Practiceand Analysis of Deep Foundation Pit in Soft Soil Area and Complex Environment
-
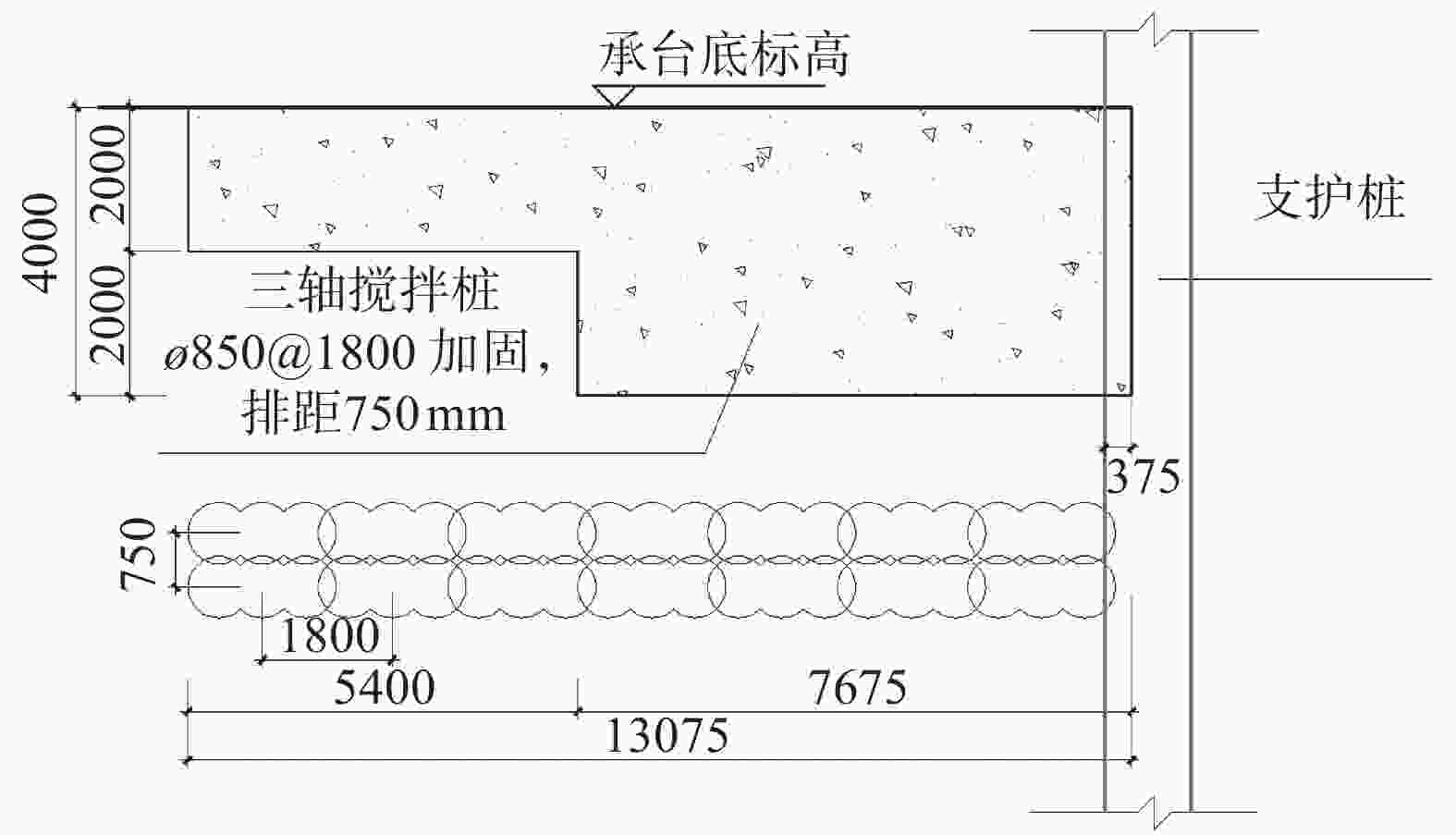
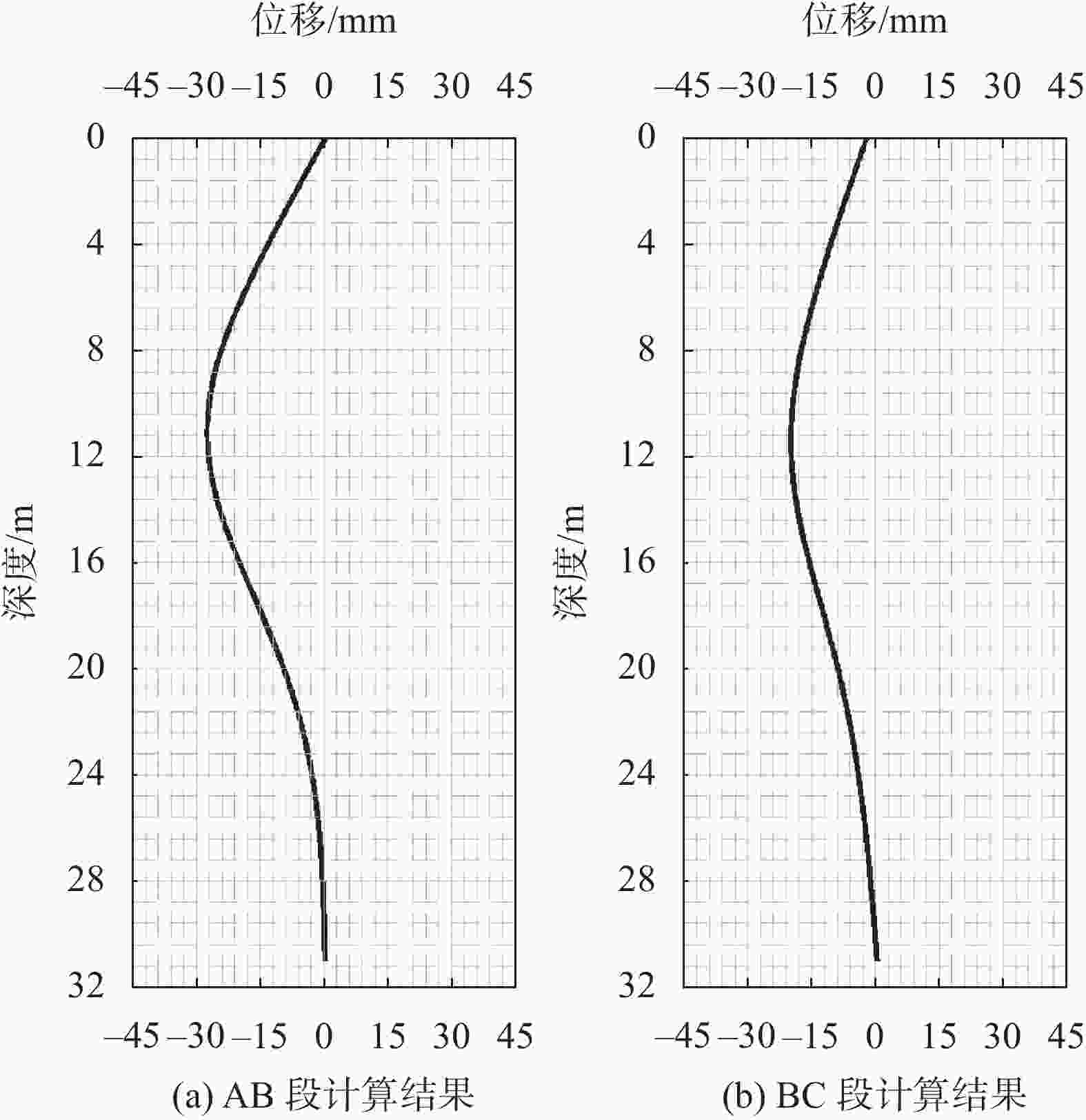
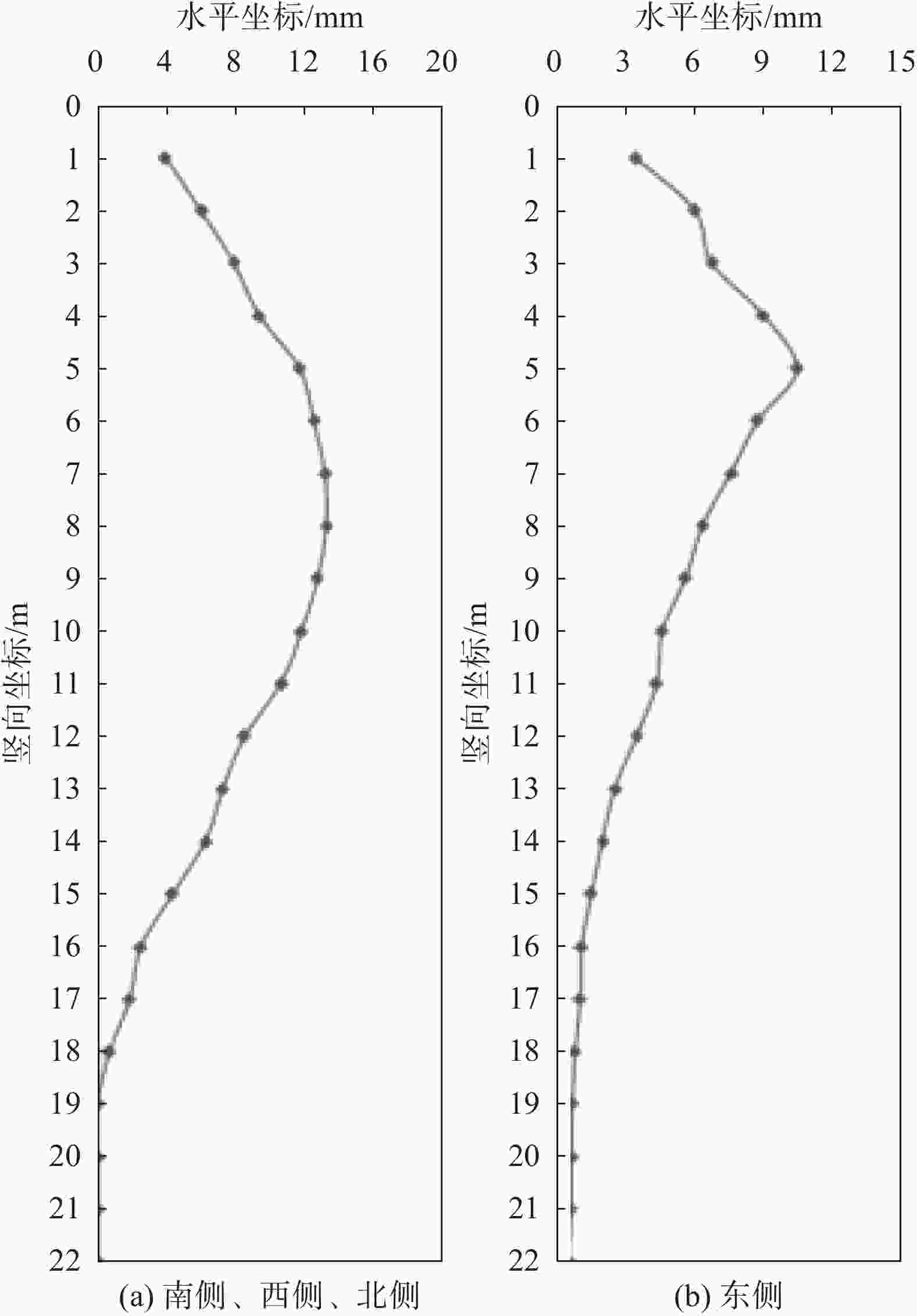
摘要: 以武汉市某复杂环境下的软土基坑工程为例,介绍该深厚软土基坑设计的重点、难点及应对措施。该项目紧邻住宅区、市政道路及高架桥,基坑侧壁及基底存在约8~10 m的深厚软土。通过方案对比,最终采用灌注桩+两层钢筋混凝土内支撑+三轴搅拌桩止水的支护方式,其中对变形要求较严格的高架桥一侧,采用了增设被动区加固的针对性保护措施,以减少基坑开挖对其影响。基坑整个开挖过程的监测数据显示,设置被动区加固一侧的变形量比其它部位减少约27.2%,验证了支护方案及保护措施的合理性,对类似工程具有借鉴意义。Abstract: Taking a soft soil foundation pit project in a complex environment in Wuhan as an example, the key points, difficulties and countermeasures of the deep soft soil foundation pit design is introduced. The project is close to residential areas, municipal roads and viaducts. There is about 8~10 m deep soft soil on the side wall and base of the foundation pit. Through the scheme comparison, the support mode of cast-in-place pile + two-layer reinforced concrete internal support + triaxial mixing pile water stop is finally adopted. For one side of the viaduct with strict deformation requirements, targeted protection measures of adding passive area reinforcement are adopted to reduce the impact of foundation pit excavation. The monitoring data of the whole excavation process of the foundation pit show that the deformation of the reinforcement side of the passive area is about 27.2% less than that of other parts, which verifies the rationality of the support scheme and protection measures, and has reference significance for similar projects.
-
Key words:
- deep foundation pit /
- soft soil area /
- complex environment /
- cast-in-place pile /
- foundation pile design
-
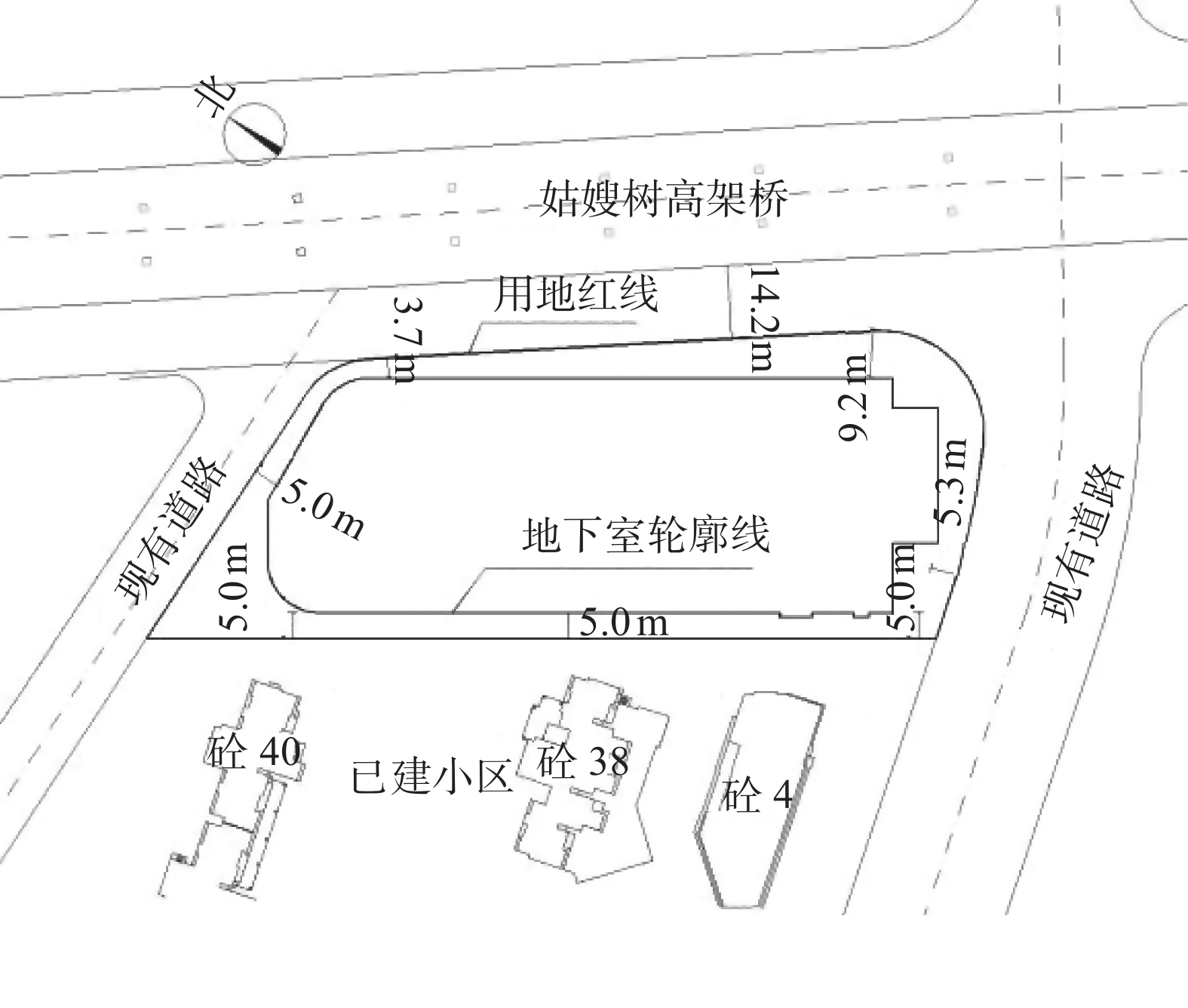
表 1 基坑周边环境情况说明
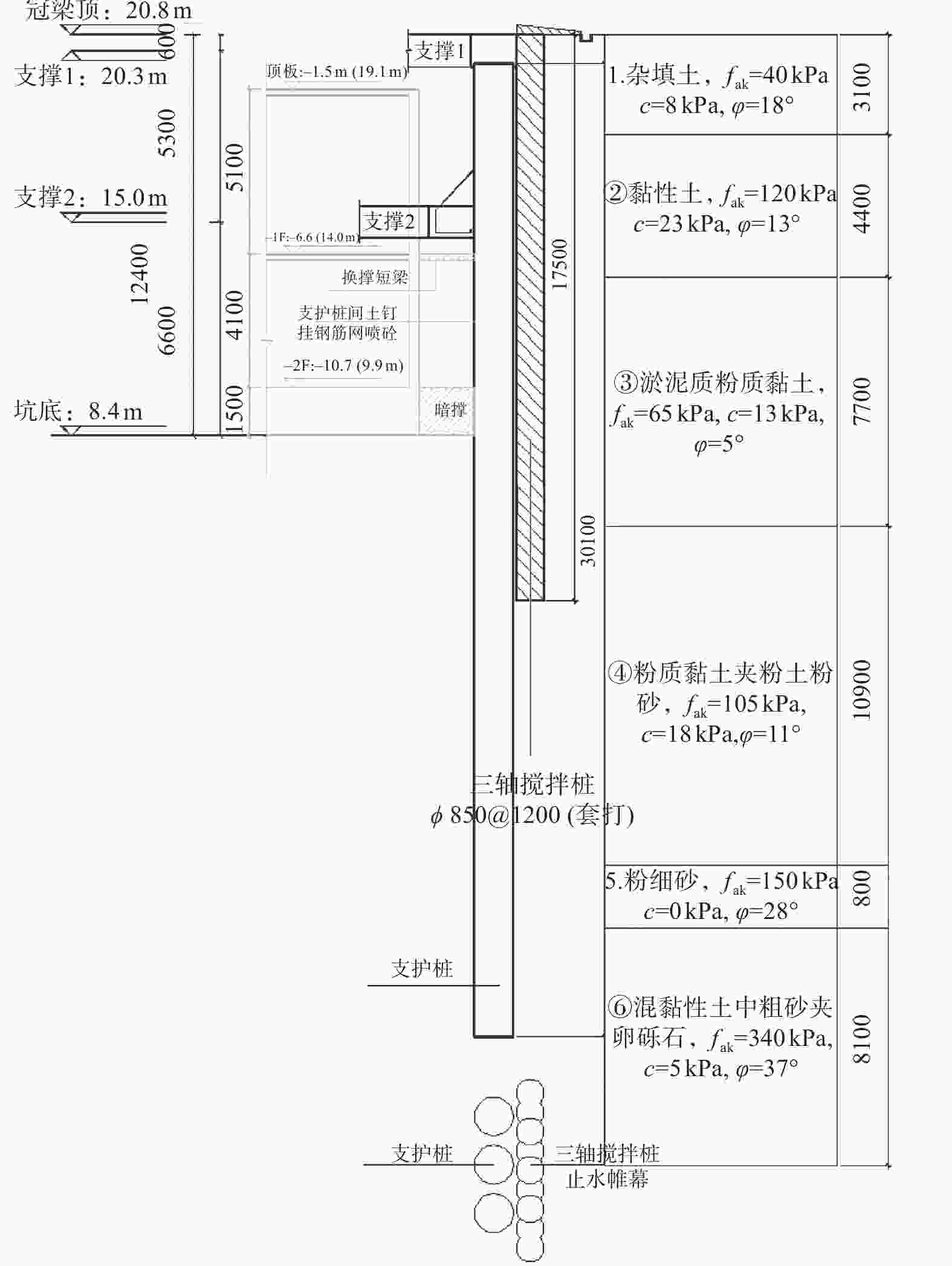
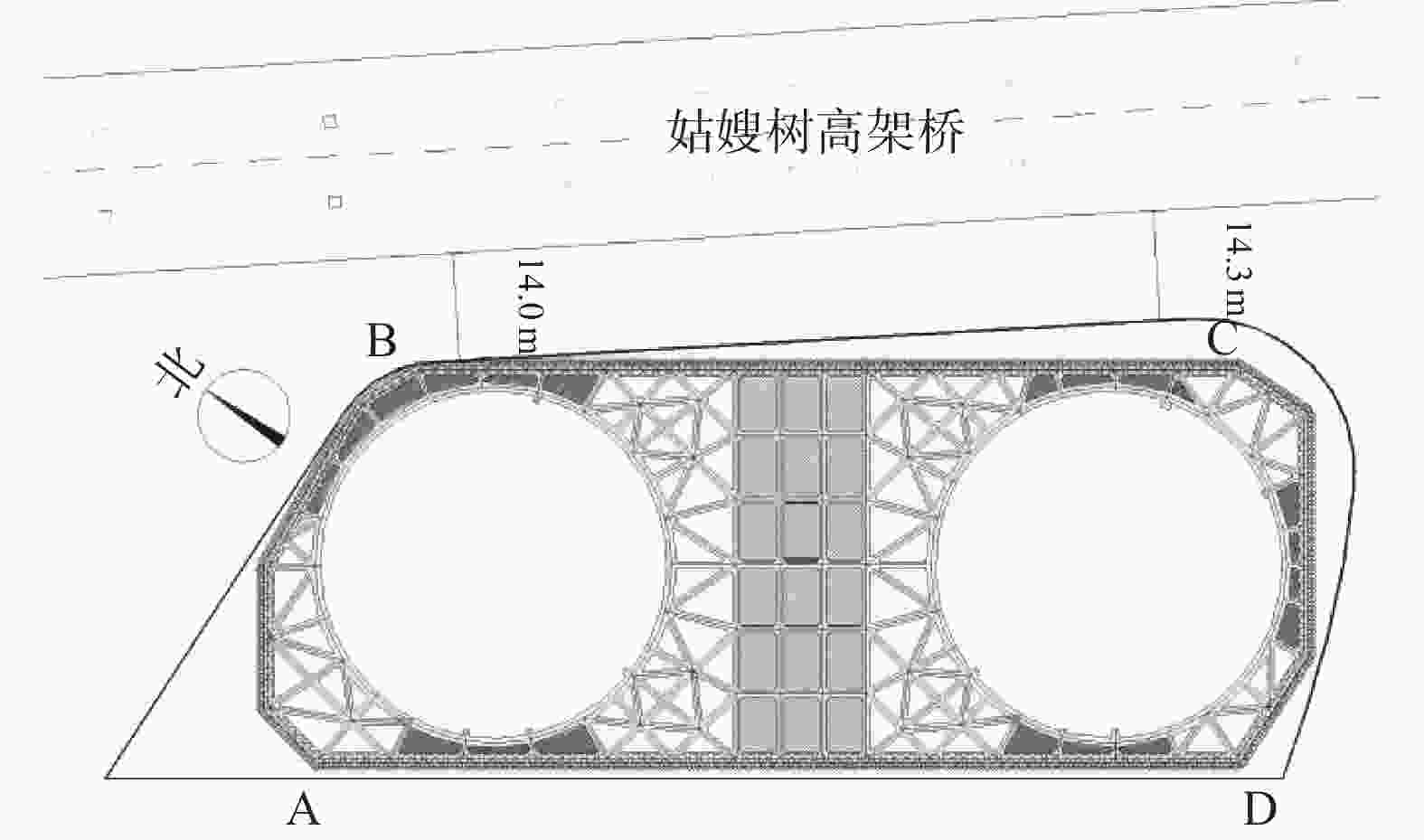
方位 具体说明 北侧 地下室北侧距离用地红线约3.7~5.1 m,红线外为9.0 m宽的现有道路,红线外1.0 m左右有埋深约1.0 m的管线,施工空间紧张 东侧 地下室轮廓线距离用地红线约3.7~9.2 m,红线外为姑嫂树路,红线外1.0 m左右有埋深约1.0 m的管线,红线外14 m为现有姑嫂树路高架桥,该侧环境条件紧张 南侧 地下室轮廓线距离用地红线约5.3~7.9 m,红线外为常青五路。红线外3 m范围有埋深约1.0 m的管线,施工空间紧张 西侧 地下室轮廓线距离用地红线约4.1~5.0 m,红线外为已建小区(一层地下室,桩基础)。该侧场地内无任何管线,环境条件紧张 表 2 土层参数一览表
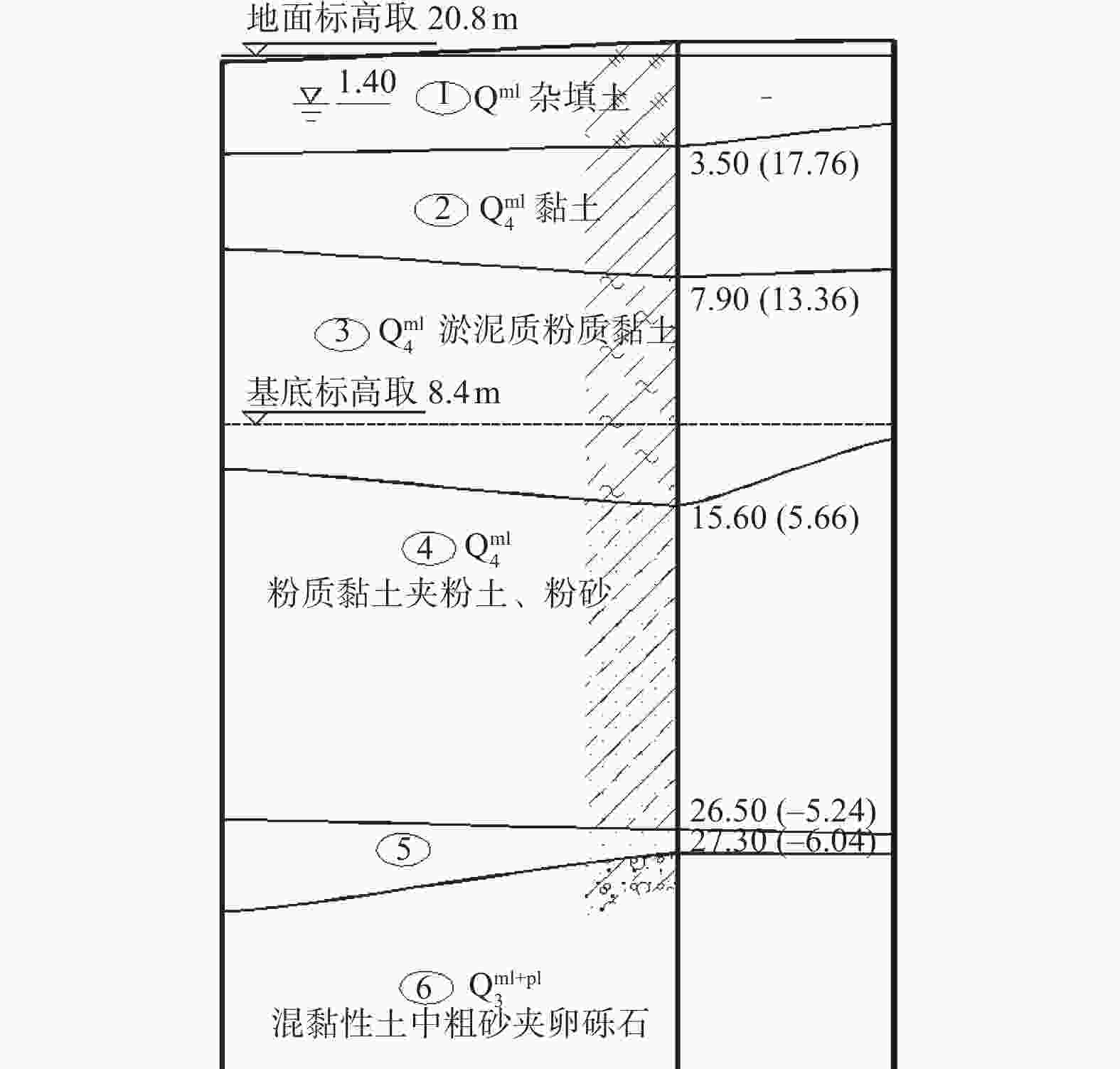
地层层号及名称 层面埋深/m 厚度/m 状态 重度γ/(kN·m−3) 黏聚力c/kPa 内摩擦角φ/(°) 承载力特征值fak/kPa 压缩模量/MPa ①杂填土 0 1.8~6.0 松散 17.5 8 18 ②黏土 1.8~6.0 2.4~6.1 可塑 18.1 23 13 120 6.0 ③淤泥质粉质黏土 6.2~8.8 3.5~9.0 软塑—流塑 17.3 13 5 65 3.5 ④粉质黏土夹粉土、粉砂 11.9~16.6 10.0~18.8 可塑 17.9 18 11 105 5.5 ⑤粉细砂混黏性土 23.7~29.1 0.3~5.0 稍密—中密 19 0 28 150 13.0 ⑥中粗砂夹卵砾石 26.4~30.9 0~31.6 中密 19.3 5 37 340 22.0 -
[1] 王笃礼,匡 健,沈宇鹏. 临近建筑物的基坑支护结构体系设计研究[J]. 岩土工程技术,2009,31(4):173-179. [2] 张 戈,毛海和. 软土地区深基坑围护结构综合刚度研究[J]. 岩土力学,2016,37(5):1467-1474. [3] 耿华宽,高芬芬,周成君. 深厚软土地区基坑大变形机理与控制对策研究[J]. 岩土工程技术,2018,32(6):313-316. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2018.06.009 [4] 刘国斌, 王卫东. 基坑工程手册(第二版)[M]. 北京: 北京建筑出版社, 2009. [5] 罗战友,刘 薇,夏建中. 基坑内土体加固对围护结构变形的影响分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2006,28(S1):1538-1540. [6] 高大钊. 软土深基坑支护技术中的若干土力学问题[J]. 岩土力学,1995,16(3):1-6. [7] 何世达, 祝世平. 被动区加固的基坑支护分析[M]//王立. 基坑工程应用技术. 武汉: 武汉出版社, 2008. [8] 程杰林, 徐扬青. 深厚淤泥土基坑工程坑底多孔板加固抗隆起技术[M]//王立. 基坑工程应用技术. 武汉: 武汉出版社, 2008. [9] 殷一弘. 深厚软土地层紧邻地铁深大基坑分区设计与实践[J]. 岩土工程学报,2019,41(S1):129-132. [10] 罗 康,郑玉辉,许 敬. 深基坑支护变形研究[J]. 岩土工程技术,2017,31(6):306-310. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2017.06.009 [11] 尤 波. 软土地区紧临即有建筑物地库深大基坑支护设计与分析[J]. 岩土工程技术,2020,34(2):63-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2020.02.001 [12] 刘合寨,周 元,尤 波. 软土地区大面积不规则深基坑支护设计实践与分析[J]. 岩土工程技术,2018,32(4):212-216. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2018.04.011 [13] 何世达,徐 忠,李燕枫. 船式支护在基坑中的应用[J]. 岩土工程技术,2021,35(1):43-47. [14] 李夕林,魏 祥,梁志荣. 软土基坑深基坑变形控制设计实践与分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2014,36(S1):160-164. [15] 周赞良,付艳斌,邱建金,等. 复杂软土地区深基坑内支撑与锚索共同作用初探[J]. 岩土工程学报,2014,36(S2):396-399. -





 下载:
下载: