Research Progress on Application of Cement Soil Mixing Pile in Gravel Stratum
-
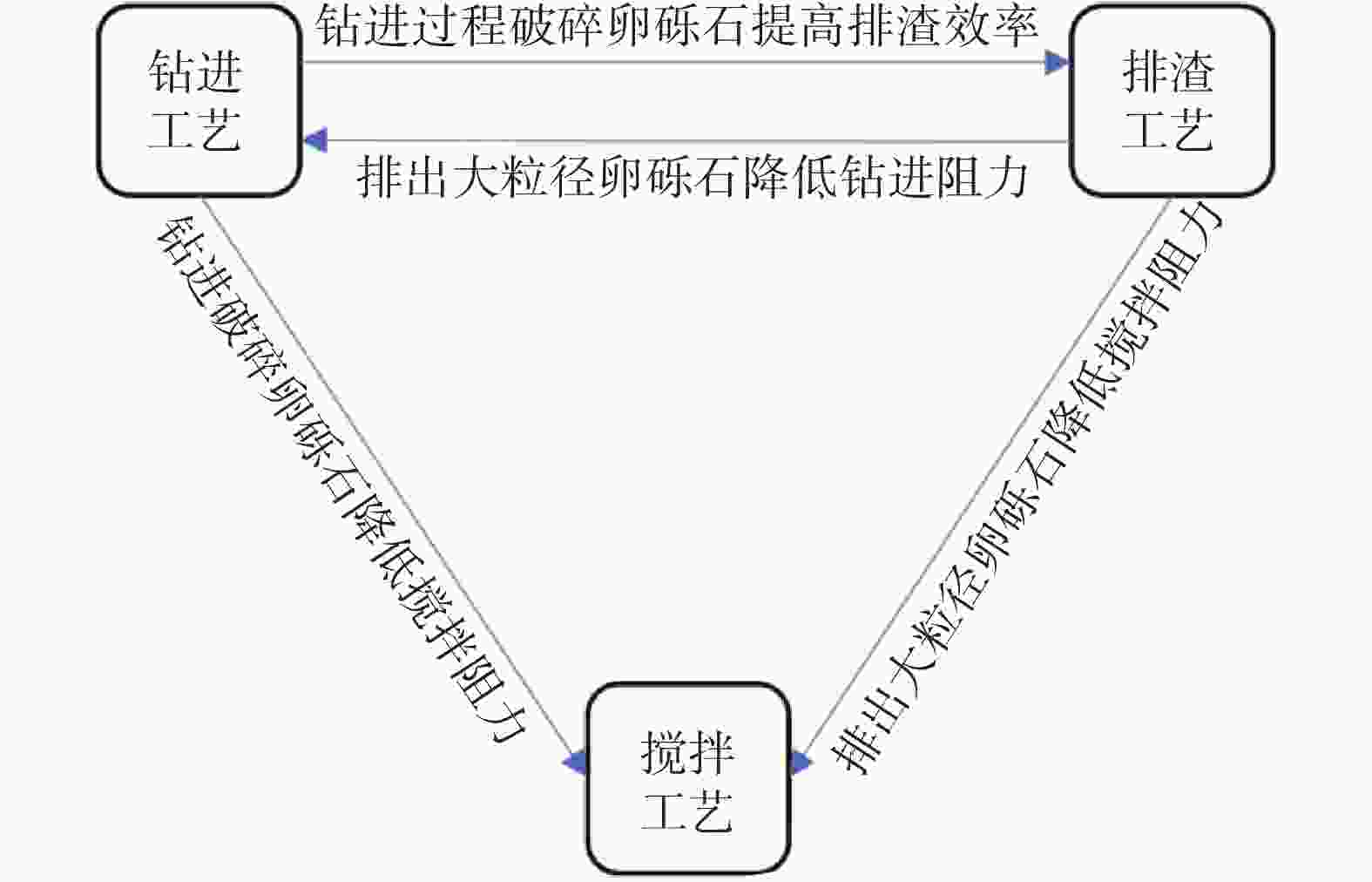
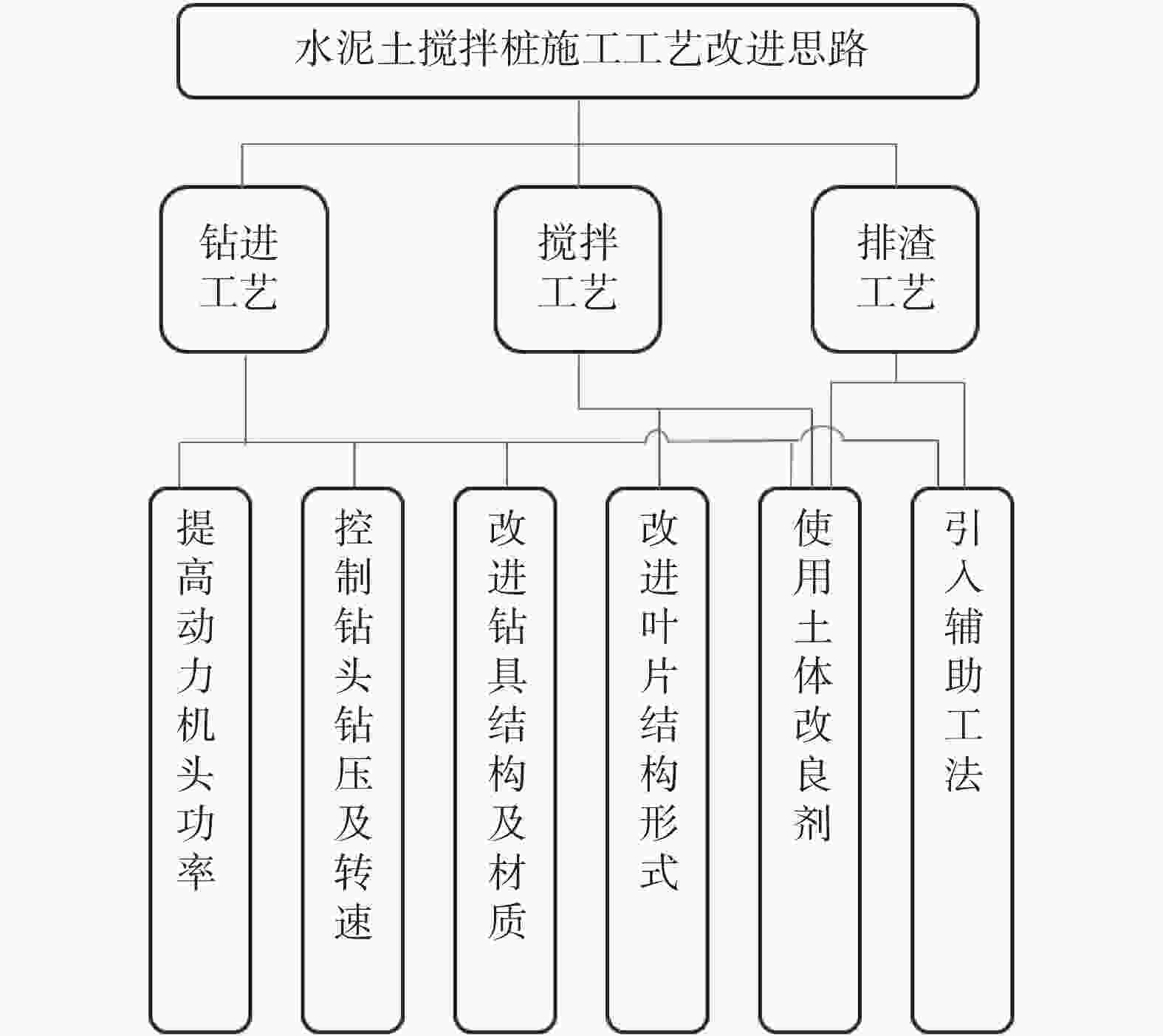
摘要: 卵砾石地层可压缩性低、抗剪强度大,水泥土搅拌桩工法在应用于卵砾石地层时存在若干技术问题。系统总结了水泥土搅拌桩工法在卵砾石地层的应用情况,重点对水泥土搅拌桩应用于卵砾石地层的技术难点及主要的改进措施进行了论述,并分析了各改进方法的作用机理、适用性、利弊等。水泥土搅拌桩在穿越卵砾石地层过程中存在施工效率低下、钻具磨损大、施工质量不易控制等技术难题,目前已有水泥土搅拌桩应用于卵砾石地层的成功案例中主要改进工艺可分为钻进、搅拌、排渣共计三大类别,具体可细化为提高动力机头功率、控制钻头钻压及转速、提高钻具材料强度、改进钻头及搅拌叶片结构形式、使用土体改良剂等措施,必要时可引入引孔换填、冲击破碎等工法辅助施工。但总体上应用成功的案例中,卵砾石地层的颗粒粒径及厚度较小,一般粒径不超过150 mm,且未形成系统性的卵砾石地层特征与机械设备技术参数的匹配方法。搅拌桩设备与卵砾石地层相互作用机理研究等工作亟待深化。Abstract: Gravel stratum has low compressibility and high shear strength. There are some technical problems in the application of cement soil mixing pile method in gravel stratum. The application of cement soil mixing pile in gravel stratum was summarized, and the technical difficulties and main improvement measures of cement soil mixing pile in gravel stratum were also discussed. The action mechanism, applicability, advantages and disadvantages of each improvement method were analyzed. During the process of cement soil mixing pile crossing gravel stratum, there are technical problems such as low construction efficiency, large wear of drilling tools and difficult control of construction quality. At present, there are successful cases of cement soil mixing pile applied to gravel stratum. The main improved processes can be divided into three types, including drilling, mixing and slag discharge, which can be subdivided into improving the power of power machine head, controlling the bit weight and speed, improving the strength of drilling tool materials, improving the structural form of bit and mixing blade, and using soil modifier. If necessary, pilot hole replacement and impact crushing can be introduced to assist the construction. However, in the successful cases, the particle size and thickness of gravel stratum are small, generally no more than 150 mm in particle size, and there is no systematic matching method between gravel stratum characteristics and mechanical equipment technical parameters. The research on the interaction mechanism between mixing pile equipment and gravel stratum needs to be deepened.
-
Key words:
- foundation treatment /
- cement soil mixing pile /
- gravel stratum /
- waterproof curtain
-
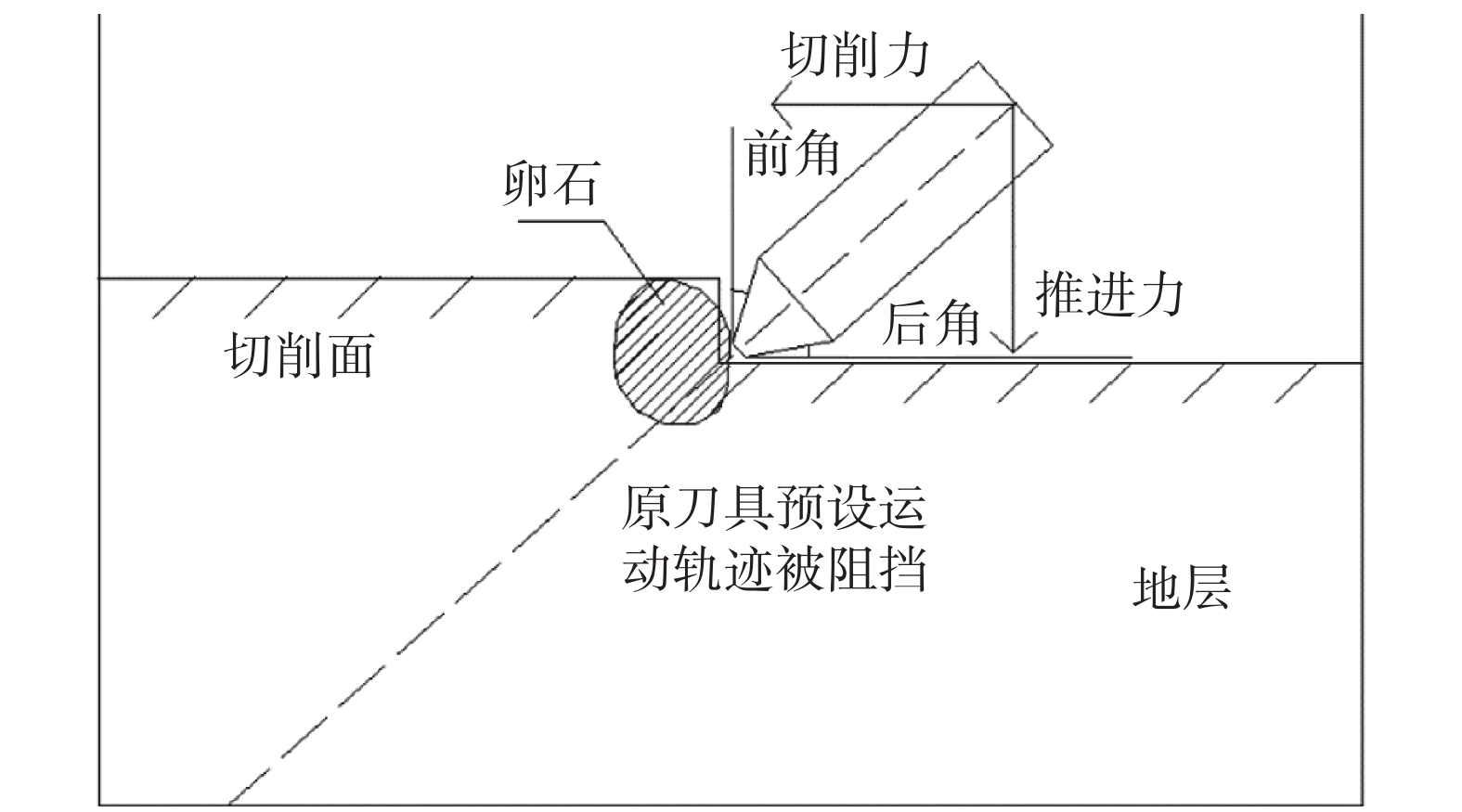
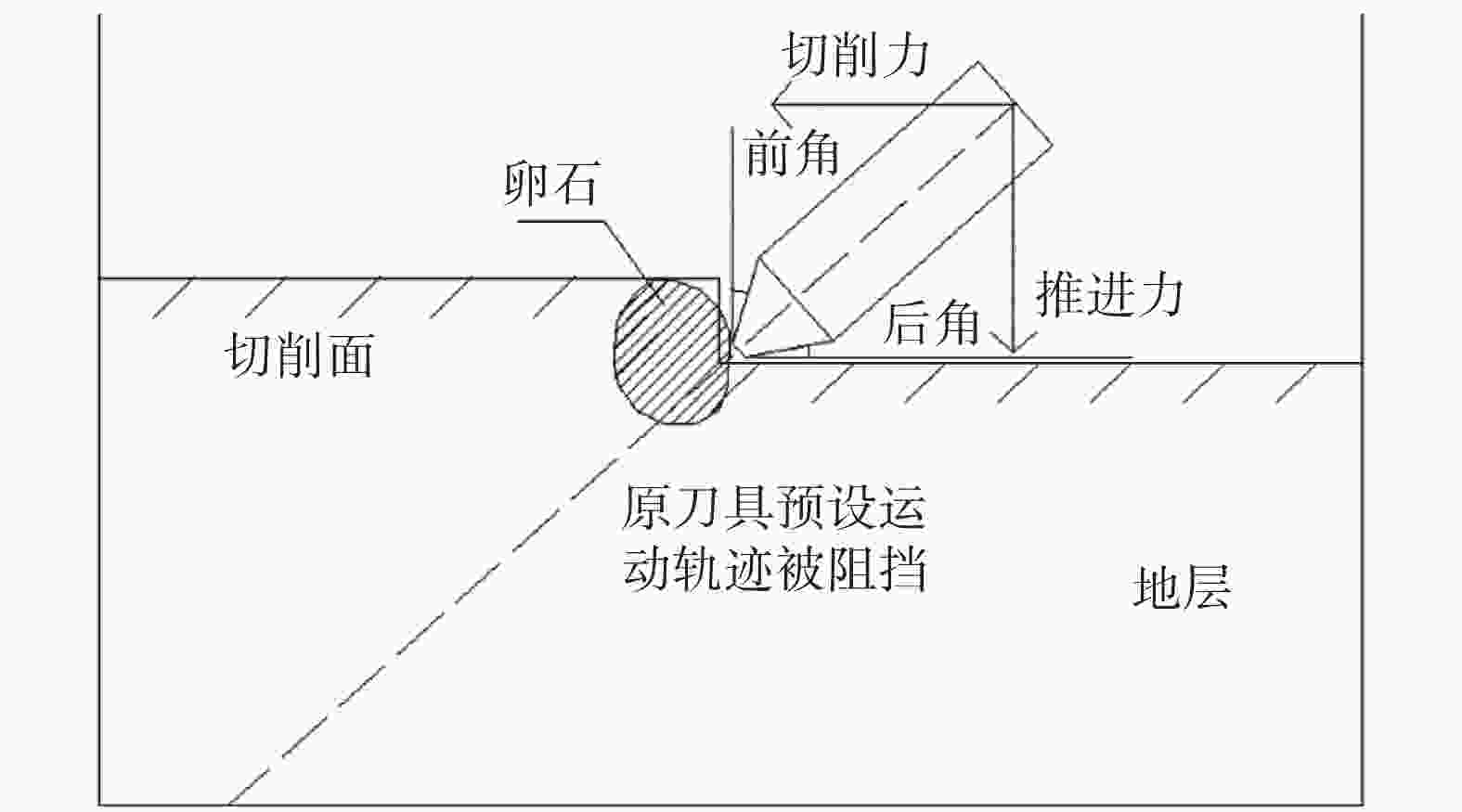
图 1 卵石阻挡叶片钻进路径[21]
Figure 1. Pebble blocks blade drilling path
表 1 卵砾石地层条件下水泥土搅拌桩工法成功案例
Table 1. Successful case of cement soil mixing pile construction method in Sandy Cobble Stratum
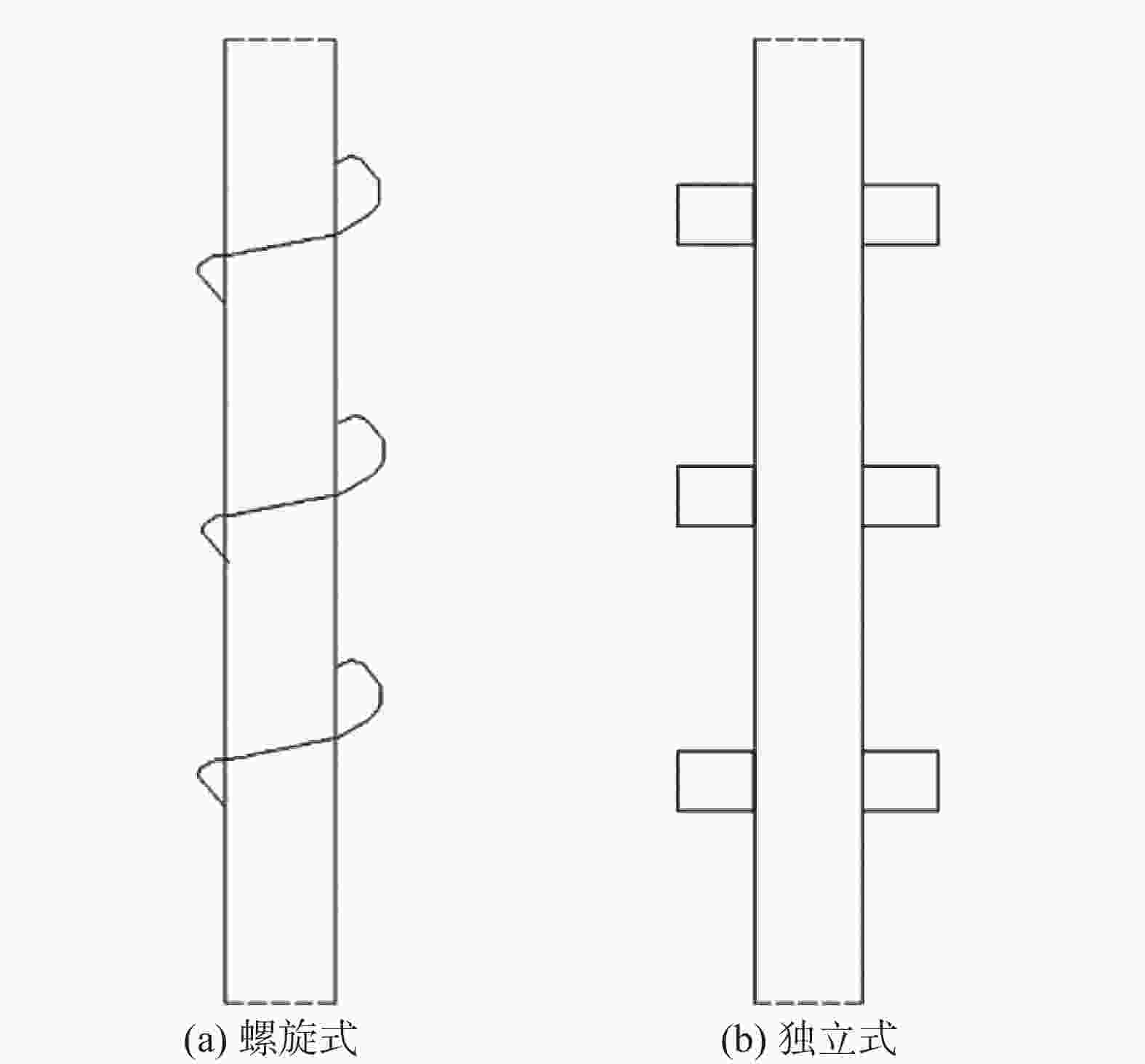
工程名称 卵砾石地层特性 改进方法 福建莆田某工程二层地下室基坑SMW工法桩[23] 最大厚度约13m,卵石含量约50%~55%,砂粒含量30%~40%,一般卵石粒径3~6 cm,少数颗粒可大于10 cm 提高动力机头功率,改进钻头及搅拌叶片结构形式,使用加固剂,钻进困难时进行引孔换填工作 北京地铁10 号线北土城东路站—芍药居站区间隧道明挖段SMW工法桩[24] 卵砾石层厚1~3 m,卵石粒径一般为20~30 mm,最大100 mm,亚圆形,含量达55% 提高动力机头功率 杭州某电梯试验塔基坑SMW工法桩[25] 卵砾石层厚4.3~4.8 m,粒径一般为20~100 mm,局部含漂石 提高动力机头功率,改进钻头及搅拌叶片结构形式 丽水市丽水绿城秀丽春江基坑项目止水帷幕[26] 含圆砾地层厚1.4~6.5 m,圆砾含量约占35%~40%, 直径多介于2~6 cm, 最大约15 cm, 次圆状质地坚硬 改进传统三轴搅拌桩机的钻头、叶片和动力头 遂宁市观音湖下穿隧道SMW工法桩[27] 卵石粒径多小于15 cm 引孔辅助施工,利用旋挖机(钻头直径为0.8 m)进行导孔后回填 表 2 部分国内外深层搅拌机械技术参数[23-24, 29]
Table 2. Technical parameters of some deep mixing machines at home and abroad
机型 轴数 叶片
直径/mm搅拌转速
/(r·min−1)功率
/kWDJB-14D 1 500 60 2×22 GZB-600 1 600 50 2×30 SJB-30 2 700 43 2×30 SJB-40 2 700 43 2×40 GDP-72 2 700 46 2×37 ZKD65-3 3 650 17.6 2×45 ZKD58-33 3 850 16 2×75 日本550SMW 3 650 16.5/33.1 2×55 日本850SMW 3 850 15.6/31.3 2×90 ZLD180/85-3-M2-CS 3 850 中14.2/外14.2 2×90 ZLD220/85-3-M2-CS 3 850 中13.8/外13.8 2×110 -
[1] 王卫东. 超深等厚度水泥土搅拌墙技术与工程应用实例 [M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2017. [2] BELLATO D. Experimental study on the hydro-mechanical behavior of soils improved using the CSM technology [D]. Padova: University of Padova, 2013. [3] DENIES N,HUYBRECHTS N. Deep Mixing Method: Equipment and Field of Applications[J]. Ground Improvement Case Histories,2015:311-350. [4] 申玉生, 陈先智, 卢治仁, 等. 富水圆砾地层地铁车站超深基坑施工关键技术 [M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社有限公司, 2019. [5] 周济民,李名淦. 北京地区地铁车站深基坑地下水控制技术研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2014,10(S2):2042-2048. [6] CHIOU J S,TSAI C C,et al. Analysis of in situ bridge columns with exposed caisson foundations in a gravel stratum under lateral loading[J]. Advances in Structural Engineering,2019,23(3):424-37. [7] 苏 艺, 苏 斌, 陶连金. 砂卵石地层盾构施工及列车运行环境振动影响 [M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2015. [8] GUAN C,YANG Y. Field study on the waterstop of the rodin jet pile method in a water-rich sandy gravel stratum[J]. Applied Sciences,2019,9(8):1709-1724. doi: 10.3390/app9081709 [9] 王金龙, 吴 瑜. 一种型钢水泥土搅拌墙在卵石层中的成桩方法: CN111455978A [P]. 2020-07-28. [10] ZHANG L,GUO Z,LIANG Z. Tri-axial confining numerical test and settlement analysis of the gravel layer[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering,2020,24(3):2572-2580. [11] WEI Y,YANG Y,TAO M. Effects of gravel content and particle size on abrasivity of sandy gravel mixtures[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,243:26-35. [12] ZHANG S,GAO F,HE X,et al. Experimental study of particle migration under cyclic loading: effects of load frequency and load magnitude[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2021,16(2):367-380. doi: 10.1007/s11440-020-01137-x [13] 牟 迪. 成都地铁四号线砂卵石层分布规律及工程特性研究 [D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2012. [14] 刘永勤,金 淮,高 涛,等. 北京地铁九号线沿线卵石地层特性研究[J]. 铁道建筑技术,2011,39(S2):28-32. [15] 江 华. 北京典型砂卵石地层土压平衡盾构适应性研究 [D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2012. [16] 王 煜. 成都地区砂卵石层超重型动力触探击数规律[J]. 四川地质学报,2000,(2):118-121. [17] LARSSON S. State of Practice Report Session 6: Execution, monitoring and quality control[C]. Proceedings of the International Conference on Deep Mixing, 2005. [18] 周书东. 水泥土搅拌桩(墙)应用现状[J]. 工业建筑,2013,43(S1):446-449. [19] 潘秀明, 雷崇红. 北京地铁砂卵石砾岩地层综合工程技术 [M]. 北京:人民交通出版社, 2012. [20] 代婷蓉, 潘中艇, 钱纪恩, 等. 圆砾层三轴搅拌机钻头及施工方法: CN111155934A[P]. 2020-05-15. [21] 王 飞. 盾构直接掘削大直径钢筋混凝土群桩研究 [D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2014. [22] 高明忠, 张 茹, 龚秋明. 砂卵石地层条件下盾构掘进机理与实践 [M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2012. [23] 钟贵荣. SMW工法桩在卵石层及风化岩地层深大基坑工程中的实践[J]. 福建建设科技,2016,(5):9-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3943.2016.03.004 [24] 余家兴,宋德聪,刘增祥. SMW工法在北京地区深基坑支护中的应用研究[J]. 市政技术,2009,27(5):510-514. [25] 沈杰超,马晓华,朱怀甫,等. 超级三轴(SSMW)工法在深厚卵石层中的围护施工应用[J]. 施工技术,2018,47(1):32-35. [26] 张晓峰, 楼志群, 金旭勇, 等. 超级三轴水泥土搅拌桩在圆砾层中的施工[C]//2014年建筑科技与管理学术交流会论文集, 2014. [27] 王养锋. 下穿隧道卵石地层组合式SMW搅拌桩施工技术[J]. 工程建设与设计,2017,(1):148-150. [28] 马德坤. 牙轮钻头工作力学 [M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2009. [29] 徐至钧. 水泥土搅拌法处理地基 [M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2004. [30] 王义军. 三轴搅拌桩入岩施工技术[J]. 隧道建设,2015,35(5):478-483. [31] TIAN K,GANESH R,DETOURNAY E. Influence of bit design on the stability of a rotary drilling system[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics,2020,100(1):51-75. [32] 彭振斌, 孙平贺, 曹 函. 复杂地层钻探技术 [M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2016. [33] KITAZUME M, TERASHI M. The Deep Mixing Method [M]. Florida: CRC Press, 2013. [34] MOMENI S,MOSELEY S,ANTE M,et al. The wear of WC-Co drill bits during rotary-percussive drilling of reinforced concrete[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials,2017,62:202-209. [35] ZHANG K,WANG D G,WANG Z Q,et al. Friction and wear behavior of wear-resistant belts in drill joints for deep and ultra-deep wells[J]. Strength of Materials,2013,1(2):192-195. [36] FENG S J,LU S F. Failure of a retaining structure in a metro station excavation in Nanchang City, China[J]. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities,2016,30(4):1-12. [37] 何智钢, 李 嘉, 刘 洋, 等. 硬土层预破碎三轴水泥搅拌桩钻具: CN205894066U [P]. 2017-01-18. [38] 莫 凡, 黄 贵, 高宗立, 等. 一种适用于复杂地质情况下的三轴搅拌机钻头: CN205858186U[P]. 2017-01-04. [39] 李小青, 马晓华, 占 宏, 等. 一种超级三轴水泥搅拌桩设备: CN104420462A[P]. 2015-03-18. [40] 曾令新, 贾祥怀, 廖亚国, 等. 一种适用于穿透圆砾层土质的三轴搅拌机钻头: CN103437712B[P]. 2015-11-25. [41] 马晓华, 朱怀甫, 郭 峰, 等. 一种卵石地层超级三轴搅拌桩及其搅拌方法: CN106089084A[P]. 2016-11-09. [42] ZHEN Z,GE X,ZHANG J. Soil conditioning tests on sandy and cobbly soil for shield tunneling[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering,2021,25(4):1229-1238. [43] PEILA D,MARTINELLI D,TODARO C,et al. Soil conditioning in EPB shield tunnelling – An overview of laboratory tests[J]. Geomechanics and Tunnelling,2019,12(5):491-498. [44] 刘国彬, 王卫东. 基坑工程手册 (第2版) [M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2009. [45] 龚晓南. 深基坑工程设计施工手册 [M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 1999. [46] 刘全林, 宋伟民, 张 涵, 等. 超硬土层三轴水泥土搅拌桩施工方法: CN102979095A[P]. 2013-03-20. [47] YU D G. Self-centering positioner and principle for locating and guiding deep-hole drills using oil films[J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2017,92(6):639-649. [48] 张生雨, 白汉民, 王冬生, 等. 基于卵石的换土搅拌止水帷幕施工方法: CN105735332A [P]. 2016-07-06. [49] LI Y,PENG J,LI K,et al. An abrasive water jet assisted back reaming technique based on percussion drilling for reducing non-production time in geothermal energy development[J]. Geothermics,2020,89:101967. [50] SLIWA T,SAPIŃSKA-LIWA A,KORZEC M,et al. Investigation of old exploration boreholes in the Lublin Basin with regard to potential rotary-percussion drilling of shale gas wells[J]. Energies,2021,14(10):2734. doi: 10.3390/en14102734 -





 下载:
下载: