Horizontal bearing capacity of piles and effects of engineering treatments considering strain hardening of soil on thick silt nuclear power site
-
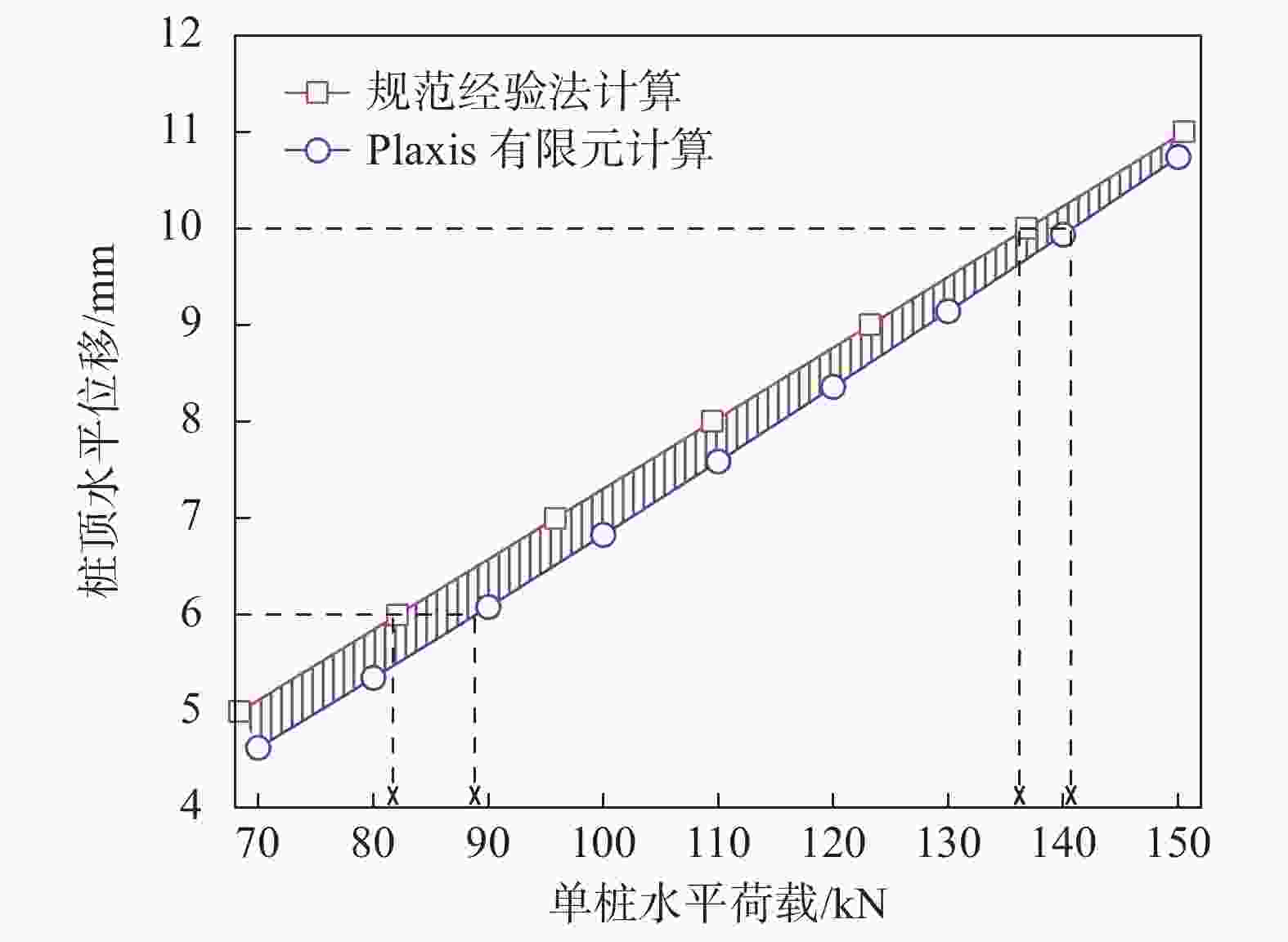
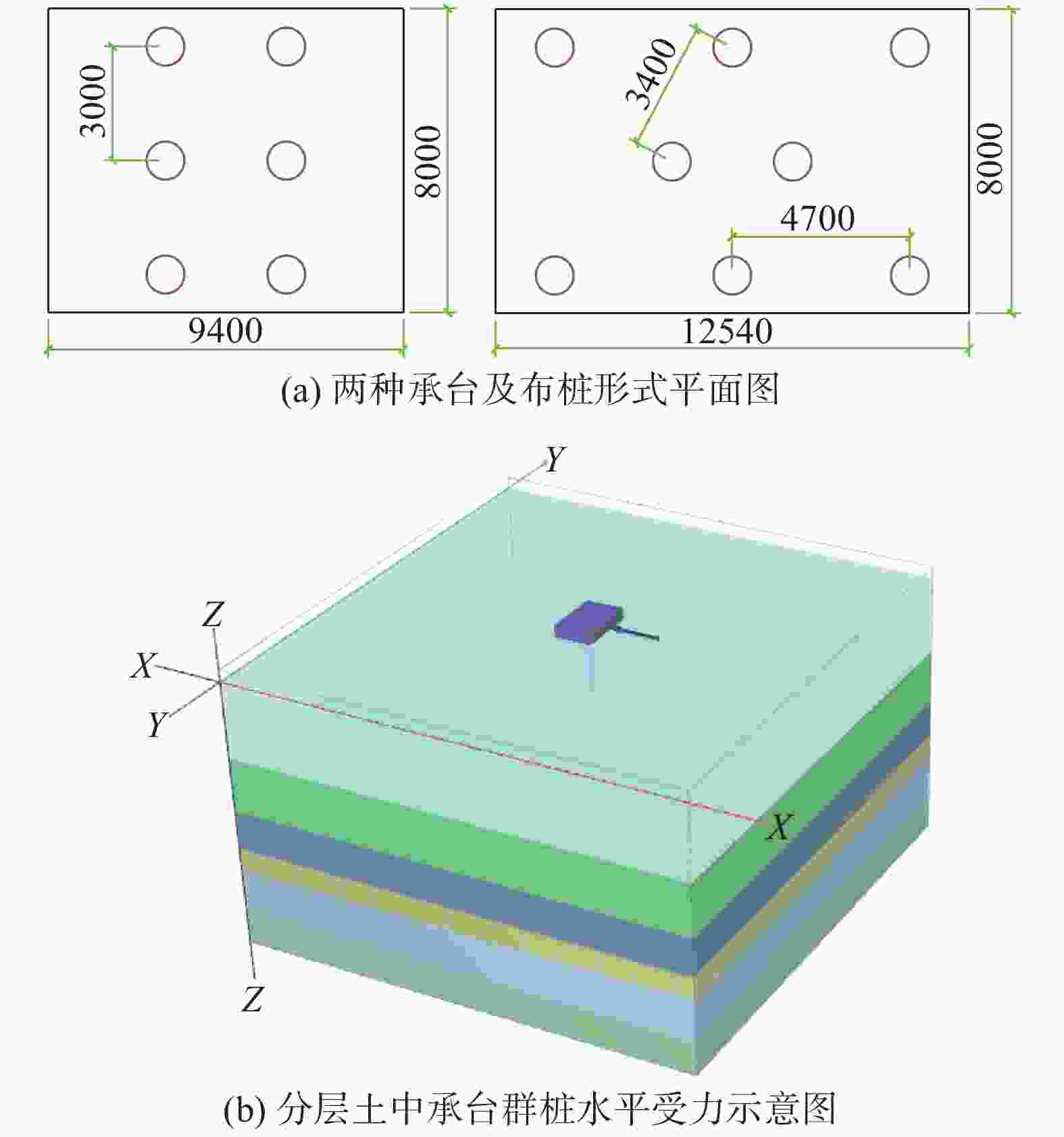
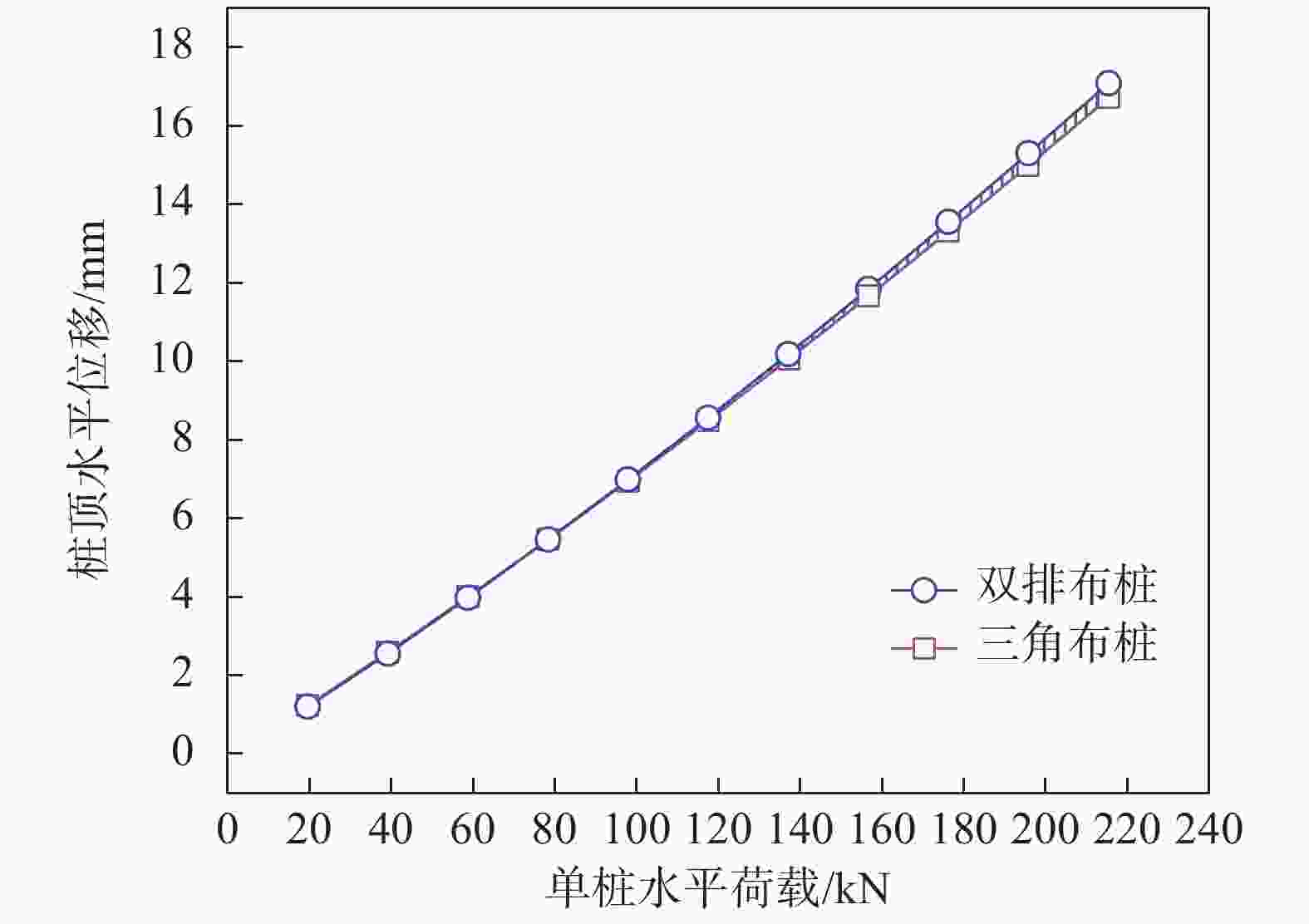
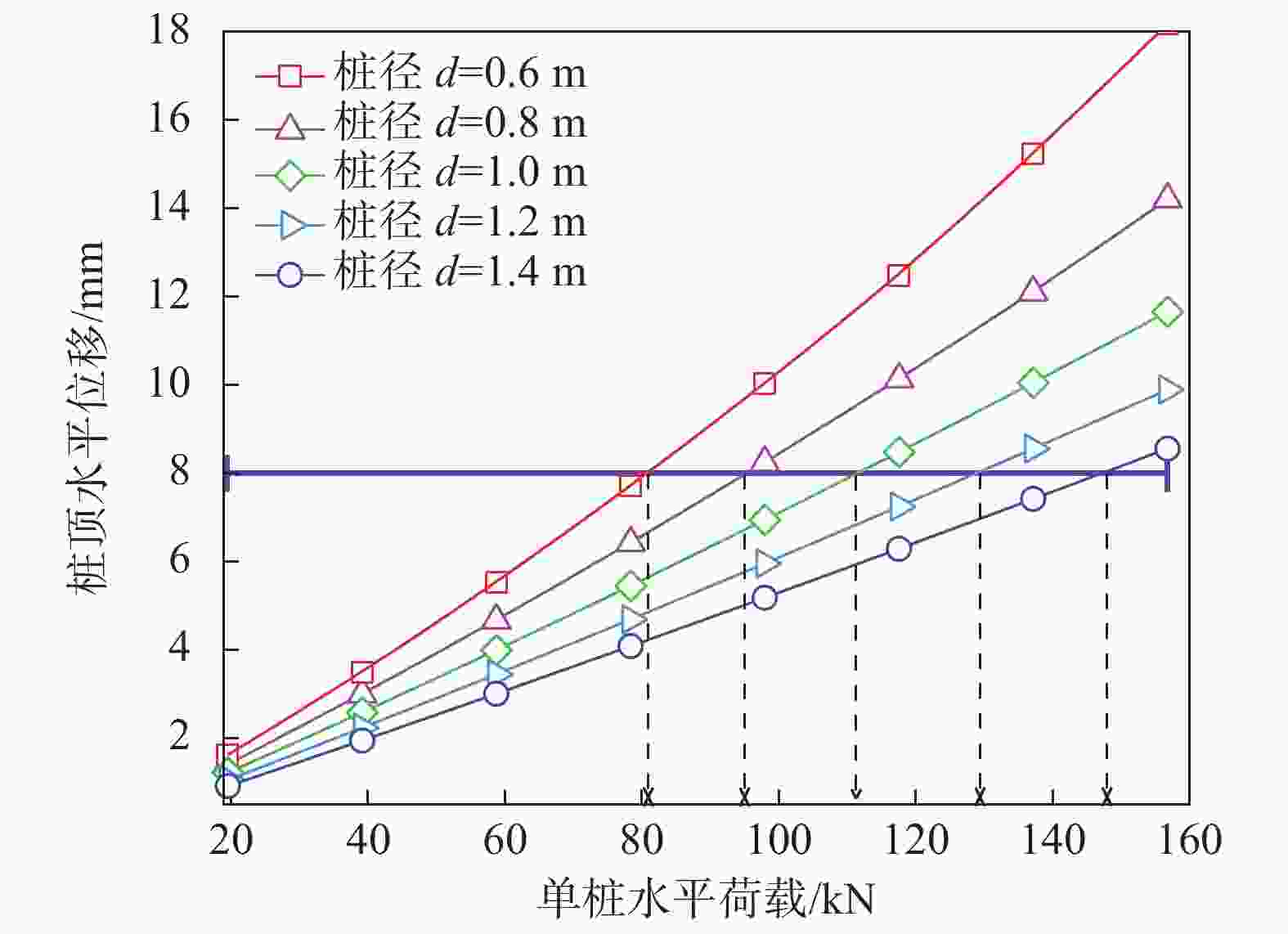
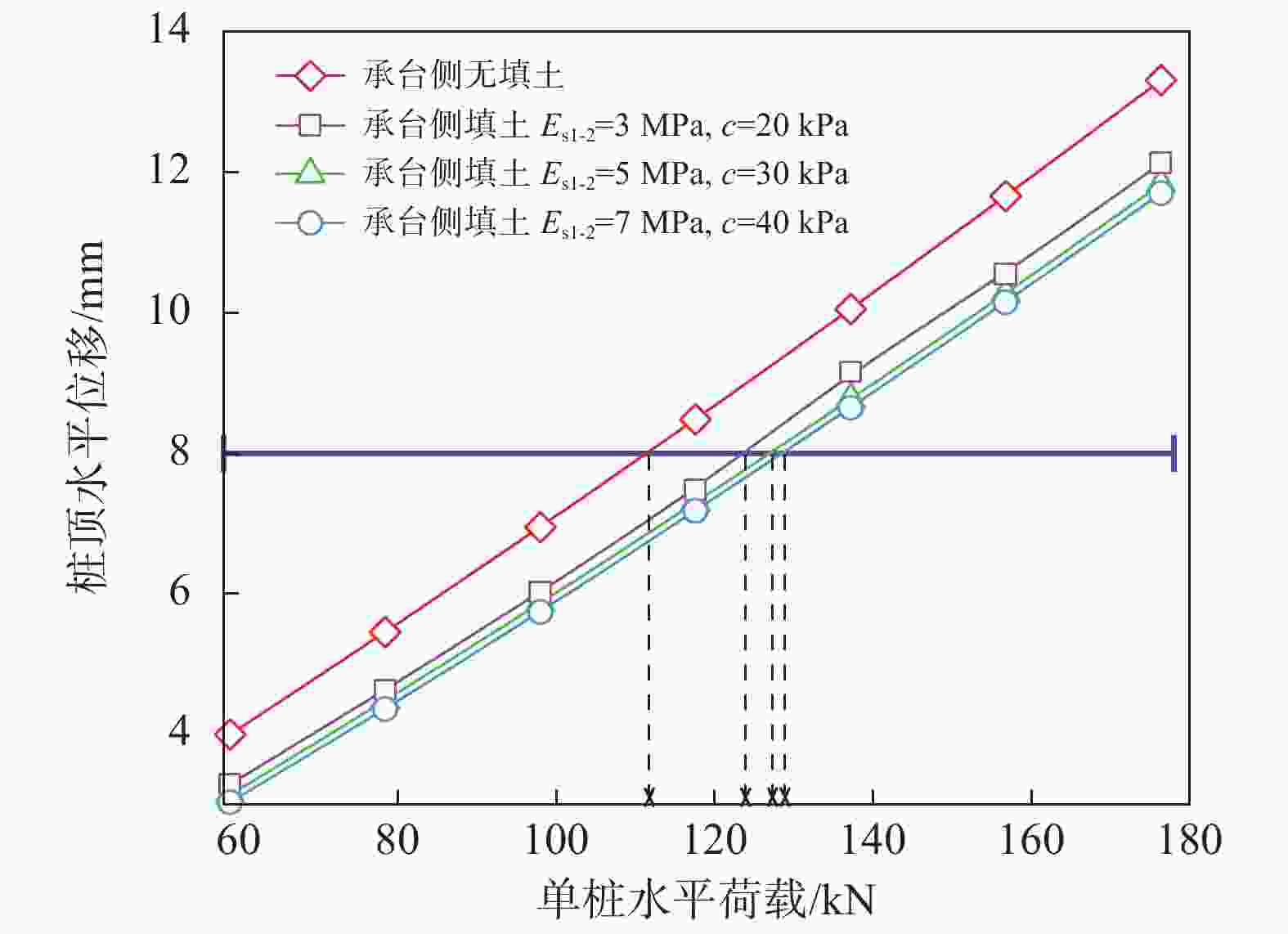
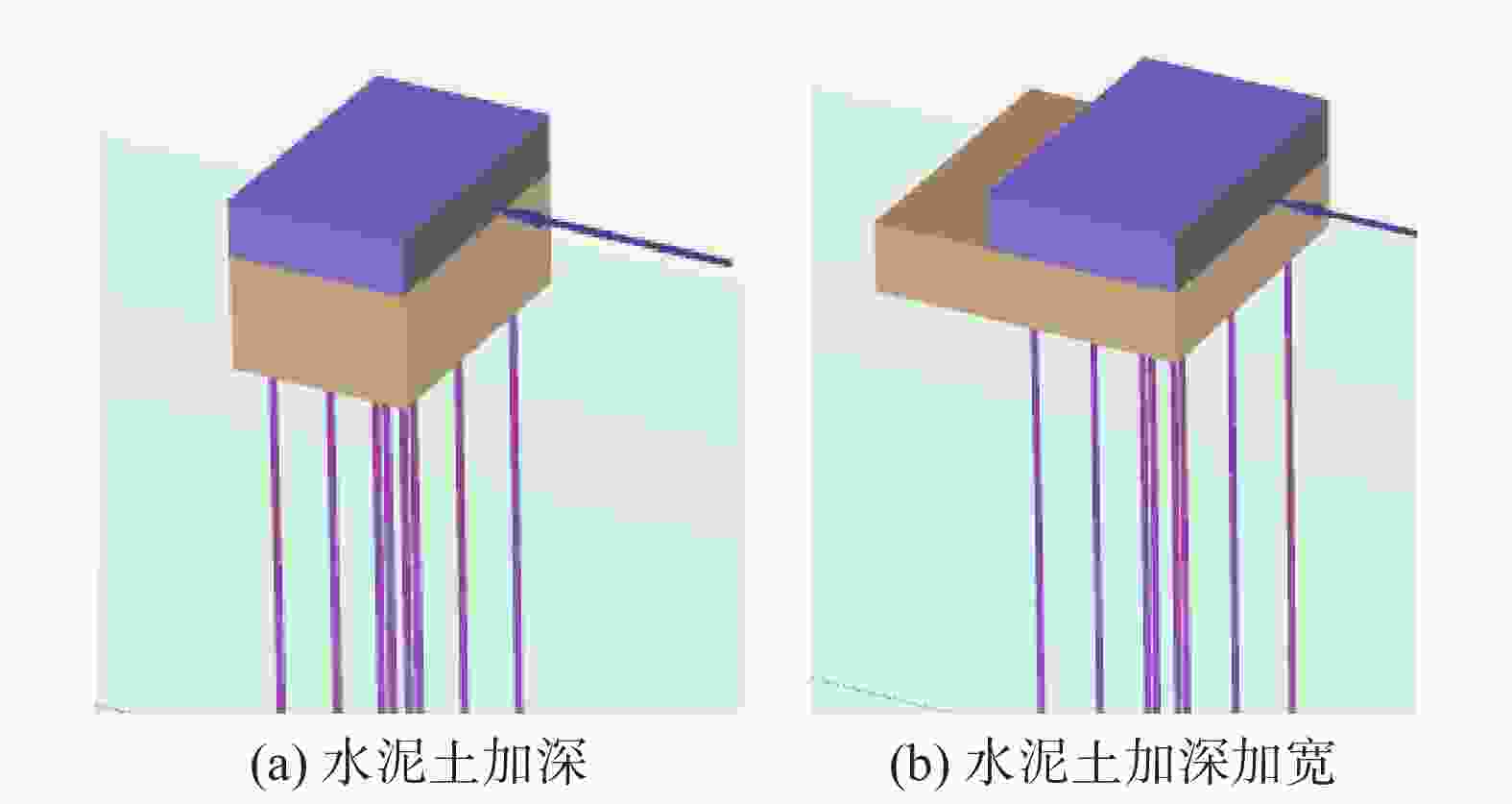
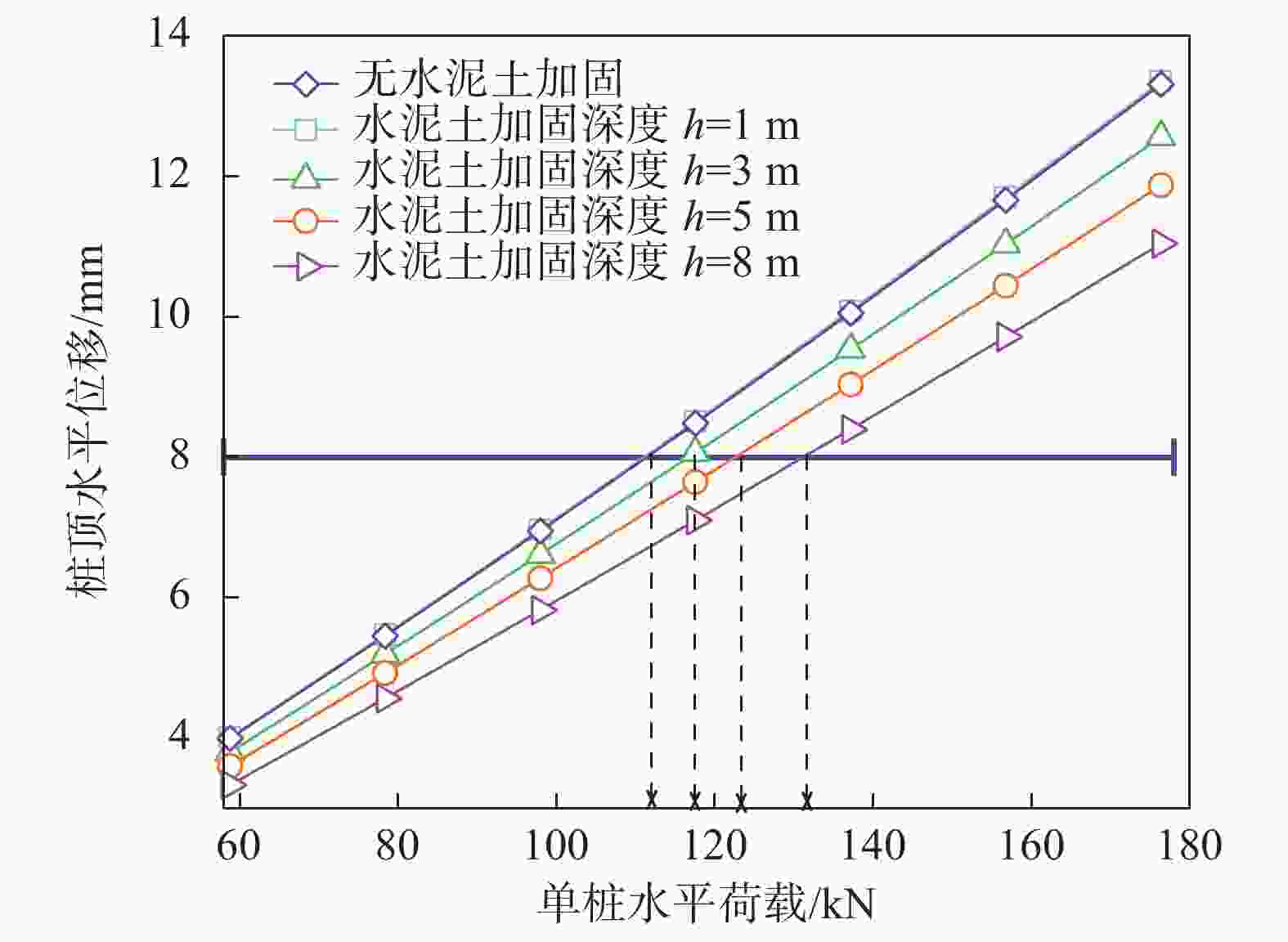
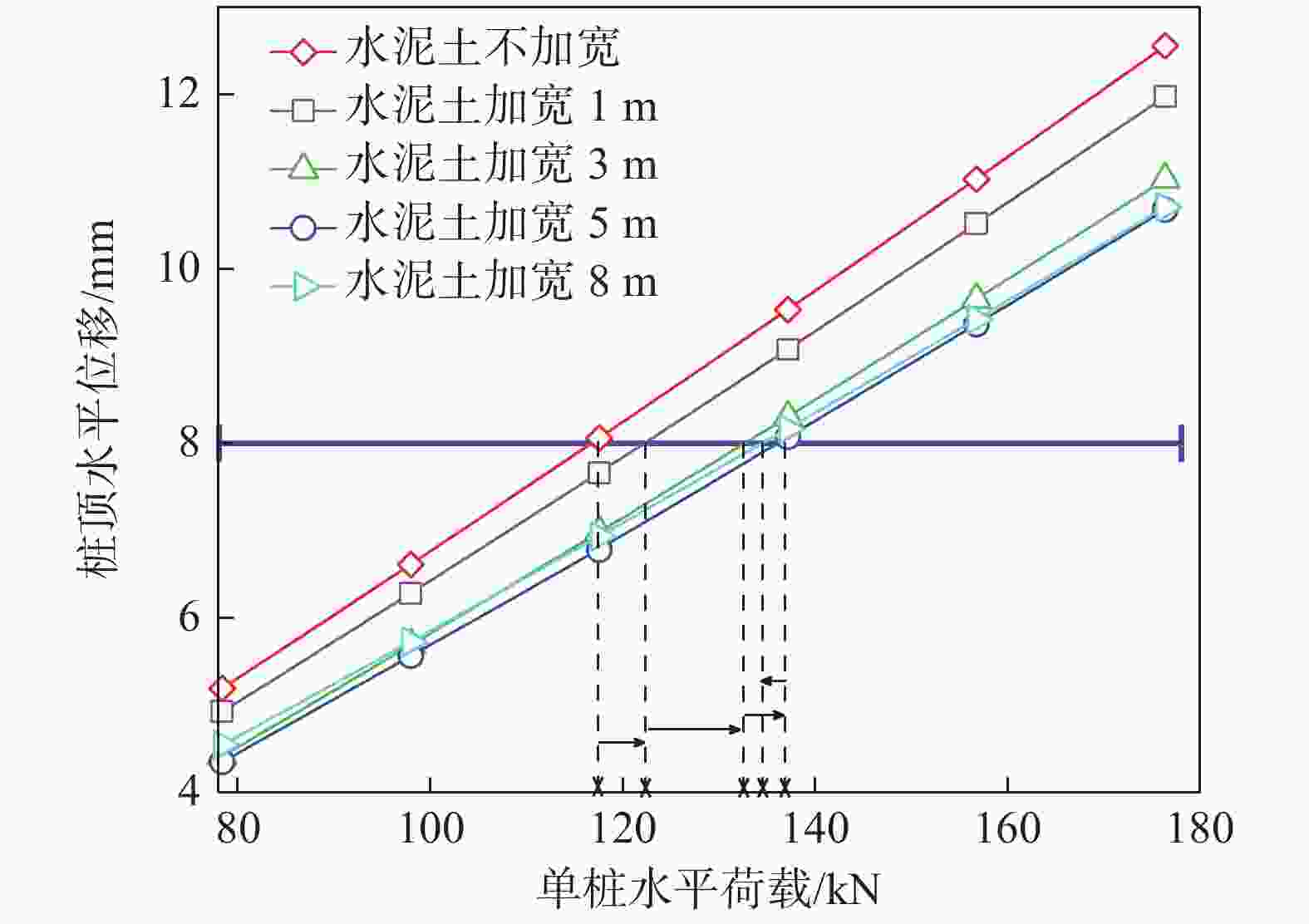
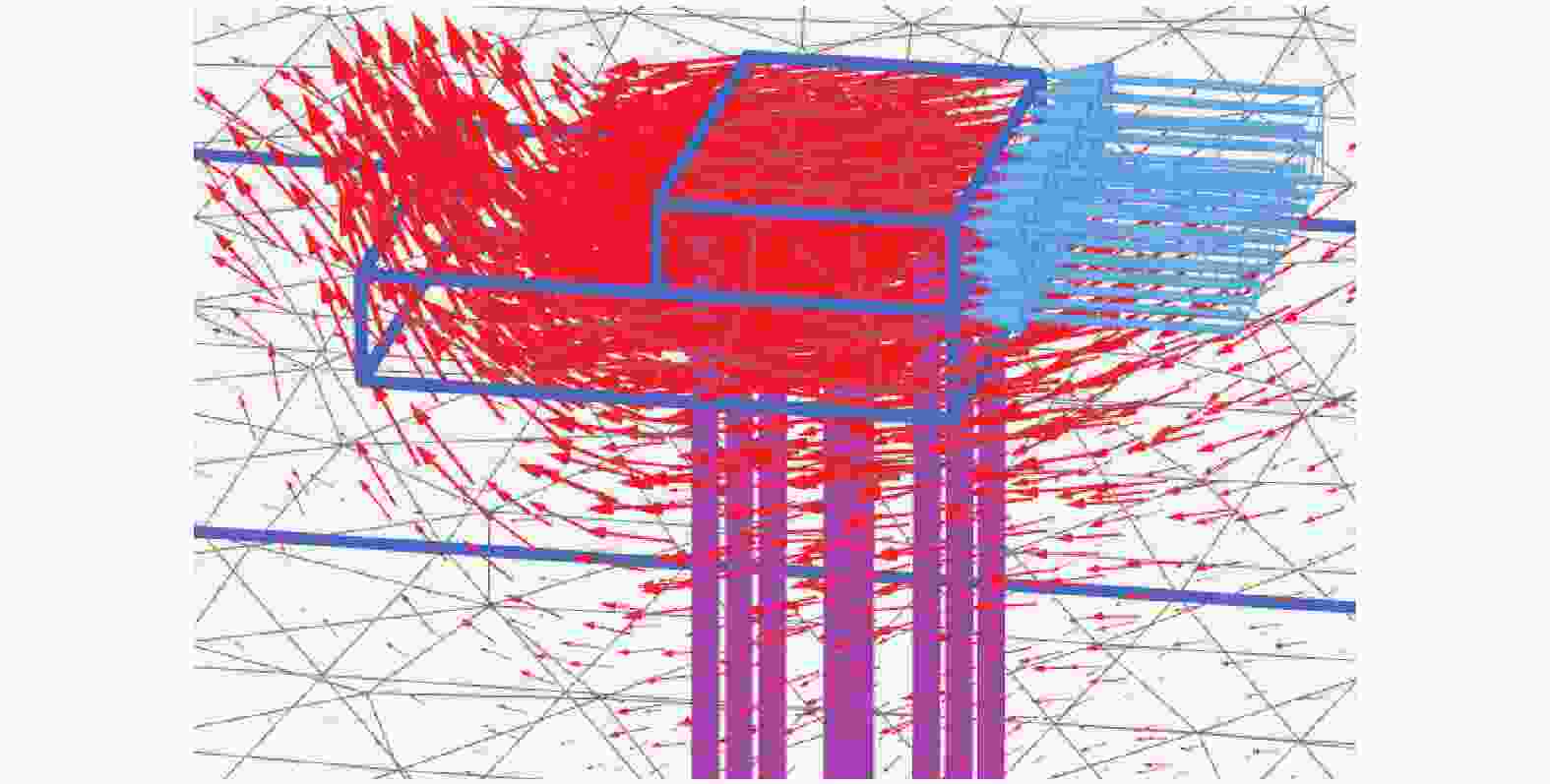
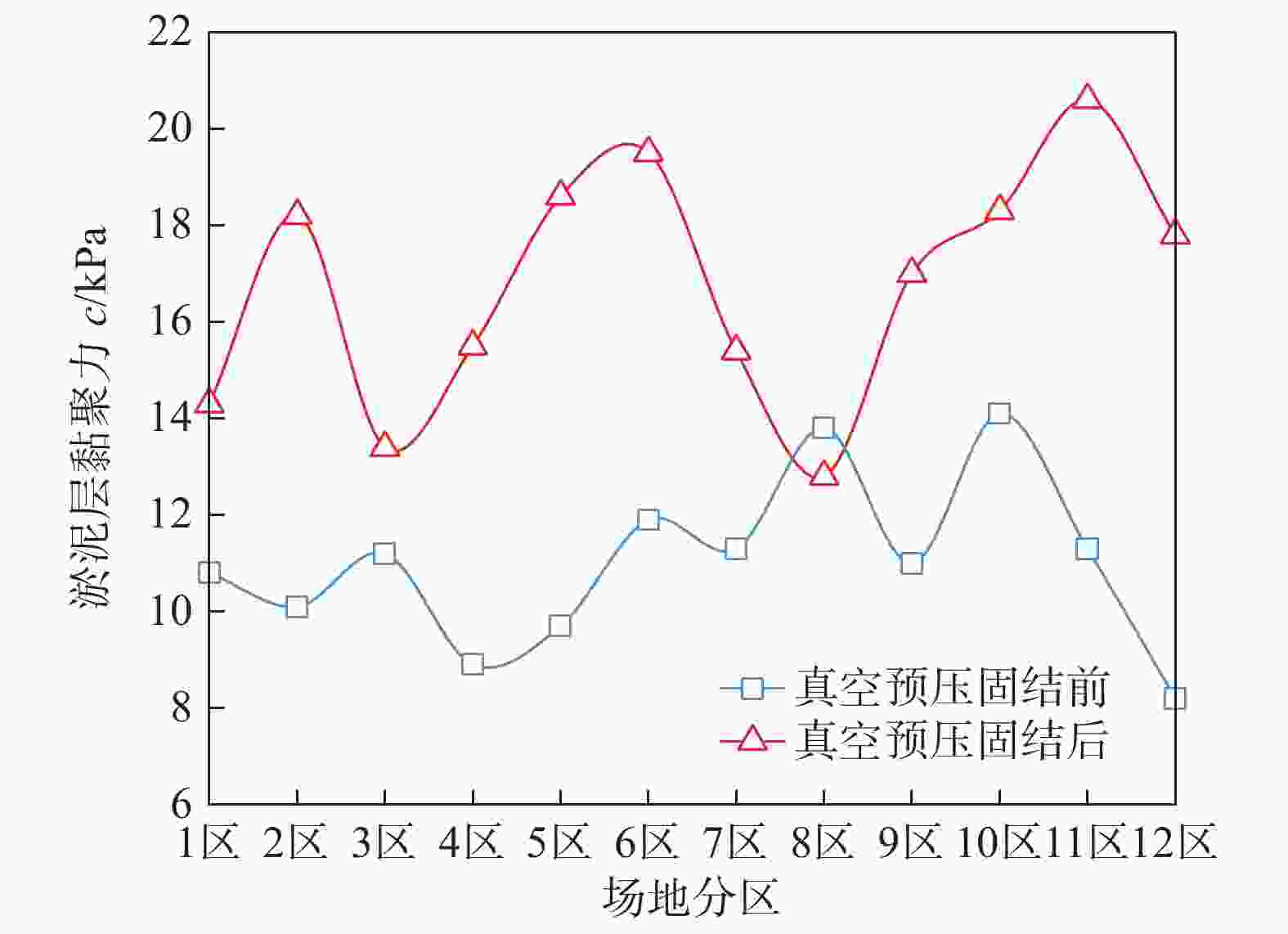
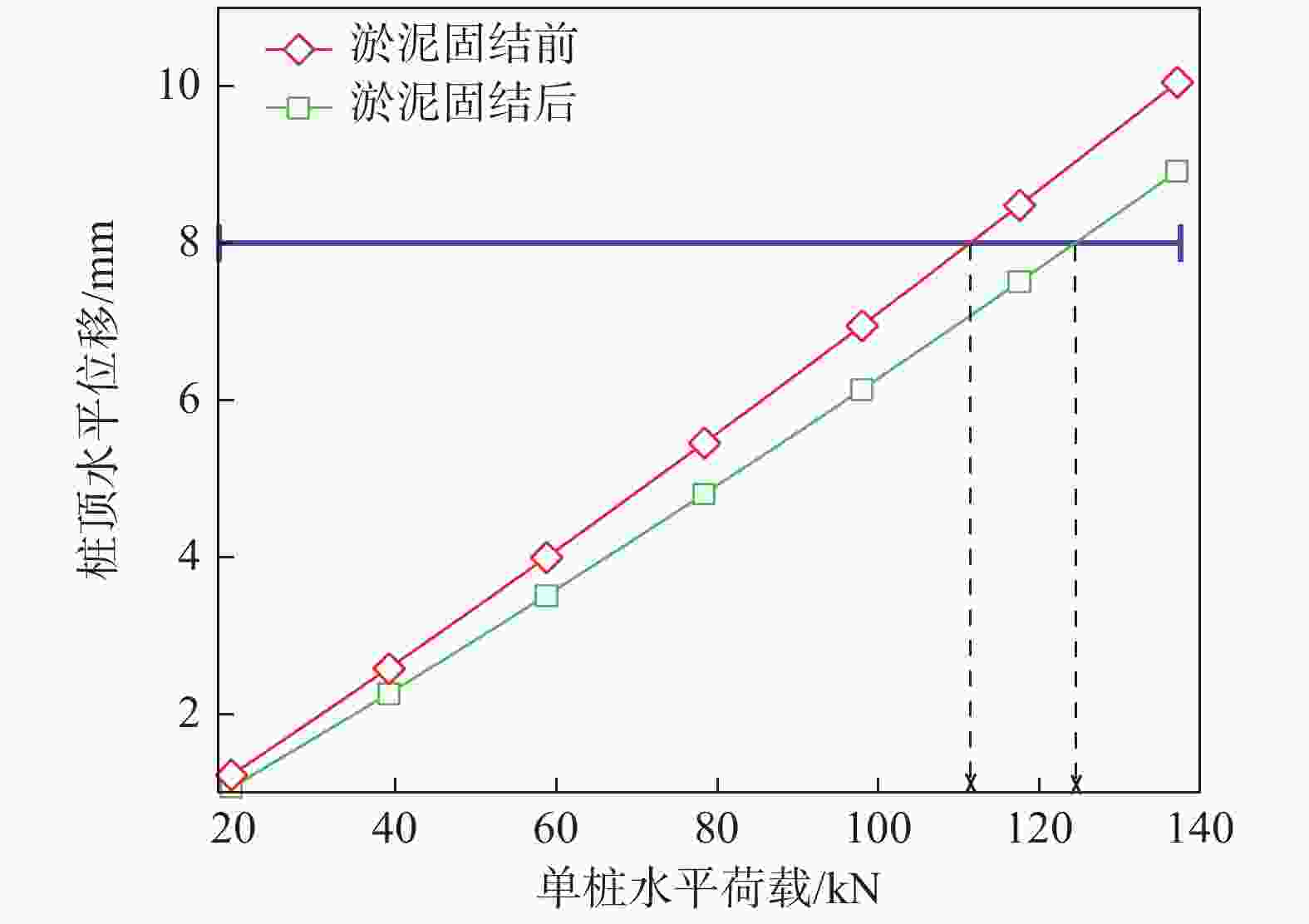
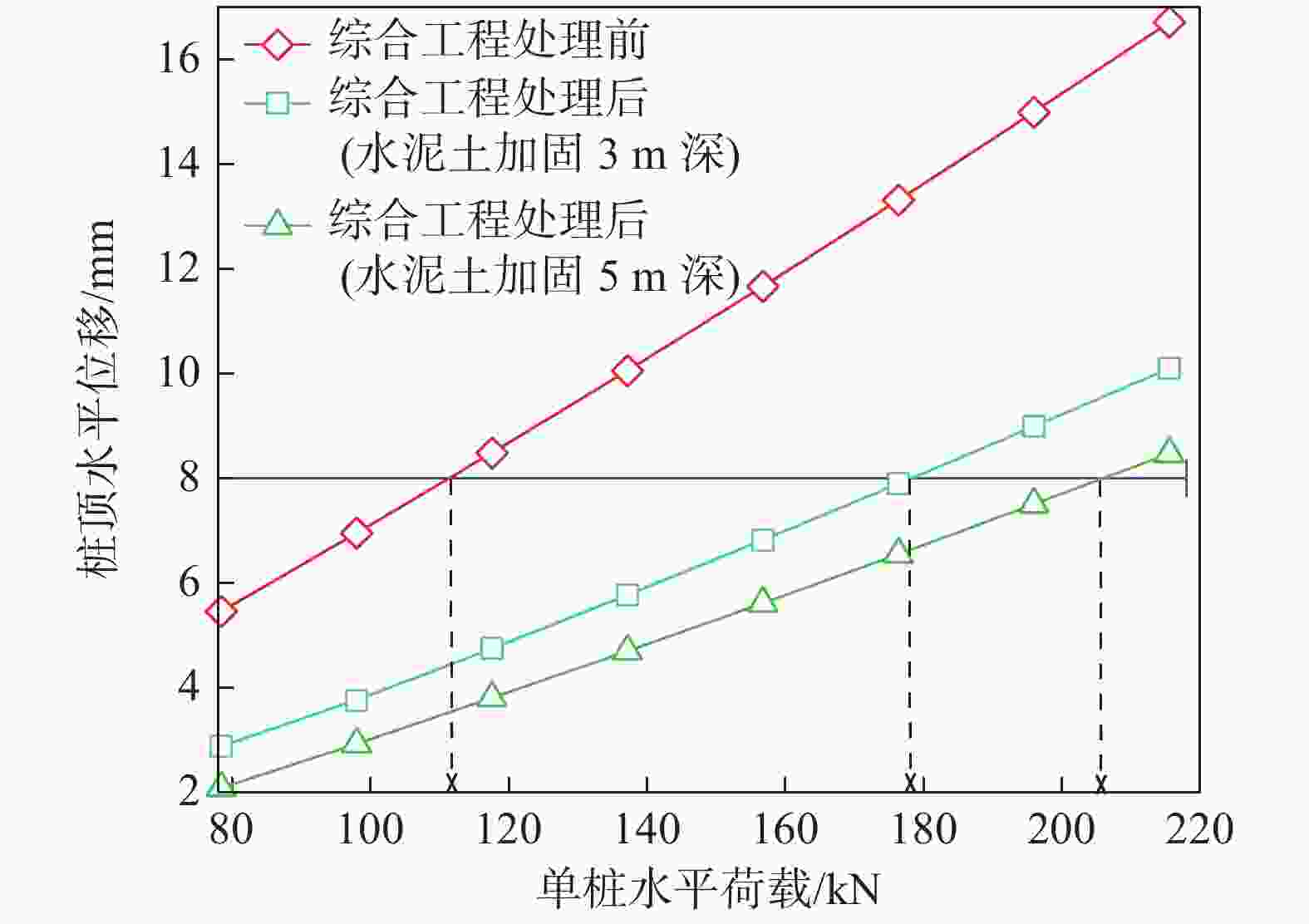
摘要: 桩基在非基岩区核电厂相关建筑中的应用日益广泛,其水平承载力的确定与优化问题十分重要。考虑土体硬化本构模型并基于勘察资料确定合理取参方法,围绕核电厂工况构建水平承载桩基有限元模型,通过对比模型计算结果与规范经验法计算结果验证了模型的合理性,应用该模型重点分析了各类工程处理措施对桩基水平承载力的影响,研究成果表明:均匀布桩情况下,布桩形式对桩基水平承载力的影响很小,而桩径与桩基水平承载力直接相关;一般压实承台侧土可将桩基水平承载力提升10%以上,但随压实度增加后进一步提升的效果不明显;承台下进行局部土体加固的深度、宽度及加固土体刚度均会显著影响桩基水平承载力,但加固区宽度并非越宽越好;上部淤泥层预固结处理后,可将桩基水平承载力提升10%以上。另外,通过施加以上各类综合处理措施,可将桩基水平承载力提升85%以上。相关成果可为具体工况下桩基水平承载力的预测及优化提供方法路径,为工程前期阶段方案设计提供参考。Abstract: Under the current development of nuclear power plants in thick soil area, the application of piles is increasing while the determination and optimization of their horizontal bearing capacity comes to be important issues. A reasonable method was provided to determine the parameters of strain hardening model of soil based on survey data, and the finite element model was established to analyze horizontal bearing piles under nuclear power plants condition. The model was compared with the empirical method suggested by standard to verify its rationality. The impact of various engineering treatment measures on the horizontal bearing capacity of piles was analyzed in detail. The results show that as uniformly arranged, the pile arrangement form has little effect on the horizontal bearing capacity of pile group, while the pile diameter is directly related to this horizontal bearing capacity. Generally compacted soil on the side of the pile cap can increase the horizontal bearing capacity of piles by more than 10%, but the effect of further increasing compaction is not significant. The depth, width, and stiffness of the locally reinforced soil under the pile cap will significantly affect the horizontal bearing capacity of piles, but the width is not necessarily the wider the better. With the pre-consolidation treatment of the upper soft caly layer, the horizontal bearing capacity of the piles can be increased by more than 10%. Besides, by implementing the comprehensive treatment measures above, the horizontal bearing capacity of the piles can be increased by more than 85%. This study can provide a method for predicting and optimizing the horizontal bearing capacity of piles under specific conditions, and the results can provide references for the foundation design at an early stage of various engineering.
-
表 1 某核电项目勘察资料测定各土层参数值
Table 1. Soil parameters determined from site investigation for a nuclear power project
主要土层 土层厚
/m含水率
w/%天然密度$ {\rho }_{0} $
/(g·cm−3)土粒比重
Gs孔隙比
e塑性指数Ip 液性指数IL CU试验
总黏聚力c/kPaCU试验
总摩擦角φ/(°)压缩模量
Es1-2/kPa②淤泥层 16.4 60.8 1.62 2.76 1.744 24.31 1.35 10.08 11.07 1714 ③1粉质黏土 11.5 26.8 1.98 2.74 0.756 16.96 0.234 35.59 13.76 7047 ④粉质黏土 8.3 29.3 1.92 2.74 0.799 16.89 0.424 37.57 12.19 6906 ⑤2粉砂 4.7 1.90 2.72 2.00 28.00 11000 ⑥黏土 9.8 37.6 1.85 2.75 1.056 20.40 0.673 36.44 12.27 7590 ⑧黏土 6.81388 23.8 2.01 2.73 0.678 17.09 0.138 51.24 14.41 9766 表 2 有限元模拟各土层HS本构模型参数取值
Table 2. Parameters of the HS constitutive model for each soil layer
主要土层 有效黏聚力$ {c}^{\prime} $/kPa 有效内摩擦角φ'/(°) 剪胀角$ \psi $/ (°) 破坏比Rf $ E_{\rm{oed}}^{\rm{ref}} $/kPa $ E_{50}^{\rm{ref}} $/kPa $ E_{\rm{ur}}^{\rm{ref}} $/kPa $ {p}^{\rm{ref}} $/kPa $ {\nu }_{\rm{vr}} $ k0 m1 ②淤泥层 11.78 14.53 0 0.5 1542.6 1388.3 8330.0 100 0.2 0.749 0.8 ③1粉质黏土 43.73 16 0 0.95 6342.3 6976.5 27906.1 100 0.2 0.724 0.8 ④粉质黏土 44.5 14.79 0 0.95 6215.4 6836.9 27347.8 100 0.2 0.745 0.8 ⑤2粉砂 2.00 28.00 0 0.95 11000 12047 75900 100 0.2 0.531 0.6 ⑥黏土 39.94 15.55 0 0.90 6831.0 8197.2 24591.6 100 0.2 0.732 0.9 ⑧黏土 54.42 17.48 0 0.95 8789.4 10547.3 31641.8 100 0.2 0.699 0.9 回填土* 20~40 15 0 0.95 0.9Es1-2 1.1$ E_{\rm{oed}}^{\rm{ref}} $ 4$ E_{50}^{\rm{ref}} $ 100 0.2 0.741 0.9 注:*为承台侧回填土,其性质根据回填土类型及施工确定。 表 3 文献中基于试验测试的m1值
Table 3. The m1 value based on experiments in the literature
表 4 桩体实际工程设计值(含淤泥层m值)
Table 4. Engineering design value of the pile (including m value of soft clay layers)
参数 工程设计值 参数 工程设计值 桩径d/m 1 混凝土弹性模量Ec/kPa 3.35×107 配筋率ρ/% 0.968 钢筋弹性模量Es/kPa 2×108 桩长l/m 55 钢筋保护层厚d0/mm 50 淤泥m值/(MN·m–4) 2.5 表 5 综合工程处理措施对应的输入参数值
Table 5. Input parameters corresponding to engineering measures
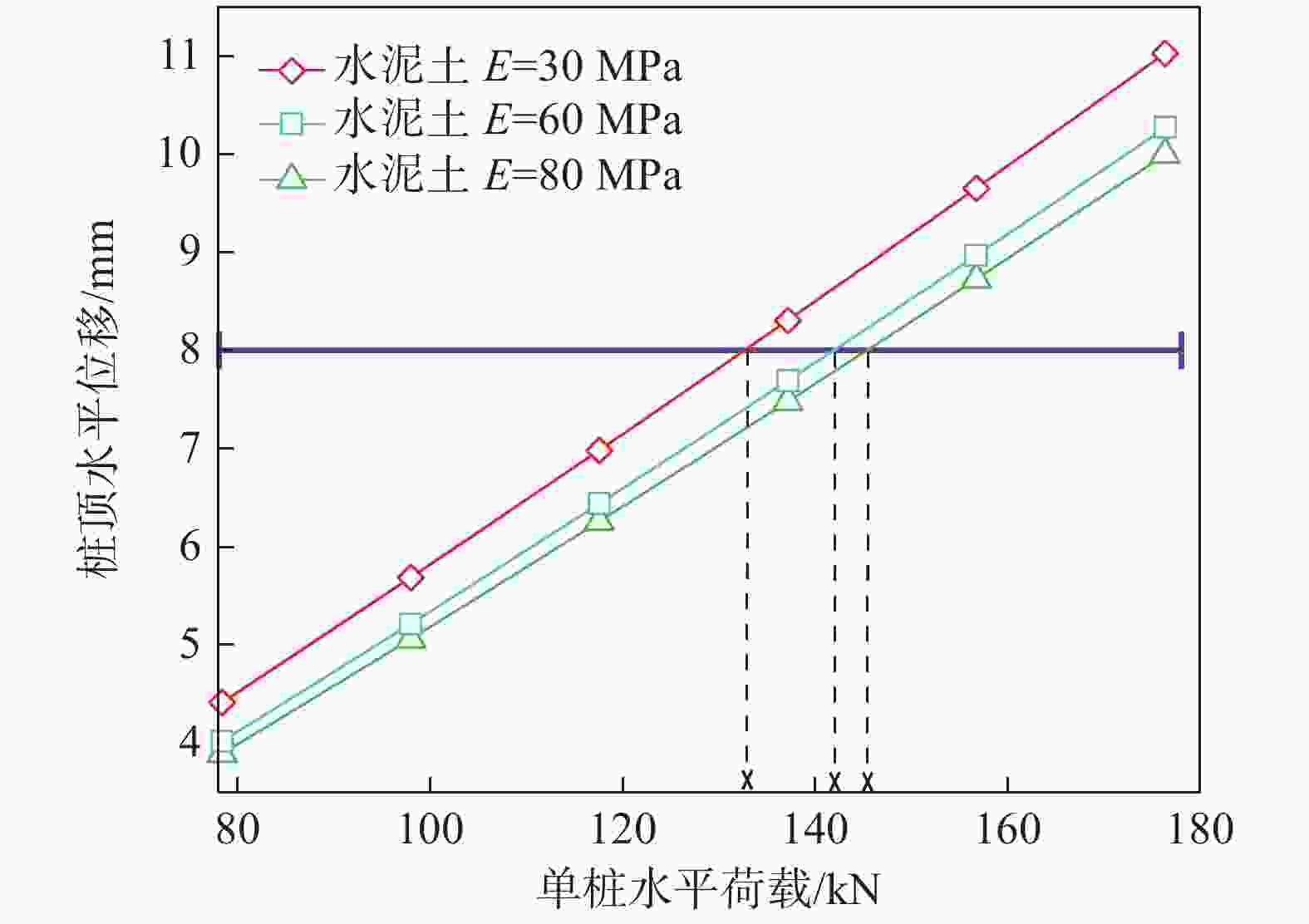
参数 工程设计值 参数 工程设计值 桩径d/m 1 水泥土深度h/m 3/5 承台侧土Es1-2/MPa 7 水泥土加宽d′/m 3 淤泥层预固结 是 水泥土E/MPa 80 -
[1] 侯胜男. 上海地区单桩水平承载力的若干影响因素研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2015, 36(S2): 565-570. (HOU S N. Research on influencing factors of lateral capacity of single pile in Shanghai[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(S2): 565-570. (in Chinese)HOU S N. Research on influencing factors of lateral capacity of single pile in Shanghai[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(S2): 565-570. (in Chinese) [2] 马志涛. 水平荷载下桩基受力特性研究综述[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 34(5): 546-551. (MA Z T. Study on behavior of pile foundation under lateral loading[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2006, 34(5): 546-551. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1980.2006.05.017MA Z T. Study on behavior of pile foundation under lateral loading[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2006, 34(5): 546-551. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1980.2006.05.017 [3] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑桩基技术规范: JGJ 94—2008[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2008. (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Technical code for building pile foundations: JGJ 94—2008[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2008. (in Chinese)Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Technical code for building pile foundations: JGJ 94—2008[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2008. (in Chinese) [4] REESE L C, COX W R, KOOP F D. Analysis of laterally loaded piles in sand[C]//Proceedings of the Sixth Annual Offshore Technology Conference. Houston: OnePetro, 1974: 473-483. [5] MATLOCK H. Correlation for design of laterally loaded piles in soft clay[C]//Proceedings of the Second Annual Offshore Technology Conference. Houston: OnePetro, 1970: 577-594. [6] American Petroleum Institute. Recommended practice for planning, designing and constructing fixed offshore platforms[M]. Washington: American Petroleum Institute, 2000: 65-66. [7] FARO V P, CONSOLI N C, SCHNAID F, et al. Field tests on laterally loaded rigid piles in cement treated soils[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2015, 141(6): 06015003. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001296 [8] TAGHAVI A, MURALEETHARAN K K, MILLER G A, et al. Centrifuge modeling of laterally loaded pile groups in improved soft clay[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2016, 142(4): 04015099. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001443 [9] 黄朝煊, 李俊杰. 置换硬壳层对成层软土中桩基水平承载特性的影响研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(S2): 3472-3482. (HUANG C X, LI J J. Research on the influence of displacing hard shell on the horizontal bearing characteristics of pile foundation in layered soft soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(S2): 3472-3482. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2021.0094HUANG C X, LI J J. Research on the influence of displacing hard shell on the horizontal bearing characteristics of pile foundation in layered soft soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(S2): 3472-3482. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2021.0094 [10] 黄朝煊, 袁文喜, 胡国杰. 成层软土地基预固结处理后桩基水平承载力估算方法[J]. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(1): 113-124,134. (HUANG C X, YUAN W X, HU G J. An estimation method of horizontal bearing capacity of piles after pre-consolidation treatment for layered soft foundation[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(1): 113-124,134. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2020.0797HUANG C X, YUAN W X, HU G J. An estimation method of horizontal bearing capacity of piles after pre-consolidation treatment for layered soft foundation[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(1): 113-124,134. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2020.0797 [11] 康 舜, 赵其华, 彭社琴, 等. 碎石土土体性状对桩基水平承载能力的影响[J]. 工程地质学报, 2019, 27(3): 559-568. (KANG S, ZHAO Q H, PENG S Q, et al. Effect of gravel-soil characters on lateral bearing capacity of pile foundation[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2019, 27(3): 559-568. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2018-231KANG S, ZHAO Q H, PENG S Q, et al. Effect of gravel-soil characters on lateral bearing capacity of pile foundation[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2019, 27(3): 559-568. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2018-231 [12] 杨 亮. 袖阀管分层注浆技术在软土地基中对桩基水平承载力的影响研究[J]. 工程与试验, 2021, 61(3): 81-84. (YANG L. Research on the influence of sleeve valve pipe layered grouting technology on the horizontal bearing capacity of pile foundation in soft soil foundation[J]. Engineering & Test, 2021, 61(3): 81-84. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3407.2021.03.027YANG L. Research on the influence of sleeve valve pipe layered grouting technology on the horizontal bearing capacity of pile foundation in soft soil foundation[J]. Engineering & Test, 2021, 61(3): 81-84. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3407.2021.03.027 [13] 任鑫健, 高文生. 桩基水平承载力群桩效应系数试验研究[J]. 建筑科学, 2020, 36(7): 106-114. (REN X J, GAO W S. Experimental study on the effect coefficient of pile group horizontal bearing capacity[J]. Building Science, 2020, 36(7): 106-114. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13614/j.cnki.11-1962/tu.2020.07.016REN X J, GAO W S. Experimental study on the effect coefficient of pile group horizontal bearing capacity[J]. Building Science, 2020, 36(7): 106-114. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13614/j.cnki.11-1962/tu.2020.07.016 [14] 刘 越, 黄朝煊. 多层软土地基中桩基水平承载计算研究[J]. 人民长江, 2022, 53(7): 187-192. (LIU Y, HUANG C X. Research on calculation of horizontal bearing capacity of pile foundation in multi-layer soft soil foundation[J]. Yangtze River, 2022, 53(7): 187-192. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2022.07.028LIU Y, HUANG C X. Research on calculation of horizontal bearing capacity of pile foundation in multi-layer soft soil foundation[J]. Yangtze River, 2022, 53(7): 187-192. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2022.07.028 [15] 杨烨勋, 李杰明. 深基坑桩基承载力影响因素分析[J]. 水利规划与设计, 2023(9): 153-159. (YANG Y X, LI J M. Analysis of the influence factors of FRWS on pile bearing capacity of deep foundation pit[J]. Water Resources Planning and Design, 2023(9): 153-159. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2469.2023.09.028YANG Y X, LI J M. Analysis of the influence factors of FRWS on pile bearing capacity of deep foundation pit[J]. Water Resources Planning and Design, 2023(9): 153-159. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2469.2023.09.028 [16] 莫连华. 软基处理对桩基水平承载力提高的影响研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2024, 20(2): 398-407. (MO L H. Research on the influence of soft soil foundation pretreatment on the improvement of pile foundation’s horizontal bearing capacity[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2024, 20(2): 398-407. (in Chinese) doi: 10.20174/j.JUSE.2024.02.06MO L H. Research on the influence of soft soil foundation pretreatment on the improvement of pile foundation’s horizontal bearing capacity[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2024, 20(2): 398-407. (in Chinese) doi: 10.20174/j.JUSE.2024.02.06 [17] BOLTON M D. The strength and dilatancy of sands[J]. Géotechnique, 1986, 36(1): 65-78. [18] 罗敏敏, 陈 赟, 周 江. 小应变土体硬化模型参数取值研究现状与展望[J]. 工业建筑, 2021, 51(4): 172-180. (LUO M M, CHEN Y, ZHOU J. Research status and prospect of parameter selection for the HS-small model[J]. Industrial Construction, 2021, 51(4): 172-180. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13204/j.gyjzg20123002LUO M M, CHEN Y, ZHOU J. Research status and prospect of parameter selection for the HS-small model[J]. Industrial Construction, 2021, 51(4): 172-180. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13204/j.gyjzg20123002 [19] 顾晓强, 吴瑞拓, 梁发云, 等. 上海土体小应变硬化模型整套参数取值方法及工程验证[J]. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(3): 833-845. (GU X Q, WU R T, LIANG F Y, et al. On HSS model parameters for Shanghai soils with engineering verification[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(3): 833-845. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2020.0741GU X Q, WU R T, LIANG F Y, et al. On HSS model parameters for Shanghai soils with engineering verification[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(3): 833-845. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2020.0741 [20] 王卫东, 王浩然, 徐中华. 基坑开挖数值分析中土体硬化模型参数的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2012, 33(8): 2283-2290. (WANG W D, WANG H R, XU Z H. Experimental study of parameters of hardening soil model for numerical analysis of excavations of foundation pits[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(8): 2283-2290. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2012.08.006WANG W D, WANG H R, XU Z H. Experimental study of parameters of hardening soil model for numerical analysis of excavations of foundation pits[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(8): 2283-2290. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2012.08.006 [21] 顾晓强, 陆路通, 李雄威, 等. 土体小应变刚度特性的试验研究[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(3): 312-317. (GU X Q, LU L T, LI X W, et al. Experimental study of small strain stiffness properties of soil[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2018, 46(3): 312-317. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2018.03.005GU X Q, LU L T, LI X W, et al. Experimental study of small strain stiffness properties of soil[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2018, 46(3): 312-317. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2018.03.005 [22] BRINKGREVE R B J. Selection of soil models and parameters for geotechnical engineering application[M]//YAMAMURO J A, KALIAKIN V N. Soil Constitutive Models: Evaluation, Selection, and Calibration. Reston: American Society of Civil Engineers, 2005: 69-98. [23] 叶跃鸿. 地下通道施工引起下卧地铁隧道上浮规律及控制措施研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017. (YE Y H. Influence of construction of open-cut tunnelling on uplift displacement of the underneath metro tunnel and its control measures[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017. (in Chinese)YE Y H. Influence of construction of open-cut tunnelling on uplift displacement of the underneath metro tunnel and its control measures[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017. (in Chinese) [24] JÁKY J. A nyugalmi nyomás tényezöje[J]. A Magyar Mérnö k-és É pítész-Egylet Kö zlö nyének, 1944, 78(22): 355-358. [25] JANBU N. Soil compressibility as determined by oedometer and triaxial tests[C]//Proceedings of the 3rd European Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. Wiesbaden, 1963: 19-25. [26] BENZ T. Small-strain stiffness of soils and its numerical consequences[D]. Stuttgart: University of Stuttgart, 2007. [27] 李亚玲, 张 彬, 苏海峰, 等. Hardening-Soil模型中参数选取试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2012, 20(S1): 164-169. (LI Y L, ZHANG B, SU H F, et al. Parameter selection based on test with hardening-soil model[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2012, 20(S1): 164-169. (in Chinese)LI Y L, ZHANG B, SU H F, et al. Parameter selection based on test with hardening-soil model[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2012, 20(S1): 164-169. (in Chinese) [28] 谢东武, 管 飞, 丁文其. 小应变硬化土模型参数的确定与敏感性分析[J]. 地震工程学报, 2017, 39(5): 898-906. (XIE D W, GUAN F, DING W Q. Determination and sensitivity analysis of the parameters of hardening soil model with small strain stiffness[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2017, 39(5): 898-906. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2017.05.0898XIE D W, GUAN F, DING W Q. Determination and sensitivity analysis of the parameters of hardening soil model with small strain stiffness[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2017, 39(5): 898-906. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2017.05.0898 [29] 程麦理. 黄土场地桩基横向力学行为数值模拟[J]. 工程力学, 2019, 36(S1): 229-233. (CHENG M L. Numerical simulation of transverse mechanical behavior of pile foundation in loess site[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2019, 36(S1): 229-233. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2018.05.S045CHENG M L. Numerical simulation of transverse mechanical behavior of pile foundation in loess site[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2019, 36(S1): 229-233. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2018.05.S045 [30] 郭光照. 水泥土搅拌桩力学特性室内试验研究[J]. 路基工程, 2012(5): 72-74,78. (GUO G Z. Indoor experimental study on mechanical properties of cement-soil mixing pile[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2012(5): 72-74,78. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8825.2012.05.019GUO G Z. Indoor experimental study on mechanical properties of cement-soil mixing pile[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2012(5): 72-74,78. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8825.2012.05.019 -





 下载:
下载: