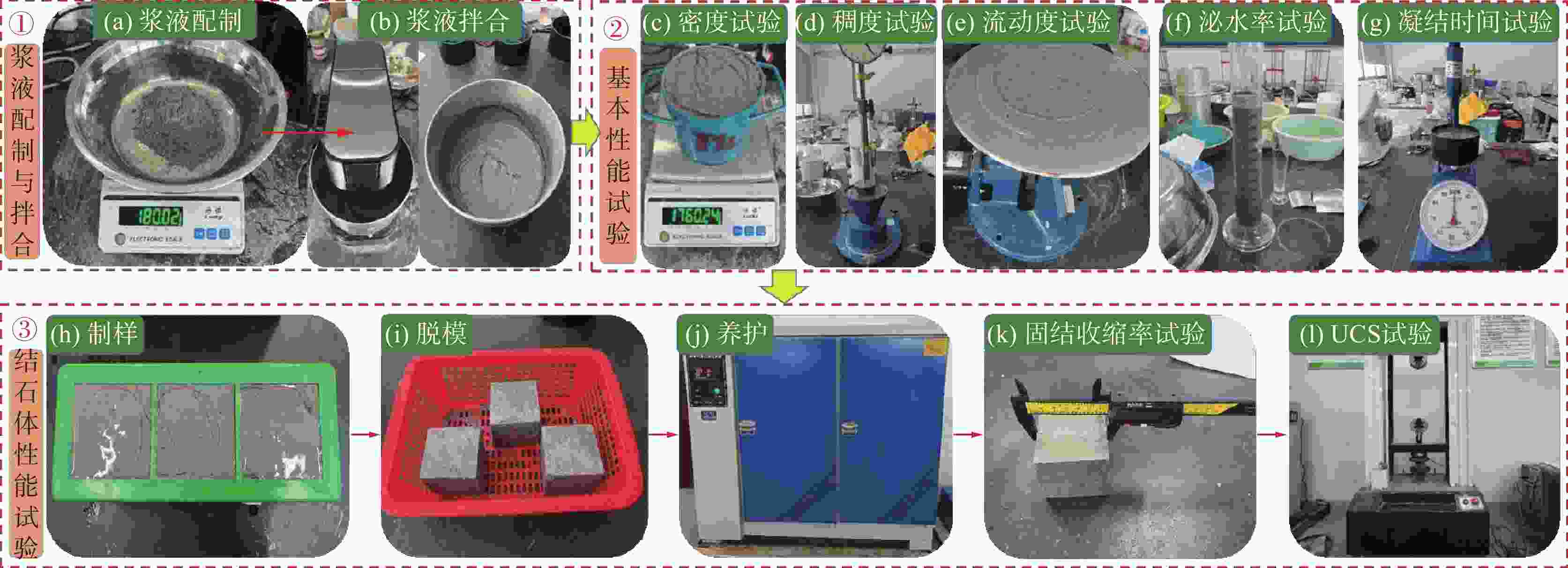
Performance improvement of shield synchronous grouting slurry based on multi-objective optimization
-
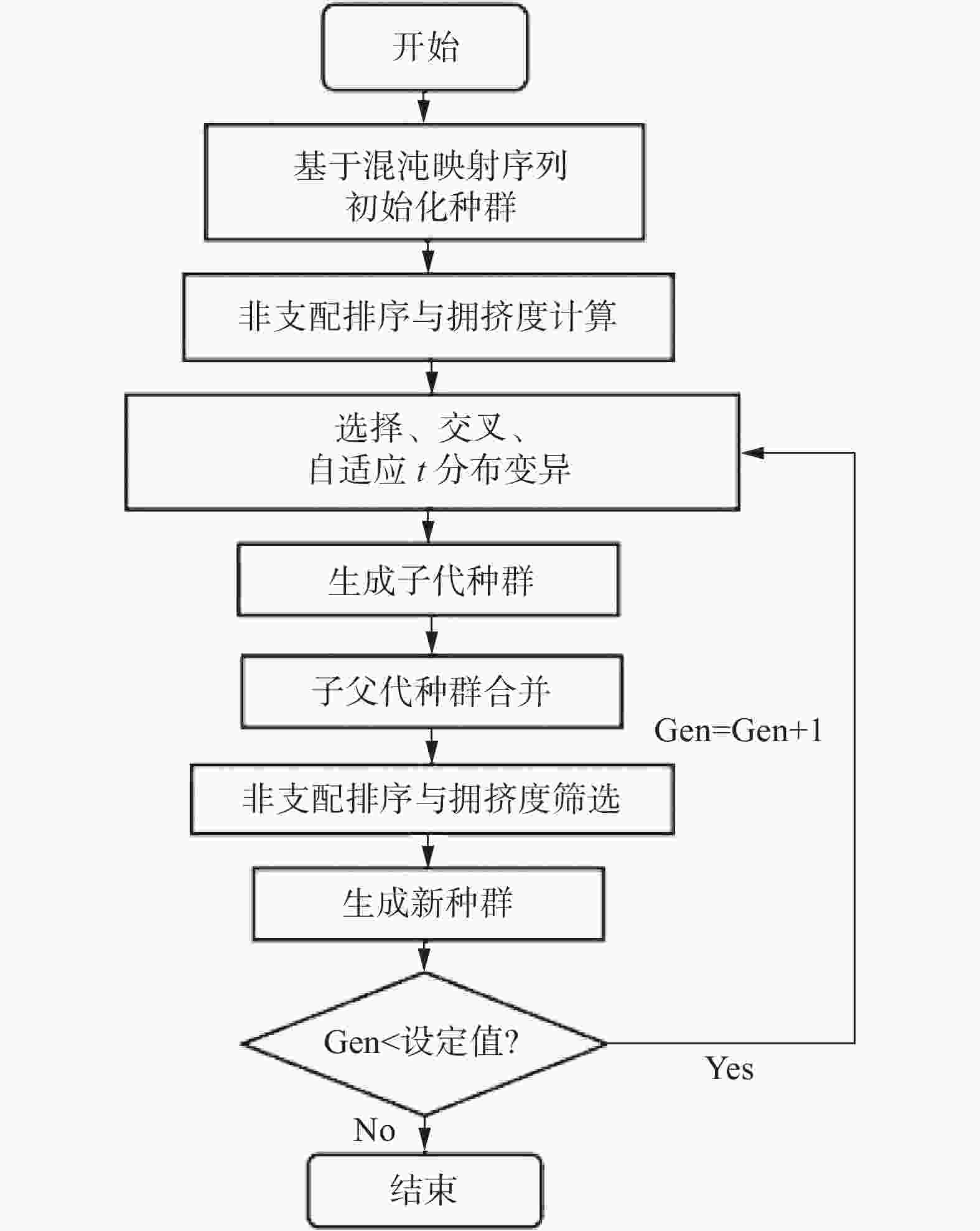
摘要: 针对盾构同步注浆中易发生的浆液稀释、离析等问题,通过分析实际工程案例,确定浆液配比后进行室内试验,采用SPSS及MINITAB分析试验结果,并结合MATLAB开展符合施工要求的浆液配比优化研究。分析表明:浆液水胶比集中在0.6~0.9,胶砂比集中在0.4~1.0,膨水比集中在0.1~0.3,灰粉比集中在0.2~0.6;水胶比对密度和稠度影响较大,膨水比主要影响流动度、泌水率和固结收缩率,灰粉比对凝结时间和强度影响显著;与MATLAB工具箱求解器的fmincon函数相比,改进的多目标遗传算法(NSGA-Ⅱ)优化结果精度更高,经优化得到最优配比:水胶比0.60、胶砂比0.87、膨水比0.25、灰粉比0.60。基于此,对北京12号线某盾构区间施工进行验证分析,结果表明相较于已有方案,基于多目标优化的浆液在地层变形控制上效果更优。Abstract: During the synchronous grouting process of shield tunneling, problems such as grout dilution and segregation are prone to occur. By analyzing actual engineering cases and determining the range of orthogonal design ratios, laboratory experiments were conducted. The experimental results were analyzed using SPSS and MINITAB, and the MATLAB multi-objective optimization tool was employed to study the optimization of grout ratios that meet the requirements of shield tunnel synchronous grouting engineering. The analysis showed that the water-cement ratio ranges from 0.6 to 0.9, the cement-sand ratio ranges from 0.4 to 1.0, the bentonite-water ratio ranges from 0.1 to 0.3, and the fly ash-cement ratio ranges from 0.2 to 0.6. The water-cement ratio significantly affects density and consistency, the bentonite-water ratio primarily influences fluidity, bleeding rate, and consolidation shrinkage rate, and the fly ash-cement ratio has a notable impact on setting time and strength. The regression formula for the grouts fits well and could be used for ratio optimization. Compared with the fmincon function of the MATLAB toolbox solver, the precision of the optimization results from the improved multi-objective genetic algorithm (Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II) is higher. The optimal grout ratio obtained after optimization is a water-cement ratio of 0.60, a cement-sand ratio of 0.87, a bentonite-water ratio of 0.25, and a fly ash-cement ratio of 0.60. Based on this, a validation analysis was conducted on a shield section of Beijing Metro Line 12. The results indicated that, compared to the existing scheme, the grout based on multi-objective optimization of the ratios shows better performance in controlling ground deformation.
-
表 1 正交试验因素水平
Table 1. Orthogonal test factor levels
因子水平 A B C D 1 0.6 0.4 0.1 0 2 0.7 0.6 0.15 0.2 3 0.8 0.8 0.2 0.4 4 0.9 1.0 0.25 0.6 表 2 浆液原材料性能指标
Table 2. Performance indicators of grout raw materials
材料名称 性能指标 水泥 P∙O 42.5普通硅酸盐水泥 粉煤灰 Ⅱ级粉煤灰,含水率≤1.0% 膨润土 钠基膨润土,过200目筛量超95% 砂 细中砂,含泥量≤3.0% 水 城市自来水,pH值7~8 表 3 浆液基本性能试验结果
Table 3. Basic performance test results of grout
浆液编号 密度/(g·cm−3) 流动度/cm 泌水率/% 稠度/cm 固结收缩率/% 凝结时间/h 无侧限抗压强度/MPa 3 d 7 d 28 d 1 1.645 23.7 1.42 12.3 5.13 2 1.730 23.6 2.59 11.8 4.79 11.5 0.50 1.21 3.14 3 1.767 21.9 1.28 10.9 4.32 10.6 1.22 2.56 6.10 4 1.796 20.1 0.61 10.3 3.98 7.9 2.34 4.58 8.52 5 1.654 24.5 2.98 12.9 5.15 11.2 1.32 2.52 5.29 6 1.678 25.4 2.54 13.1 5.49 10.5 1.60 3.53 7.23 7 1.648 / 0.03 / 4.06 8 1.756 23.1 2.08 11.5 4.54 13.3 0.51 1.07 2.28 9 1.622 24.3 3.15 12.9 4.70 11.5 1.16 2.61 5.46 10 1.671 23.4 1.84 11.8 4.49 12.1 0.71 1.55 3.74 11 1.674 * 3.83 13.2 5.97 16.7 0.22 0.68 1.50 12 1.665 24.8 1.01 12.1 5.26 13 1.583 22.5 1.47 12.0 4.34 15.6 0.25 0.59 1.28 14 1.575 / 0.01 / 4.94 15 1.647 26.8 4.68 13.1 5.65 12.0 0.78 1.67 3.90 16 1.702 * 4.89 13.0 6.50 13.4 0.44 0.93 2.62 表 4 浆液基本性能极差分析结果
Table 4. Results of the basic performance deviation analysis of grout
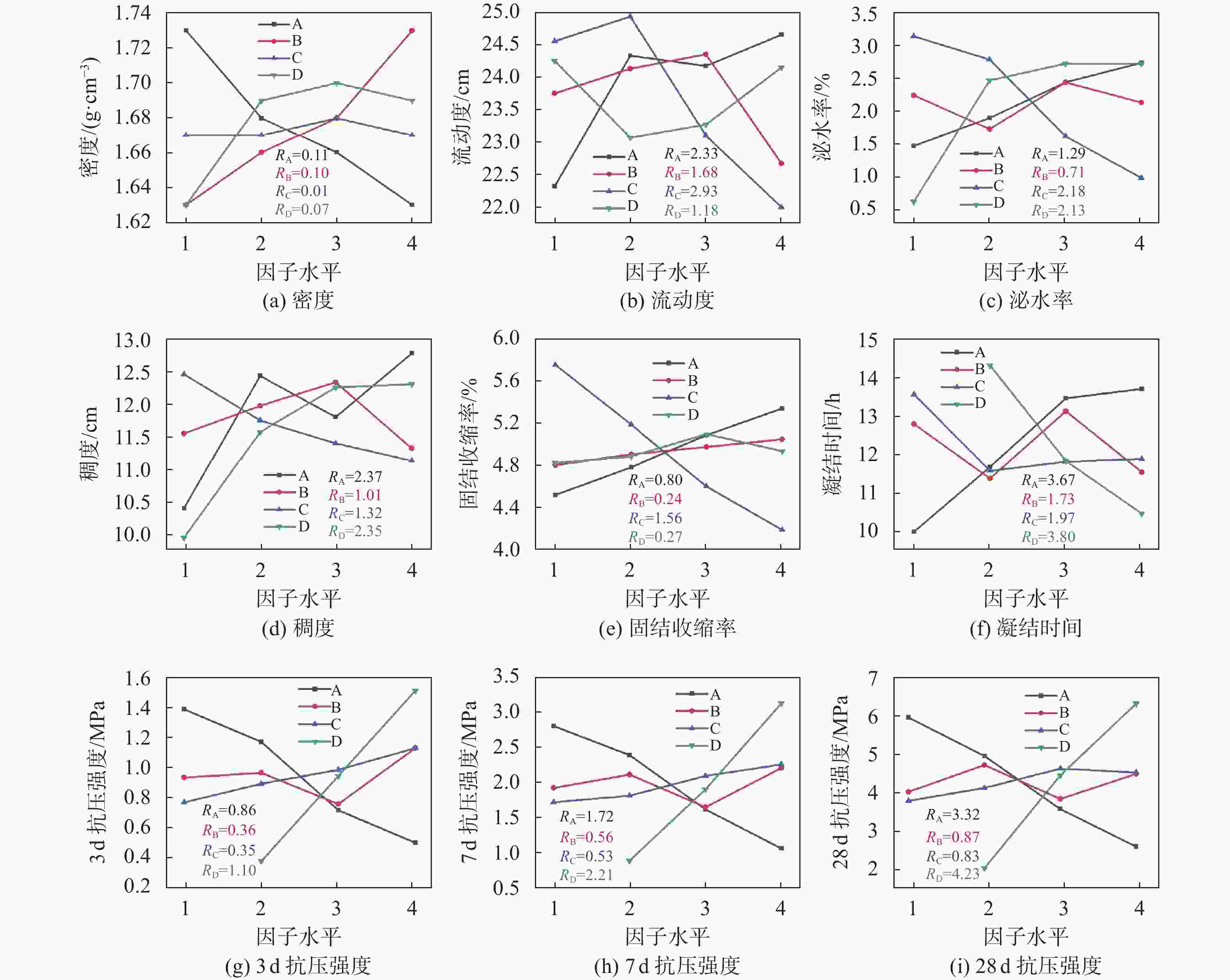
性能指标 因素 因素水平 极差R 排秩 1 2 3 4 密度 A 1.73 1.68 1.66 1.63 0.11 1 B 1.63 1.66 1.68 1.73 0.10 2 C 1.67 1.67 1.68 1.67 0.01 4 D 1.63 1.69 1.70 1.69 0.07 3 流动度 A 22.32 24.33 24.17 24.65 2.33 2 B 23.75 24.13 24.35 22.67 1.68 3 C 24.55 24.93 23.10 22.00 2.93 1 D 24.25 23.07 23.27 24.15 1.18 4 泌水率 A 1.48 1.91 2.46 2.76 1.29 3 B 2.26 1.74 2.46 2.15 0.71 4 C 3.17 2.81 1.63 0.99 2.18 1 D 0.62 2.49 2.75 2.75 2.13 2 稠度 A 10.40 12.43 11.8 12.77 2.37 1 B 11.55 11.97 12.33 11.32 1.01 4 C 12.45 11.75 11.4 11.13 1.32 3 D 9.95 11.57 12.25 12.3 2.35 2 固结收缩率 A 4.55 4.81 5.11 5.36 0.80 2 B 4.83 4.93 5.00 5.07 0.24 4 C 5.77 5.21 4.63 4.22 1.56 1 D 4.85 4.91 5.12 4.96 0.27 3 凝结时间 A 10.00 11.67 13.43 13.67 3.67 2 B 12.77 11.37 13.10 11.53 1.73 4 C 13.53 11.57 11.80 11.87 1.97 3 D 14.28 11.82 10.47 3.80 1 3 d抗压强度 A 1.35 1.14 0.70 0.49 0.86 2 B 0.91 0.94 0.74 1.10 0.36 3 C 0.75 0.87 0.96 1.10 0.35 4 D 0.37 0.92 1.47 1.10 1 7 d抗压强度 A 2.78 2.37 1.61 1.06 1.72 2 B 1.91 2.10 1.64 2.19 0.56 3 C 1.71 1.80 2.08 2.24 0.53 4 D 0.89 1.89 3.10 2.21 1 28 d抗压强度 A 5.92 4.93 3.57 2.60 3.32 2 B 4.01 4.70 3.83 4.47 0.87 3 C 3.78 4.11 4.61 4.51 0.83 4 D 2.05 4.44 6.28 4.23 1 表 5 多元回归拟合结果
Table 5. Multiple regression fitting results
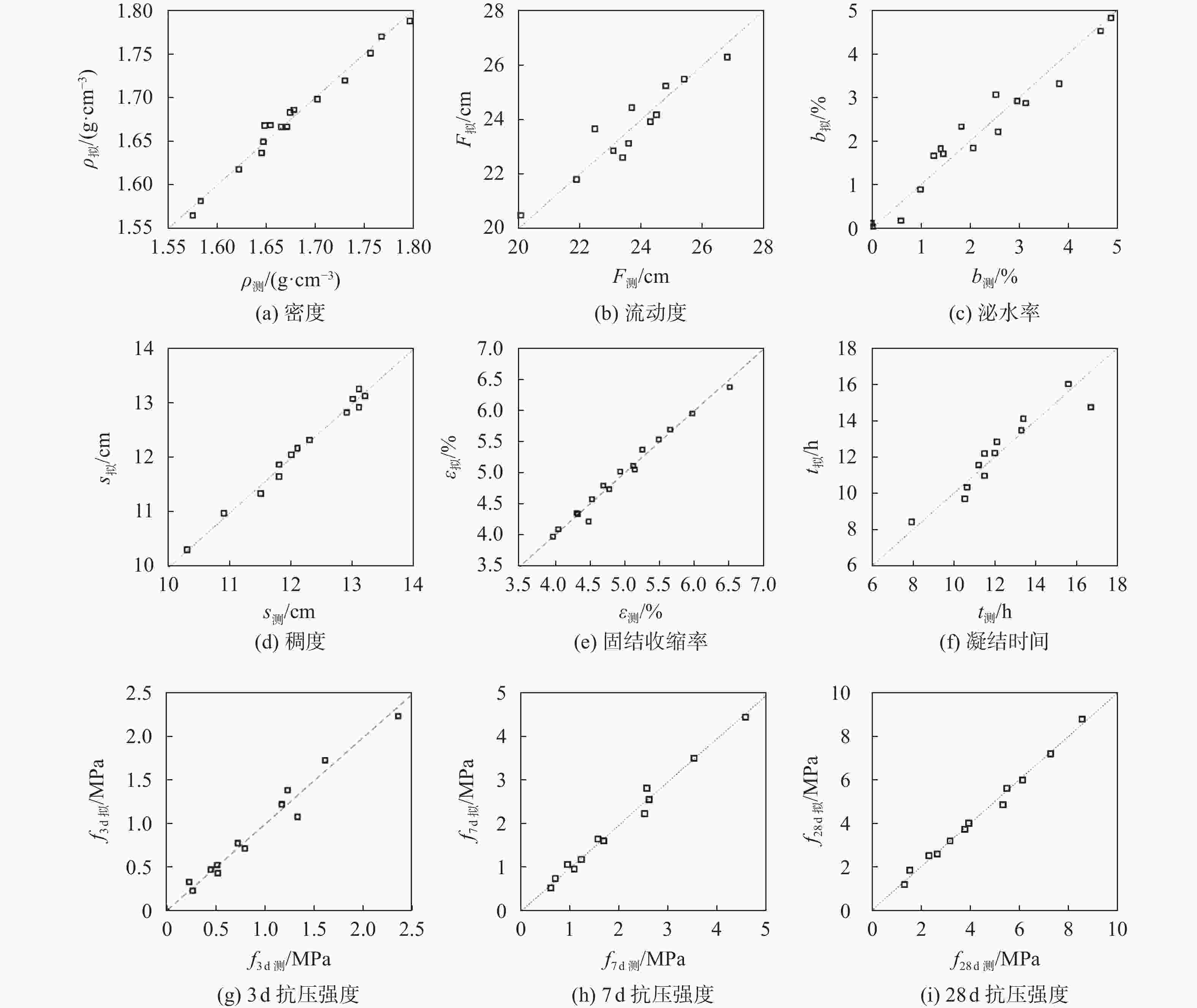
变量 回归公式 R2 $ R_{\mathrm{adj}}^2 $ 密度 ρ=1.78−0.349A+0.166B+0.33D−0.408D2 0.979 0.972 流动度 F=20.73+10.56A−26.25C 0.888 0.863 泌水率 b=4.01−1.57A−12.28C−4.59D−11.73D2+19.93AD 0.949 0.923 稠度 s=1.99+30.47A−1.299B−11.058C+0.711D−17.54A2 0.986 0.978 固结收缩率 ε=2.167+6.171A+4.36C−19.82AC 0.981 0.976 凝结时间 t=6.42+12.77A−9.5D 0.883 0.856 3 d抗压强度 f3d=−0.962+1.043A+10.4D−10.2AD 0.967 0.955 7 d抗压强度 f7d=−1.362+1.48A+19.4D−18.5AD 0.987 0.982 28 d抗压强度 f28d=1.57−2.06A+27.95D−23.18AD 0.992 0.989 表 6 优化浆液试验结果验证
Table 6. Validation of test results of optimized grout
最优配比来源 项目 密度
/(g·cm−3)流动度/cm 泌水率
/%稠度
/cm固结收缩率/% 凝结时间/h 无侧限抗压强度/MPa 3 d 7 d 28 d fmincon函数 最优配比试验值 1.806 19.9 1.2 11.5 4.43 7.9 2.10 4.31 8.15 最优配比理论值 1.756 21.3 0.56 10.9 4.21 8.4 2.23 4.51 8.76 误差率/% 2.77 7.04 53.33 5.22 4.97 6.33 6.19 4.64 7.48 改进NSGA-II算法 最优配比试验值 1.844 19.5 0.29 10.2 4.11 8.0 2.16 4.36 8.20 最优配比理论值 1.766 20.5 0.2 10.5 3.99 8.4 2.23 4.51 8.76 误差率/% 4.23 5.13 31.03 2.94 3.16 5.00 3.24 3.44 6.83 表 7 优化算法对比
Table 7. Comparison of optimization algorithms
验证组 优化方法 A B C D 其余函数求解值 目标函数求解值 更优 ① fmincon函数 0.6 0.82 0.25 0.54 ρ=1.766 g/cm3,F=20.5 cm,s=10.5 cm,t=9.0 h
f3d=1.98 MPa,f7d=4.01 MPa,f28d=7.92 MPa,cost=366.2元ԑ=3.99%,b=0.52% 改进NSGA-Ⅱ 改进NSGA-Ⅱ 0.6 0.7 0.25 0.6 ρ=1.738 g/cm3,F=20.5 cm,s=10.7 cm,t=8.4 h
f3d=2.23 MPa,f7d=4.51 MPa,f28d=8.76 MPa,cost=373.6元ԑ=3.99%,b=0.20% ② fmincon函数 0.6 0.72 0.19 0.35 ρ=1.755 g/cm3,F=22.1 cm,b=1.88%, s=11.2 cm,t=10.8 h
f3d=1.16 MPa,f7d=2.43 MPa,f28d=5.25 MPaԑ=4.48%,cost=314.6元 改进NSGA-Ⅱ 改进NSGA-Ⅱ 0.6 0.47 0.21 0.22 ρ=1.701 g/cm3,F=21.6 cm,b=1.54%, s=11.2 cm,t=12.0 h
f3d=0.61 MPa,f7d=1.35 MPa,f28d=3.42 MPaԑ=4.29%,cost=294.6元 ③ fmincon函数 0.6 0.75 0.19 0.43 ρ=1.761 g/cm3,F=22.1 cm,b=1.73%,s=11.2 cm,t=10.0 h
f3d=1.50 MPa,f7d=3.10 MPaԑ=4.44%,f28d=6.37 MPa,
cost=335.8元改进NSGA-Ⅱ 改进NSGA-Ⅱ 0.6 0.6 0.19 0.43 ρ=1.736 g/cm3,F=22.1 cm,b=1.73%,s=11.4 cm, t=10.0 h
f3d=1.50 MPa,f7d=3.10 MPaԑ=4.44%,f28d=6.37 MPa,
cost=335.6元④ fmincon函数 0.6 0.75 0.21 0.43 ρ=1.761 g/cm3,F=21.6 cm,s=11.0 cm,t=10.0 h
f3d=1.50 MPa,f7d=3.10 MPa,f28d=6.37 MPaԑ=4.29%,b=1.49%,
cost=341元改进NSGA-Ⅱ 改进NSGA-Ⅱ 0.6 0.49 0.24 0.22 ρ=1.704 g/cm3,F=21.6 cm,s=11.2 cm,t=12.0 h
f3d=0.61 MPa,f7d=1.35 MPa,f28d=3.42 MPaԑ=4.06%,b=1.17%,
cost=302.9元表 8 关键计算参数取值
Table 8. Key calculation parameter values
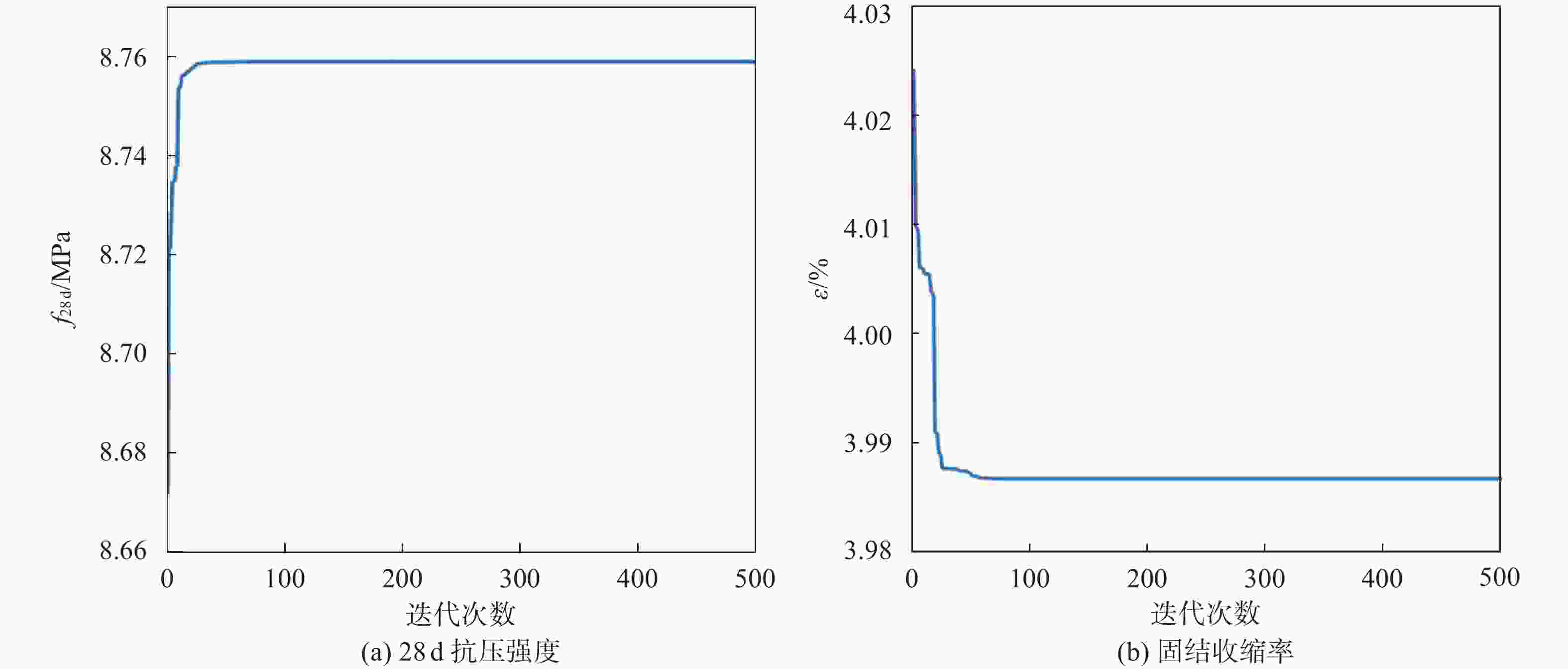
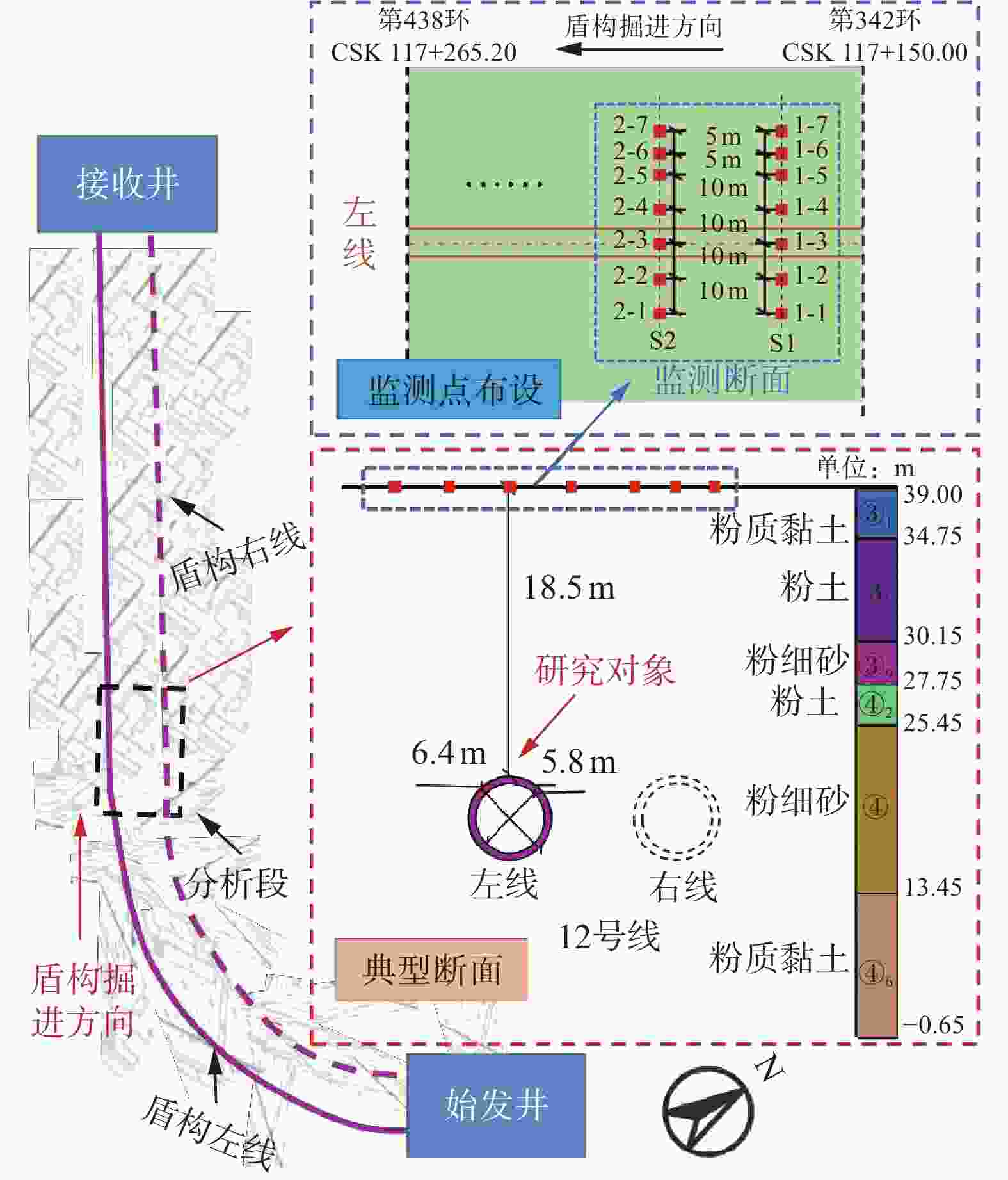
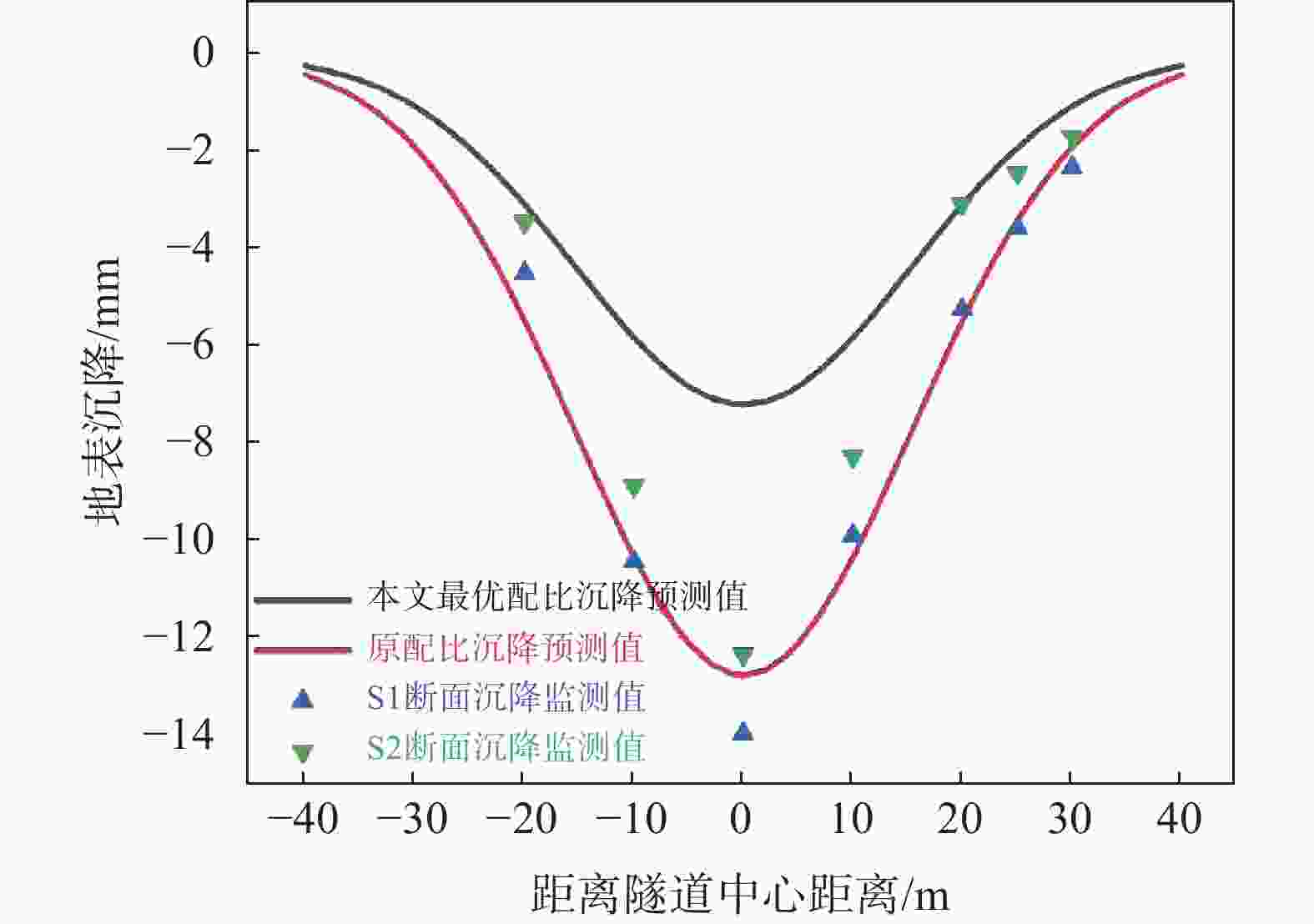
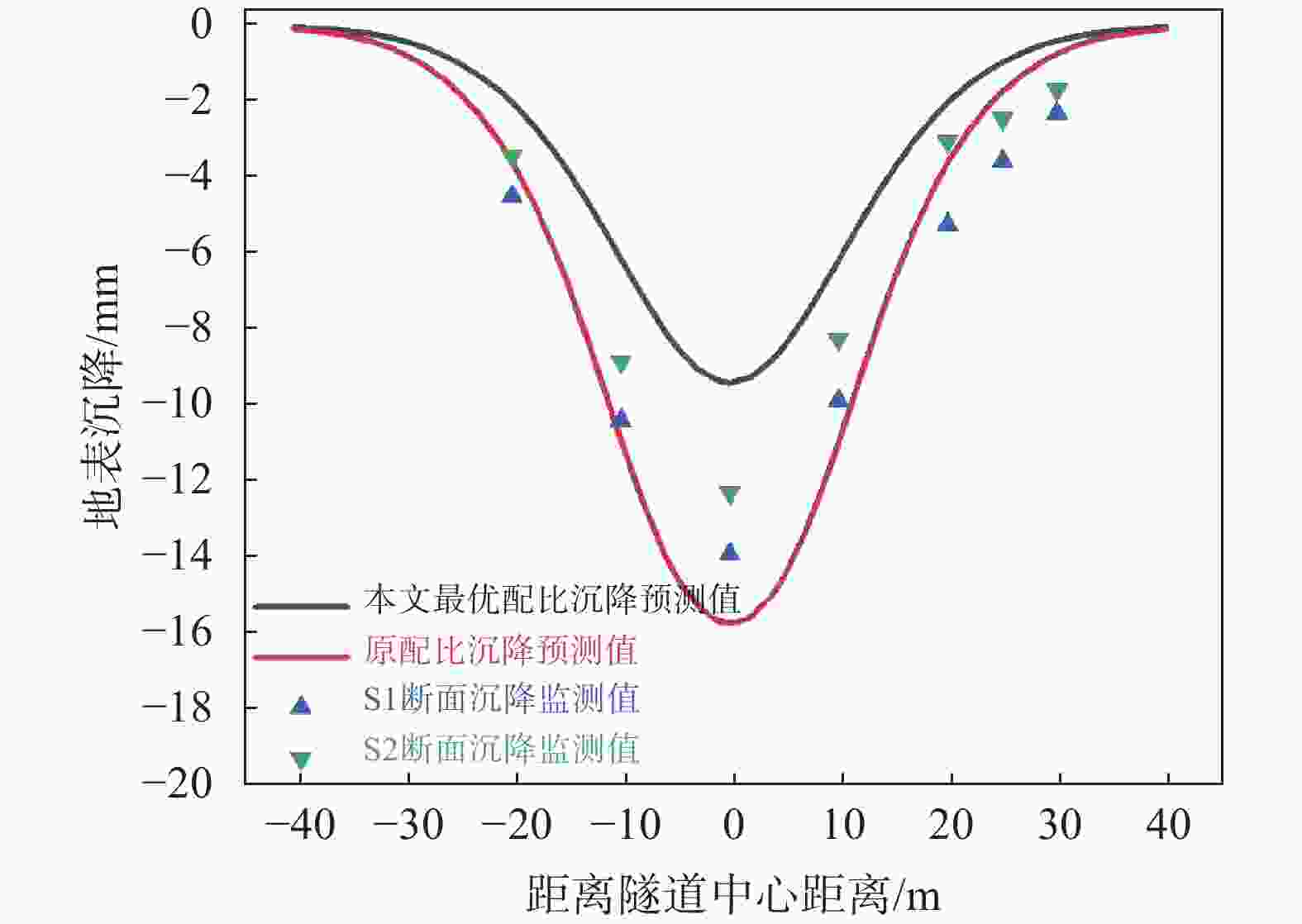
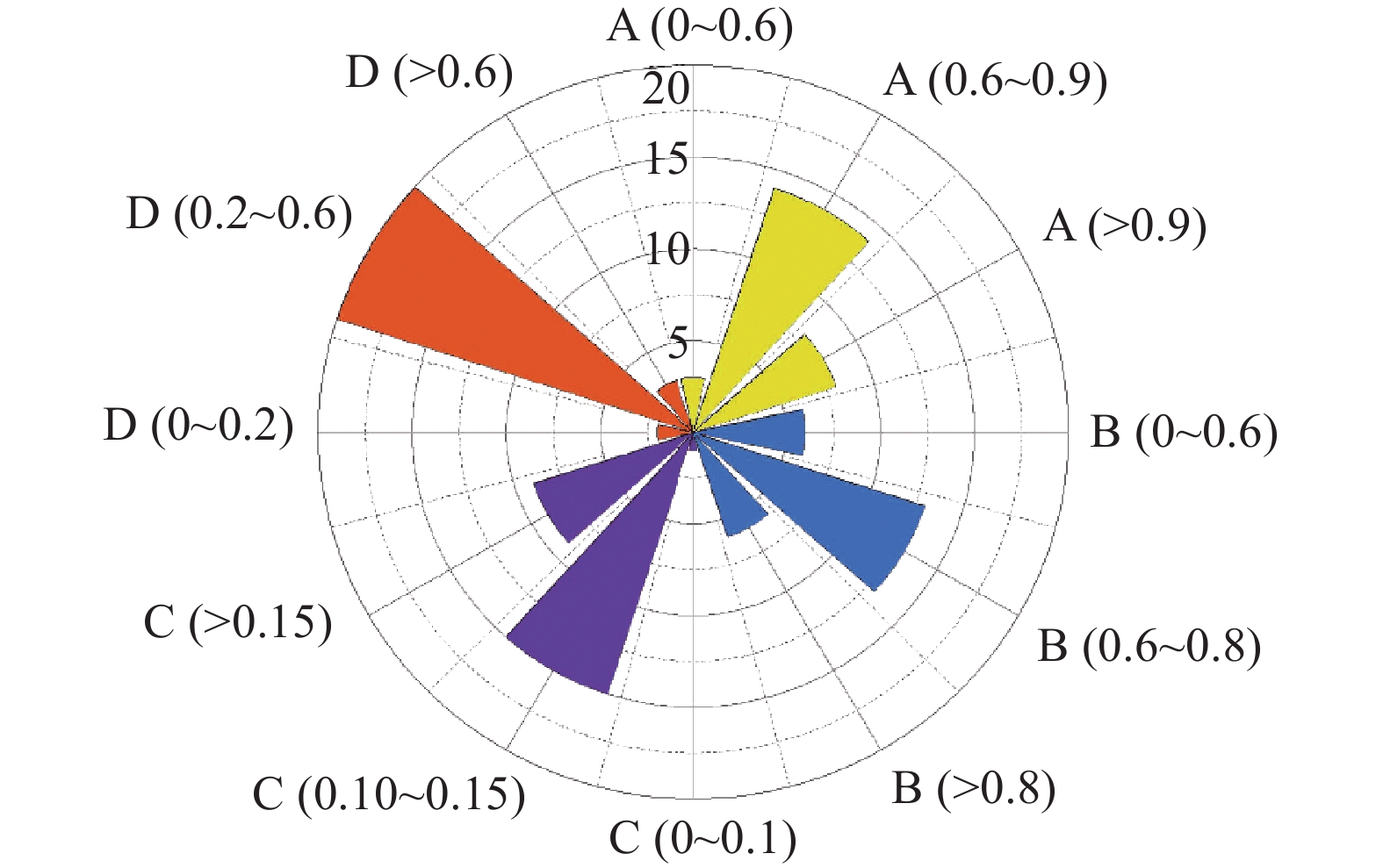
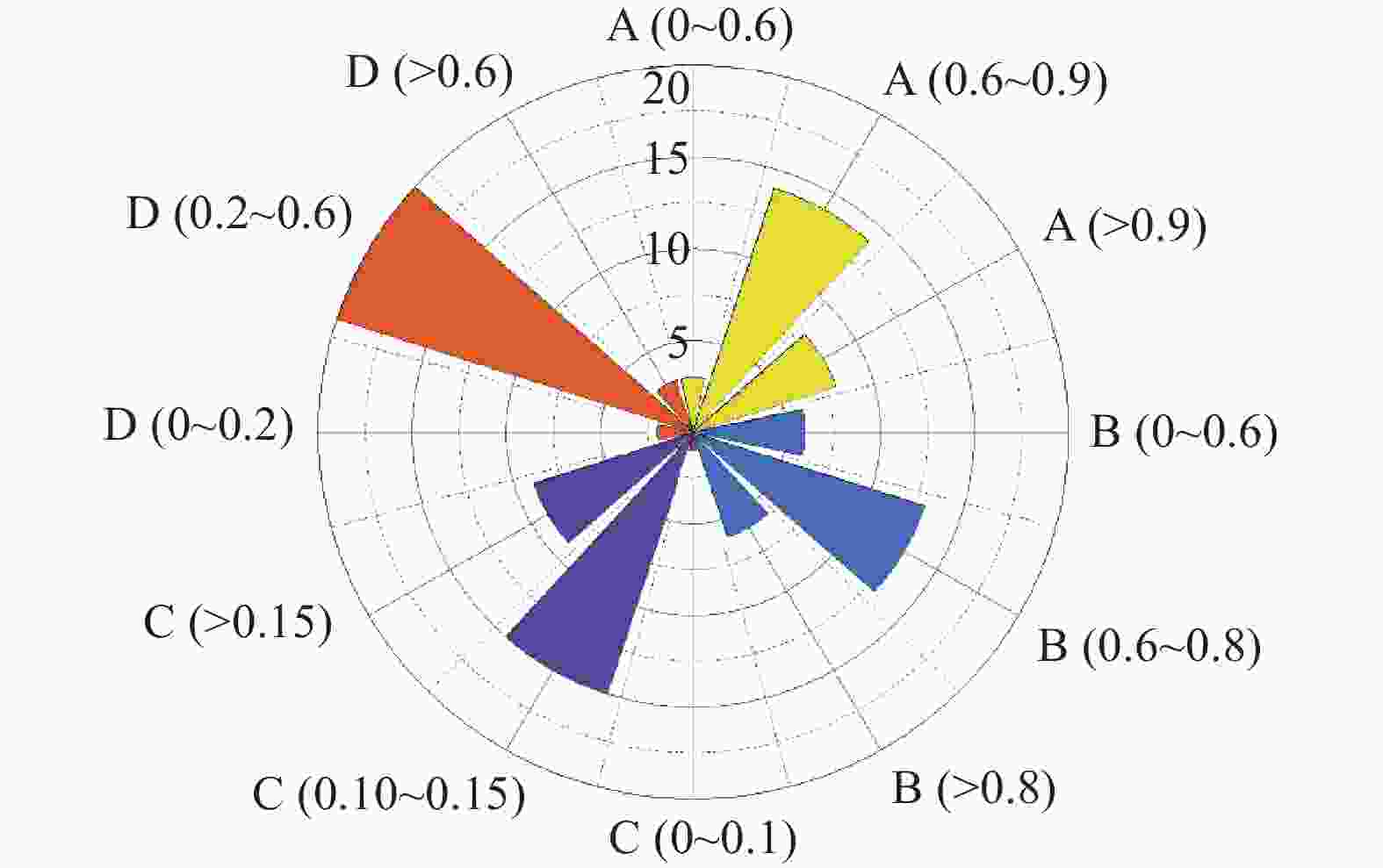
浆液 A B C D ԑ/% g/m R/m φ/(°) Z0/m H/m 原配比 1.21 0.71 0.13 0.83 7.08 0.048 3.305 32 21.4 24.3 本文最优配比 0.60 0.87 0.25 0.60 3.99 0.027 1 盾构隧道同步注浆材料配比案例统计
1. Case statistics of synchronous grouting material proportioning in shield tunnels
序号 项目名称 水泥/kg 粉煤灰/kg 膨润土/kg 砂/kg 水/kg 粉灰比 膨水比 水胶比 胶砂比 1 武汉长江隧道 100 312 25.5 814 288 3.12 0.09 0.70 0.51 2 武汉地铁3号线王家湾站—宗关站 120 460 50 760 350 3.83 0.14 0.60 0.76 3 西安地铁4号线15标 110 395 55 787 512 3.59 0.11 1.01 0.64 4 莞惠城际轨道交通 90 450 100 670 400 5.00 0.25 0.74 0.81 5 狮子洋隧道 150 430 50 750 344 2.87 0.15 0.59 0.77 6 哈尔滨地铁2号线一期工程 130 300 30 250 290 2.31 0.10 0.67 1.72 7 广佛地铁一期工程 9 23 3 44 214 2.56 0.13 0.65 0.73 8 郑州轨道交通4号线土建01标 195 340 106 840 475 1.74 0.22 0.89 0.64 9 太原地铁2号线学府街站—长风街站 180 350 60 750 450 1.94 0.13 0.85 0.71 10 长沙轨道交通1号线汽车北站—开福区政府站 300 245 65 750 405 0.82 0.16 0.74 0.73 11 广州地铁7号线谢村站—钟村站 120 200 200 360 400 1.67 0.50 1.25 0.89 12 常德沅江隧道 110 280 50 935 320 2.55 0.16 0.82 0.42 13 成都地铁8号线一期工程 200 450 150 800 500 2.25 0.30 0.77 0.81 14 上海地铁11号线13标 100 360 20 400 210 3.60 0.10 0.46 1.15 15 武汉地铁8号线一期工程 43 222 68 1233 401 5.16 0.17 1.51 0.21 16 深圳地铁10号线华为站—岗头站 130 300 50 630 380 2.31 0.13 0.88 0.68 17 沈阳地铁10号线理工大学站—张沙布站 170 500 60 800 420 2.94 0.14 0.63 0.84 18 广州地铁2号线越秀公园站—三元里站 80 421 56 779 463 5.26 0.12 0.92 0.64 19 沈阳地铁1号线洪湖北街站—重工街站 210 315 84 1180 580 1.50 0.14 1.10 0.44 20 深圳地铁9号线9104-3标 160 314 56 779 446 1.96 0.13 0.94 0.61 21 南京宁高城际轨道交通禄口新城南站—铜山站 120 360 120 700 500 3.00 0.24 1.04 0.69 22 长沙轨道交通2号线橘子洲站—湘江中路站 210 315 84 1180 294 1.50 0.29 0.56 0.44 23 成都地铁2号线东广场站—东洪路站 160 300 65 780 423 1.88 0.15 0.92 0.59 24 大连地铁2号线201标 140 381 55 820 460 2.72 0.12 0.88 0.64 25 天津轨道交通6号线西站站—河北大街站 200 380 55 930 460 1.90 0.12 0.79 0.62 -
[1] 《中国公路学报》编辑部. 中国交通隧道工程学术研究综述·2022[J]. 中国公路学报, 2022, 35(4): 1-40. (Editorial Department of China Journal of Highway and Transport. Review on China's traffic tunnel engineering research: 2022[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022, 35(4): 1-40. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2022.04.001Editorial Department of China Journal of Highway and Transport. Review on China's traffic tunnel engineering research: 2022[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022, 35(4): 1-40. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2022.04.001 [2] LIU W, LIANG J X, XU T. Tunnelling-induced ground deformation subjected to the behavior of tail grouting materials[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2023, 140: 105253. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2023.105253 [3] 魏广造, 王余德, 李俊青, 等. 合肥地铁盾构施工浆液配比优化试验研究[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2015, 35(5): 611-616. (WEI G Z, WANG Y D, LI J Q, et al. Synchronous grouting material optimization of the shield construction in Hefei subway[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2015, 35(5): 611-616. (in Chinese)WEI G Z, WANG Y D, LI J Q, et al. Synchronous grouting material optimization of the shield construction in Hefei subway[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2015, 35(5): 611-616. (in Chinese) [4] 李培楠, 英 旭, 石 来, 等. 基于CFD的盾构同步注浆填充扩散运动力学分析[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2021, 17(S1): 126-132. (LI P N, YING X, SHI L, et al. Hydrodynamics analysis on fill diffusion in shield synchronous grouting based on CFD[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2021, 17(S1): 126-132. (in Chinese)LI P N, YING X, SHI L, et al. Hydrodynamics analysis on fill diffusion in shield synchronous grouting based on CFD[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2021, 17(S1): 126-132. (in Chinese) [5] 李 涛, 王颖轶, 黄醒春. 基于冲击映像法盾构同步注浆效果检测与评价[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2022, 18(6): 1962-1967,1978. (LI T, WANG Y Y, HUANG X C. Detection and evaluation of shield synchronous grouting effect based on impact image method[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2022, 18(6): 1962-1967,1978. (in Chinese)LI T, WANG Y Y, HUANG X C. Detection and evaluation of shield synchronous grouting effect based on impact image method[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2022, 18(6): 1962-1967,1978. (in Chinese) [6] 梁精华. 盾构隧道壁后注浆材料配比优化及浆体变形特性研究[D]. 南京: 河海大学, 2006. (LIANG J H. Study on the proportion of backfill-grouting materials and grout deformation properties of shield tunnel[D]. Nanjing: Hohai University, 2006. (in Chinese)LIANG J H. Study on the proportion of backfill-grouting materials and grout deformation properties of shield tunnel[D]. Nanjing: Hohai University, 2006. (in Chinese) [7] 梁小英. 富水地层盾构施工同步注浆材料性能及配合比设计研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2009. (LIANG X Y. Study of material performance and material ratio design in synchronized grouting technology for shield tunneling on watery strata[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2009. (in Chinese)LIANG X Y. Study of material performance and material ratio design in synchronized grouting technology for shield tunneling on watery strata[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2009. (in Chinese) [8] 刘 玮, 谢佳伟, 赖友君, 等. 富水复合砂层大直径盾构掘进同步注浆性能配比试验研究[J]. 铁道标准设计, 2018, 62(4): 141-145. (LIU W, XIE J W, LAI Y J, et al. Experimental study on the optimization of mixture ratio of synchronous grouting for large-diameter shield tunneling in water-rich sandy ground[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2018, 62(4): 141-145. (in Chinese)LIU W, XIE J W, LAI Y J, et al. Experimental study on the optimization of mixture ratio of synchronous grouting for large-diameter shield tunneling in water-rich sandy ground[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2018, 62(4): 141-145. (in Chinese) [9] 张 箭, 金俊杰, 丰土根, 等. 土压平衡盾构渣土浆液配比优化研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2023, 45(4): 748-757. (ZHANG J, JIN J J, FENG T G, et al. Optimization of mixture ratio of muck grout by earth pressure balance shield machine[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2023, 45(4): 748-757. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE20220024ZHANG J, JIN J J, FENG T G, et al. Optimization of mixture ratio of muck grout by earth pressure balance shield machine[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2023, 45(4): 748-757. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE20220024 [10] 赵一民. 基于沥青集料粉尘的同步注浆浆液性能及地表沉降控制研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2022. (ZHAO Y M. Research on performance of synchronous grouting slurry and control of surface settlement based on Asphalt Aggregate Dust[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong University, 2022. (in Chinese)ZHAO Y M. Research on performance of synchronous grouting slurry and control of surface settlement based on Asphalt Aggregate Dust[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong University, 2022. (in Chinese) [11] 李立涛, 高 谦, 杨志强, 等. 矿用充填胶凝材料激发剂配比智能优化决策[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2019, 51(10): 137-143. (LI L T, GAO Q, YANG Z Q, et al. Intelligent optimization for the activator proportion of filling cementitions material[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019, 51(10): 137-143. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.201806028LI L T, GAO Q, YANG Z Q, et al. Intelligent optimization for the activator proportion of filling cementitions material[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019, 51(10): 137-143. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.201806028 [12] 韩 斌, 吉 坤, 胡亚飞, 等. ANN-PSO-GA模型在湿喷混凝土强度预测及配合比优化中的应用[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2021, 38(3): 584-591. (HAN B, JI K, HU Y F, et al. Application of ANN-PSO-GA model in UCS prediction and mix proportion optimization of wet shotcrete[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2021, 38(3): 584-591. (in Chinese)HAN B, JI K, HU Y F, et al. Application of ANN-PSO-GA model in UCS prediction and mix proportion optimization of wet shotcrete[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2021, 38(3): 584-591. (in Chinese) [13] 肖文丰, 陈建宏, 陈 毅, 等. 基于神经网络与遗传算法的多目标充填料浆配比优化[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2019, 27(4): 581-588. (XIAO W F, CHEN J H, CHEN Y, et al. Optimization of multi-objective filling slurry ratio based on neural network and genetic algorithm[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2019, 27(4): 581-588. (in Chinese)XIAO W F, CHEN J H, CHEN Y, et al. Optimization of multi-objective filling slurry ratio based on neural network and genetic algorithm[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2019, 27(4): 581-588. (in Chinese) [14] 陈 阳, 刘 文, 刘文黎, 等. 盾构法隧道开挖面稳定性下的多目标优化研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2024, 24(18): 7882-7888. (CHEN Y, LIU W, LIU W L, et al. Multi-objective optimization based on the stability of shield tunnel excavation surface[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2024, 24(18): 7882-7888. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12404/j.issn.1671-1815.2303494CHEN Y, LIU W, LIU W L, et al. Multi-objective optimization based on the stability of shield tunnel excavation surface[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2024, 24(18): 7882-7888. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12404/j.issn.1671-1815.2303494 [15] 吴贤国, 刘 俊, 曹 源, 等. 基于CatBoost-NSGA-Ⅲ算法的盾构姿态预测与优化[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(8): 69-77. (WU X G, LIU J, CAO Y, et al. Shield attitude prediction and optimization based on CatBoost-NSGA-Ⅲ algorithm[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(8): 69-77. (in Chinese)WU X G, LIU J, CAO Y, et al. Shield attitude prediction and optimization based on CatBoost-NSGA-Ⅲ algorithm[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(8): 69-77. (in Chinese) [16] 任秋兵, 李文伟, 李明超, 等. 水工高性能混凝土配合比多目标智能优化设计与分析方法[J]. 水利学报, 2022, 53(1): 98-108. (REN Q B, LI W W, LI M C, et al. Multi-objective intelligent optimization design and analysis method for mix proportion of hydraulic high performance concrete[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2022, 53(1): 98-108. (in Chinese)REN Q B, LI W W, LI M C, et al. Multi-objective intelligent optimization design and analysis method for mix proportion of hydraulic high performance concrete[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2022, 53(1): 98-108. (in Chinese) [17] 叶倩琳, 王万良, 王 铮. 多目标粒子群优化算法及其应用研究综述[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2024, 58(6): 1107-1120,1232. (YE Q L, WANG W L, WANG Z. Survey of multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithms and their applications[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2024, 58(6): 1107-1120,1232. (in Chinese)YE Q L, WANG W L, WANG Z. Survey of multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithms and their applications[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2024, 58(6): 1107-1120,1232. (in Chinese) [18] 阮 雷. 高渗透富水地层盾构同步注浆抗水分散机理研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2019. (RUAN L. Study on mechanism of synchronous grouting anti-washout property of shield in high permeability water-rich formation[D] Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019. (in Chinese)RUAN L. Study on mechanism of synchronous grouting anti-washout property of shield in high permeability water-rich formation[D] Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019. (in Chinese) [19] 吴昌胜. 大直径盾构隧道施工引起的地层变形研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2018. (WU C S. Study on the ground deformation induced by large diameter shield tunnelling construction[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2018. (in Chinese)WU C S. Study on the ground deformation induced by large diameter shield tunnelling construction[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2018. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: