩散区域中的不均匀沉降,计算结果表明扩散效应对周边民建房结构稳定性构成潜在威胁,可能引发倾斜和裂缝等结构安全问题。建议在大型工程周边的重要位置设立沉降观测点,以实时监测并及时采取防范措施。Abstract: With the increasing number of high-fill embankments, multi-level platform embankments, and embankment reinforcement projects, the stress diffusion effect of embankment loads may pose a serious threat to surrounding buildings. In traditional design schemes, due to insufficient consideration of the stress diffusion effect of embankment loads, the additional stress in the top area of the embankment is often overestimated, while the horizontal diffusion effect is underestimated, resulting in insufficient evaluation of the potential threat of embankment loads to surrounding buildings in the design. The law of one high and one low in the diffusion of embankment loads has brought great difficulties to engineering design and analysis judgment, and also provided new ideas for optimizing design schemes. Based on the stress diffusion angle method, this article divides the embankment load into slope area load and embankment top area load, quantifies the influence of stress diffusion effect on the distribution range and magnitude of base pressure, and provides a new tool for enhancing safety in embankment design. By comparison, this method can more accurately reflect the actual distribution of base pressure compared to traditional methods. After analysis, its diffusion degree is related to the geometric dimensions of the embankment section. In addition, the uneven settlement in the diffusion area outside the embankment based on engineering measurement data was quantified. The results show that the diffusion effect poses a potential threat to the stability of surrounding residential buildings, which may cause structural safety issues such as tilting and cracks. In view of this, setting up settlement observation points at important locations around large-scale projects to monitor in real time and take timely preventive measures is suggested.
-
Key words:
- base pressure /
- diffusion effect /
- stress diffusion angle /
- additional stress /
- uneven settlement
-
表 1 文献案例的基底压力
Table 1. Contact stress for literature cases
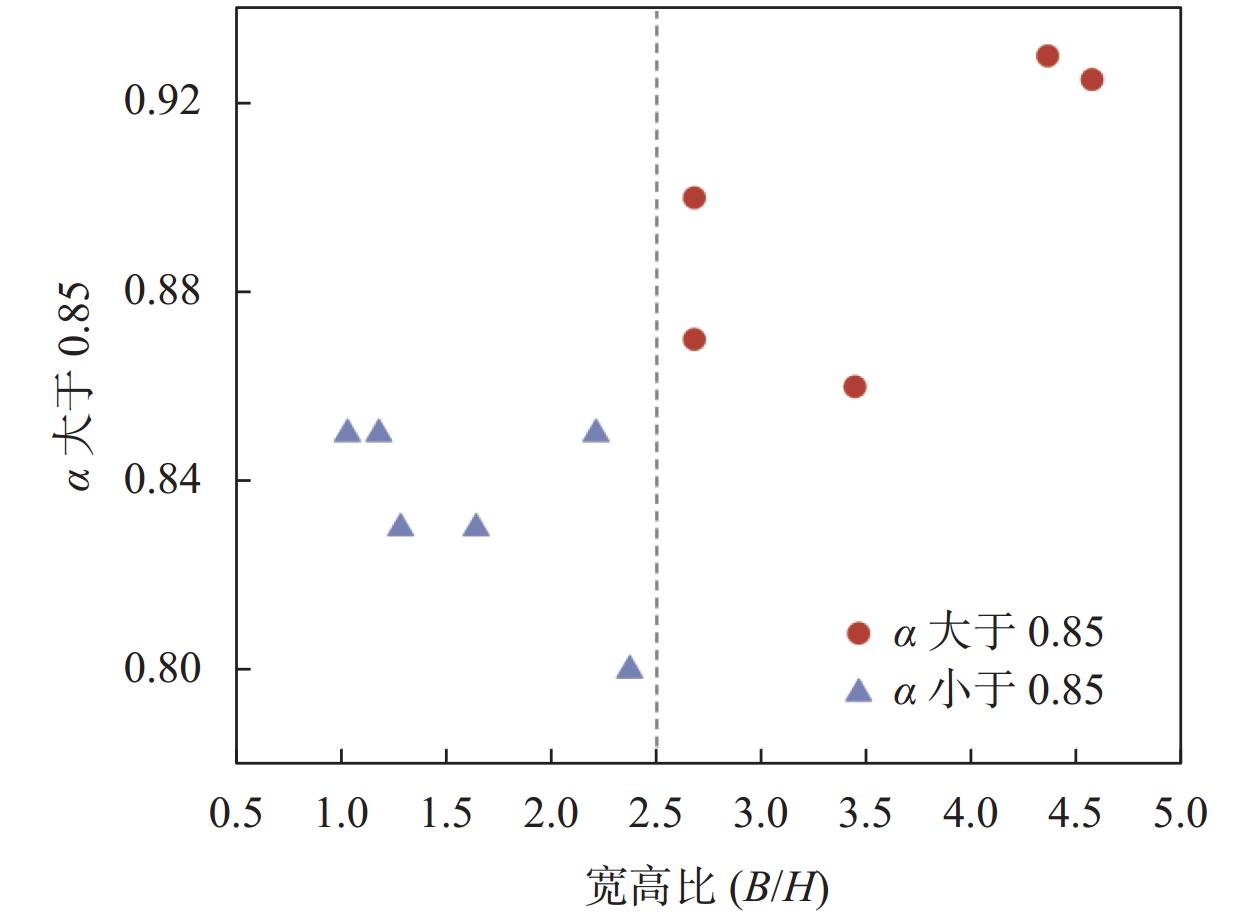
案例 堤顶宽度B/m 高度H/m 坡度比 γ/(kN∙m−3) γH/kPa 基底中心压力实测P/kPa α 海东线现场DK67+620[14] 13.4 5 1∶1.5 20 100 87 0.87 海东线现场DK67+630[14] 13.4 5 1∶1.5 20 100 90 0.90 海东线现场DK79+399[14] 13.7 3.14 1∶1.5 20 62.8 58.5 0.93 海东线DK67+620离心模型第一层[14] 19.6 1.2 1∶1.5 20 24 23.5 0.98 海东线DK67+620离心模型第二层[24] 16 2.4 1∶1.5 20 48 46 0.96 海东线DK67+620离心模型第三层[24] 12.4 3.6 1∶1.5 20 72 62 0.86 海东线DK67+620离心模型第四层[24] 8.2 5 1∶1.5 20 100 83 0.83 海东线DK67+620离心模型整体填筑[24] 8.2 5 1∶1.5 20 100 83 0.83 胶济线DK218+950离心模型第一层[23] 25.5 1.6 1∶1.5 20 32 29.4 0.92 胶济线DK218+950离心模型第二层[23] 18.3 4 1∶1.5 20 80 74 0.925 胶济线DK218+950离心模型第三层[23] 13.5 5.6 1∶1.5 20 112 95 0.85 胶济线DK218+950离心模型第四层[23] 7.7 7.5 1∶1.5 20 150 116 0.85 胶济线DK218+950离心模型整体填筑[23] 7.7 7.5 1∶1.5 20 150 114 0.85 Gloucester堤防[25] 9.14 3.66 1∶1.46 17.9 65.57 52.66 0.80 表 2 工程案例物理力学指标及压缩模量
Table 2. Physical and mechanical indexes and compression modulus of the engineering cases
表 3 地基沉降实测值与计算值
Table 3. Measured and calculated values of foundation settlement
表 4 柯桥区钱塘江海塘某一断面物理力学指标及压缩模量
Table 4. Physical and mechanical indicators and compression modulus of a certain section of the Qiantang River seawall in Keqiao District
土层 土层深度范围/m 重度γ/(kN∙m−3) 孔隙比e 压缩模量Es/MPa ②-1砂质粉土3 0~19 18.2 0.947 3.03 ②-2粉土夹粉砂 19~27 18.7 0.809 4.17 ③淤泥质粉质黏土 27~ 18.1 1.043 1.52 -
[1] ZHANG K, FENG D, WANG Z K. Study on the mechanical properties of embankment soil under long-term immersion conditions[J]. Frontiers in Materials, 2023, 10: 1270082. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2023.1270082 [2] 覃莲超, 涂澜涛, 王彩虹, 等. 蓄滞洪区转移道路工程规划布设研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2024(7): 191-195. (QIN L C, TU L T, WANG C H, et al. Study on planning and layout of transfer road engineering in flood storage and detention areas[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2024(7): 191-195. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12396/znsd.240147QIN L C, TU L T, WANG C H, et al. Study on planning and layout of transfer road engineering in flood storage and detention areas[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2024(7): 191-195. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12396/znsd.240147 [3] CHU J, YAN S W, LI W. Innovative methods for dike construction – An overview[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2012, 30: 35-42. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2011.01.008 [4] 薛林德. 水利工程建设中堤防工程施工技术的应用研究[J]. 水上安全, 2023(8): 94-96. (XUE L D. Research on the application of embankment construction technology in water conservancy engineering construction[J]. Maritime Safety, 2023(8): 94-96. (in Chinese)XUE L D. Research on the application of embankment construction technology in water conservancy engineering construction[J]. Maritime Safety, 2023(8): 94-96. (in Chinese) [5] 姚燕明, 赵永胜, 宫全美, 等. 玉环县漩门二期海堤沉降分析[J]. 岩土工程技术, 2001, 15(4): 217-220,225. (YAO Y M, ZHAO Y S, GONG Q M, et al. Settlement analysis of Xuan men second sea bank in Yuhuan county[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique, 2001, 15(4): 217-220,225. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2001.04.008YAO Y M, ZHAO Y S, GONG Q M, et al. Settlement analysis of Xuan men second sea bank in Yuhuan county[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique, 2001, 15(4): 217-220,225. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2001.04.008 [6] 李春意. 排水固结加固软土堤防稳定性分析[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2023. (LI C Y. Stability analysis of soft soil embankments reinforced by drainage consolidation method[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2023. (in Chinese)LI C Y. Stability analysis of soft soil embankments reinforced by drainage consolidation method[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2023. (in Chinese) [7] TAECHAKUMTHORN C, ROWE R K. Performance of a reinforced embankment on a sensitive Champlain clay deposit[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2012, 49(8): 917-927. doi: 10.1139/t2012-053 [8] WU H N, SHEN S L, MA L, et al. Evaluation of the strength increase of marine clay under staged embankment loading: a case study[J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 2015, 33(6): 532-541. [9] 何元瑭, 金泰赛. 组合型轨道梁结构在码头中的应用[J]. 水运工程, 2023(2): 87-91,115. (HE Y T, JIN T S. Application of combined rail beam structure in wharf[J]. Port & Waterway Engineering, 2023(2): 87-91,115. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2023.02.016HE Y T, JIN T S. Application of combined rail beam structure in wharf[J]. Port & Waterway Engineering, 2023(2): 87-91,115. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2023.02.016 [10] 姚群勇, 陈志强. “W”型钢结构桁架工程现场吊装技术方案研究[J]. 价值工程, 2023, 42(29): 64-66. (YAO Q Y, CHEN Z Q. Study on the technical scheme of on-site hoisting of "W" steel structure truss project[J]. Value Engineering, 2023, 42(29): 64-66. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4311.2023.29.020YAO Q Y, CHEN Z Q. Study on the technical scheme of on-site hoisting of "W" steel structure truss project[J]. Value Engineering, 2023, 42(29): 64-66. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4311.2023.29.020 [11] 张兰霞, 周宣珊, 袁 涛. 既有铁路增设车站方案可行性: 以三亚至乐东铁路为例[J]. 综合运输, 2024, 46(3): 180-185. (ZHANG L X, ZHOU X S, YUAN T. Feasibility study on the scheme of adding stations to existing railway: Sanya-Ledong railway as an example[J]. China Transportation Review, 2024, 46(3): 180-185. (in Chinese)ZHANG L X, ZHOU X S, YUAN T. Feasibility study on the scheme of adding stations to existing railway: Sanya-Ledong railway as an example[J]. China Transportation Review, 2024, 46(3): 180-185. (in Chinese) [12] WANG H, ZENG L L, BIAN X, et al. Evaluation of vertical superimposed stress in subsoil induced by embankment loads[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 19(1): 04018182. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0001325 [13] 张 良, 罗 强, 裴富营, 等. 基于离心模型试验的软土地基路堤加筋垫层效应研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2009, 31(4): 108-114. (ZHANG L, LUO Q, PEI F Y. Research of effect of reinforced cushion of soft soil subgrade embankment based on centrifugal model tests[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2009, 31(4): 108-114. (in Chinese)ZHANG L, LUO Q, PEI F Y. Research of effect of reinforced cushion of soft soil subgrade embankment based on centrifugal model tests[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2009, 31(4): 108-114. [14] 王 恒. 堤防长期荷载下天然地基土中应力与土结构性损伤演化规律研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2019. (WANG H. Change law in stress distribution in subsoil and engineering properties of naturally structured clays under long term embankment loads[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2019. (in Chinese)WANG H. Change law in stress distribution in subsoil and engineering properties of naturally structured clays under long term embankment loads[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2019. (in Chinese) [15] 张 楠, 李 波, 王天成, 等. 软土地基堤防稳定性离心模型试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2023, 45(S1): 222-225. (ZHANG N, LI B, WANG T C, et al. Centrifugal model tests on stability of embankment on soft soil foundation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2023, 45(S1): 222-225. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE2023S10032ZHANG N, LI B, WANG T C, et al. Centrifugal model tests on stability of embankment on soft soil foundation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2023, 45(S1): 222-225. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE2023S10032 [16] 蒋关鲁, 王海龙, 李安洪. 高速铁路路基基底应力计算方法研究[J]. 铁道建筑, 2009, 49(4): 65-69. (JIANG G L, WANG H L, LI A H. Research on calculation method of foundation stress of high speed railway roadbed[J]. Railway Engineering, 2009, 49(4): 65-69. (in Chinese)JIANG G L, WANG H L, LI A H. Research on calculation method of foundation stress of high speed railway roadbed[J]. Railway Engineering, 2009, 49(4): 65-69. (in Chinese) [17] 储锡君, 侯先明, 张 策. 某软土堤基堤防加高工程断面型式设计[J]. 科技与创新, 2023(23): 22-25. (CHU X J, HOU X M, ZHANG C. Section design of a soft soil embankment foundation embankment heightening project[J]. Science and Technology & Innovation, 2023(23): 22-25. (in Chinese)CHU X J, HOU X M, ZHANG C. Section design of a soft soil embankment foundation embankment heightening project[J]. Science and Technology & Innovation, 2023(23): 22-25. (in Chinese) [18] 张心欣, 任晓磊, 王永亮, 等. 水利工程建设中压实质量高效检测方法对比[J]. 南水北调与水利科技(中英文), 2024, 22(1): 166-174. (ZHANG X X, REN X L, WANG Y L, et al. Comparison of efficient testing methods for compaction quality in hydraulic engineering construction[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2024, 22(1): 166-174. (in Chinese)ZHANG X X, REN X L, WANG Y L, et al. Comparison of efficient testing methods for compaction quality in hydraulic engineering construction[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2024, 22(1): 166-174. (in Chinese) [19] 甘 磊, 吴 健, 戴寿晔, 等. 含施工裂缝隧道穿越段堤防渗流和稳定分析[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 50(1): 85-90,101. (GAN L, WU J, DAI S Y, et al. Seepage and stability analysis of embankment with construction cracks in tunnel crossing section[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2022, 50(1): 85-90,101. (in Chinese)GAN L, WU J, DAI S Y, et al. Seepage and stability analysis of embankment with construction cracks in tunnel crossing section[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2022, 50(1): 85-90,101. (in Chinese) [20] 彭 望, 陈思宇, 肖长安. 城市渠道堤防结构综合检测技术应用——以某机场外排水渠为例[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 45(S1): 174-180. (PENG W, CHEN S Y, XIAO C A. Application of comprehensive detection technology for urban channel embankment structure: take an airport drainage channel as an example[J]. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2023, 45(S1): 174-180. (in Chinese)PENG W, CHEN S Y, XIAO C A. Application of comprehensive detection technology for urban channel embankment structure: take an airport drainage channel as an example[J]. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2023, 45(S1): 174-180. (in Chinese) [21] LANG R Q, YAN S W, SUN L Q, et al. Analysis of stress diffusion angle method for PTC pile composite foundation[J]. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering, 2018, 22(S1): s434-s448. [22] 黄佑鹏. 多层硬壳软土地基竖向附加应力扩散计算方法分析[J]. 安徽建筑, 2024, 31(3): 149-152. (HUANG Y P. Analysis of calculation method for vertical additional stress diffusion of multi-layer hard shell soft soil foundation[J]. Anhui Architecture, 2024, 31(3): 149-152. (in Chinese)HUANG Y P. Analysis of calculation method for vertical additional stress diffusion of multi-layer hard shell soft soil foundation[J]. Anhui Architecture, 2024, 31(3): 149-152. (in Chinese) [23] 吴丽君, 蒋关鲁, 李安洪. 基于离心模型试验的地基附加应力修正[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2015, 50(4): 662-668. (WU L J, JIANG G L, LI A H. Revision of additional stress in soils based on centrifuge model tests[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(4): 662-668. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.04.014WU L J, JIANG G L, LI A H. Revision of additional stress in soils based on centrifuge model tests[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(4): 662-668. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.04.014 [24] 肖红兵. 高速铁路深厚全风化花岗岩地基沉降特性及加固技术研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2016. (XIAO H B. Study on settlement behaviour and reinforced technique of high-speed railway on deep completely decomposed granite ground[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016. (in Chinese)XIAO H B. Study on settlement behaviour and reinforced technique of high-speed railway on deep completely decomposed granite ground[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016. (in Chinese) [25] BOZOZUK M, LEONARDS G A. The Gloucester test fill[C]//ASCE Specialty Conference on Performance of Earth and Earth-supported Structures. Indiana: Purdue University, 1972: 1-205. [26] 李春意, 曾 甄, 温晓贵, 等. 基于地基实际应力状态的堤防极限平衡分析[J]. 地基处理, 2024, 6(2): 107-115. (LI C Y, ZENG Z, WEN X G, et al. Ultimate equilibrium analysis of embankment based on actual stress states of soil foundation[J]. Journal of Ground Improvement, 2024, 6(2): 107-115. (in Chinese)LI C Y, ZENG Z, WEN X G, et al. Ultimate equilibrium analysis of embankment based on actual stress states of soil foundation[J]. Journal of Ground Improvement, 2024, 6(2): 107-115. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: