Pumping Test and Numerical Simulation in an Excavation Engineering
-
摘要: 江西宜春某工程因涉及喀斯特地貌及古河道,设计方案未充分考虑地下水的影响,且基坑开挖过程中不当降水,导致基坑周边出现大规模沉降及裂缝,基坑被迫回填至地下水水位以上。为保证二次开挖时基坑周边环境的安全,需重新制定地下水控制方案。通过现场抽水试验测定数据,结合地勘资料,并运用Midas GTS有限元数值分析软件,推算用于数值分析的场地各土层渗流系数,运用该参数进行基坑降水数值模拟,经安全性和经济性对比后确定最终的地下水控制方案。对于基坑工程,应充分考虑地下水条件,进行反复分析求证,充分估计降水对周边环境的影响。将抽水试验与数值模拟相结合,可以对不同的地下水控制方案进行预测分析,制定出合理的设计方案,该方法对复杂水文地质条件下的基坑降水工程有一定的借鉴意义。Abstract: The design scheme of a project in Yichun, Jiangxi Province involved karst landform and ancient river and did not fully consider the impact of groundwater. The large-scale settlement and cracks were begot around the excavation which accompanied construction dewatering. The foundation pit was forced to backfill above the groundwater level. In order to ensure the safety of the surrounding environment of the foundation pit during the secondary excavation, it was necessary to re-formulate the groundwater control scheme. The foundation pit dewatering numerical simulation was carried out by using the field pumping test data, geological survey data and Midas GTS finite element numerical analysis. The final groundwater control scheme was determined after the comparison of safety and economy. The excavation engineering should considered the groundwater conditions and the surrounding environment, and could be tested by the numerical simulation. Combining pumping test and numerical simulation, different groundwater control schemes were analyzed and reasonable design scheme was proposed. This method has certain reference significance to the foundation pit dewatering project under the complex hydrogeological condition.
-
Key words:
- excavations /
- groundwater control /
- numerical simulation /
- Midas GTS
-
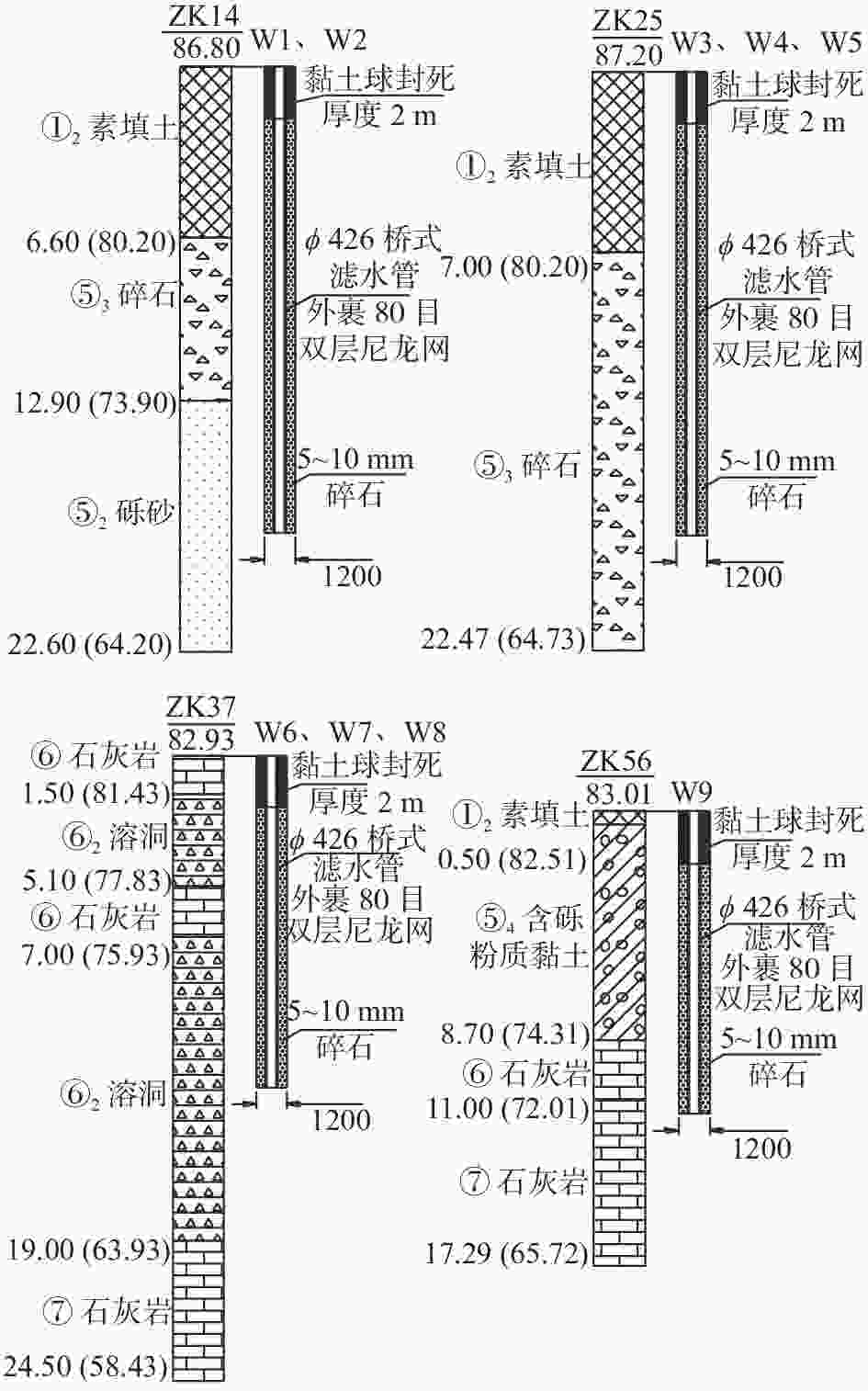
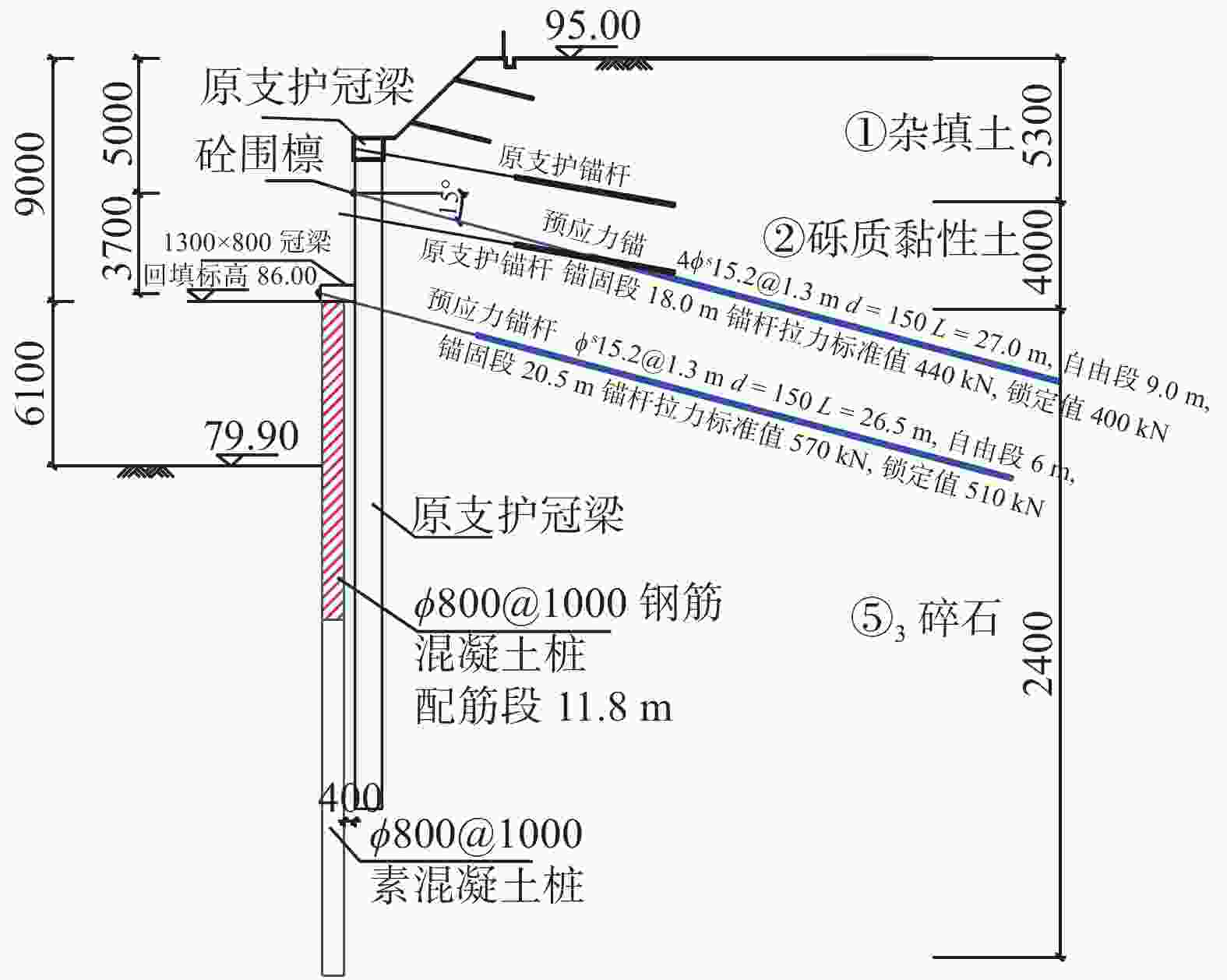
表 1 各岩土层物理力学参数
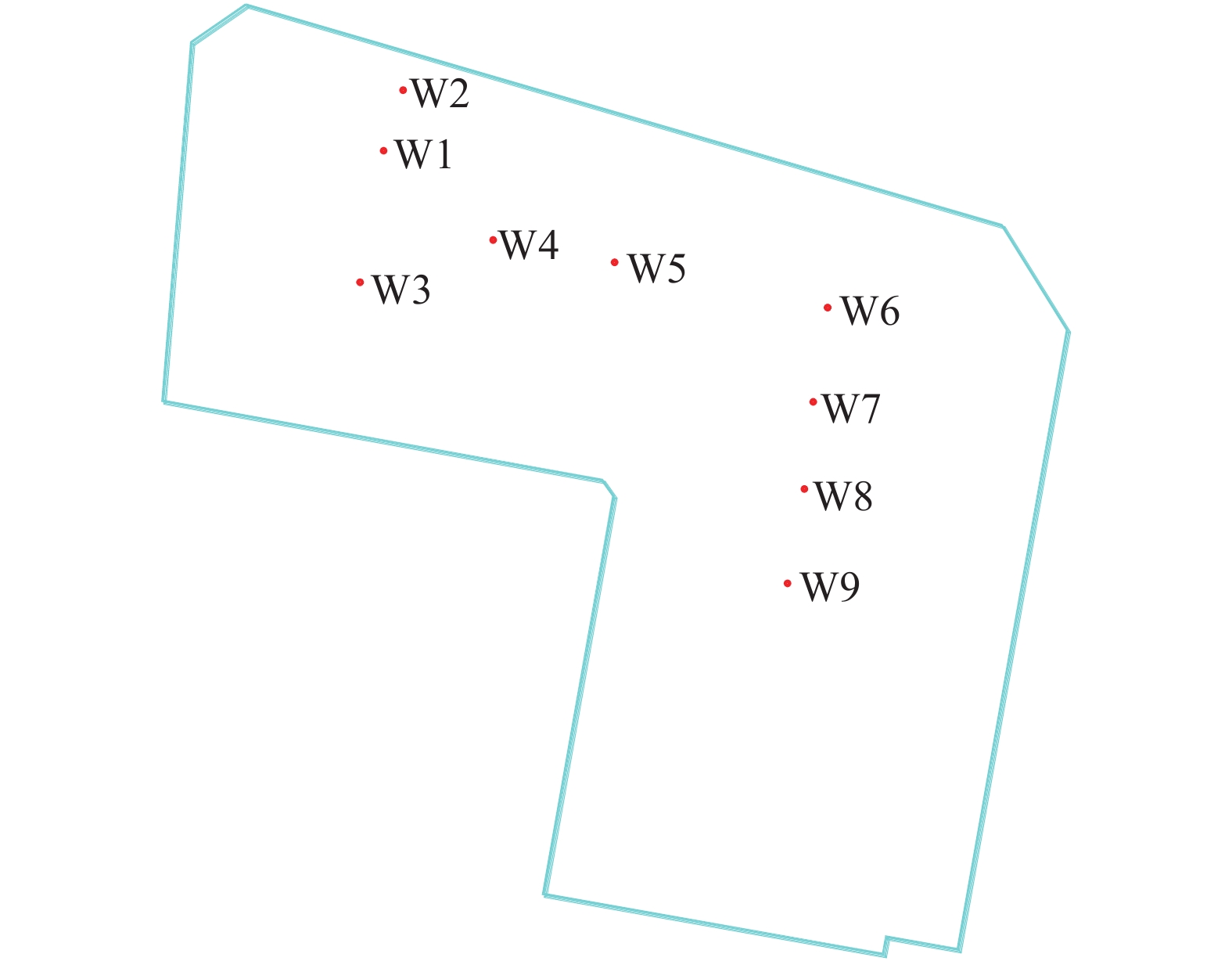
地层名称 层厚/m 承载力特征值fak/kPa (压缩模量Es/变形模量E0)/MPa 天然重度$\gamma $/(kN·m−3) 黏聚力c/kPa 内摩擦角$\varphi $/(°) ①1杂填土 1.3~8.0 40 2.0/ 18.0 5 10 ①2素填土 0.5~3.5 30 1.5/ 18.0 0 8 ②含砾粉质黏土 0.7~16.5 155 6.2/ 19.5 24.2 15.8 ③粗砂 1.5~5.3 150 /30 19.0 35 ④砾砂 2.0~9.1 200 /38 19.0 45 ⑤1粉质黏土 1.2~10.2 100 4.6/ 18.8 14.3 13.3 ⑤2砾砂 0.9~9.2 180 /35 19.0 40 ⑤3碎石土 1.3~23.2 260 /45 19.0 50 ⑤4含砾粉质黏土 0.9~15.0 158 6.4/ 19.6 24.1 14.1 ⑥石灰岩 0.8~15.0 85 4.0/ 18.0 8 10 ⑥1溶洞 1.0~3.8 180 /35 19.0 40 ⑥2溶洞 0.8~16.2 1500 ⑦中等风化石灰岩 1.1~8.7 10000 表 2 试验井数据统计及承压水情况表
井号 井口标高/m 井深/m 水位降深/m 出水量/(m3·h−1) 承压性判断 W1 88.48 16.3 0.83 33~35 承压水 W2 87.73 18.0 3.10 16~17 承压水 W3 88.02 17.1 14.50 5~6 无承压性 W4 87.69 18.6 11.07 13~17 微承压性 W5 87.88 17.8 10.74 4~5 无承压性 W6 83.62 13.5 3.19 16~17 承压水 W7 83.58 13.2 11.32 8~10 承压水 W8 82.70 12.8 10.95 4~6 微承压性 W9 83.27 11.5 10.39 0.2~0.3 无承压性 表 3 出水量结果对比
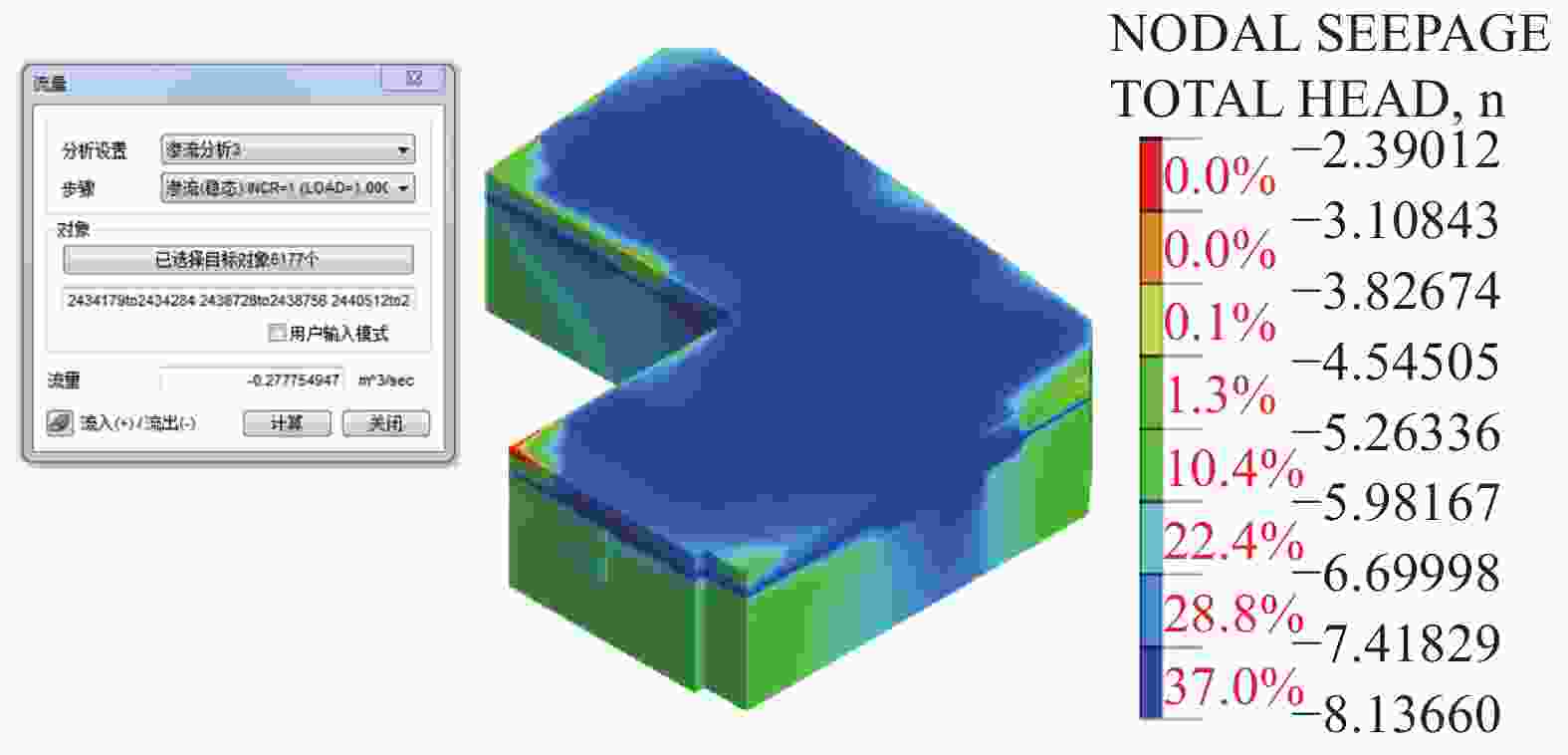
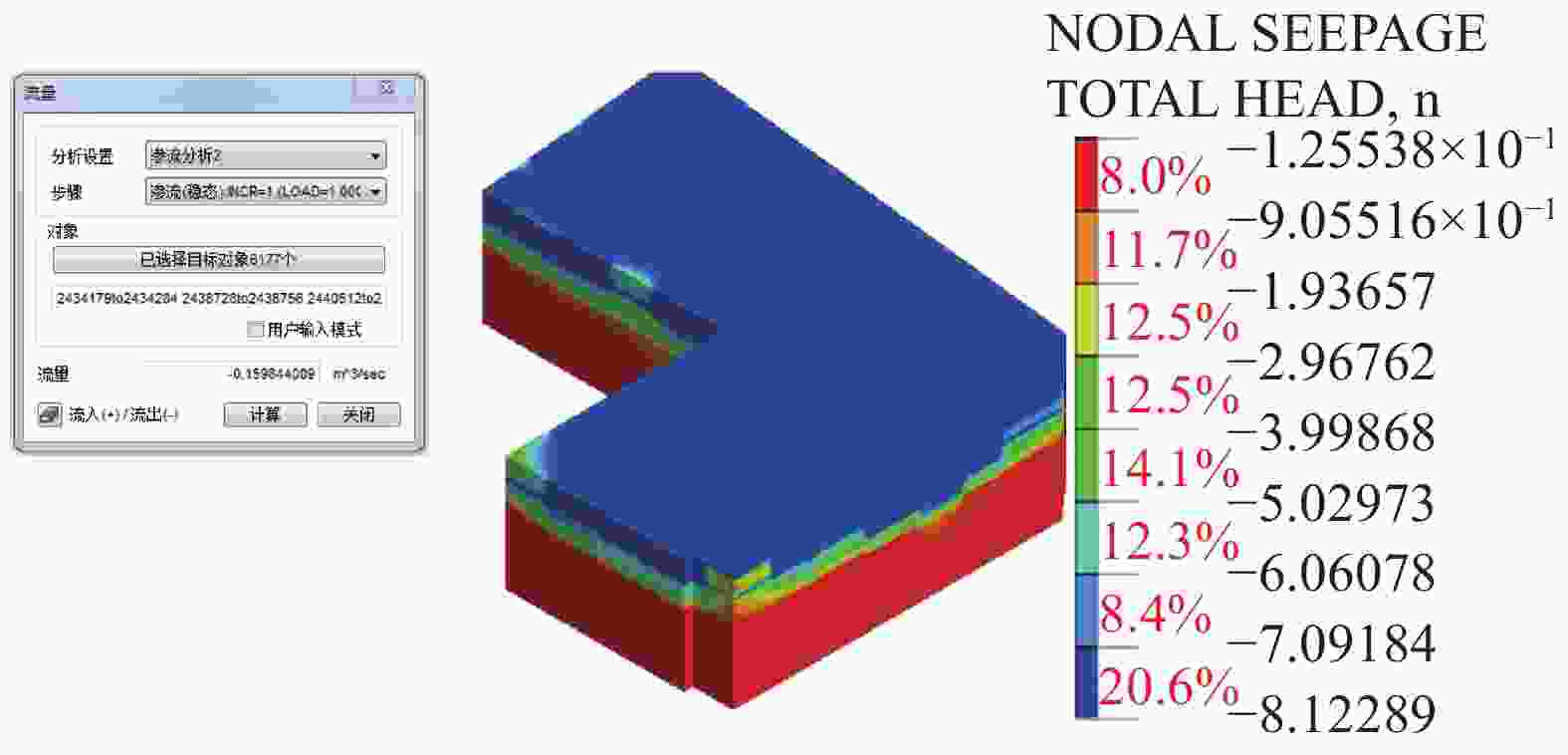
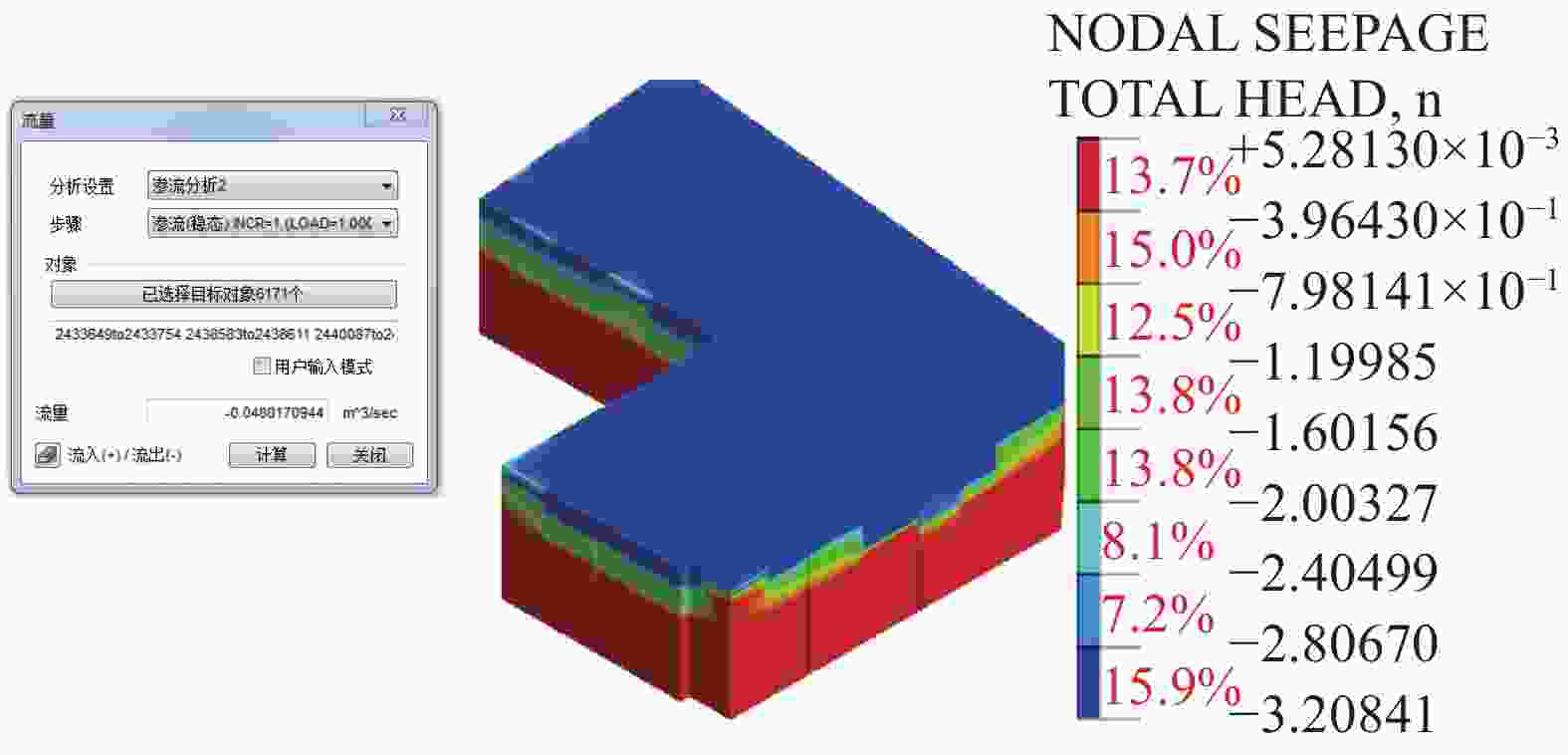
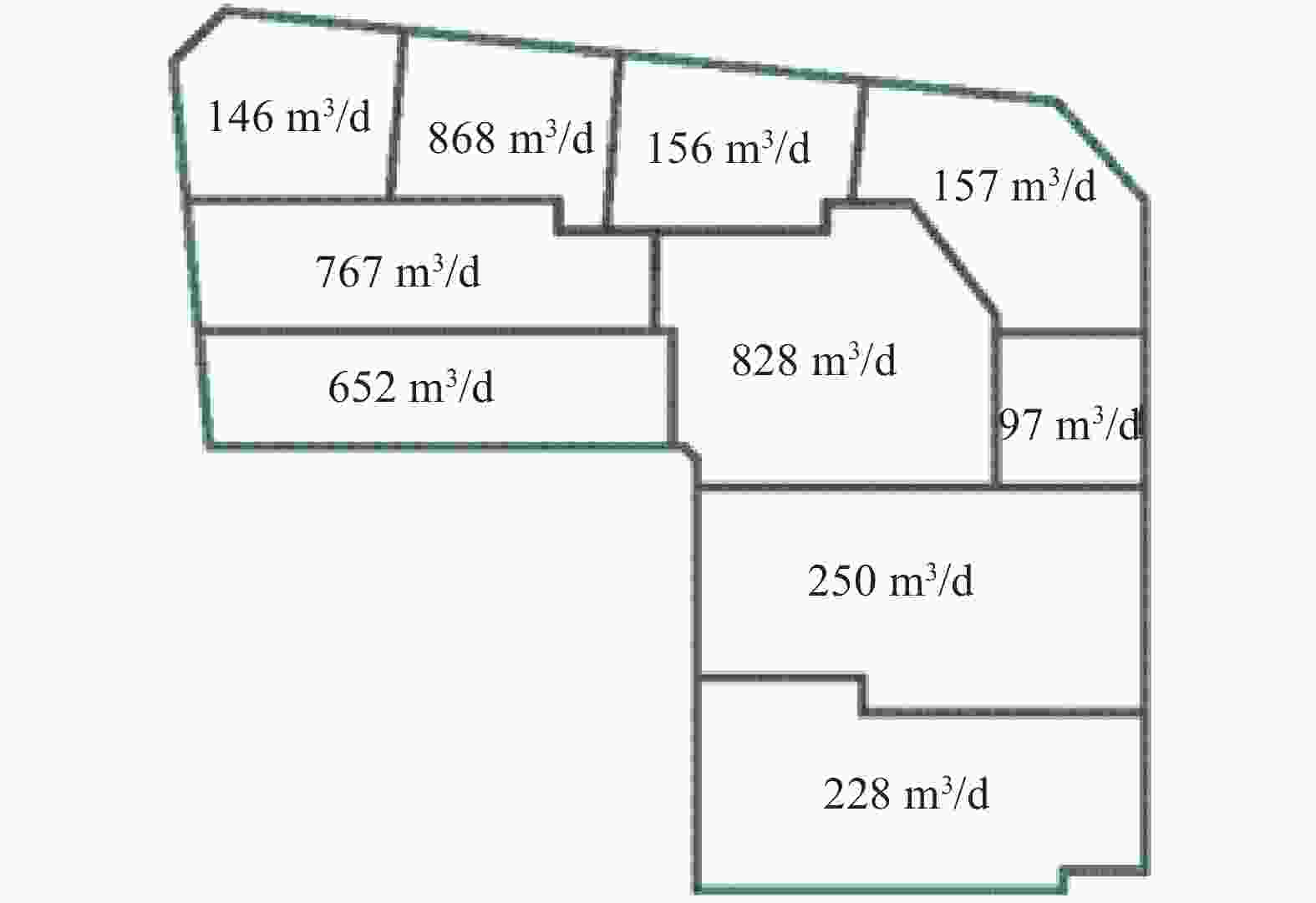
井号 W1 W2 W3 W4 W5 W6 W7 W8 W9 数值模拟流量/(m3·h−1) 33 12.4 10.9 19.1 19.2 6.9 12.7 13.1 0.67 试验井出水量/(m3·h−1) 33~35 16~17 5~6 13~17 4~5 16~17 8~10 4~6 0.2~0.3 表 4 各土层渗透系数取值对比
土层 ②含砾粉质黏土 ③粗砂 ④砾砂 ⑤1粉质黏土 ⑤2砾砂 ⑤3碎石土 ⑤4含砾粉质黏土 ⑥2溶洞充填物 渗透系数/(m·d−1) 数值模拟 0.1 34.6 51.8 0.05 51.8 19.2 0.09 25.9 地勘建议 0.02~0.05 30~40 45~55 0.02~0.05 45~55 55~65 0.02~0.05 30~40 表 5 出水量数值模拟结果
帷幕长度/m 25 30 35 40 50 坑底出水量/(m3·d−1) 13811 11522 9336 7304 5015 -
[1] 廖俊发,吴林高,王璋群. 大型深井点降水引起地面沉降的研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,1991,13(3):60-64. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1991.03.007 [2] 吴林高. 工程降水设计施工与基坑渗流理论[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2003. [3] 李广信,吴剑敏. 浮力计算与黏土中的有效应力原理[J]. 岩土工程技术,2003,(2):63-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2003.02.001 [4] 姚天强, 石振华, 等. 基坑降水手册[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2006. [5] 周 健, 屠洪权, 等. 地下水位与环境岩土工程[M]. 上海: 上海科技文献出版社, 1996. [6] 顾宝和,周 红. 基坑工程若干基本问题的讨论−基坑开挖与支护研讨会综述[J]. 工程勘察,1997,(3):12-17. [7] 薛禹群,张 云,叶淑君,等. 中国地面沉降及其需要解决的几个问题[J]. 第四纪研究,2003,23(6):587-593. [8] 赵建康,孙乐玲,刘思秀. 浙江省滨海平原地面沉降现状及防治对策[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,2004,14(2):16-20. [9] 许乃政,姜月华,王敬东,等. 我国东南沿海地面沉降类型及其特点[J]. 灾害学,2005,(4):67-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2005.04.015 [10] 杨 勇,李国敏,窦艳兵,等. 抽取地下水引起地面沉降的研究现状与进展[J]. 工程勘察,2010,(11):32-37. [11] JGJ/T 111—2016 建筑与市政工程地下水控制技术规范[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2016. [12] 冯晓腊,熊文林,胡 涛,等. 三维水–土耦合模型在深基坑降水计算中的应用[J]. 岩土力学与工程学报,2005,24(7):1196-1201. [13] 黄应超,徐杨青. 深基坑降水与回灌过程的数值模拟分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2014,36(S2):299-303. [14] 廖 翔,骆祖江,于丹丹. 深基坑降水地下水渗流三维数值模拟[J]. 工程勘察,2014,42(7):22-26. -





 下载:
下载: