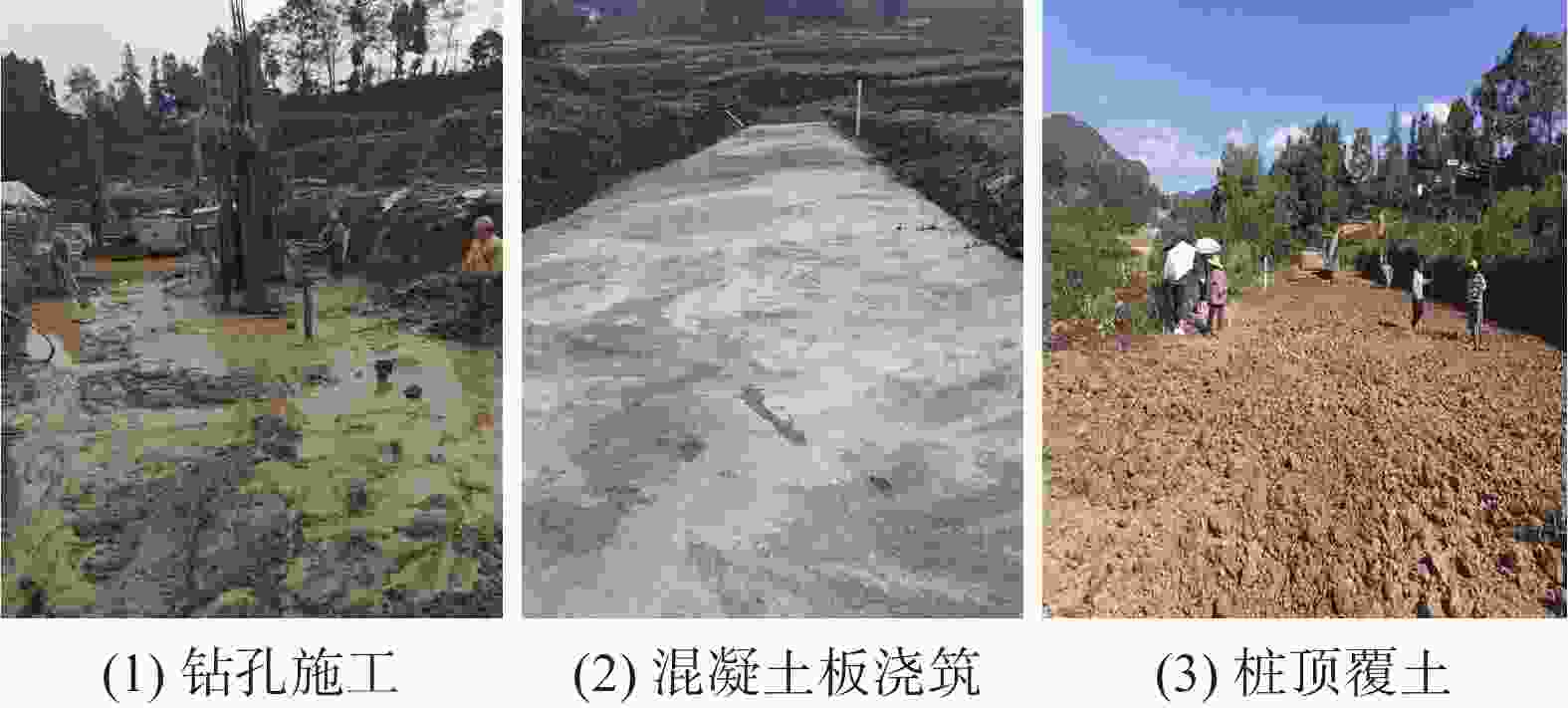
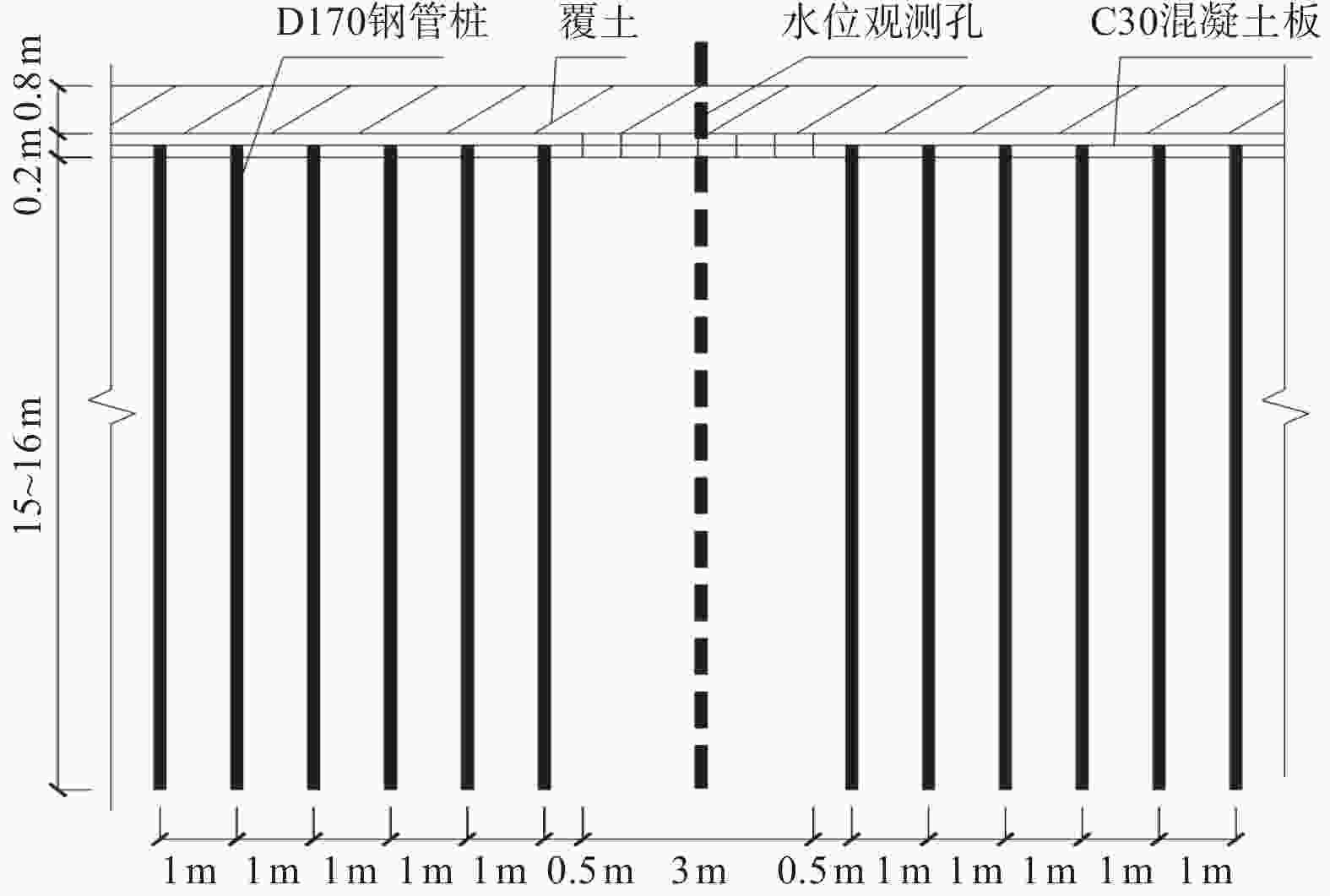
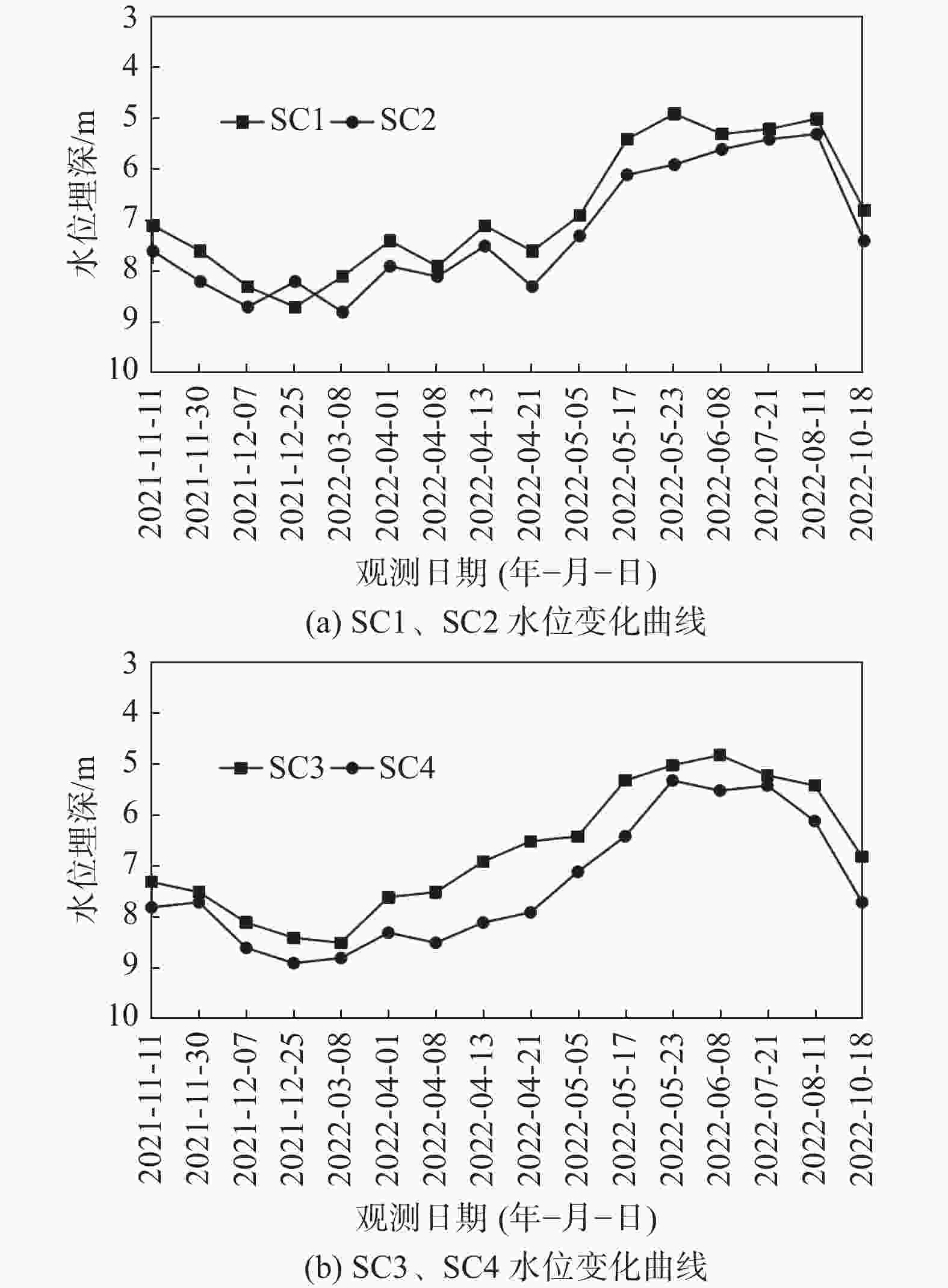
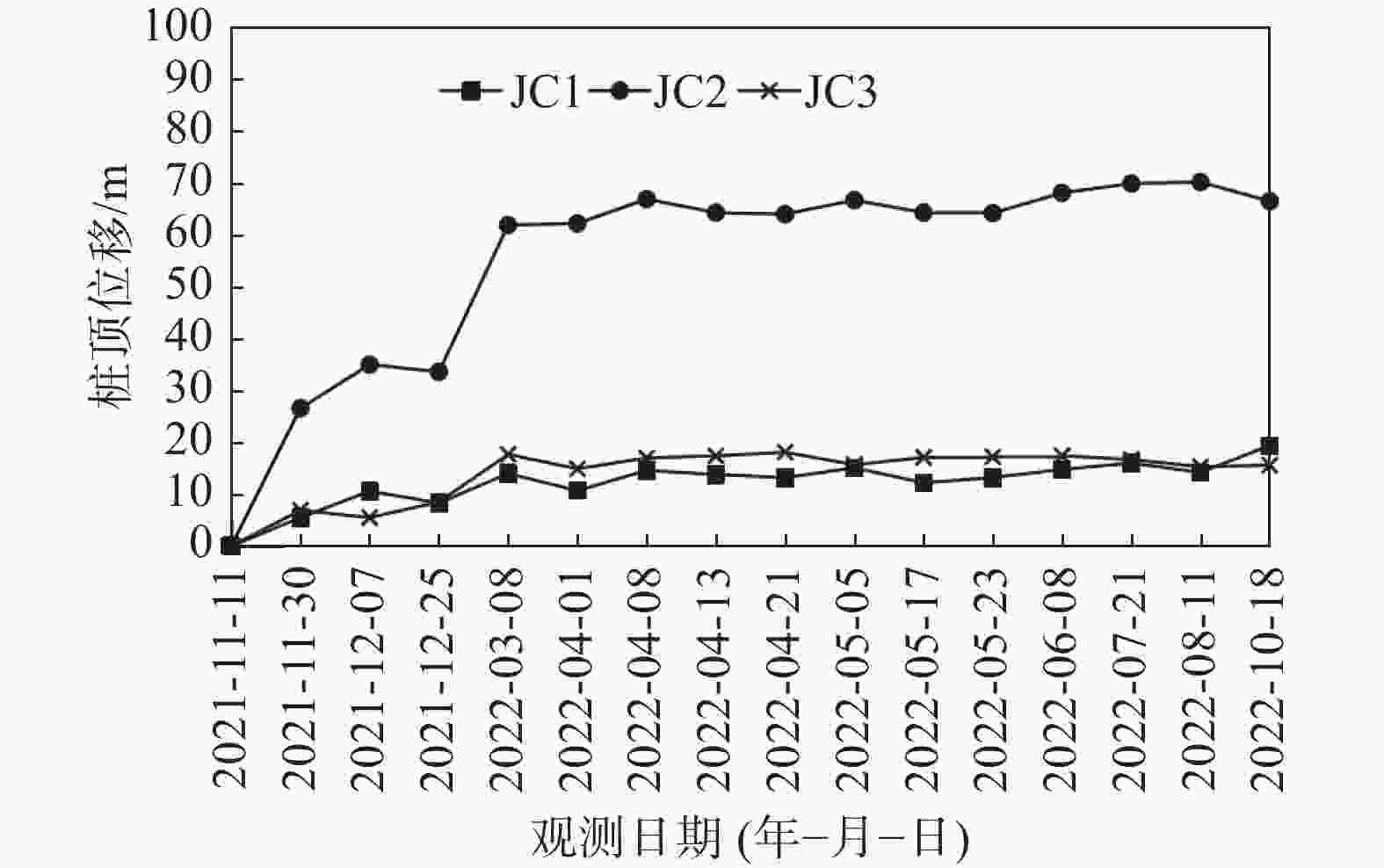
Application of micro-stell grouting steel pipe piles in landslide emergency control project
-
摘要: 微型钢管桩具有造价低、工期短、布置灵活等优点,逐渐被应用于滑坡治理工程。然而由于微型钢管桩多为大面积成群布桩,注浆施工将对地下水自然排泄产生影响,进而影响滑坡治理效果。因此,采用微型钢管桩进行滑坡治理时,应考虑桩群后部坡体地下水排泄问题。以贵州某天然气管道滑坡应急治理工程为例,通过优化钢管桩平面布置及施工工艺,在桩群之间合理留设地下水排泄通道,有效降低了桩群后部的地下水位,减小了桩后滑坡推力。钢管桩施工完成后,滑坡整体处于稳定状态,表明治理方案合理可行,可为类似滑坡防治工程设计和施工提供借鉴。Abstract: Micro-steel pipe piles are widely used in landslide control project for their low cost, short construction period, and flexible layout. Due to the fact that most micro steel pipe piles are arranged in large groups, grouting construction will have an impact on the natural discharge of groundwater, leading to an increase in the groundwater level on the slope and thus affecting the effect of landslide control. Therefore, when using micro steel pipe piles for landslide control, the issue of groundwater discharge at the back of the pile group should be considered. Taking the emergency control project of a natural gas pipeline landslide in Guizhou as an example. By optimizing the layout and construction technology of steel pipe piles, a reasonable groundwater drainage channel was reserved between pile groups, effectively reducing the groundwater level at the back of the pile group and reducing the landslide thrust behind the piles. After the completion of steel pipe pile construction, the overall stability of the landslide indicates that the treatment plan is reasonable and feasible, which can provide reference for the design and construction of similar landslide prevention projects.
-
Key words:
- micro-steel pipe pile /
- landslide control /
- groundwater /
- drainage channel
-
表 1 滑带土物理力学参数表
土体名称 饱和重度/(kN·m−3) 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 黏土夹碎石 20 10 8 表 2 滑坡推力计算结果
计算区域 计算工况 安全系数Fst 滑坡推力/(kN·m−1) 剪出口 老滑坡 暴雨工况 1.25 359.2 管沟处 复活区 暴雨工况 1.25 196.7 管沟处 表 3 钢管强度参数
材料名称 屈服强度/MPa 抗拉强度/MPa 断后伸长率/% 检验数量
/根无缝钢管
D108×4.5344 413 27.5 50 -
[1] 丁光文, 王 新. 微型桩复合结构在滑坡整治中的应用[J]. 岩土工程技术,2004,18(1):47-50. (DING G W, WANG X. Application of micropiling compound structure in a landslide treatment engineering[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique,2004,18(1):47-50. (in Chinese)DING G W, WANG X. Application of micropiling compound structure in a landslide treatment engineering[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique, 2004, 18(1): 47-50. (in Chinese) [2] 张小兵, 石 磊. 微型钢管桩在大厚度黄土地区的承载性能研究[J]. 铁道工程学报,2023,40(1):91-96. (ZHANG X B, SHI L. Research on the bearing capacity of micro steel pipe pile in loess area with large thickness[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society,2023,40(1):91-96. (in Chinese)ZHANG X B, SHI L. Research on the bearing capacity of micro steel pipe pile in loess area with large thickness[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2023, 40(1): 91-96. (in Chinese) [3] 周春雷, 舒中文, 刘 欣, 等. 加筋微型钢管桩配筋优化及受力特征[J]. 科学技术与工程,2022,22(31):13870-13879. (ZHOU C L, SHU Z W, LIU X, et al. Reinforcement optimization and stress characteristics of reinforced micro steel pile[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2022,22(31):13870-13879. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.31.033ZHOU C L, SHU Z W, LIU X, et al. Reinforcement optimization and stress characteristics of reinforced micro steel pile[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2022, 22(31): 13870-13879. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.31.033 [4] 肖成志, 司 雨, 王子寒, 等. 注浆微型钢管桩体抗弯力学性能[J]. 建筑科学与工程学报,2020,37(4):87-96. (XIAO C Z, SI Y, WANG Z H, et al. Flexural mechanical properties of grouted micro-steel-pipe-piles[J]. Journal of architecture and Civil Engineering,2020,37(4):87-96. (in Chinese)XIAO C Z, SI Y, WANG Z H, et al. Flexural mechanical properties of grouted micro-steel-pipe-piles[J]. Journal of architecture and Civil Engineering, 2020, 37(4): 87-96. (in Chinese) [5] 张卫民, 毛宜宾. 微型钢管群桩及预应力锚索综合加固已有滑坡[J]. 铁道建筑, 2012, 52(2): 72-74. (ZHANG W M, MAO Y B. Comprehensive reinforcement of landslides using micro steel pipe piles and prestressed anchor cables[J]. Railway Engineering, 2012, 52(2): 72-74. (in Chinese)ZHANG W M, MAO Y B. Comprehensive reinforcement of landslides using micro steel pipe piles and prestressed anchor cables[J]. Railway Engineering, 2012, 52(2): 72-74. (in Chinese) [6] 潘 健, 朱姣利, 陈红兵. 广东省韶关某黏质土坡滑坡治理方法[J]. 岩土力学,2007,28(S1):591-594. (PAN J, ZHU J L, CHEN H B. A repairing method for a clay landslide in Shaoguan of Guangdong province[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2007,28(S1):591-594. (in Chinese)PAN J, ZHU J L, CHEN H B. A repairing method for a clay landslide in Shaoguan of Guangdong province[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2007, 28(S1): 591-594. (in Chinese) [7] 李 舟, 姜暑芳, 陈 洋. 钢管桩在滑坡治理工程中的应用[J]. 铁道建筑, 2012, 52(12): 96-98. (LI Z, JIANG S F, CHEN Y. Application of steel pipe piles in landslide control engineering[J]. Railway Engineering, 2012, 52(12): 96-98. (in Chinese)LI Z, JIANG S F, CHEN Y. Application of steel pipe piles in landslide control engineering[J]. Railway Engineering, 2012, 52(12): 96-98. (in Chinese) [8] 贺可强. 大型堆积层滑坡的多层滑移规律分析[J]. 金属矿山,1998,27(7):15-18. (HE K Q. An analysis on the multilayered slide law of the large-scale accumulative landslides[J]. Metal Mine,1998,27(7):15-18. (in Chinese)HE K Q. An analysis on the multilayered slide law of the large-scale accumulative landslides[J]. Metal Mine, 1998, 27(7): 15-18. (in Chinese) [9] 贺可强, 白建业, 王思敬. 降雨诱发型堆积层滑坡的位移动力学特征分析[J]. 岩土力学,2005,26(5):705-709. (HE K Q, BAI J Y, WANG S J. Analysis of displacement dynamic features of colluvial landslide induced by rainfall[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2005,26(5):705-709. (in Chinese)HE K Q, BAI J Y, WANG S J. Analysis of displacement dynamic features of colluvial landslide induced by rainfall[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2005, 26(5): 705-709. (in Chinese) [10] 郭 涛, 魏业清, 王 旭. 雨水入渗下土体抗剪强度劣化时残坡积土边坡的稳定性及加固研究[J]. 自然灾害学报,2021,30(2):176-182. (GUO T, WEI Y Q, WANG X. Stability analysis and landslide reinforcement study for residual and diluvia soil slop under rainfall infiltration[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2021,30(2):176-182. (in Chinese)GUO T, WEI Y Q, WANG X. Stability analysis and landslide reinforcement study for residual and diluvia soil slop under rainfall infiltration[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2021, 30(2): 176-182. (in Chinese) [11] 王 卫. 堆积层滑坡发生机理及防治措施[J]. 铁道建筑, 2015, 55(6): 121-124. (WANG W. Formation mechanism and prevention measures of accumulation landslide[J]. Railway Engineering, 2015, 55(6): 121-124. (in Chinese)WANG W. Formation mechanism and prevention measures of accumulation landslide[J]. Railway Engineering, 2015, 55(6): 121-124. (in Chinese) [12] 成国文, 李善涛, 李 晓, 等. 万州近水平地层区堆积层滑坡成因与变形破坏特征[J]. 工程地质学报,2008,16(3):304-310. (CHENG G W, LI S T, LI X, et al. Forming causes and deformation-destruction characters of accumulative stratum landslide in horizontal stratum in Wanzhou[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2008,16(3):304-310. (in Chinese)CHENG G W, LI S T, LI X, et al. Forming causes and deformation-destruction characters of accumulative stratum landslide in horizontal stratum in Wanzhou[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2008, 16(3): 304-310. (in Chinese) [13] 李 雷, 周益民, 田 乐. 云南石门坎水电站业主营地古滑坡特征及稳定性分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2015,26(3):26-30. (LI L, ZHOU Y M, TIAN L. The characteristic and stability analysis on the ancient landslide at the Yezhuying hydropower station in Yunnan province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2015,26(3):26-30. (in Chinese)LI L, ZHOU Y M, TIAN L. The characteristic and stability analysis on the ancient landslide at the Yezhuying hydropower station in Yunnan province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2015, 26(3): 26-30. (in Chinese) [14] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 滑坡防治工程勘查规范: GB/T 32864–2016[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. (General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Code for geological investigation of landslide prevention: GB/T 32864–2016[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017. (in Chinese)General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Code for geological investigation of landslide prevention: GB/T 32864–2016[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017. (in Chinese) [15] 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 滑坡防治设计规范: GB/T 38509–2020[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2020. (State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration. Code for the design of landslide stabilization: GB/T 38509–2020[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2020. (in Chinese)State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration. Code for the design of landslide stabilization: GB/T 38509–2020[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2020. (in Chinese) [16] 贺可强, 雷建和, 陈喜山. 堆积层滑坡的基本特征与防治原则[J]. 黄金,1998,19(11):28-31. (HE K Q, LEI J H, CHEN X S. Basic characteristics of the landslide of accumulation horizon and its preventive and controlling principle[J]. Gold,1998,19(11):28-31. (in Chinese)HE K Q, LEI J H, CHEN X S. Basic characteristics of the landslide of accumulation horizon and its preventive and controlling principle[J]. Gold, 1998, 19(11): 28-31. (in Chinese) [17] 司胜利. 预应力锚固技术在昆河线402滑坡治理工程中的应用[J]. 中国煤炭地质,2010,22(7):48-51. (SI S L. Application of stressed anchorage technology in Kunming-Hekou railway No. 402 landslide governing engineering[J]. Coal Geology of China,2010,22(7):48-51. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2010.07.11SI S L. Application of stressed anchorage technology in Kunming-Hekou railway No. 402 landslide governing engineering[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2010, 22(7): 48-51. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2010.07.11 [18] 陈金宏, 王彤标, 王刘文, 等. 贵州山区堆积层滑坡形成机制及防治措施[J]. 资源环境与工程,2023,37(2):183-190. (CHEN J H, WANG T B, WANG L W, et al. Formation mechanism and control measures of accumulation landslide in Guizhou mountainous area[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering,2023,37(2):183-190. (in Chinese)CHEN J H, WANG T B, WANG L W, et al. Formation mechanism and control measures of accumulation landslide in Guizhou mountainous area[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2023, 37(2): 183-190. (in Chinese) -





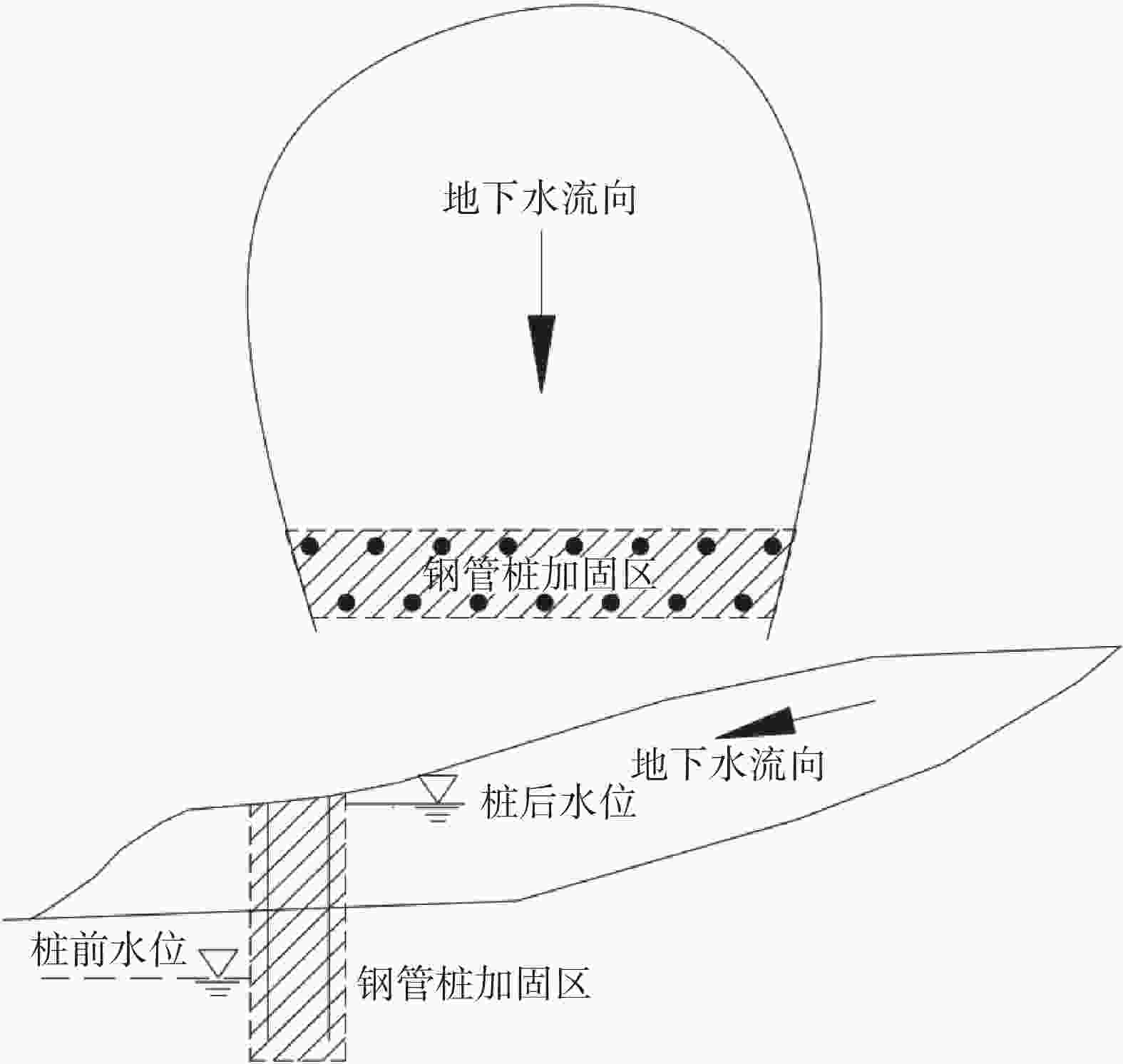
 下载:
下载: